Wired Guest Access
The Wired Guest Access feature enables guest users of an enterprise network that supports both wired and wireless access to connect to the guest access network from a wired Ethernet connection. The wired Ethernet connection is designated and configured for guest access. Wired session guests on mobility agents are directed to a wireless guest controller in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) through a Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) tunnel.
Wired guest access can be configured in a standalone configuration or in a dual-controller configuration that uses both an anchor controller and a foreign controller. A dual-controller configuration isolates wired guest access traffic; however it is not required for deployment of the wired guest access.
Wired-guest-access ports initially terminate on a Layer 2 access switch or switch port that is configured with VLAN interfaces for wired guest access traffic. The wired guest traffic is then trunked from the access switch to a controller. This controller is configured with an interface that is mapped to aWired-guest-access VLAN on the access switch.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Wired Guest Access
- Information About Wired Guest Access
- How to Configure Wired Guest Access
- Configuration Examples for Wired Guest Access
- Additional References for Wired Guest Access
- Feature Information for Wired Guest Access
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Wired Guest Access
- Tunneling of wired clients is not supported when the client is attached to a port at the Cisco Next Generation Wiring Closet (NGWC) device that is configured for open mode.
- Tunneling of wired clients is not supported after successful web authentication at the NGWC device because automated IP address reassignment is not supported after web-authentication.
- The NGWC device supports network access only via the tunnel based on the web authentication that occurs at the controller.
- The Network Advertisement and Selection Protocol (NASP) is not supported for wired clients.
- High availability is not supported for wireless sessions. If the wireless controller fails while providing tunneled guest access for a wired client, the state is not automatically recovered.
- Inactivity aging is not enforced for a wired client that is provisioned to the wireless controller; for example, within a RADIUS Access-Accept request that is received after web authentication is performed at the controller.
Information About Wired Guest Access
Wired Guest Access Overview
Enterprise networks that support both wired and wireless access need to provide guest services that are consistent across the two access media, from a perspective of both client experience and manageability. For wireless networks, guest traffic from a mobility anchor device is directed typically through a Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) tunnel to an array of controllers in the demilitarized zone (DMZ), where either web-authenticated access or open access is provided. Wired guest traffic can also be backhauled to the DMZ using more traditional tunneling mechanisms like Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE). The Cisco Next Generation Wiring Closet (NGWC) platforms, with converged wired and wireless access, can extend CAPWAP tunneling to wired guests also, allowing for very similar handling at the controller platform (in the DMZ) and reducing the provisioning overhead.
However, security remains an issue because it is not possible to determine, prior to authentication, whether a wired client is a guest or requires access to the corporate network. Consequently, the decision to tunnel a wired client’s traffic to the DMZ cannot be made with the certain knowledge that the client is a guest.
Due to the lack of network selection for wired clients, open mode cannot be supported with guest tunneling. Open mode is when an IP address is allocated as soon as a client connects to the access switch. Once the client is connected via a tunnel, it must be reassigned an IP address from a subnet provisioned at the DMZ, before web authentication can be attempted.
Converged Guest Access Solution
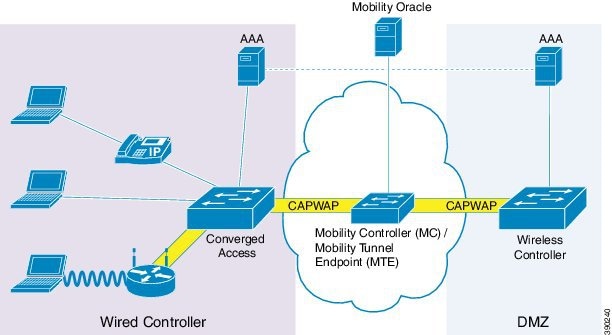
In the preceding figure, the Cisco Next Generation Wiring Closet (NGWC) device forms the attachment point for both wired and wireless sessions and provides Layer 2 authentication, where applicable. Wired session guests on a mobility agent (a foreign device) are directed through a Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) tunnel to the wireless controller (the anchor device) in the demilitarized zone (DMZ). The wired session guests are provided open or web-authenticated access from the wireless controller. This approach simplifies the management of guest access because only one network device is provisioned to manage HTTP traffic and serve web pages.
Tunneling wired guest traffic to the DMZ allows the same controller platform to provide web-authenticated and open access to wired guests also, further simplifying the management of guest access and ensuring a consistent experience for end users. To activate the CAPWAP tunnel, matching guest LAN profiles must be configured on foreign and anchor devices.
Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) services are required at the access layer for Layer 2 authentication and, optionally, to direct the device to open a tunnel for a wired client. A DMZ uses AAA for client guest authentication. The Mobility Controller/Mobility Tunnel Endpoint (MC/MTE) allows the CAPWAP tunnel to the DMZ to be load-balanced across an array of wireless controllers.
CAPWAP Tunneling
In an enterprise Edge (eEdge) implementation of wired guest access, Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) tunneling is implemented as an Enterprise Policy Manager (EPM) plug-in.
When a tunnel is specified within a user profile or a service template, the EPM invokes the CAPWAP tunnel. The EPM requests that the Wireless Controller Module (WCM) establish a CAPWAP tunnel for the session on which the EPM is installed. If the WCM returns an error or indicates unsolicited tunnel termination at any subsequent point, the CAPWAP tunnel notifies the EPM of failure. The failure results in an authorization-failure event at the session manager, and a control policy rule can be specified to determine the failure handling.
The Session Manager is responsible for creating and managing wired sessions in the eEdge framework. It assigns an audit-session-id at session creation and stores client identity data in a session entry in the database. It also manages the authentication of connecting endpoints where authentication is specified under a control policy.
Based on requests, the WCM is responsible for the CAPWAP tunneling of wired clients at an NGWC switch. The WCM also provides identical handling of tunneled wireless and wired guest sessions at the controller.
 Note | A new tunnel is established only if it does not exist between the access switch and the relevant controller. If a tunnel exists, a client is added to it. |
 Note | The Vendor-specific attribute (VSA) for activating CAPWAP tunneling using user profiles is “subscriber:capwap-tunnel-profile-name= name”. |
How to Configure Wired Guest Access
Configuring a Guest LAN
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
guest-lan
profile-name
[lan-id]
4.
shutdown
5.
client
{association
limit
[max-connections] |
vlan
[vlan-id]}
6.
security
web-auth [parameter-map
parameter-name]
7.
mobility
anchor [ip-address |
mac-address]
8.
no shutdown
9.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a CAPWAP Tunnel in a Service Template
Perform the following task to configure a Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) tunnel in a service template. Perform the following task to activate a tunnel service when Layer 2 authentication failure occurs.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
service-template
template-name
4.
tunnel
type
capwap
name
tunnel-name
5.
exit
6.
policy-map type control subscriber
control-policy-name
7.
event
session-started
[match-all
|
match-any]
8.
priority-number
class {control-class-name | always}
[do-all |
do-until-failure |
do-until-success]
9.
action-number
authenticate
using {dot1x |
mab |
webauth}
10.
exit
11.
exit
12.
event
authentication-failure [match-all |
match-any]
13.
priority-number
class {control-class-name | always}
[do-all |
do-until-failure |
do-until-success]
14.
action-number
activate {policy type control subscriber
control-policy-name |
service-template
template-name [aaa-list
list-name] [precedence
[replace-all]]}
15.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring CAPWAP Forwarding
Perform the following task to configure a specific VLAN for CAPWAP forwarding. Once configured, this VLAN can be used only for CAPWAP forwarding.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
vlan
vlan-id
4.
exit
5.
access-session
tunnel vlan
vlan-id
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Wired Guest Access
Example: Configuring a CAPWAP Tunnel in a Service Template
The following example shows how to configure a CAPWAP tunnel in a service template to enable wired guest access.
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# service-template GUEST-TUNNEL Device(config-service-template)# tunnel type capwap name TUNNEL-CAPWAP Device(config-service-template)# exit Device(config)# policy-map type control subscriber TUNNELLED-GUEST Device(config-event-control-policymap)# event seesion-started Device(config-class-control-policymap)# 1 class always Device(config-action-control-policymap)# 1 authenticate using dot1x Device(config-action-control-policymap)# exit Device(config-class-control-policymap)# 1 class DOT1X-NO-RESP Device(config-action-control-policymap)# 1 activate service-template GUEST-TUNNEL Device(config-action-control-policymap)# end
Example: Configuring the Mobility Agent
The following example shows how to configure interface ports on the mobility agent (anchor).
Wired-guest-access ports initially terminate on a Layer 2 access switch or switch port configured with VLAN interfaces for wired-guest-access traffic. The wired guest traffic is then trunked from the access switch to a controller. This controller is configured with an interface that is mapped to a wired-guest-access VLAN on the access switch.
! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/44 description Connected to Client_Laptop switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access access-session host-mode single-host access-session closed access-session port-control auto access-session control-direction in mab dot1x pae authenticator dot1x timeout tx-period 5 service-policy type control subscriber Guest-Access ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description Connected_to_MobilityController switchport mode trunk ! interface Vlan10 description CLIENT-VLAN ip address 172.16.10.201 255.255.255.0 ip helper-address 172.16.10.200 ! interface Vlan80 description MANAGEMENT-VLAN ip address 10.20.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! wireless management interface Vlan80 wireless mobility controller ip 10.20.1.2 public-ip 10.20.1.2 << Mobility Controller IP >> ! guest-lan glan-1 1 shutdown client vlan Vlan10 no security web-auth << Use "security webauth" for webauth access & "no security webauth" for open access. >> mobility anchor 10.20.1.3 << Guest Controller IP >> no shutdown !
Example: Configuring the Mobility Controller
The following example shows how to configure the interface ports and wireless mobility on the mobility controller to enable wired guest access.
! interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/2 description Connected-to-MobilityAgent switchport mode trunk ! interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1 description Connected-to-GuestController switchport mode trunk ! interface Vlan80 description MANAGEMENT-VLAN ip address 10.20.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! wireless management interface Vlan80 ! wireless mobility controller peer-group pg-name wireless mobility controller peer-group pg-name member ip 10.20.1.1 public-ip 10.20.1.1 << Mobility Agent IP >> ! wireless mobility group member ip 10.20.1.3 public-ip 10.20.1.3 << Guest Controller IP >> wireless mobility group name mcg-name !
Example: Configuring the Guest Controller
The following example shows how to configure interface ports on the guest controller (anchor) and how to set up DHCP snooping.
The guest (local WLAN) controller anchors the client onto a demilitarized zone (DMZ) anchor WLAN controller that is configured for wired and wireless guest access. After a successful handoff of the client to the DMZ anchor controller, the DHCP IP address assignment, client authentication, and so on are handled in the DMZ Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). After WLC completes the authentication, the client is allowed to send and receive traffic.
! interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1 description Connected_to_MC switchport mode trunk ! interface Vlan10 description CLIENT-VLAN ip address 172.16.10.200 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan80 description MANAGEMENT-VLAN ip address 10.20.1.3 255.255.255.0 ! ip dhcp snooping vlan 10 ip dhcp snooping ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.10.100 172.16.10.255 ip dhcp pool vlan10 network 172.16.10.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 172.16.10.200 ! wireless management interface Vlan80 ! wireless mobility group name mcg-name wireless mobility group member ip 10.20.1.2 public-ip 10.20.1.2 << Mobility Controller IP >> ! guest-lan glan-1 1 shutdown client vlan Vlan10 no security web-auth << Use "security web-auth" for web-auth access & "no security web-auth" for open access. >> mobility anchor no shutdown !
Example: Configuring CAPWAP Forwarding
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# vlan 1755 Device(config-vlan)# exit Device(config)# access-session tunnel vlan 1775 Device(config)# end
Additional References for Wired Guest Access
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Cisco Identity-Based Networking Services commands |
Cisco IOS Identity-Based Networking Services Command Reference |
Standards and RFCs
|
RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
IEEE 802.1X |
Port based Network Access Control |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Wired Guest Access
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Wired Guest Access |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SE |
The Wired Guest Access feature enables guest users of an enterprise network, that supports both wired and wireless access, to connect to the guest access network from a wired Ethernet connection. The wired Ethernet connection is designated and configured for guest access. Wired session guests on mobility agents are directed to a wireless guest controller in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) through a Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) tunnel. The following commands were introduced or modified: access-session tunnel vlan, event, match authorization-failure, tunnel type capwap. |
 Feedback
Feedback