- OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
- OSPF Update Packet-Pacing Configurable Timers
- OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
- OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
- OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- OSPF Inbound Filtering Using Route Maps with a Distribute
- OSPF Shortest Path First Throttling
- OSPF Support for Fast Hello Packets
- OSPF Incremental SPF
- OSPF Limit on Number of Redistributed Routes
- OSPF Link-State Advertisement Throttling
- OSPF Support for Unlimited Software VRFs per PE Router
- OSPF Area Transit Capability
- OSPF Per-Interface Link-Local Signaling
- OSPF Link-State Database Overload Protection
- OSPF MIB Support of RFC 1850 and Latest Extensions
- OSPF Support for Forwarding Adjacencies over MPLS TE Tunnels
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Information About OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- How to Suppress OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Configuration Examples for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Additional References
- Feature Information for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
The OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs feature causes a not-so-stubby area (NSSA) area border router (ABR) to translate Type-7 link state advertisements (LSAs) to Type-5 LSAs, but use the address 0.0.0.0 for the forwarding address instead of that specified in the Type-7 LSA. This feature causes routers that are configured not to advertise forwarding addresses into the backbone to direct forwarded traffic to the translating NSSA ABRs.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Information About OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- How to Suppress OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Configuration Examples for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Additional References
- Feature Information for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
This document presumes you have OSPF configured on the networking device; it does not document other steps to configure OSPF.
Information About OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- Benefits of OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
- When to Suppress OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
Benefits of OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
The OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs feature causes an NSSA ABR to translate Type-7 LSAs to Type-5 LSAs, but use the 0.0.0.0 as the forwarding address instead of that specified in the Type-7 LSA. This feature causes routers that are configured not to advertise forwarding addresses into the backbone to direct forwarded traffic to the translating NSSA ASBRs.
When to Suppress OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
In the figure below, it would be advantageous to filter Area 2 addresses from Area 0 to minimize the number of routes introduced into the backbone (Area 0). However, using the area rangecommand to consolidate and summarize routes at the area boundary--filtering the Area 2 addresses--will not work because the Area 2 addresses include forwarding addresses for Type-7 LSAs that are generated by the ASBR. If these Type-7 LSA forwarding addresses have been filtered out of Area 0, the backbone routers cannot reach the prefixes advertised in the translated Type-5 LSAs (autonomous system external LSAs).
| Figure 1 | OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs |
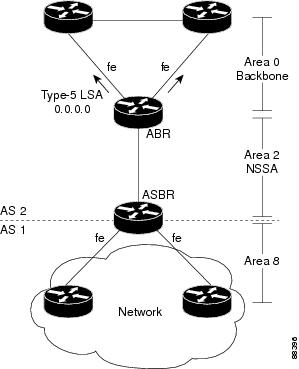
This problem is solved by suppressing the forwarding address on the ABR so that the forwarding address is set to 0.0.0.0 in the Type-5 LSAs that were translated from Type-7 LSAs. A forwarding address set to 0.0.0.0 indicates that packets for the external destination should be forwarded to the advertising OSPF router, in this case, the translating NSSA ABR.
Before configuring this feature, consider the following caution.
 Caution |
Configuring this feature causes the router to be noncompliant with RFC 1587. Also, suboptimal routing might result because there might be better paths to reach the destination’s forwarding address. This feature should not be configured without careful consideration and not until the network topology is understood. |
How to Suppress OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
Suppressing OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
 Caution |
Configuring this feature causes the router to be noncompliant with RFC 1587. Also, suboptimal routing might result because there might be better paths to reach the destination’s forwarding address. This feature should not be configured without careful consideration and not until the network topology is understood. |
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
Example Suppressing OSPF Forwarding Address in Translated Type-5 LSAs
This example suppresses the forwarding address in translated Type-5 LSAs:
interface ethernet 0 ip address 10.93.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip ospf cost 1 ! interface ethernet 1 ip address 10.94.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 network 10.93.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.94.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 10 area 10 nssa translate type7 suppress-fa
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| OSPF commands |
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference |
Standards
| Standards |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
| MIBs |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFCs |
Title |
|---|---|
| Configuring the OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs feature causes the router to be noncompliant with RFC 1587. |
The OSPF NSSA Option |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs |
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback