- IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity
- IPv6 Unicast Routing
- IPv6 Anycast Address
- IPv6 Switching: Cisco Express Forwarding and Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding Support
- IPv6 Services: AAAA DNS Lookups over an IPv4 Transport
- IPv6 MTU Path Discovery
- ICMP for IPv6
- IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
- ICMP for IPv6 Redirect
- IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
- IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Cache
- IPv6 Default Router Preference
- IPv6 Stateless Autoconfiguration
- IPv6 Generic Prefix
- IPv6 Support on BVI Interfaces
- IPv6 RA Guard
- Telnet Access over IPv6
- IPv6 Support for TFTP
- SSH Support Over IPv6
- SNMP over IPv6
- IPv6 MIBs
- IPv6 Embedded Management Components
- IPv6 CNS Agents
- IPv6 HTTP(S)
- IP SLAs for IPv6
- IPv6 RFCs
IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
The IPv6 ICMP rate limiting feature implements a token bucket algorithm for limiting the rate at which IPv6 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) error messages are sent out on the network.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
ICMP for IPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) in IPv6 functions the same as ICMP in IPv4. ICMP generates error messages, such as ICMP destination unreachable messages, and informational messages, such as ICMP echo request and reply messages. Additionally, ICMP packets in IPv6 are used in the IPv6 neighbor discovery process, path MTU discovery, and the Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) protocol for IPv6. MLD is used by IPv6 devices to discover multicast listeners (nodes that want to receive multicast packets destined for specific multicast addresses) on directly attached links. MLD is based on version 2 of the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) for IPv4.
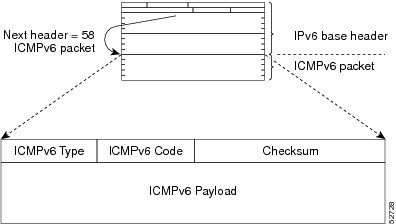
A value of 58 in the Next Header field of the basic IPv6 packet header identifies an IPv6 ICMP packet. ICMP packets in IPv6 are like a transport-layer packet in the sense that the ICMP packet follows all the extension headers and is the last piece of information in the IPv6 packet. Within IPv6 ICMP packets, the ICMPv6 Type and ICMPv6 Code fields identify IPv6 ICMP packet specifics, such as the ICMP message type. The value in the Checksum field is derived (computed by the sender and checked by the receiver) from the fields in the IPv6 ICMP packet and the IPv6 pseudoheader. The ICMPv6 Data field contains error or diagnostic information relevant to IP packet processing. The figure below shows the IPv6 ICMP packet header format.
| Figure 1 | IPv6 ICMP Packet Header Format |
IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
The IPv6 ICMP rate limiting feature implements a token bucket algorithm for limiting the rate at which IPv6 ICMP error messages are sent out on the network. The initial implementation of IPv6 ICMP rate limiting defined a fixed interval between error messages, but some applications such as traceroute often require replies to a group of requests sent in rapid succession. The fixed interval between error messages is not flexible enough to work with applications such as traceroute and can cause the application to fail.
Implementing a token bucket scheme allows a number of tokens--representing the ability to send one error message each--to be stored in a virtual bucket. The maximum number of tokens allowed in the bucket can be specified, and for every error message to be sent, one token is removed from the bucket. If a series of error messages is generated, error messages can be sent until the bucket is empty. When the bucket is empty of tokens, no IPv6 ICMP error messages are sent until a new token is placed in the bucket. The token bucket algorithm does not increase the average rate limiting time interval, and it is more flexible than the fixed time interval scheme.
How to Configure IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
Customizing IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
- Example: IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting Configuration
- Example: Displaying Information About ICMP Rate-Limited Counters
Example: IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting Configuration
The following example shows an interval of 50 milliseconds and a bucket size of 20 tokens being configured for IPv6 ICMP error messages:
ipv6 icmp error-interval 50 20
Example: Displaying Information About ICMP Rate-Limited Counters
In the following example, information about ICMP rate-limited counters is displayed:
Device# show ipv6 traffic
ICMP statistics:
Rcvd: 188 input, 0 checksum errors, 0 too short
0 unknown info type, 0 unknown error type
unreach: 0 routing, 0 admin, 0 neighbor, 0 address, 0 port
parameter: 0 error, 0 header, 0 option
0 hopcount expired, 0 reassembly timeout,0 too big
0 echo request, 0 echo reply
0 group query, 0 group report, 0 group reduce
1 router solicit, 175 router advert, 0 redirects
0 neighbor solicit, 12 neighbor advert
Sent: 7376 output, 56 rate-limited
unreach: 0 routing, 15 admin, 0 neighbor, 0 address, 0 port
parameter: 0 error, 0 header, 0 option
0 hopcount expired, 0 reassembly timeout,0 too big
15 echo request, 0 echo reply
0 group query, 0 group report, 0 group reduce
0 router solicit, 7326 router advert, 0 redirects
2 neighbor solicit, 22 neighbor advert
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
| IPv6 addressing and connectivity |
IPv6 Configuration Guide |
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| IPv6 commands |
Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference |
| Cisco IOS IPv6 features |
Cisco IOS IPv6 Feature Mapping |
Standards and RFCs
| Standard/RFC | Title |
|---|---|
| RFCs for IPv6 |
IPv6 RFCs |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting |
| Feature Name | Releases | Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting |
12.2(8)T Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1 |
The IPv6 ICMP Rate Limiting feature implements a token bucket algorithm for limiting the rate at which IPv6 ICMP error messages are sent out on the network. The following commands were introduced or modified: ipv6 icmp error-interval. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback