- Implementing IPv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity
- Implementing ADSL for IPv6
- Implementing Bidirectional Forwarding Detection for IPv6
- Implementing DHCP for IPv6
- Implementing EIGRP for IPv6
- Configuring First Hop Redundancy Protocols in IPv6
- Implementing IPsec in IPv6 Security
- Implementing IS-IS for IPv6
- Implementing IPv6 for Network Management
- Implementing IPv6 over MPLS
- Implementing IPv6 VPN over MPLS
- Implementing IPv6 Multicast
- PIMv6 Anycast RP Solution
- Implementing Multiprotocol BGP for IPv6
- Implementing NAT-PT for IPv6
- Implementing OSPFv3
- Implementing Policy-Based Routing for IPv6
- Implementing QoS for IPv6
- Implementing RIP for IPv6
- Implementing Selective Packet Discard in IPv6
- Implementing Static Routes for IPv6
- Implementing Traffic Filters for IPv6 Security
- IPv6 ACL Extensions for Hop by Hop Filtering
- Implementing Tunneling for IPv6
- IPv6 Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly
- IPv6 RFCs
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Function
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Client Function
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Relay Agent
- Configuring Route Addition for Relay and Server
- Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Function
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Options
- Configuring the Information Refresh Server Option
- Importing the Information Refresh Server Option
- Configuring NIS- and NISP-Related Server Options
- Importing NIS- and NIS+-Related Server Options
- Importing SIP Server Options
- Configuring the SNTP Server
- Importing the SNTP Server Option
- Importing Stateless DHCPv6 Server Options
- Defining a General Prefix with the DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation Client Function
- Configuring a VRF-Aware Relay and Server for MPLS VPN Support
- Restarting the DHCPv6 Client on an Interface
- Deleting Automatic Client Bindings from the DHCPv6 Binding Table
- Troubleshooting DHCPv6
- Verifying DHCPv6 Configuration and Operation
Implementing DHCP for IPv6
This module describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for IPv6.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About Implementing DHCP for IPv6
DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
The IPv6 Access Services--DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation feature can be used to manage link, subnet, and site addressing changes. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) can be used in environments to deliver stateful and stateless information. The definitions are given below:
- Stateful--Address assignment is centrally managed and clients must obtain configuration information that is not available through protocols such as address autoconfiguration and neighbor discovery.
- Stateless--Stateless configuration parameters do not require a server to maintain any dynamic state for individual clients, such as Domain Name System (DNS) server addresses and domain search list options.
Extensions to DHCPv6 also enable prefix delegation, through which an ISP can automate the process of assigning prefixes to a customer for use within the customer's network. Prefix delegation occurs between a provider edge (PE) device and customer premises equipment (CPE) using the DHCPv6 prefix delegation option. Once the ISP has delegated prefixes to a customer, the customer may further subnet and assign prefixes to the links in the customer's network.
- Configuring Nodes Without Prefix Delegation
- Client and Server Identification
- Rapid Commit
- DHCPv6 Client, Server, and Relay Functions
- DHCPv6 Server and Relay--MPLS VPN Support
Configuring Nodes Without Prefix Delegation
Stateless DHCPv6 allows DHCPv6 to be used for configuring a node with parameters that do not require a server to maintain any dynamic state for the node. The use of stateless DHCP is controlled by router advertisement (RA) messages multicasted by routers. The Cisco IOS XE DHCPv6 client will invoke stateless DHCPv6 when it receives an RA. The Cisco IOS XE DHCPv6 server will respond to a stateless DHCPv6 request with configuration parameters, such as the DNS servers and domain search list options.
Client and Server Identification
Each DHCPv6 client and server is identified by a DHCP unique identifier (DUID). The DUID is carried in client identifier and server identifier options. The DUID is unique across all DHCP clients and servers, and it is stable for any specific client or server. DHCPv6 uses DUIDs based on link-layer addresses for both the client and server identifier. The device uses the MAC address from the lowest-numbered interface to form the DUID. The network interface is assumed to be permanently attached to the device.
When a DHCPv6 client requests two prefixes with the same DUID but with different IAIDs on two different interfaces, these prefixes are considered to be for two different clients, and the interface information is maintained for both.
Rapid Commit
The DHCPv6 client can obtain configuration parameters from a server either through a rapid two-message exchange (solicit, reply) or through a normal four-message exchange (solicit, advertise, request, reply). By default, the four-message exchange is used. When the rapid-commit option is enabled by both client and server, the two-message exchange is used.
DHCPv6 Client, Server, and Relay Functions
The DHCPv6 client, server, and relay functions are mutually exclusive on an interface. When one of these functions is enabled and a user tries to configure a different function on the same interface, one of the following messages is displayed: "Interface is in DHCP client mode," "Interface is in DHCP server mode," or "Interface is in DHCP relay mode."
The following sections describe these functions:
Client Function
The DHCPv6 client function can be enabled on individual IPv6-enabled interfaces.
The DHCPv6 client can request and accept those configuration parameters that do not require a server to maintain any dynamic state for individual clients, such as DNS server addresses and domain search list options.
The DHCPv6 client can also request the delegation of prefixes. The prefixes acquired from a delegating router will be stored in a local IPv6 general prefix pool. The prefixes in the general prefix pool can then be referred to from other applications; for example, the general prefix pool can be used to number router downstream interfaces.
Server Selection
A DHCPv6 client builds a list of potential servers by sending a solicit message and by collecting advertise message replies from servers. These messages are ranked based on the preference value, and servers may add a preference option to their advertise messages explicitly stating their preference value. If the client needs to acquire prefixes from servers, only servers that have advertised prefixes are considered.
IAPD and IAID
An Identity Association for Prefix Delegation (IAPD) is a collection of prefixes assigned to a requesting router. A requesting router may have more than one IAPD; for example, one for each of its interfaces.
Each IAPD is identified by an IAID. The IAID is chosen by the requesting router and is unique among the IAPD IAIDs on the requesting router. IAIDs are made consistent across reboots by using information from the associated network interface, which is assumed to be permanently attached to the device.
Server Function
The DHCPv6 server function can be enabled on individual IPv6-enabled interfaces.
The DHCPv6 server can provide configuration parameters that do not require the server to maintain any dynamic state for individual clients, such as DNS server addresses and domain search list options. The DHCPv6 server may be configured to perform prefix delegation.
All the configuration parameters for clients are independently configured into DHCPv6 configuration pools, which are stored in the NVRAM. A configuration pool can be associated with a particular DHCPv6 server on an interface when it is started. Prefixes that are to be delegated to clients may be specified either as a list of preassigned prefixes for a particular client or as IPv6 local prefix pools that are also stored in the NVRAM. The list of manually configured prefixes or IPv6 local prefix pools can be referenced and used by DHCPv6 configuration pools.
The DHCPv6 server maintains an automatic binding table in memory to track the assignment of some configuration parameters, such as prefixes between the server and its clients. Automatic bindings can be stored permanently in the database agent, such as a remote TFTP server or a local NVRAM file system.
Configuration Information Pool
A DHCPv6 configuration information pool is a named entity that includes information about available configuration parameters and policies that the control assignment of the parameters to clients from the pool. A pool is configured independently and is associated with the DHCPv6 service through the CLI.
Each configuration pool can contain the following configuration parameters and operational information:
Prefix Assignment
A prefix-delegating router (DHCPv6 server) selects prefixes to be assigned to a requesting router (DHCPv6 client) upon receiving a request from the client. The server can select prefixes for a requesting client by using static and dynamic assignment mechanisms. Administrators can manually configure a list of prefixes and associated preferred and valid lifetimes for an IAPD of a specific client that is identified by its DUID.
When the delegating router receives a request from a client, it checks if there is a static binding configured for the IAPD in the client's message. If a static binding is present, the prefixes in the binding are returned to the client. If no such binding is found, the server attempts to assign prefixes for the client from other sources.
The Cisco IOS XE DHCPv6 server can assign prefixes dynamically from an IPv6 local prefix pool. When the server receives a prefix request from a client, it attempts to obtain unassigned prefixes from the pool. After the client releases the previously assigned prefixes, the server returns them to the pool for reassignment.
An IPv6 prefix delegating router can also select prefixes for a requesting router based on an external authority such as a RADIUS server using the Framed-IPv6-Prefix attribute.
Automatic Binding
Each DHCPv6 configuration pool has an associated binding table. The binding table contains records of all prefixes in the configuration pool that have been explicitly delegated to clients. Each entry in the binding table contains the following information:
- Client DUID.
- Client IPv6 address.
- A list of IAPDs associated with the client.
- A list of prefixes delegated to each IAPD.
- Preferred and valid lifetimes for each prefix.
- The configuration pool to which this binding table belongs.
- The network interface on which the server that is using the pool is running.
A binding table entry is automatically created whenever a prefix is delegated to a client from the configuration pool, and the entry is updated when the client renews, rebinds, or confirms the prefix delegation. A binding table entry is deleted when the client voluntarily releases all the prefixes in the binding, the valid lifetimes of all prefixes have expired, or administrators run the clear ipv6 dhcp binding command.
Binding Database
Each permanent storage to which the binding database is saved is called the database agent. A database agent can be a remote host, such as an FTP server, or a local file system, such as the NVRAM.
Automatic bindings are maintained in the RAM and can be saved to some permanent storage so that information about configurations, such as prefixes assigned to clients, is not lost after a system reload. The bindings are stored as text records for easy maintenance. Each record contains the following information:
- DHCPv6 pool name from which the configuration was assigned to the client.
- Interface identifier from which the client requests were received.
- The client IPv6 address.
- The client DUID.
- IAID of the IAPD.
- Prefix delegated to the client.
- The prefix length.
- The prefix preferred lifetime in seconds.
- The prefix valid lifetime in seconds.
- The prefix expiration time stamp.
- Optional local prefix pool name from which the prefix was assigned.
DHCPv6 Server Stateless Autoconfiguration
Hierarchical DHCPv6 for stateless configuration parameters allows a stateless or stateful DHCPv6 client to export configuration parameters (DHCPv6 options) to a local DHCPv6 server pool. The local DHCPv6 server can then provide the imported configuration parameters to other DHCPv6 clients.
The figure below shows a typical broadband deployment.
| Figure 1 | Broadband Topology |
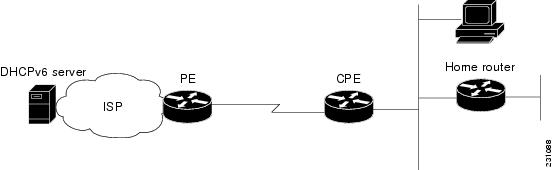
The CPE interface towards the PE can be a stateless or stateful DHCPv6 client. In either case, the ISP-side DHCPv6 server may provide configuration parameters such as DNS server addresses, domain names, and Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) servers to the DHCP client on the CPE. Such information can be specific to ISPs.
In addition to being a DHCPv6 client (for example, towards the ISP), the CPE may act as a DHCPv6 server to the home network. For example, neighbor discovery followed by a stateless or stateful DHCPv6 client can occur on the link between the CPE and the home devices (such as the home router or PC). In some cases, the information to be provided to the home network is the same as that obtained from the ISP-side DHCPv6 server. Because this information can be dynamically changed, it cannot be hard-configured in the CPE's configuration. Therefore, the DHCPv6 component on the CPE allows automatic importing of configuration parameters from the DHCPv6 client to the DHCPv6 server pool.
DHCPv6 supports the following options for IPv6 on the server:
Information Refresh Server Option
The DHCPv6 information refresh option can specify a maximum limit for the length of time a client should wait before refreshing the information retrieved from DHCPv6. This option is used with stateless DHCPv6 because there are no addresses or other entities with lifetimes that can tell the client when to contact the DHCPv6 server to refresh its configuration.
NIS- and NIS+-Related Server Options
Users can configure the network information service (NIS) or NIS plus (NIS+) address or domain name of a DHCPv6 server using NIS- and NIS+-related options, and then import that information to the DHCPv6 client.
SIP Server Options
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) server options contain either a list of domain names or a list of IPv6 addresses that can be mapped to one or more SIP outbound proxy servers. One option carries a list of domain names, and the other option carries a list of 128-bit IPv6 addresses.
SIP is an application-layer control protocol that can establish, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions or calls. A SIP system has several logical components: user agents, proxy servers, redirect servers, and registrars. User agents may contain SIP clients; proxy servers always contain SIP clients.
SNTP Server Option
The SNTP server option provides a list of one or more IPv6 addresses of SNTP servers available to the client for synchronization. Clients use these SNTP servers to synchronize their system time to that of the standard time servers. The DHCPv6 server may list the SNTP servers in decreasing order of preference, but clients treat the list of SNTP servers as an ordered list.
DHCP Relay Agent
A DHCP relay agent, which may reside on the client's link, is used to relay messages between the client and server. DHCP relay agent operation is transparent to the client. A client locates a DHCP server using a reserved, link-scoped multicast address. Therefore, it is a requirement for direct communication between the client and the server that the client and the server be attached to the same link. However, in some situations in which ease of management, economy, or scalability is a concern, it is desirable to allow a DHCP client to send a message to a DHCP server that is not connected to the same link.
DHCPv6 Relay Agent Notification for Prefix Delegation
DHCPv6 relay agent notification for prefix delegation allows the router working as a DHCPv6 relay agent to find prefix delegation options by reviewing the contents of a DHCPv6 RELAY-REPLY packet that is being relayed by the relay agent to the client. When a prefix delegation option is found by the relay agent, the relay agent extracts the information about the prefix being delegated and inserts an IPv6 static route matching the prefix delegation information onto the relay agent. Future packets destined to that prefix via relay will be forwarded based on the information contained in the prefix delegation. The IPv6 static route is then left in the routing table until the prefix delegation lease time expires or the relay agent receives a release packet from the client releasing the prefix delegation.
No user configuration is required for this feature. Static route management is done automatically by the relay agent.
The IPv6 routes are added when the relay agent relays a RELAY-REPLY packet, and the IPv6 routes are deleted when the prefix delegation lease time expires or the relay agent receives a release message. An IPv6 static route in the routing table of the relay agent can be updated when the prefix delegation lease time is extended.
This feature leaves a static IPv6 route on the routing table of the relay agent. This registered IPv6 address allows unicast reverse packet forwarding (uRPF) to work by allowing the router doing the reverse lookup to confirm that the IPv6 address on the relay agent is not malformed or spoofed. The static route left in the routing table of the relay agent can be redistributed to other routing protocols to advertise the subnets to other nodes. The static routes will be removed when an DHCP_DECLINE message is sent by the client.
DHCPv6 Relay Options: Remote-ID for GigabitEthernet and FastEthernet Interfaces
This feature adds the remote identification (remote-ID) option to relayed (RELAY-FORWARD) DHCPv6 packets.
The remote-ID option provides information to the DHCPv6 server, including port information, the system's DUID, and the VLAN ID. Collectively, this information can be used to uniquely identify both the relay and the port on the relay through which the client's packet arrived. The DHCPv6 server uses this information to select parameters specific to a particular user, host, or subscriber modem.
This feature introduces no user configuration. Because the addition of the remote-ID option to the RELAY-FORWARD packet occurs automatically, no user configuration is necessary.
The DHCPv6 server does not need to echo the remote-ID option in the RELAY-REPLY packet. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has assigned the DHCPv6 option code 37 for the relay agent remote-ID option.
If the remote-ID option is included in the RELAY-REPLY packet, the option is stripped out of the packet before the packet is relayed to the client.
DHCPv6 Relay Options: Reload Persistent Interface-ID
This feature makes the interface-ID option, which is used by relay agents to decide which interface should be used when forwarding a RELAY-REPLY packet, persistent. A persistent interface-ID option will not change if the router acting as a relay agent goes offline (such as during a reload or a power outage). When the router acting as a relay agent returns online, it is possible that changes to the internal interface index of the relay agent may have occurred in certain scenarios (such as cases where the relay agent reboots and has a change in the number of interfaces in the interface index, or the relay agents boots up and has more virtual interfaces than it did before the reboot). This feature prevents this scenario from causing any problems.
This feature changes the DHCPv6 interface-ID option to be expressed as simply the short form of the interface name. This syntax helps avoid potential problems that could arise due to physical or logical interfaces changing on the relay agent after a reload.
DHCPv6 Relay Chaining
DHCPv6 messages can be relayed through multiple relay agents. This configuration is called relay chaining. A relay chaining configuration can be supported only when each relay agent adds certain information to DHCPv6 messages before relaying them. The additional information helps in relaying the DHCPv6 reply back to the DHCPv6 client through the same path.
The delegated IPv6 prefix must be routable in order to be useful. The actual DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation (PD) client may not be permitted to inject routes into the delegating network. In service-provider (SP) networks, for example, an edge router typically acts as a DHCPv6 relay agent, and this edge router often has the responsibility to maintain routes within the SP network for clients' PD bindings. In the event that DHCPv6 requests and responses are relayed through a chain of DHCPv6 relays, there may be a need to introduce appropriate routes (particularly with DHCPv6 PD) in the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) so that routing is handled transparently.DHCPv6 Server and Relay--MPLS VPN Support
To facilitate managed central services in a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)-based network, DHCPv6 must be made MPLS-aware so a single resource can be used to serve multiple virtual private networks (VPNs) instead of dedicating a resource to a single VPN.
The DHCPv6 server implementation of MPLS VPN support allows a per-pool configuration so DHCPv6 pools can be associated with a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance. The DHCPv6 server differentiates clients from various VRFs and assigns an IPv6 prefix accordingly from the respective VRF pools. Meanwhile, the DHCPv6 bindings store clients' VRF information.
The DHCPv6 relay implementation allows the configuration of the destination VRF instance to which the relay messages will be forwarded. The relay adds the client's VPN information while forwarding the client's DHCPv6 requests toward the server, and the relay then processes the client's VPN information in reply packets from server.
The relay adds IPv6 static routes for delegated prefixes in corresponding clients' VRF, and the relay's high availability (HA) functionality synchronizes the VRF information while synchronizing static routes created by the relay process.
The DHCPv6 relay and server VRF-aware features are disabled by default for backward compatibility.
How to Implement DHCP for IPv6
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Function
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Client Function
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Relay Agent
- Configuring Route Addition for Relay and Server
- Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Function
- Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Options
- Defining a General Prefix with the DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation Client Function
- Configuring a VRF-Aware Relay and Server for MPLS VPN Support
- Restarting the DHCPv6 Client on an Interface
- Deleting Automatic Client Bindings from the DHCPv6 Binding Table
- Troubleshooting DHCPv6
- Verifying DHCPv6 Configuration and Operation
Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Function
The tasks in the following sections explain how to configure DHCPv6 server function:
- Creating and Configuring the DHCPv6 Configuration Pool
- Configuring a Binding Database Agent for the Server Function
Creating and Configuring the DHCPv6 Configuration Pool
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Binding Database Agent for the Server Function
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the DHCPv6 Client Function
General prefixes can be defined dynamically from a prefix received by a DHCPv6 prefix delegation client. The delegated prefix is stored in a general prefix.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the DHCPv6 Relay Agent
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Route Addition for Relay and Server
To enable route addition by DHCPv6 relay and server for the delegated prefix, use the ipv6 dhcp iapd-route-add command in global configuration mode.
To add routes for individually assigned IPv6 addresses on the relay or server, use the ipv6 dhcp iana-route-add command in global configuration mode
Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Function
The server maintains no state related to clients; for example, no prefix pools and records of allocation are maintained. Therefore, this function is "stateless" DHCPv6.
- Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Server
- Enabling Processing of Packets with Source Routing Header Options
Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Server
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling Processing of Packets with Source Routing Header Options
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Options
- Configuring the Information Refresh Server Option
- Importing the Information Refresh Server Option
- Configuring NIS- and NISP-Related Server Options
- Importing NIS- and NIS+-Related Server Options
- Importing SIP Server Options
- Configuring the SNTP Server
- Importing the SNTP Server Option
- Importing Stateless DHCPv6 Server Options
Configuring the Information Refresh Server Option
DETAILED STEPS
Importing the Information Refresh Server Option
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring NIS- and NISP-Related Server Options
DETAILED STEPS
Importing NIS- and NIS+-Related Server Options
DETAILED STEPS
Importing SIP Server Options
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the SNTP Server
DETAILED STEPS
Importing the SNTP Server Option
DETAILED STEPS
Importing Stateless DHCPv6 Server Options
DETAILED STEPS
Defining a General Prefix with the DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation Client Function
Perform this task to configure the DHCPv6 client function on an interface and enable prefix delegation on an interface. The delegated prefix is stored in a general prefix.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a VRF-Aware Relay and Server for MPLS VPN Support
Configuring a VRF-Aware Relay
 Note |
You do not have to configure this feature on specified interfaces. If you want the feature to be enabled globally only on the router, perform steps 1, 2, and 3 |
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a VRF-Aware Server
DETAILED STEPS
Restarting the DHCPv6 Client on an Interface
Perform this task to restart the DHCPv6 client on a specified interface after first releasing and unconfiguring previously acquired prefixes and other configuration options.
DETAILED STEPS
Deleting Automatic Client Bindings from the DHCPv6 Binding Table
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting DHCPv6
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying DHCPv6 Configuration and Operation
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
Sample Output from the show ipv6 dhcp Command
The following sample output from the show ipv6 dhcp command shows the DUID of the device:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp
This device's DHCPv6 unique identifier(DUID): 000300010002FCA5DC1C
Sample Output from the show ipv6 dhcp binding Command
In the following example, the show ipv6 dhcp binding command shows information about two clients, including their DUIDs, IAPDs, prefixes, and preferred and valid lifetimes:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp binding
Client: FE80::202:FCFF:FEA5:DC39 (GigabitEthernet2/1/0)
DUID: 000300010002FCA5DC1C
IA PD: IA ID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:11::/68
preferred lifetime 180, valid lifetime 12345
expires at Nov 08 2002 02:24 PM (12320 seconds)
Client: FE80::202:FCFF:FEA5:C039 (GigabitEthernet2/1/0)
DUID: 000300010002FCA5C01C
IA PD: IA ID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:1::/72
preferred lifetime 240, valid lifetime 54321
expires at Nov 09 2002 02:02 AM (54246 seconds)
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:2::/72
preferred lifetime 300, valid lifetime 54333
expires at Nov 09 2002 02:03 AM (54258 seconds)
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:3::/72
preferred lifetime 280, valid lifetime 51111
Sample Output from the show ipv6 dhcp database Command
The following sample output from the show ipv6 dhcp database command shows information on the binding database agents TFTP, NVRAM, and flash:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp database
Database agent tftp://172.19.216.133/db.tftp:
write delay: 69 seconds, transfer timeout: 300 seconds
last written at Jan 09 2003 01:54 PM,
write timer expires in 56 seconds
last read at Jan 06 2003 05:41 PM
successful read times 1
failed read times 0
successful write times 3172
failed write times 2
Database agent nvram:/dhcpv6-binding:
write delay: 60 seconds, transfer timeout: 300 seconds
last written at Jan 09 2003 01:54 PM,
write timer expires in 37 seconds
last read at never
successful read times 0
failed read times 0
successful write times 3325
failed write times 0
Database agent flash:/dhcpv6-db:
write delay: 82 seconds, transfer timeout: 3 seconds
last written at Jan 09 2003 01:54 PM,
write timer expires in 50 seconds
last read at never
successful read times 0
failed read times 0
successful write times 2220
failed write times 614
Sample Output from the show ipv6 dhcp interface Command
The following is sample output from the show ipv6 dhcp interface command. In the first example, the command is used on a router that has an interface acting as a DHCPv6 server. In the second example, the command is used on a router that has an interface acting as a DHCPv6 client:
Router1# show ipv6 dhcp interface GigabitEthernet2/1/0 is in server mode Using pool: svr-p1 Preference value: 20 Rapid-Commit is disabled Router2# show ipv6 dhcp interface GigabitEthernet2/1/0 is in client mode State is OPEN (1) List of known servers: Address: FE80::202:FCFF:FEA1:7439, DUID 000300010002FCA17400 Preference: 20 IA PD: IA ID 0x00040001, T1 120, T2 192 Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:1::/72 preferred lifetime 240, valid lifetime 54321 expires at Nov 08 2002 09:10 AM (54319 seconds) Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:2::/72 preferred lifetime 300, valid lifetime 54333 expires at Nov 08 2002 09:11 AM (54331 seconds) Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:3::/72 preferred lifetime 280, valid lifetime 51111 expires at Nov 08 2002 08:17 AM (51109 seconds) DNS server: 2001:DB8:1001::1 DNS server: 2001:DB8:1001::2 Domain name: example1.net Domain name: example2.net Domain name: example3.net Prefix name is cli-p1 Rapid-Commit is enabled
Sample Output from the show ipv6 dhcp pool Command
In the following example, the show ipv6 dhcp pool command provides information on the configuration pool named svr-p1, including the static bindings, prefix information, the DNS server, and the domain names found in the svr-p1 pool:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp pool
DHCPv6 pool: svr-p1
Static bindings:
Binding for client 000300010002FCA5C01C
IA PD: IA ID 00040002,
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:3::/72
preferred lifetime 604800, valid lifetime 2592000
IA PD: IA ID not specified; being used by 00040001
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:1::/72
preferred lifetime 240, valid lifetime 54321
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:2::/72
preferred lifetime 300, valid lifetime 54333
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:3::/72
preferred lifetime 280, valid lifetime 51111
Prefix from pool: local-p1, Valid lifetime 12345, Preferred lifetime 180
DNS server: 2001:DB8:1001::1
DNS server: 2001:DB8:1001::2
Domain name: example1.net
Domain name: example2.net
Domain name: example3.net
Active clients: 2
Current configuration : 22324 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 14:59:38 PST Tue Jan 16 2009
! NVRAM config last updated at 04:25:39 PST Tue Jan 16 2009 by name01
!
hostname Router
!
ip cef
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 cef
ipv6 cef accounting prefix-length
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.4.9.11 255.0.0.0
media-type 10BaseT
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:C18:1::/64 eui-64
Configuration Examples for Implementing DHCPv6
- Example: Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Function
- Example: Configuring the DHCPv6 Client Function
- Example: Configuring a Database Agent for the Server Function
- Example: Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Function
Example: Configuring the DHCPv6 Server Function
DHCPv6 clients are connected to the DHCPv6 server on Gigabit Ethernet interface 0/0/0. The server is configured to use parameters from the DHCP pool called dhcp-pool. This pool provides clients with the IPv6 address of a DNS server and the domain name to be used. It also specifies that prefixes can be delegated from the prefix pool called client-prefix-pool1. The prefixes delegated will have valid and preferred lifetimes of 1800 and 600 seconds respectively. The prefix pool named client-prefix-pool1 has a prefix of length /40 from which it will delegate (sub) prefixes of length /48.
ipv6 dhcp pool dhcp-pool prefix-delegation pool client-prefix-pool1 lifetime 1800 600 dns-server 2001:DB8:3000:3000::42 domain-name example.com ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 description downlink to clients ipv6 address FEC0:240:104:2001::139/64 ipv6 dhcp server dhcp-pool ! ipv6 local pool client-prefix-pool1 2001:DB8:1200::/40 48
The following example from the show ipv6 dhcp command shows the DUID of the device:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp
This device's DHCPv6 unique identifier(DUID): 000300010002FCA5DC1C
In the following example, the show ipv6 dhcp binding command shows information about two clients, including their DUIDs, IAPDs, prefixes, and preferred and valid lifetimes:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp binding
Client: FE80::202:FCFF:FEA5:DC39 (GigabitEthernet2/1/0)
DUID: 000300010002FCA5DC1C
IA PD: IA ID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:11::/68
preferred lifetime 180, valid lifetime 12345
expires at Nov 08 2002 02:24 PM (12320 seconds)
Client: FE80::202:FCFF:FEA5:C039 (GigabitEthernet2/1/0)
DUID: 000300010002FCA5C01C
IA PD: IA ID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:1::/72
preferred lifetime 240, valid lifetime 54321
expires at Nov 09 2002 02:02 AM (54246 seconds)
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:2::/72
preferred lifetime 300, valid lifetime 54333
expires at Nov 09 2002 02:03 AM (54258 seconds)
Prefix: 3FFE:C00:C18:3::/72
preferred lifetime 280, valid lifetime 51111
In the following example, the show ipv6 dhcp database command provides information on the binding database agents TFTP, NVRAM, and flash:
Router# show ipv6 dhcp database
Database agent tftp://172.19.216.133/db.tftp:
write delay: 69 seconds, transfer timeout: 300 seconds
last written at Jan 09 2003 01:54 PM,
write timer expires in 56 seconds
last read at Jan 06 2003 05:41 PM
successful read times 1
failed read times 0
successful write times 3172
failed write times 2
Database agent nvram:/dhcpv6-binding:
write delay: 60 seconds, transfer timeout: 300 seconds
last written at Jan 09 2003 01:54 PM,
write timer expires in 37 seconds
last read at never
successful read times 0
failed read times 0
successful write times 3325
failed write times 0
Database agent flash:/dhcpv6-db:
write delay: 82 seconds, transfer timeout: 3 seconds
last written at Jan 09 2003 01:54 PM,
write timer expires in 50 seconds
last read at never
successful read times 0
failed read times 0
successful write times 2220
failed write times 614
Example: Configuring the DHCPv6 Client Function
This DHCPv6 client has three interfaces: Gigabit Ethernet interface 0/0/0 is the upstream link to a service provider, which has a DHCPv6 server function enabled. The Fast Ethernet interfaces 0/0/0 and 0/1/0 are links to local networks.
The upstream interface, Gigabit Ethernet interface 0/0/0, has the DHCPv6 client function enabled. Prefixes delegated by the provider are stored in the general prefix called prefix-from-provider.
The local networks, Fast Ethernet interfaces 0/0/0 and 0/1/0, both assign interface addresses based on the general prefix called prefix-from-provider. The bits on the left of the addresses come from the general prefix, and the bits on the right of the addresses are specified statically.
interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 description uplink to provider DHCP IPv6 server ipv6 dhcp client pd prefix-from-provider ! interface FastEthernet 0/0/0 description local network 0 ipv6 address prefix-from-provider ::5:0:0:0:100/64 ! interface FastEthernet 0/1/0 description local network 1 ipv6 address prefix-from-provider ::6:0:0:0:100/64
Example: Configuring a Database Agent for the Server Function
The DHCPv6 server is configured to store table bindings to the file named dhcp-binding on the server at address 10.0.0.1 using the TFTP protocol. The bindings are saved every 120 seconds.
ipv6 dhcp database tftp://10.0.0.1/dhcp-binding write-delay 120
The following example shows how to specify DHCP for IPv6 binding database agent parameters and store binding entries in bootflash:
ipv6 dhcp database bootflash
Example: Configuring the Stateless DHCPv6 Function
The following example shows how to use the DHCPv6 function to configure clients with information about the name lookup system. The server is configured with a DHCP pool, which contains the name lookup information that is to be passed to clients. It does not need to contain a prefix pool. This DHCP pool is attached to the access link to customers (GigabitEthernet0/0/0) using the ipv6 dhcp server command. The access link also has the ipv6 nd other-config-flag command enabled. RA messages sent from this interface will inform clients that they should use DHCPv6 for "other" (for example, nonaddress) configuration information.
ipv6 dhcp pool dhcp-pool dns-server 2001:DB8:A:B::1 dns-server 2001:DB8:3000:3000::42 domain-name example.com ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 description Access link down to customers ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1234:42::1/64 ipv6 nd other-config-flag ipv6 dhcp server dhcp-pool
The client has no obvious DHCPv6 configuration. However, the ipv6 address autoconfig command on the uplink to the service provider (GigabitEthernet 0/0/0) causes the following two events:
Additional References
Related Documents
Standards and RFCs
| Standards/RFCs |
Title |
|---|---|
| RFC 3315 |
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 |
| RFC 3319 |
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv6) Options for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers |
| RFC 3633 |
IPv6 Prefix Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Version 6 |
| RFC 3646 |
DNS Configuration Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) |
| RFC 3898 |
Network Information Service (NIS) Configuration Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) |
| RFC 4075 |
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Configuration Option for DHCPv6 |
| RFC 4242 |
Information Refresh Time Option for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) |
| RFC 4649 |
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Relay Agent Remote-ID Option |
MIBs
| MIBs |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Implementing DHCP for IPv6
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for Implementing DHCP for IPv6 |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback