- Example: Configuring IPv6 ND Inspection
- Example: Configuring IPv6 ND Inspection and RA Guard
- Example: Configuring IPv6 Binding Table Content
- Example: Configuring IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table Recovery
- Example: Configuring Address Gleaning and Associating Recovery Protocols with Prefix Lists
- Example: Verifying IPv6 Device Tracking
IPv6 Snooping
The IPv6 Snooping feature bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 neighbor discovery inspection, IPv6 device tracking, IPv6 address glean, and IPv6 binding table recovery, to provide security and scalability. IPv6 ND inspection operates at Layer 2, or between Layer 2 and Layer 3, to provide IPv6 functions with security and scalability.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for IPv6 Snooping
- Information About IPv6 Snooping
- How to Configure IPv6 Snooping
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 Snooping
- Additional References for IPv6 Source Guard and Prefix Guard
- Feature Information for IPv6 Snooping
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for IPv6 Snooping
The IPv6 snooping feature is not supported on Etherchannel ports.
Information About IPv6 Snooping
IPv6 Global Policies
IPv6 global policies provide storage and access policy database services. IPv6 ND inspection and IPv6 RA guard are IPv6 global policies features. Every time an ND inspection or RA guard is configured globally, the policy attributes are stored in the software policy database. The policy is then applied to an interface, and the software policy database entry is updated to include this interface to which the policy is applied.
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Inspection
The IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Inspection, or IPv6 "snooping," feature bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 Address Glean and IPv6 Device Tracking. IPv6 neighbor discovery (ND) inspection operates at Layer 2, or between Layer 2 and Layer 3, and provides IPv6 features with security and scalability. This feature mitigates some of the inherent vulnerabilities for the neighbor discovery mechanism, such as attacks on duplicate address detection (DAD), address resolution, device discovery, and the neighbor cache.
IPv6 ND inspection learns and secures bindings for stateless autoconfiguration addresses in Layer 2 neighbor tables and analyzes ND messages in order to build a trusted binding table. IPv6 ND messages that do not have valid bindings are dropped. An ND message is considered trustworthy if its IPv6-to-MAC mapping is verifiable.
When IPv6 ND inspection is configured on a target (which varies depending on platform target support and may include device ports, switch ports, Layer 2 interfaces, Layer 3 interfaces, and VLANs), capture instructions are downloaded to the hardware to redirect the ND protocol and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for IPv6 traffic up to the switch integrated security features (SISF) infrastructure in the routing device. For ND traffic, messages such as NS, NA, RS, RA, and REDIRECT are directed to SISF. For DHCP, UDP messages sourced from port 546 or 547 are redirected.
IPv6 ND inspection registers its "capture rules" to the classifier, which aggregates all rules from all features on a given target and installs the corresponding ACL down into the platform-dependent modules. Upon receiving redirected traffic, the classifier calls all entry points from any registered feature (for the target on which the traffic is being received), including the IPv6 ND inspection entry point. This entry point is the last to be called, so any decision (such as drop) made by another feature supersedes the IPv6 ND inspection decision.
IPv6 ND Inspection
IPv6 ND inspection learns and secures bindings for stateless autoconfiguration addresses in Layer 2 neighbor tables. IPv6 ND inspection analyzes neighbor discovery messages in order to build a trusted binding table database, and IPv6 neighbor discovery messages that do not have valid bindings are dropped. A neighbor discovery message is considered trustworthy if its IPv6-to-MAC mapping is verifiable.
This feature mitigates some of the inherent vulnerabilities for the neighbor discovery mechanism, such as attacks on duplicate address detection (DAD), address resolution, device discovery, and the neighbor cache.
IPv6 Device Tracking
IPv6 device tracking provides IPv6 host liveness tracking so that a neighbor table can be immediately updated when an IPv6 host disappears.
IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table
The IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table recovery mechanism feature enables the binding table to recover in the event of a device reboot. A database table of IPv6 neighbors connected to the device is created from information sources such as ND snooping. This database, or binding, table is used by various IPv6 guard features to validate the link-layer address (LLA), the IPv4 or IPv6 address, and prefix binding of the neighbors to prevent spoofing and redirect attacks.
This mechanism enables the binding table to recover in the event of a device reboot. The recovery mechanism will block any data traffic sourced from an unknown source; that is, a source not already specified in the binding table and previously learned through ND or DHCP gleaning. This feature recovers the missing binding table entries when the resolution for a destination address fails in the destination guard. When a failure occurs, a binding table entry is recovered by querying the DHCP server or the destination host, depending on the configuration.
Recovery Protocols and Prefix Lists
The IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table Recovery Mechanism feature introduces the capability to provide a prefix list that is matched before the recovery is attempted for both DHCP and NDP.
If an address does not match the prefix list associated with the protocol, then the recovery of the binding table entry will not be attempted with that protocol. The prefix list should correspond to the prefixes that are valid for address assignment in the Layer 2 domain using the protocol. The default is that there is no prefix list, in which case the recovery is attempted for all addresses. The command to associate a prefix list to a protocol is protocol {dhcp | ndp} [prefix-list prefix-list-name].
IPv6 Device Tracking
IPv6 device tracking provides IPv6 host liveness tracking so that a neighbor table can be immediately updated when an IPv6 host disappears.
IPv6 Address Glean
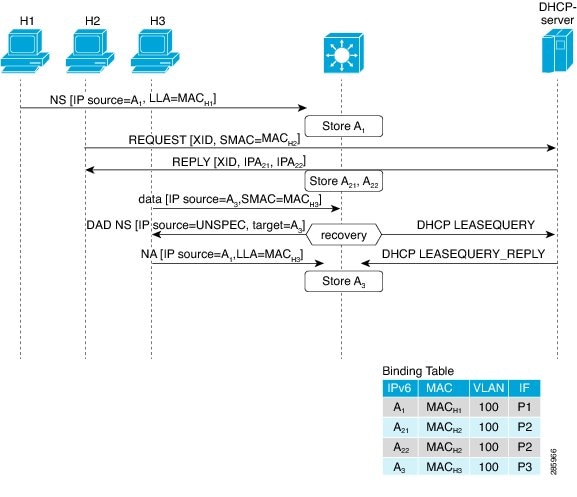
IPv6 address glean is the foundation for many other IPv6 features that depend on an accurate binding table. It inspects ND and DHCP messages on a link to glean addresses, and then populates the binding table with these addresses. This feature also enforces address ownership and limits the number of addresses any given node is allowed to claim.
The following figure shows how IPv6 address glean works.
How to Configure IPv6 Snooping
Configuring IPv6 ND Inspection
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6 snooping policy
snooping-policy
4.
ipv6
snooping
attach-policy
snooping-policy
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring IPv6 ND Inspection Globally
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6
nd
inspection
policy
policy-name
4.
drop-unsecure
5.
sec-level
minimum
value
6.
device-role
{host |
monitor |
router}
7.
tracking
{enable [reachable-lifetime {value |
infinite}] |
disable [stale-lifetime {value |
infinite}]}
8.
trusted-port
DETAILED STEPS
Applying IPv6 ND Inspection on an Interface
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4.
ipv6
nd
inspection
[attach-policy [policy
policy-name] |
vlan {add |
except |
none |
remove |
all}
vlan [vlan1,
vlan2,
vlan3...]]
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying and Troubleshooting IPv6 ND Inspection
1.
enable
2.
show
ipv6
snooping
capture-policy
[interface
type
number]
3.
show
ipv6
snooping
counter
[interface
type
number]
4.
show
ipv6
snooping
features
5.
show
ipv6
snooping
policies
[interface
type
number]
6.
debug
ipv6
snooping
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring IPv6 Device Tracking
Configuring IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table Recovery
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6
neighbor
binding
vlan
vlan-id
{interface
type
number |
ipv6-address |
mac-address} [tracking [disable |
enable |
retry-interval
value] |
reachable-lifetime
value]
4.
ipv6
neighbor
binding
max-entries
entries
[vlan-limit
number |
interface-limit
number |
mac-limit
number]
5.
ipv6
neighbor
binding
logging
6.
exit
7.
show
ipv6
neighbor
binding
[vlan
vlan-id |
interface
type
number |
ipv6
ipv6-address |
mac
mac-address]
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table Recovery Mechanism
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6 neighbor binding vlan
vlan-id
ipv6-address
interface
type number
4.
ipv6 prefix-list
list-name
permit
ipv6-prefix/prefix-length
ge
ge-value
5.
ipv6 snooping policy
snooping-policy-id
6.
destination-glean {recovery |
log-only} [dhcp]
7.
protocol dhcp [prefix-list
prefix-list-name]
8.
exit
9.
ipv6 destination-guard policy
policy-name
10.
enforcement {always |
stressed}
11.
exit
12.
ipv6 dhcp guard policy
policy-name
13.
device-role server
14.
exit
15.
vlan configuration
vlan-list-id
16.
ipv6 snooping attach-policy
policy-name
17.
ipv6 destination-guard attach-policy
policy-name
18.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Address Gleaning and Associating Recovery Protocols with Prefix Lists
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6 snooping policy
snooping-policy-id
4.
protocol {dhcp |
ndp} [prefix-list
prefix-list-name]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ipv6 snooping policy
snooping-policy-id
Example: Device(config)# ipv6 snooping policy 200 |
Enters IPv6 snooping configuration mode and allows you to modify the configuration of the snooping policy specified. |
| Step 4 | protocol {dhcp |
ndp} [prefix-list
prefix-list-name]
Example: Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# protocol dhcp prefix-list dhcp_prefix_list | Specifies that address should be gleaned with dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and associates a recovery protocol (DHCP) with the prefix list. |
| Step 5 | end
Example: Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# end |
Exits IPv6 snooping configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring IPv6 Device Tracking
Perform this task to provide fine tuning for the life cycle of an entry in the binding table for the IPv6 Device Tracking feature. For IPv6 device tracking to work, the binding table needs to be populated.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6
neighbor
tracking
[retry-interval
value]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
ipv6
neighbor
tracking
[retry-interval
value]
Example: Device(config)# ipv6 neighbor tracking |
Tracks entries in the binding table. |
Configuring IPv6 Prefix Glean
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ipv6 snooping policy
snooping-policy
4.
prefix-glean [only]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ipv6 snooping policy
snooping-policy
Example: Device(config)# ipv6 snooping policy policy1 | Configures an IPv6 snooping policy and enters IPv6 snooping policy configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | prefix-glean [only]
Example: Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# prefix-glean | Enables the device to glean prefixes from IPv6 RAs or DHCPv6 traffic. |
Configuration Examples for IPv6 Snooping
Example: Configuring IPv6 ND Inspection
Device(config)# ipv6 snooping policy policy1 Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# ipv6 snooping attach-policy policy1 Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# exit . . . Device# show ipv6 snooping policies policy1 Policy policy1 configuration: trusted-port device-role node Policy applied on the following interfaces: Et0/0 vlan all Et1/0 vlan all Policy applied on the following vlans: vlan 1-100,200,300-400
Example: Configuring IPv6 ND Inspection and RA Guard
This example provides information about an interface on which both the Neighbor Discovery Inspection and RA Guard features are configured:
Device# show ipv6 snooping capture-policy interface ethernet 0/0
Hardware policy registered on Ethernet 0/0
Protocol Protocol value Message Value Action Feature
ICMP 58 RS 85 punt RA Guard
punt ND Inspection
ICMP 58 RA 86 drop RA guard
punt ND Inspection
ICMP 58 NS 87 punt ND Inspection
ICM 58 NA 88 punt ND Inspection
ICMP 58 REDIR 89 drop RA Guard
punt ND Inspection
Example: Configuring IPv6 Binding Table Content
ipv6 neighbor binding vlan 100 ethernet 0/0 reachable-entries 100 ipv6 neighbor binding max-entries 100 ipv6 neighbor binding logging exit
Example: Configuring IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table Recovery
ipv6 dhcp-client leasequery server 2001:db8::1 vlan 100 ipv6 neighbor binding vlan 100 2001:db8::1 interface ethernet3/0 ipv6 prefix-list abc permit 2001:DB8::/64 ge 128 ipv6 snooping policy xyz destination-glean recovery dhcp protocol dhcp prefix-list abc ipv6 destination-guard policy xyz exit ipv6 dhcp guard policy server_side device-role server vlan configuration 100 ipv6 snooping attach-policy xyz ipv6 destination-guard attach-policy xyz interface ethernet3/0 switchport switchport access vlan 100 switchport mode access duplex auto ipv6 dhcp guard attach-policy server_side interface vlan100 no ip address ipv6 address 2001:DB8::100/64
Example: Configuring Address Gleaning and Associating Recovery Protocols with Prefix Lists
The following example shows that NDP will be used for the recovery for all addresses and that DHCP will be used to recover addresses that match the prefix list called dhcp_prefix_list:
Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# protocol ndp Device(config-ipv6-snooping)# protocol dhcp prefix-list dhcp_prefix_list
Example: Verifying IPv6 Device Tracking
Device# show ipv6 neighbor
IPv6 address Link-Layer addr Interface vlan prlvl age state Time left
ND FE80::A8BB:CCFF:FE01:F500 AABB.CC01.F500 Et0/0 100 0002 0 REACHABLE 8850
L FE80::21D:71FF:FE99:4900 001D.7199.4900 Vl100 100 0080 7203 DOWN N/A
ND 2001:600::1 AABB.CC01.F500 Et0/0 100 0003 0 REACHABLE 3181
ND 2001:300::1 AABB.CC01.F500 Et0/0 100 0007 0 REACHABLE 9559
L 2001:400::1 001D.7199.4900 Vl100 100 0080 7188 DOWN N/A
Additional References for IPv6 Source Guard and Prefix Guard
Related Documents
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
IPv6 addressing and connectivity |
IPv6 Configuration Guide |
|
IPv4 addressing |
IP Addressing: IPv4 Addressing Configuration Guide |
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
IPv6 commands |
Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference |
|
Cisco IOS IPv6 features |
Standards and RFCs
Standard/RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
RFCs for IPv6 |
IPv6 RFCs |
Technical Assistance
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 Snooping
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
IPv6 Snooping |
12.2(50)SY 15.0(1)SY 15.0(2)SE 15.1(2)SG 15.3(1)S Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2SE Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E |
IPv6 snooping bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 ND inspection, IPv6 device tracking, IPv6 address glean, and IPv6 first-hop security binding table recovery, to provide security and scalability. IPv6 snooping operates at Layer 2, or between Layer 2 and Layer 3, to provide IPv6 functions with security and scalability. The following commands were introduced or modified: data-glean, debug ipv6 snooping, destination-glean, device-role, drop-unsecure, ipv6 nd inspection, ipv6 nd inspection policy, ipv6 neighbor binding logging, ipv6 neighbor binding max-entries, ipv6 neighbor binding vlan, ipv6 neighbor tracking, ipv6 snooping attach-policy, ipv6 snooping policy, prefix-glean, protocol (IPv6), sec-level minimum, show ipv6 neighbor binding, show ipv6 snooping capture-policy, show ipv6 snooping counters, show ipv6 snooping features, show ipv6 snooping policies, tracking, trusted-port. |
 Feedback
Feedback