- Configuring Mobile IP
- Mobile IP MIB Support for SNMP
- Mobile IP NAT Detect
- Mobile IP Support for Foreign Agent Reverse Tunneling
- Mobile IP Challenge and Response Extensions
- Mobile IP Generic NAI Support and Home Address Allocation
- Mobile IP Home Agent Policy Routing
- Mobile IP Home Agent Accounting
- Mobile IP Dynamic Security Association and Key Distribution
- Mobile IP Support for RFC 3519 NAT Traversal
- Mobile IPv6 High Availability
- IPv6 ACL Extensions for Mobile IPv6
- Mobile IPv6 Home Agent
- IPv6 NEMO
- Index
Contents
- Configuring Mobile IP
- Finding Feature Information
- Mobile IP Overview
- Why is Mobile IP Needed
- Mobile IP Components
- How Mobile IP Works
- Agent Discovery
- Registration
- Routing
- Mobile IP Security
- MN-HA
- MN-FA
- FA-HA
- HA-HA
- Storing Security Associations
- Storing SAs on AAA
- Caching SAs on HA
- Home Agent Redundancy
- HSRP Groups
- How HA Redundancy Works
- Managing Mobility Binding Tables
- Prerequisites
- Mobile IP Configuration Task List
- Enabling Home Agent Services
- Enabling Foreign Agent Services
- Configuring AAA in the Mobile IP Environment
- Configuring RADIUS in the Mobile IP Environment
- Configuring TACACS+ in the Mobile IP Environment
- Verifying Setup
- Monitoring and Maintaining Mobile IP
- Shutting Down Mobile IP
- Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Task List
- Enabling Mobile IP
- Enabling HSRP
- Configuring HSRP Group Attributes
- Enabling HA Redundancy for a Physical Network
- Enabling HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using One Physical Network
- Enabling HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using Multiple Physical Networks
- Enabling HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using One Physical Network
- Enabling HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using Multiple Physical Networks
- Verifying HA Redundancy
- Monitoring and Maintaining HA Redundancy
- Mobile IP Configuration Examples
- Home Agent Configuration Example
- Home Agent Using AAA Server Example
- Foreign Agent Configuration Example
- Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Examples
- HA Redundancy for Physical Networks Example
- HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using One Physical Network Example
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
- HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using Multiple Physical Networks Example
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
- HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using One Physical Network Example
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
- HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using Multiple Physical Networks Example
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
- Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
Configuring Mobile IP
This chapter describes how to configure Mobile IP. For a complete description of the Mobile IP commands in this chapter, refer to the "Mobile IP Commands" chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 1 of 3: Addressing and Services . To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this chapter, use the command reference master index or search online.
- Finding Feature Information
- Mobile IP Overview
- How Mobile IP Works
- Prerequisites
- Mobile IP Configuration Task List
- Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Task List
- Mobile IP Configuration Examples
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Mobile IP Overview
If an IP node, for example, a personal digital assistant (PDA), moves from one link to another, the network prefix of its IP address no longer equals the network prefix assigned to its current link. As a result, packets are not delivered to the current location of the PDA.
Mobile IP enables an IP node to retain the same IP address and maintain existing communications while traveling from one link to another.
Mobile IP is an IETF standards based solution for mobility at the network layer, which is Layer 3. Mobile IP supports the following RFCs:
RFC 2002, IP Mobility Support
RFC 2003, IP Encapsulation within IP
RFC 2005, Applicability Statement for Mobile IP
RFC 2006, The Definitions of Managed Objects for IP Mobility Support
To identify the hardware platform or software image information associated with a feature, use the Feature Navigator on Cisco.com to search for information about the feature or refer to the software release notes for a specific release. For more information, see the "Identifying Supported Platforms" section in the "Using Cisco IOS Software" chapter in this book.
Why is Mobile IP Needed
New devices and business practices, such as PDAs and the next-generation of data-ready cellular phones and services, are driving interest in the ability of a user to roam while maintaining network connectivity. The requirement for data connectivity solutions for this group of users is very different than it is for the fixed dialup user or the stationary wired LAN user. Solutions need to accommodate the challenge of movement during a data session or conversation.
IP routing decisions are based on the network prefix of the IP address to be scalable for the Internet. All nodes on the same link share a common network prefix. If a node moves to another link, the network prefix does not equal the network prefix on the new link. Consequently, IP routing would fail to route the packets to the node after movement to the new link.
An alternative to network-prefix routing is host-specific routing. Host-specific routing is not a problem in small networks. However, considering there are billions of hosts on the Internet, this solution is not feasible for Internet connections. Routers would need enough memory to store tens of millions of routing table entries and would spend most of their computing resources updating routing tables.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is commonly used in corporate environments and allows a server to dynamically assign IP addresses and deliver configuration parameters to nodes. The DHCP Server verifies the identity of the node, "leases" it the IP address from a pool of addresses for a predetermined period of time, and reclaims the address for reassignment when the lease expires. The node can terminate existing communication sessions, move to a new point-of-attachment to the network, reconnect to the network, and receive a new IP address from DHCP. This arrangement conserves IP addresses and reduces Internet access costs. However, if users are mobile and need continuous communications and accessibility without any interruptions in their sessions, DHCP is not an adequate solution. DHCP won’t allow applications to maintain connections across subnet/network boundaries.
Mobile IP is scalable for the Internet because it is based on IP--any media that supports IP can support Mobile IP. Mobile IP does not drop the network prefix of the IP address of the node, which is critical to the proper routing of packets throughout the Internet. Also, certain network services, such as software licenses and access privileges, are based on IP addresses. Changing these IP addresses could compromise the network services. Certain applications, such as remote login, remote printing, and file transfers are examples of applications where it is undesirable to interrupt communications while a mobile node moves from one link to another. Thus, Mobile IP provides the solution for continuous connectivity that is scalable for the Internet.
Mobile IP Components
Mobile IP is comprised of the following three components, as shown in the figure below:
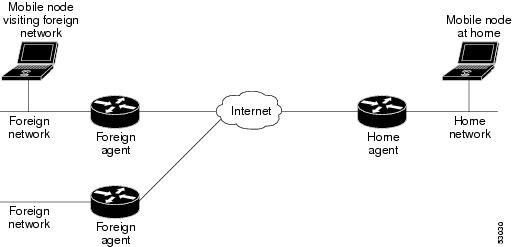
An MN is a node, for example, a PDA, a laptop computer, or a data-ready cellular phone, that can change its point of attachment from one network or subnet to another. This node can maintain ongoing communications while using only its home IP address.
An HA is a router on the home network of the MN that maintains an association between the home IP address of the MN and its care-of address , which is the current location of the MN on a foreign or visited network. The HA redirects packets by tunneling them to the MN while it is away from home.
An FA is a router on a foreign network that assists the MN in informing its HA of its current care-of address. The FA detunnels and delivers packets to the MN that were tunneled by the HA. The FA also acts as the default router for packets generated by the MN while it is connected to the foreign network.
It is recommended that HA and FA functionality be designed with interfaces with line protocol states that are normally up.
How Mobile IP Works
This section explains how Mobile IP works. The Mobile IP process includes three main phases, which are discussed in the following sections:
- Agent Discovery
- Registration
- Routing
- Mobile IP Security
- Storing Security Associations
- Home Agent Redundancy
Agent Discovery
During the agent discovery phase, HAs and FAs advertise their presence on their attached links by periodically multicasting or broadcasting messages called agent advertisements . MNs listen to these advertisements and determine if they are connected to their home link or a foreign link. Rather than waiting for agent advertisements, an MN can also send an agent solicitation. This solicitation forces any agents on the link to immediately send an agent advertisement.
If an MN determines that it is connected to a foreign link, it acquires a care-of address. Two types of care-of addresses exist:
FA care-of address
Collocated care-of address
An FA care-of address is a temporary, loaned IP address that the MN acquires from the FA agent advertisement. This type of care-of address is the exit point of the tunnel from the HA to the FA. A collocated care-of address is an address temporarily assigned to an MN interface. This address is assigned by DHCP or by manual configuration.
Registration
After receiving a care-of address, the MN registers this address with its HA through an exchange of messages. The HA creates a mobility binding table that maps the home IP address of the MN to the current care-of address of the MN. An entry in this table is called a mobility binding . The main purpose of registration is to create, modify, or delete the mobility binding of an MN at its HA.
During registration, the MN also asks for service from the FA.
The HA advertises reachability to the home IP address of the MN, thereby attracting packets that are destined for that address. When a device on the Internet, called a corresponding node (CN), sends a packet to the MN, the packet is routed to the home network of the MN. The HA intercepts the packet and tunnels it to the registered care-of address of the MN. At the care-of address, the FA extracts the packet from the tunnel and delivers it to the MN.
If the MN is sending registration requests through a FA, the FA keeps track of all visiting MNs by keeping a visitor list. The FA relays the registration request directly to the HA without the need for tunneling. The FA serves as the router for all packets sent by the visiting MN.
When the MN powers down or determines that it is reconnected to its home link, it deregisters by sending a deregistration request to the HA. The HA then reclaims the MN.
Routing
Because the major function of a Layer 3 protocol is routing, the major features of Mobile IP deal with how to route packets to users who are mobile.
Mobile IP is a tunneling-based solution that takes advantage of the Cisco-created generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunneling technology and simpler IP-in-IP tunneling protocol. The traffic destined for the MN is forwarded in a triangular manner. When the CN (a device on the Internet) sends a packet to the MN, the HA redirects the packet by tunneling to the care-of address (current location) of the MN on the foreign network. The FA receives the packet from the HA and forwards it locally to the MN. However, packets sent by the MN are routed directly to the CN.
See the figure below for a diagram of typical packet forwarding in Mobile IP.

Mobile IP Security
Mobile IP provides the following guidelines on security between its components:
Communication between MN and HA must be authenticated.
Communication between MN and FA can optionally be authenticated.
Communication between FA and HA can optionally be authenticated.
Also, communication between an active HA and a standby HA, as implemented when using the HA redundancy feature, must be authenticated. For more information on this feature, see the Home Agent Redundancy section later in this chapter.
MN-HA
In particular, the Mobile IP registration process is vulnerable to security attacks, because it informs the HA where to tunnel packets to a traveling MN. An illegitimate node could send a bogus registration request to an HA and cause all packets to be tunneled to the illegitimate node instead of the MN. This type of attack, called a denial-of-service attack , prevents the MN from receiving and sending any packets. To prevent denial-of-service attacks, Mobile IP requires that all registration messages between an MN and an HA be authenticated.
Cisco IOS software supports the Mobile-Home Authentication Extension (MHAE). All registration messages between an MN and an HA include a mandatory authentication extension.
Message Digest 5 (MD5) is an algorithm that takes the registration message and a key to compute the smaller chunk of data, called a message digest , plus a secret key. The MN and HA both have a copy of the key, called a symmetric key , and authenticate each other by comparing the results of the computation.
The time stamp is an identifier in the message that ensures the origination of the registration request and the time it was sent, thereby preventing replay attacks . A replay attack occurs when an individual records an authentic message that was previously transmitted and replays it at a later time. The time stamp is also protected by MD5.
This authentication process begins when a MN sends the registration request. The MN adds the time stamp, computes the message digest, and appends the MHAE to the registration request. The HA receives the request, checks that the time stamp is valid, computes the message digest using the same key, and compares the message digest results. If the results match, the request is successfully authenticated. For the registration reply, the HA adds the time stamp, computes the message digest, and appends the MHAE to the registration reply. The MN authenticates the registration reply upon arrival from the HA.
MN-FA
Mobile IP does not require that communication between an MN and an FA be authenticated. Cisco IOS software supports the optional Mobile-Foreign Authentication Extension (MFAE). MFAE protects the communication between the MN and FA by keeping a shared key between them.
FA-HA
Mobile IP does not require that communication between an FA and an HA be authenticated. Cisco IOS software supports the optional Foreign-Home Authentication Extension (FHAE). FHAE protects the communication between the FA and HA by keeping a shared key between them.
HA-HA
Communication between an active HA and a standby HA in an HA redundancy topology must be authenticated. The authentication process works in the same manner as described in the previous MN-HA section. However, HA-HA authentication is an added Cisco-proprietary authentication extension needed to secure communication between peer HAs for HA redundancy. (Active HAs and standby HAs are peers to each other.)
Use the ip mobile secure home-agent global configuration command to configure the security associations between all peer HAs within a standby group for each of the other HAs within the standby group. The configuration is necessary because any HA within the standby group can become active HA or standby HA at any time. See the Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Task List section later in this chapter for more information on HA-HA authentication.
Storing Security Associations
As discussed in the Mobile IP Security section earlier in this chapter, authentication between the MN and the HA involves keys. You can store the keys or security associations (SAs) on one of the following locations:
NVRAM of an HA
Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server that can be accessed using either TACACS+ or RADIUS
Because the NVRAM of an HA is typically limited, you should store the SAs on the HA only if your organization has a small number of MNs. If your organization has a large number of MNs, you should store the SAs on a AAA server.
Storing SAs on AAA
A AAA server can store a large number of SAs and scale well for future SA storage. It can accommodate not only the SAs for MN-HA authorization, but SAs for authorization between other Mobile IP components as well. Storing all SAs in a centralized location can streamline administrative and maintenance tasks related to the SAs.
Caching SAs on HA
When an MN is registering with an HA, keys are needed for the MN-HA authorization process, which requires AAA authorization for Mobile IP. If SAs are stored on a AAA server, the HA must retrieve the appropriate SA from the server. The SA is downloaded to the HA, and the HA caches the SA and reuses it when necessary rather than retrieving it from the AAA server again.
Home Agent Redundancy
During the Mobile IP registration process, an HA creates a mobility binding table that maps the home IP address of an MN to the current care-of address of the MN. If the HA fails, the mobility binding table will be lost and all MNs registered with the HA will lose their connectivity. To reduce the impact of an HA failure, Cisco IOS software supports the HA redundancy feature.
The functionality of HA redundancy runs on top of the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP). HSRP is a protocol developed by Cisco that provides network redundancy in a way that ensures that user traffic will immediately and transparently recover from failures.
HSRP Groups
Before configuring HA redundancy, you must understand the concept of HSRP groups.
An HSRP group is composed of two or more routers that share an IP address and a MAC (Layer 2) address and act as a single virtual router. For example, your Mobile IP topology can include one active HA and one or more standby HAs that the rest of the topology view as a single virtual HA.
You must define certain HSRP group attributes on the interfaces of the HAs so that Mobile IP can implement the redundancy. You can use the groups to provide redundancy for MNs with a home link on either the interface of the group (a physical network ) or on virtual networks. Virtual networks are logical circuits that are programmed and share a common physical infrastructure.
How HA Redundancy Works
The HA redundancy feature enables you to configure an active HA and one or more standby HAs.
HA functionality is a service provided by the router and is not interface specific. Therefore, the HA and the MN must agree on which HA interface the MN should send its registration requests, and conversely, on which HA interface the HA should receive the registration requests. This agreement must factor in the following two scenarios:
An MN that has an HA interface (HA IP address) that is not on the same subnet as the MN
An MN that requires the HA interface to be on the same subnet as the MN, that is, the HA and the MN must be on the same home network
For MNs on physical networks, an active HA accepts registration requests from the MN and sends binding updates to the standby HA. This process keeps the mobility binding table on the active and standby HAs synchronized. See (a) in the figure below for an example of this process.
For MNs on virtual networks, the active and standby HAs are peers--either HA can handle registration requests from the MN and update the mobility binding table on the peer HA.
When a standby HA comes up, it must request all mobility binding information from the active HA. The active HA responds by downloading the mobility binding table to the standby HA. The standby HA acknowledges that it has received the requested binding information. See (b) in the figure below for an example of an active HA downloading the mobility bindings to a standby HA. A main concern in this stage of the process is which HA IP interface the standby HA should use to retrieve the appropriate mobility binding table and on which interface of the standby HA the binding request should be sent.

Managing Mobility Binding Tables
When a binding is cleared on an active home agent, it will not be cleared on the standby/peer home agent. If you want to clear the binding on the standby/peer home agent, you must manually clear it using the clear ip mobile binding command. This design ensures that binding information will not be accidentally lost.
It is possible that binding tables of two home agents in a redundancy group might be out of synchronization because of a network problem. You can force the synchronization of the binding tables by using the clear ip mobile binding all loadstandby-group-name command.
Prerequisites
To configure home agent functionality on your router, you need to determine IP addresses or subnets for which you want to allow roaming service. If you intend to support roaming on virtual networks, you need to identify the subnets for which you will allow this service and place these virtual networks appropriately on the home agent. It is possible to enable home agent functionality for a physical or virtual subnet. In the case of virtual subnets, you must define the virtual networks on the router using the ip mobile virtual-network global configuration command. Mobile IP home agent and foreign agent services can be configured on the same router or on separate routers to enable Mobile IP service to users.
Because Mobile IP requires support on the host device, each mobile node must be appropriately configured for the desired Mobile IP service with client software. Please refer to the manual entries in your mobile aware IP stack vendor documentation for details.
Mobile IP Configuration Task List
To enable Mobile IP services on your network, you need to determine not only which home agents will facilitate the tunneling for selected IP address, but also where these devices or hosts will be allowed to roam. The areas, or subnets, into which the hosts will be allowed to roam will determine where foreign agent services need to be set up.
To configure Mobile IP, perform the tasks described in the following sections as related to the functions you intend to support. The tasks in the first two sections are required; the tasks in the remaining sections are optional.
- Enabling Home Agent Services
- Enabling Foreign Agent Services
- Configuring AAA in the Mobile IP Environment
- Configuring RADIUS in the Mobile IP Environment
- Configuring TACACS+ in the Mobile IP Environment
- Verifying Setup
- Monitoring and Maintaining Mobile IP
- Shutting Down Mobile IP
Enabling Home Agent Services
Home agent functionality is useful within an enterprise network to allow users to retain an IP address while they move their laptop PCs from their desktops into conference rooms or labs or common areas. It is especially beneficial in environments where wireless LANs are used because the tunneling of datagrams hides the movement of the host and thus allows seamless transition between base stations. To support the mobility of users beyond the bounds of the enterprise network, home agent functionality can be enabled for virtual subnets on the DMZ or periphery of the network to communicate with external foreign agents.
To enable home agent service for users having homed or virtually homed IP addresses on the router, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
1. Router(config)# router mobile
2. Router(config-router)# exit
3. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent
4. Router(config)# ip mobile virtual-network net mask[address address]
5. Router(config)# router protocol
6. Router(config)# redistribute mobile
7. Router(config)# ip mobile host lower [upper] virtual-network net mask[aaa [load-sa]]
8. Router(config)# ip mobile host lower[upper] {interface name}
9. Router(config)# ip mobile secure host lower-address[upper-address]{inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out | spi spi} key hex string
10. Router(config)# ip mobile secure foreign-agent address{inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out| spi spi} key hex string
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router(config)# router mobile |
Enables Mobile IP on the router. |
| Step 2 | Router(config-router)# exit |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent |
Enables home agent service. |
| Step 4 | Router(config)# ip mobile virtual-network net mask[address address] |
Adds virtual network to routing table. If not using a virtual network, go to step 6. |
| Step 5 | Router(config)# router protocol |
Configures a routing protocol. |
| Step 6 | Router(config)# redistribute mobile |
Enables redistribution of a virtual network into routing protocols. |
| Step 7 | Router(config)# ip mobile host lower [upper] virtual-network net mask[aaa [load-sa]] |
Specifies mobile nodes (on a virtual network) and where their security associations are stored.1 |
| Step 8 | Router(config)# ip mobile host lower[upper] {interface name} |
Specifies mobile nodes on an interface and where their security associations are stored. Omit this step if no mobile nodes are on the interface. |
| Step 9 | Router(config)# ip mobile secure host lower-address[upper-address]{inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out | spi spi} key hex string |
Sets up mobile host security associations. Omit this step if using AAA. |
| Step 10 | Router(config)# ip mobile secure foreign-agent address{inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out| spi spi} key hex string |
(Optional) Sets up foreign agent security associations. Omit this step unless you have security associations with remote foreign agents. |
Enabling Foreign Agent Services
Foreign agent services need to be enabled on a router attached to any subnet into which a mobile node may be roaming. Therefore, you need to configure foreign agent functionality on routers connected to conference room or lab subnets, for example. For administrators that want to utilize roaming between wireless LANs, foreign agent functionality would be configured on routers connected to each base station. In this case it is conceivable that both home agent and foreign agent functionality will be enabled on some of the routers connected to these wireless LANs.
To start a foreign agent providing default services, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
1. Router(config)# router mobile
2. Router(config-router)# exit
3. Router(config)# ip mobile foreign-agent care-of interface
4. Router(config-if)# ip mobile foreign-service
5. Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address {inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out| spi spi} key hex string
6. Router(config)# ip mobile secure visitor address {inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out | spi spi} key hex string [replay timestamp]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router(config)# router mobile |
Enables Mobile IP on the router. |
| Step 2 | Router(config-router)# exit |
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | Router(config)# ip mobile foreign-agent care-of interface |
Sets up care-of addresses advertised to all foreign agent-enabled interfaces. |
| Step 4 | Router(config-if)# ip mobile foreign-service |
Enables foreign agent service on the interface. |
| Step 5 | Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address {inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out| spi spi} key hex string |
(Optional) Sets up home agent security association. Omit steps 4 and 5 unless you have security association with remote home agents or visitors. |
| Step 6 | Router(config)# ip mobile secure visitor address {inbound-spi spi-in outbound-spi spi-out | spi spi} key hex string [replay timestamp] |
(Optional) Sets up visitor security association. |
Configuring AAA in the Mobile IP Environment
To configure AAA in the Mobile IP environment, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
1. Router(config)# aaa new-model
2. Router(config)# aaa authorization ipmobile{tacacs+| radius}
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router(config)# aaa new-model |
Enables the AAA access control model. |
| Step 2 | Router(config)# aaa authorization ipmobile{tacacs+| radius} |
Authorizes Mobile IP to retrieve security associations from the AAA server using TACACS+ or RADIUS. |
Configuring RADIUS in the Mobile IP Environment
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) is a method for defining the exchange of AAA information in the network. In the Cisco implementation, RADIUS clients run on Cisco routers and send authentication requests to a RADIUS server that contains all user authentication and network server access information. For detailed information about RADIUS configuration options, refer to the "Configuring RADIUS" chapter in the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide .
To configure RADIUS in the Mobile IP environment, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
1. Router(config)# radius-server host
2. Router(config)# radius-server key
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router(config)# radius-server host |
Specifies a RADIUS server host. |
| Step 2 | Router(config)# radius-server key |
Sets the authentication and encryption key for all RADIUS communications between the router and the RADIUS daemon. |
Configuring TACACS+ in the Mobile IP Environment
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+) is an authentication protocol that provides remote access authentication and related services, such as event logging. For detailed information about TACACS+ configuration options, refer to the "Configuring TACACS+" chapter in the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide .
To configure TACACS+ in the Mobile IP environment, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
1. Router(config)# tacacs-server host
2. Router(config)# tacacs-server key
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router(config)# tacacs-server host |
Specifies a TACACS+ server host. |
| Step 2 | Router(config)# tacacs-server key |
Sets the authentication encryption key used for all TACACS+ communications between the access server and the TACACS+ daemon. |
Verifying Setup
To make sure Mobile IP is set up correctly, use the following commands in EXEC mode as needed:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router# show ip mobile globals
|
Displays home agent and foreign agent global settings. |
Router# show ip mobile host group
|
Displays mobile node groups. |
Router# show ip mobile secure {host | visitor | foreign-agent | home-agent | summary} address |
Displays security associations. |
Router# show ip mobile interface
|
Displays advertisements on interfaces. |
Monitoring and Maintaining Mobile IP
To monitor and maintain Mobile IP, use any of the following EXEC commands:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router# show ip mobile host
|
Displays mobile node counters (home agent only). |
Router# show ip mobile binding
|
Displays mobility bindings (home agent only). |
Router# show ip mobile tunnel
|
Displays active tunnels. |
Router# show ip mobile visitor
|
Displays visitor bindings (foreign agent only). |
Router# show ip route mobile
|
Displays Mobile IP routes. |
Router# show ip mobile traffic
|
Displays protocol statistics. |
Router# clear ip mobile traffic
|
Clears counters. |
Router# show ip mobile violation
|
Displays information about security violations. |
Router# debug ip mobile advertise
|
Displays advertisement information.2 |
Router# debug ip mobile host
|
Displays mobility events. |
Shutting Down Mobile IP
To shut down Mobile IP, use the following commands in global configuration mode:
1. Router(config)# no ip mobile home-agent
2. Router(config)# no ip mobile foreign-agent
3. Router(config)# no router mobile
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router(config)# no ip mobile home-agent |
Disables home agent services. |
| Step 2 | Router(config)# no ip mobile foreign-agent |
Disables foreign agent services. |
| Step 3 | Router(config)# no router mobile |
Disables Mobile IP process. |
Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Task List
- Enabling Mobile IP
- Enabling HSRP
- Configuring HSRP Group Attributes
- Enabling HA Redundancy for a Physical Network
- Enabling HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using One Physical Network
- Enabling HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using Multiple Physical Networks
- Enabling HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using One Physical Network
- Enabling HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using Multiple Physical Networks
- Verifying HA Redundancy
- Monitoring and Maintaining HA Redundancy
Enabling Mobile IP
To enable Mobile IP on the router, use the following command in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router(config)# router mobile
|
Enables Mobile IP on the router. |
Enabling HSRP
To enable HSRP on an interface, use the following command in interface configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router (config-if)# standby [group-number] ip ip-address |
Enables HSRP. |
Configuring HSRP Group Attributes
To configure HSRP group attributes that affect how the local router participates in HSRP, use either of the following commands in interface configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router(config-if)# standby [group-number] priority priority [preempt delay [minimum | sync] delay]]or Router(config-if)# standby [group-number] [priority priority] preempt [delay [minimum | sync] delay |
Sets the Hot Standby priority used in choosing the active router. By default, the router that comes up later becomes standby. When one router is designated as an active HA, the priority is set highest in the HSRP group and the preemption is set. Configure the preempt delay sync command so that all bindings will be downloaded to the router before it takes the active role. The router becomes active when all bindings are downloaded or when the timer expires, whichever comes first. |
Enabling HA Redundancy for a Physical Network
To enable HA redundancy for a physical network, use following commands beginning in interface configuration mode:
1. Router (config-if)# standby[group-number] ip ip-address
2. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name
3. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name
4. Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address spi spi key hex string
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Router (config-if)# standby[group-number] ip ip-address |
Enables HSRP. |
| Step 2 | Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name |
Sets the name of the standby group. |
| Step 3 | Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name |
Configures the home agent for redundancy using the HSRP group name. |
| Step 4 | Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address spi spi key hex string |
Sets up the home agent security association between peer routers. If configured on the active HA, the IP address address argument is that of the standby HA. If configured on the standby HA, the IP address address argument is that of the active router. Note that a security association needs to be set up between all HAs in the standby group. |
Enabling HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using One Physical Network
To enable HA redundancy for a virtual network and a physical network, use the following commands beginning in interface configuration mode:
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent address address
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent
1. Router (config-if)# standby[group-number] ip ip-address
2. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name
3.
Do one of the following:
4. Router(config)# ip mobile virtual-network net mask[address address]
5. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name[[virtual-network] address address]
6. Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address spi spi key hex string
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using Multiple Physical Networks
To enable HA redundancy for a virtual network using multiple physical networks, use the following commands beginning in interface configuration mode:
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent address address
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent
1. Router(config-if)# standby[group-number] ip ip-address
2. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name1
3. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name2
4.
Do one of the following:
5. Router(config)# ip mobile virtual-network net mask [address address]
6. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name1[[virtual-network] address address]
7. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name2[[virtual-network] address address]
8. Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address spi spi key hex string
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using One Physical Network
To enable HA redundancy for multiple virtual networks using one physical network, use the following commands beginning in interface configuration mode:
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent address address
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent
1. Router(config-if)# standby[group-number] ip ip-address
2. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name
3.
Do one of the following:
4. Router(config)# ip mobile virtual-network net mask [address address]
5. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name[[virtual-network] address address]
6. Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address spi spi key hex string
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using Multiple Physical Networks
To enable HA redundancy for multiple virtual networks using multiple physical networks, use the following commands beginning in interface configuration mode:
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent address address
- Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent
1. Router (config-if)# standby[group-number] ip ip-address
2. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name1
3. Router(config-if)# standby name hsrp-group-name2
4.
Do one of the following:
5. Router(config)# ip mobile virtual-network net mask [address address]
6. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name1[[virtual-network] address address]
7. Router(config)# ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name2[[virtual-network] address address]
8. Router(config)# ip mobile secure home-agent address spi spi key hex string
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying HA Redundancy
To verify that the Mobile IP Home Agent Redundancy feature is configured correctly on the router, perform the following steps:
1. Enter the show ip mobile globalsEXECcommand.
2. Examine global information for mobile agents.
3. Enter the show ip mobile binding [home-agent address | summary] EXEC command.
4. Examine the mobility bindings associated with a home agent address.
5. Enter the show standby EXEC command.
6. Examine information associated with the HSRP group.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | Enter the show ip mobile globalsEXECcommand. |
| Step 2 | Examine global information for mobile agents. |
| Step 3 | Enter the show ip mobile binding [home-agent address | summary] EXEC command. |
| Step 4 | Examine the mobility bindings associated with a home agent address. |
| Step 5 | Enter the show standby EXEC command. |
| Step 6 | Examine information associated with the HSRP group. |
Monitoring and Maintaining HA Redundancy
To monitor and maintain HA redundancy, use the following commands in EXEC mode, as needed:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router# debug ip mobile standby
|
Displays debug messages for Mobile IP redundancy activities. |
Router# show ip mobile globals
|
Displays the global home address if configured. For each Mobile IP standby group, displays the home agent address supported. |
Router# show ip mobile binding [home-agent address|summary] |
Displays mobility bindings with specific home agent address. |
Mobile IP Configuration Examples
- Home Agent Configuration Example
- Home Agent Using AAA Server Example
- Foreign Agent Configuration Example
- Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Examples
Home Agent Configuration Example
In the following example, the home agent has five mobile hosts on interface Ethernet1 (network 11.0.0.0) and ten on virtual network 10.0.0.0. There are two mobile node groups. Each mobile host has one security association. The home agent has an access list to disable roaming capability by mobile host 11.0.0.5. The 11.0.0.0 group has a lifetime of 1 hour (3600 seconds). The 10.0.0.0 group cannot roam in areas where the network is 13.0.0.0.
router mobile ! ! Define which hosts are permitted to roam ip mobile home-agent broadcast roam-access 1 ! ! Define a virtual network ip mobile virtual-network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! ! Define which hosts are on the virtual network, and the care-of access list ip mobile host 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.10 virtual-network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 care-of-access 2 ! ! Define which hosts are on Ethernet 1, with lifetime of one hour ip mobile host 11.0.0.1 11.0.0.5 interface Ethernet1 lifetime 3600 ! ! The next ten lines specify security associations for mobile hosts ! on virtual network 10.0.0.0 ! ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 12345678123456781234567812345678 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.2 spi 200 key hex 87654321876543218765432187654321 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.3 spi 300 key hex 31323334353637383930313233343536 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.4 spi 100 key hex 45678332353637383930313233343536 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.5 spi 200 key hex 33343536313233343536373839303132 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.6 spi 300 key hex 73839303313233343536313233343536 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.7 spi 100 key hex 83930313233343536313233343536373 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.8 spi 200 key hex 43536373839313233330313233343536 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.9 spi 300 key hex 23334353631323334353637383930313 ip mobile secure host 10.0.0.10 spi 100 key hex 63738393132333435330313233343536 ! ! The next five lines specify security associations for mobile hosts ! on Ethernet1 ! ip mobile secure host 11.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 73839303313233343536313233343536 ip mobile secure host 11.0.0.2 spi 200 key hex 83930313233343536313233343536373 ip mobile secure host 11.0.0.3 spi 300 key hex 43536373839313233330313233343536 ip mobile secure host 11.0.0.4 spi 100 key hex 23334353631323334353637383930313 ip mobile secure host 11.0.0.5 spi 200 key hex 63738393132333435330313233343536 ! ! Deny access for this host access-list 1 deny 11.0.0.5 ! ! Deny access to anyone on network 13.0.0.0 trying to register access-list 2 deny 13.0.0.0
Home Agent Using AAA Server Example
In the following AAA server configuration, the home agent can use a AAA server for storing security associations. Mobile IP has been authorized using a RADIUS server to retrieve the security association information, which is used by the home agent to authenticate registrations. This format can be imported into a CiscoSecure server.
user = 20.0.0.1 {
service = mobileip {
set spi#0 = "spi 100 key hex 12345678123456781234567812345678"
}
}
user = 20.0.0.2 {
service = mobileip {
set spi#0 = "spi 100 key hex 12345678123456781234567812345678"
}
}
user = 20.0.0.3 {
service = mobileip {
set spi#0 = "spi 100 key hex 12345678123456781234567812345678"
}
}
In the example above, the user is the mobile node’s IP address. The syntax for the security association is spi# num = " string ", where string is the rest of the ip mobile secure{host | visitor | home-agent | foreign-agent} key hex string command.
The following example shows how the home agent is configured to use the AAA server:
aaa new-model aaa authorization ipmobile radius ! ip mobile home-agent ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile host 20.0.0.1 20.0.0.3 virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 aaa load-sa ! radius-server host 1.2.3.4 radius-server key cisco
Foreign Agent Configuration Example
In the following example, the foreign agent is providing service on Ethernet1 interface, advertising care-of address 68.0.0.31 and a lifetime of 1 hour:
interface Ethernet0 ip address 68.0.0.31 255.0.0.0 interface Ethernet1 ip address 67.0.0.31 255.0.0.0 ip irdp ip irdp maxadvertinterval 10 ip irdp minadvertinterval 7 ip mobile foreign-service ip mobile registration-lifetime 3600 ! router mobile ! ip mobile foreign-agent care-of Ethernet0
Mobile IP HA Redundancy Configuration Examples
The table below summarizes the Mobile IP HA redundancy configuration required to support mobile nodes on physical and virtual home networks. Refer to this table for clarification as you read the examples in this section.
|
Mobile Node Home Network |
Physical Connections |
Home Agent Address |
Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Mobile Nodes with Home Agents on Different Subnets |
|||
|
Physical network |
Single |
HSRP group address |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name |
|
Virtual network |
Single |
ip mobile home-agent address address In this configuration, address is the HSRP group address. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name virtual-network |
|
Virtual network |
Multiple |
ip mobile home-agent address address In this configuration, addressis the loopback interface address. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name2 virtual-network Repeat this command for each HSRP group associated with the physical connection. |
|
Multiple virtual networks |
Single |
ip mobile home-agent address address In this configuration, address is the HSRP group address. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name virtual-network |
|
Multiple virtual networks |
Multiple |
ip mobile home-agent address address In this configuration, addressis the loopback interface address. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name2 virtual-network Repeat this command for each HSRP group associated with the physical connection. |
|
Mobile Nodes with Home Agents on the Same Subnet |
|||
|
Physical network |
Single |
HSRP group address |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name |
|
Virtual network |
Single |
ip mobile virtual-network net mask address address In this configuration, address is the loopback interface address. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name virtual-network |
|
Virtual network |
Multiple |
ip mobile virtual-network net mask address address In this configuration, address is the loopback interface address.
|
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name2 virtual-network Repeat this command for each HSRP group associated with the physical connection. |
|
Multiple virtual networks |
Single |
ip mobile virtual-network net mask address address Repeat this command for each virtual network. The address argument is an address configured on the loopback interface to be on the same subnet. Specify the ip address address mask secondary interface configuration command to support multiple IP addresses configured on the same interface. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name virtual-network |
|
Multiple virtual networks |
Multiple |
ip mobile virtual-network net mask address address Repeat this command for each virtual network. The address argument is an address configured on the loopback interface to be on the same subnet. Specify the ip address address mask secondary interface configuration command to support multiple IP addresses configured on the same interface. |
ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby hsrp-group-name2 virtual-network Repeat this command for each HSRP group associated with the physical connection. |
- HA Redundancy for Physical Networks Example
- HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using One Physical Network Example
- HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using Multiple Physical Networks Example
- HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using One Physical Network Example
- HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using Multiple Physical Networks Example
HA Redundancy for Physical Networks Example
The figure below shows an example network topology for physical networks. The configuration example supports home agents that are on the same or a different physical network as the mobile node.

HA1 is favored to provide home agent service for mobile nodes on physical network e0 because the priority is set to 110, which is above the default of 100. HA1 will preempt any active home agent when it comes up. During preemption, it does not become the active home agent until it retrieves the mobility binding table from the current active home agent or until 100 seconds expire for home agent synchronization.
 Note | If the standby preempt command is used, the preempt synchronization delay must be set or mobility bindings cannot be retrieved before the home agent preempts to become active. |
The standby HSRP group name is SanJoseHA and the HSRP group address is 1.0.0.10. The standby HA uses this HSRP group address to retrieve mobility bindings for mobile nodes on the physical network. Mobile IP is configured to use the SanJoseHA standby group to provide home agent redundancy.
Mobile nodes are configured with HA address 1.0.0.10. When registrations come in, only the active home agent processes them. The active home agent sends a mobility binding update to the standby home agent, which also sets up a tunnel with the same source and destination endpoints. Updates and table retrievals are authenticated using the security associations configured on the home agent for its peer home agent. When packets destined for mobile nodes are received, either of the home agents tunnel them. If HA1 goes down, HA2 becomes active through HSRP and will process packets sent to home agent address 1.0.0.10.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA standby preempt delay sync 100 standby priority 110 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using One Physical Network Example
This section presents two configuration examples:
The mobile node and home agent are on different subnets.
The mobile node and home agent are on the same subnet.
Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
HA1 and HA2 share responsibility for providing home agent service for mobile nodes on virtual network 20.0.0.0. The home agents are connected on only one physical network.
The standby group name is SanJoseHA and the HSRP group address is 1.0.0.10. Mobile IP is configured to use the SanJoseHA standby group to provide home agent redundancy. Thus, HSRP allows the home agent to receive packets destined to 1.0.0.10.
This configuration differs from the physical network example in that a global HA address must be specified to support virtual networks. This address is returned in registration replies to the mobile node.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! specifies global HA address=HSRP group address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 1.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! specifies global HA address=HSRP group address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 1.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
In this example, a loopback address is configured on the HA to be on the same subnet as the virtual network. A mobile node on a virtual network uses the HA IP address=loopback address configured for the virtual network. When a standby HA comes up, it uses this HA IP address to retrieve mobility bindings for mobile nodes on the virtual network.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! loopback to receive registration from MN on virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! loopback to receive registration from MN on virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA Redundancy for a Virtual Network Using Multiple Physical Networks Example
This section presents two configuration examples:
The mobile node and home agent are on different subnets.
The mobile node and home agent are on the same subnet.
Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
HA1 and HA2 share responsibility in providing home agent service for mobile nodes on virtual network 20.0.0.0. Both home agents are configured with a global home agent address of 10.0.0.10, which is the address of their loopback interface. This configuration allows home agents to receive registration requests and packets destined to 10.0.0.10.
The loopback address is used as the global HA address instead of the HSRP group addresses 1.0.0.10 and 2.0.0.10 to allow the HAs to continue serving the virtual network even if either physical network goes down.
Mobile nodes are configured with a home agent address 10.0.0.10. When registrations come in, either home agent processes them (depending on routing protocols) and updates the peer home agent. The home agent that receives the registration finds the first HSRP group that is mapped to 10.0.0.10 with a peer in the group and sends the update out that interface. If there is a network problem (for example, the home agent network adapter fails or cable disconnects), HSRP notices the absence of the peer. The home agent does not use that HSRP group and finds another HSRP group to use.
 Note | All routers must have identical loopback interface addresses, which will be used as the global HA address. However, do not use this address as the router ID for routing protocols. |
When the peer home agent receives the registration update, both home agents tunnel the packets to the mobile nodes.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet1 interface ethernet1 ip add 2.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 interface loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 !Specifies global HA address=loopback address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 10.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet2 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet1 interface ethernet1 ip address 2.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 interface loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 !Specifies global HA address=loopback address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 10.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet2 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
In this example, a loopback address is configured on the HA to be on the same subnet as the virtual networks. A mobile node on a virtual network uses the HA IP address=loopback address configured for the virtual network. When a standby HA comes up, it uses this HA IP address to retrieve mobility bindings for mobile nodes on the virtual networks.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip addr 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet1 interface ethernet1 ip addr 2.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 ! loopback to receive registration from MN on virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA interface ethernet1 ip address 2.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 ! loopback to receive registration from MN on virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using One Physical Network Example
This section presents two configuration examples:
The mobile node and home agent are on different subnets.
The mobile node and home agent are on the same subnet.
The first figure below shows an example network topology for the first scenario. The second figure below shows an example network topology for the second scenario.


Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
HA1 and HA2 share responsibility for providing home agent service for mobile nodes on virtual networks 20.0.0.0 and 30.0.0.0. The home agents are connected on only one physical network.
The standby group name is SanJoseHA and the HSRP group address is 1.0.0.10. Mobile IP is configured to use the SanJoseHA standby group to provide home agent redundancy. Thus, HSRP allows the home agent to receive packets destined to 1.0.0.10.
This configuration differs from the physical network example in that a global HA address must be specified to support virtual networks. This address is returned in registration replies to the mobile node.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! specifies global HA address=HSRP group address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 1.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! specifies global HA address=HSRP group address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 1.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
For each virtual network, a loopback address is configured on the HA to be on the same subnet as the virtual network. It is only necessary to configure one loopback interface and to assign different IP addresses to the loopback interface for each virtual network using the ip address ip-address mask [secondary] interface configuration command. A mobile node on a particular virtual network uses the HA IP address =loopback address configured for that virtual network. When a standby HA comes up, it also uses this HA IP address to retrieve mobility bindings for mobile nodes on a particular virtual network.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! loopback to receive registration from MN on each virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 secondary ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) for ! each virtual-network ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 30.0.0.1 ! used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface e0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA ! loopback to receive registration from MN on each virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 secondary ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) for ! each virtual-network ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 30.0.0.1 ! used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHA ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHA virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA Redundancy for Multiple Virtual Networks Using Multiple Physical Networks Example
This section presents two configuration examples:
The mobile node and home agent are on different subnets.
The mobile node and home agent are on the same subnet.
The figure below shows an example network topology for this configuration type.

Mobile Node and Home Agent on Different Subnets
HA1 and HA2 share responsibility in providing home agent service for mobile nodes on virtual networks 20.0.0.0, 30.0.0.0, and 40.0.0.0. Both home agents are configured with a global home agent address of 10.0.0.10, which is the address of their loopback interface. This configuration allows home agents to receive registration requests and packets destined to 10.0.0.10.
The loopback address is used as the global HA address instead of the HSRP group addresses 1.0.0.10 and 2.0.0.10 to allow the HAs to continue serving the virtual networks even if either physical network goes down.
Mobile nodes are configured with home agent address 10.0.0.10. When registrations come in, either home agent processes them (depending on routing protocols) and updates the peer home agent. The home agent that receives the registration finds the first HSRP group that is mapped to 10.0.0.10 with a peer in the group and sends the update out that interface. If there is a network problem (for example, the home agent network adapter fails or cable disconnects), HSRP notices the absence of the peer. The home agent does not use that HSRP group and finds another HSRP group to use.
 Note | All routers must have identical loopback interface addresses, which will be used as the global HA address. However, do not use this address as the router ID for routing protocols. |
When the peer home agent receives the registration update, both home agents tunnel the packets to the mobile nodes.
HA1 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet1 interface ethernet1 ip address 2.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 interface loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 !Specifies global HA address=loopback address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 10.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile virtual-network 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet2 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet1 interface ethernet1 ip address 2.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 interface loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 !Specifies global HA address=loopback address to be used by all mobile nodes ip mobile home-agent address 10.0.0.10 ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ip mobile virtual-network 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet1 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ! Used to map to the HSRP group SanJoseHANet2 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
Mobile Node and Home Agent on Same Subnet
For each virtual network, a loopback address is configured on the HA to be on the same subnet as the virtual network. It is only necessary to configure one loopback interface and assign different IP addresses to the loopback interface for each virtual network, that is, using the ip address ip-address mask [secondary] interface configuration command. A mobile node on a particular virtual network uses the HA IP address =loopback address configured for that virtual network. When a standby HA comes up, it also uses this HA IP address to retrieve mobility bindings for mobile nodes on a particular virtual network.
HA1 Configuration
interface e0 ip address 1.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet1 interface ethernet1 ip address 2.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 ! loopback to receive registration from MN on each virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 secondary ip address 40.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 secondary ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) for ! each virtual-network ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 30.0.0.1 ip mobile virtual-network 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 40.0.0.1 ! used to map to the HSRP groups SanJoseHANet1 and SanJoseHANet2 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.2 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455
HA2 Configuration
interface ethernet0 ip address 1.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 1.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHA interface ethernet1 ip address 2.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 standby ip 2.0.0.10 standby name SanJoseHANet2 ! loopback to receive registration from MN on each virtual-network interface loopback0 ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ip address 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 secondary ip address 40.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 secondary ip mobile home-agent ! address used by Standby HA for redundancy (update and download) for ! each virtual-network ip mobile virtual-network 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 20.0.0.1 ip mobile virtual-network 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 30.0.0.1 ip mobile virtual-network 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 address 40.0.0.1 ! used to map to the HSRP groups SanJoseHANet1 and SanJoseHANet2 ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet1 virtual-network ip mobile home-agent standby SanJoseHANet2 virtual-network ip mobile secure home-agent 1.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455 ip mobile secure home-agent 2.0.0.1 spi 100 key hex 00112233445566778899001122334455