Contents
- MPLS Transport Profile
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for MPLS Transport Profile
- Information About MPLS-TP
- How MPLS Transport Profile Works
- MPLS-TP Path Protection
- Bidirectional LSPs
- Support for MPLS Transport Profile OAM
- MPLS Transport Profile Static and Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires
- MPLS-TP OAM Status for Static and Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires
- MPLS Transport Profile Links and Physical Interfaces
- Tunnel Midpoints
- How to Configure MPLS Transport Profile
- Configuring the MPLS Label Range
- Configuring the Router ID and Global ID
- Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection Templates
- Configuring Pseudowire OAM Attributes
- Configuring the Pseudowire Class
- Configuring the Pseudowire
- Configuring the MPLS-TP Tunnel
- Configuring MPLS-TP LSPs at Midpoints
- Configuring MPLS-TP Links and Physical Interfaces
- Configuring Static-to-Static Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
- Configuring a Template with Pseudowire Type-Length-Value Parameters
- Configuring Static-to-Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
- Verifying the MPLS-TP Configuration
- Configuration Examples for MPLS Transport Profile
- Example: Configuring Static-to-dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
- Additional References for MPLS Transport Profile
- Feature Information for MPLS Transport Profile
MPLS Transport Profile
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Transport Profile (TP) enables you to create tunnels that provide the transport network service layer over which IP and MPLS traffic traverses. MPLS-TP tunnels enable a transition from Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) time-division multiplexing (TDM) technologies to packet switching to support services with high bandwidth requirements, such as video.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for MPLS Transport Profile
- Information About MPLS-TP
- How to Configure MPLS Transport Profile
- Configuration Examples for MPLS Transport Profile
- Additional References for MPLS Transport Profile
- Feature Information for MPLS Transport Profile
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for MPLS Transport Profile
- Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) penultimate hop popping is not supported. Only ultimate hop popping is supported, because label mappings are configured at the MPLS-TP endpoints.
- Ethernet subinterfaces are not supported.
- IPv6 addressing is not supported.
L2VPN Restrictions
- Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) interworking is not supported.
- Local switching with Any Transport over MPLS (AToM) pseudowire as a backup is not supported.
- L2VPN pseudowire redundancy to an AToM pseudowire by one or more attachment circuits is not supported.
- Pseudowire ID Forward Equivalence Class (FEC) type 128 is supported, but generalized ID FEC type 129 is not supported.
- Static pseudowire Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) protocol and BFD VCCV attachment circuit (AC) status signaling are mutually exclusive protocols. Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) and Virtual Circuit Connectivity Verification (VCCV) in failure detection mode can be used with Static Pseudowire OAM protocol.
- BFD VCCV AC status signaling cannot be used in pseudowire redundancy configurations. You can use Static Pseudowire OAM instead.
Ping and Trace Restrictions
- Ping for static pseudowires over MPLS-TP tunnels is not supported.
- Pseudowire ping and traceroute functionality for multisegment pseudowires that have one or more static pseudowire segments is not supported.
The following packet format is supported: Default reply mode for (1) is 4—Reply via application level control channel is supported. An echo reply consists of the following elements: - The optional “do not reply” mode may be set.
The following reply modes are not allowed and are disabled in CLI: - Force-explicit-null is not supported with ping and trace.
- Optional Reverse Path Connectivity verification is not supported.
Information About MPLS-TP
- How MPLS Transport Profile Works
- MPLS-TP Path Protection
- Bidirectional LSPs
- Support for MPLS Transport Profile OAM
- MPLS Transport Profile Static and Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires
- MPLS-TP OAM Status for Static and Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires
- MPLS Transport Profile Links and Physical Interfaces
- Tunnel Midpoints
How MPLS Transport Profile Works
Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) tunnels provide the transport network service layer over which IP and MPLS traffic traverses. MPLS-TP tunnels help transition from Synchronous Optical Network/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET/SDH) and Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) technologies to packet switching to support services with high bandwidth utilization and lower cost. Transport networks are connection-oriented, statically provisioned, and have long-lived connections. Transport networks usually avoid control protocols that change identifiers (like labels). MPLS-TP tunnels provide this functionality through statically provisioned bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs), as shown in the figure below.
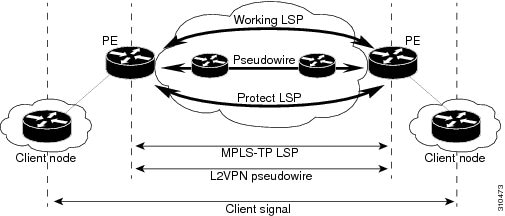
MPLS-TP Path Protection
MPLS-TP label switched paths (LSPs) support 1-to-1 path protection. There are two types of LSPs: protect LSPs and working LSPs. You can configure the both types of LSPs when configuring the MPLS-TP tunnel. The working LSP is the primary LSP used to route traffic. The protect LSP acts as a backup for a working LSP. If the working LSP fails, traffic is switched to the protect LSP until the working LSP is restored, at which time forwarding reverts back to the working LSP.
Bidirectional LSPs
Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) label switched paths (LSPs) are bidirectional and co-routed. They comprise of two unidirectional LSPs that are supported by the MPLS forwarding infrastructure. A TP tunnel consists of a pair of unidirectional tunnels that provide a bidirectional LSP. Each unidirectional tunnel can be optionally protected with a protect LSP that activates automatically upon failure conditions.
Support for MPLS Transport Profile OAM
Several Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) protocols and messages support the provisioning and maintenance of Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) tunnels and bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs).
The following OAM messages are forwarded along the specified MPLS LSP:
- OAM Fault Management—Alarm Indication Signal (AIS), Link Down Indication (LDI), and Lock Report (LKR) messages (GAL with BFD messages).
- OAM Connection Verification—Ping and traceroute messages (GAL with IP channel by default).
- OAM Continuity Check—Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) messages—non-IP BFD and IP BFD (GAL with non-IP BFD channel or IP BFD channel depending on message format).
- The following messages are forwarded along the specified pseudowire:
- MPLS-TP OAM Fault Management (LDI, AIS, and LKR messages)—LDI messages are AIS messages whose L-flags are set. The LDI messages are generated at midpoint nodes when a failure is detected. From the midpoint, an LDI message is sent to the endpoint that is reachable with the existing failure. Similarly, LKR messages are sent from a midpoint node to the reachable endpoint when an interface is administratively shut down. By default, the reception of LDI and LKR messages on the active LSP at an endpoint will cause a path protection switchover, whereas the reception of an AIS message will not.
- MPLS-TP OAM Fault Management with Emulated Protection Switching for LSP Lockout—Cisco implements a form of Emulated Protection Switching to support LSP Lockout using customized Fault messages. When a Lockout message is sent, it does not cause the LSP to be administratively down. The Cisco Lockout message causes a path protection switchover and prevents data traffic from using the LSP. The LSP remains administratively up so that BFD and other OAM messages can continue to traverse it and so that maintenance of the LSP can take place (such as reconfiguring or replacing a midpoint LSR). After OAM verifies the LSP connectivity, the Lockout is removed and the LSP is brought back to service. Lockout of the working LSP is not allowed if a protect LSP is not configured. Conversely, the Lockout of a protect LSP is allowed if a working LSP is not configured.
- LSP ping and trace—To verify MPLS-TP connectivity, use the ping mpls tp and trace mpls tp commands. You can specify that echo requests be sent along the working LSP, the protect LSP, or the active LSP. You can also specify that echo requests be sent on a locked-out MPLS-TP tunnel LSP (either working or protected) if the working or protected LSP is explicitly specified. You can also specify ping/trace messages with or without IP.
- MPLS-TP OAM Continuity Check (CC) via BFD and Remote Defect Indication (RDI)—RDI is communicated via the BFD diagnostic field in BFD CC messages. BFD sessions run on both the working LSP and the protect LSP. To perform a path protection switchover within 60 milliseconds on an MPLS-TP endpoint, use the BFD Hardware Offload feature, which enables the router hardware to construct and send BFD messages, removing the task from the software path. The BFD Hardware Offload feature is enabled automatically on supported platforms.
MPLS-TP OAM GACH—Generic Associated Channel (G-ACh) is the control channel mechanism associated with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) LSPs in addition to MPLS pseudowire. The G-ACh Label (GAL) (Label 13) is a generic alert label to identify the presence of the G-ACh in the label packet. It is taken from the reserved MPLS label space. G-ACh/GAL supports OAMs of LSPs and in-band OAMs of pseudowires (PWs). OAM messages are used for fault management, connection verification, continuity check, and so on.
MPLS Transport Profile Static and Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires
Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) supports the following combinations of static and dynamic multisegment pseudowires:
MPLS-TP OAM Status for Static and Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires
With static pseudowires, status notifications can be provided by BFD over VCCV or by the static pseudowire OAM protocol. However, BFD over VCCV sends only attachment circuit status code notifications. Hop-by-hop notifications of other pseudowire status codes are not supported. Therefore, the static pseudowire OAM protocol is preferred. You can acquire per pseudowire OAM for attachment circuit/pseudowire notification over the VCCV channel with or without the control word.
MPLS Transport Profile Links and Physical Interfaces
Multiprotocol Label Switching Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) link numbers may be assigned to physical interfaces only. Bundled interfaces and virtual interfaces are not supported for MPLS-TP link numbers.
The MPLS-TP link creates a layer of indirection between the MPLS-TP tunnel and midpoint LSP configuration and the physical interface. The mpls tp link command is used to associate an MPLS-TP link number with a physical interface and next-hop node. On point-to-point interfaces or Ethernet interfaces designated as point-to-point using the medium p2p command, the next-hop can be implicit, so the mpls tp link command just associates a link number to the interface.
Multiple tunnels and LSPs may then refer to the MPLS-TP link to indicate that they are traversing that interface. You can move the MPLS-TP link from one interface to another without reconfiguring all the MPLS-TP tunnels and LSPs that refer to the link.
Link numbers must be unique on the router or node.
See the section Configuring MPLS-TP Links and Physical Interfaces, for more information.
Tunnel Midpoints
Tunnel LSPs, whether endpoint or midpoint, use the same identifying information. However, it is entered differently.
- At the midpoint, all information for the LSP is specified with the mpls tp lsp command for configuring forward and reverse information for forwarding.
- At the midpoint, determining which end is source and which is destination is arbitrary. That is, if you are configuring a tunnel between your device and a coworker’s device, then your device is the source. However, your coworker considers his or her device to be the source. At the midpoint, either device could be considered the source. At the midpoint, the forward direction is from source to destination, and the reverse direction is from destination to source.
- At the endpoint, the local information (source) either comes from the global device ID and global ID, or from the locally configured information using the tp source command.
- At the endpoint, the remote information (destination) is configured using the tp destination command after you enter the interface tunnel-tp number command. The tp destination command includes the destination node ID, and optionally the global ID and the destination tunnel number. If you do not specify the destination tunnel number, the source tunnel number is used.
- At the endpoint, the LSP number is configured in working-lsp or protect-lsp submode. The default is 0 for the working LSP and 1 for the protect LSP.
- When configuring LSPs at midpoint devices, ensure that the configuration does not deflect traffic back to the originating node.
How to Configure MPLS Transport Profile
- Configuring the MPLS Label Range
- Configuring the Router ID and Global ID
- Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection Templates
- Configuring Pseudowire OAM Attributes
- Configuring the Pseudowire Class
- Configuring the Pseudowire
- Configuring the MPLS-TP Tunnel
- Configuring MPLS-TP LSPs at Midpoints
- Configuring MPLS-TP Links and Physical Interfaces
- Configuring Static-to-Static Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
- Configuring a Template with Pseudowire Type-Length-Value Parameters
- Configuring Static-to-Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
- Verifying the MPLS-TP Configuration
Configuring the MPLS Label Range
You must specify a static range of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) labels using the mpls label range command with the static keyword.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
mpls
label
range
minimum-value
maximum-value
static minimum-static-value maximum-static-value
4.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Router ID and Global ID
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
mpls
tp
4.
router-id
node-id
5.
global-id
num
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection Templates
The bfd-template command allows you to create a BFD template and enter BFD configuration mode. The template can be used to specify a set of BFD interval values. You invoke the template as part of the MPLS-TP tunnel. On platforms that support the BFD Hardware Offload feature and that can provide a 60-ms cutover for MPLS-TP tunnels, it is recommended to use the higher resolution timers in the BFD template.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
bfd-template
single-hop
template-name
4.
interval
[microseconds] {both time | min-tx time min-rx time} [multiplier multiplier-value]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Pseudowire OAM Attributes
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
pseudowire-static-oam
class
class-name
4.
timeout
refresh
send
seconds
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Pseudowire Class
When you create a pseudowire class, you specify the parameters of the pseudowire, such as the use of the control word, preferred path, OAM class, and VCCV BFD template.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
pseudowire-class
class-name
4.
encapsulation
mpls
5.
control-word
6.
protocol
{l2tpv2 | l2tpv3 | none} [l2tp-class-name]
7.
preferred-path {interface tunnel tunnel-number | peer {ip-address | host-name}} [disable-fallback]
8.
status
protocol
notification
static
class-name
9.
vccv
bfd
template
name
[udp | raw-bfd]
10.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Pseudowire
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4.
xconnect
peer-ip-address
vc-id
{encapsulation
{l2tpv3 [manual] |
mpls [manual]} |
pw-class pw-class-name}
[pw-class pw-class-name]
[sequencing {transmit |
receive |
both}]
5.
mpls
label
local-pseudowire-label
remote-pseudowire-label
6.
mpls
control-word
7.
backup
delay
{enable-delay-period |
never}
{disable-delay-period |
never}
8.
backup
peer
peer-router-ip-addr
vcid
[pw-class pw-class-name]
[priority value]
9.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the MPLS-TP Tunnel
On the endpoint devices, create an MPLS TP tunnel and configure its parameters. See the interface tunnel-tp command for information on the parameters.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
tunnel-tp
number
4.
description
tunnel-description
5.
tp
tunnel-name
name
6.
tp
bandwidth
num
7.
tp
source
node-id
[global-id num]
8.
tp
destination
node-id
[tunnel-tp num[ global-id num]]
9.
bfd
bfd-template
10.
working-lsp
11.
in-label
num
12.
out-label
num
out-link
num
13.
exit
14.
protect-lsp
15.
in-label
num
16.
out-label
num
out-link
num
17.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring MPLS-TP LSPs at Midpoints
 Note | When configuring LSPs at midpoint devices, ensure that the configuration does not deflect traffic back to the originating node. |
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
mpls
tp
lsp
source
node-id
[global-id
num]
tunnel-tp
num
lsp{lsp-num |
protect |
working}
destination
node-id
[global-id
num]
tunnel-tp
num
4.
forward-lsp
5.
bandwidth
num
6.
in-label
num
out-label
num
out-link
num
7.
exit
8.
reverse-lsp
9.
bandwidth
num
10.
in-label
num
out-label
num
out-link
num
11.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring MPLS-TP Links and Physical Interfaces
MPLS-TP link numbers may be assigned to physical interfaces only. Bundled interfaces and virtual interfaces are not supported for MPLS-TP link numbers.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type number
4.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
5.
mpls
tp
link
link-num
{ipv4 ip-address | tx-mac mac-address} rx-mac mac-address
6.
ip
rsvp
bandwidth
[rdm [bc0 interface-bandwidth] [[single-flow-bandwidth [bc1 bandwidth | sub-pool bandwidth]]] [interface-bandwidth [single-flow-bandwidth [bc1 bandwidth | sub-pool bandwidth]] | mam max-reservable-bw [interface-bandwidth [single-flow-bandwidth] [bc0 interface-bandwidth [bc1 bandwidth]]] | percent percent-bandwidth [single-flow-bandwidth]]
7.
end
8.
show
mpls
tp
link-numbers
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Static-to-Static Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
l2
vfi
name
point-to-point
4.
neighbor
ip-address
vc-id
{encapsulation mpls | pw-class pw-class-name}
5.
mpls
label
local-pseudowire-label
remote-pseudowire-label
6.
mpls
control-word
7.
neighbor
ip-address
vc-id
{encapsulation mpls | pw-class pw-class-name}
8.
mpls
label
local-pseudowire-label
remote-pseudowire-label
9.
mpls
control-word
10.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Template with Pseudowire Type-Length-Value Parameters
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
pseudowire-tlv
template
template-name
4.
tlv [type-name] type-value length [dec | hexstr | str] value
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
pseudowire-tlv
template
template-name
Example: Device(config)# pseudowire-tlv template statictemp |
Creates a template of pseudowire type-length-value (TLV) parameters and enters pseudowire TLV template configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
tlv [type-name] type-value length [dec | hexstr | str] value Example: Device(config-pw-tlv-template)# tlv statictemp 2 4 hexstr 1 |
Specifies the TLV parameters. |
| Step 5 |
end Example: Device(config-pw-tlv-template)# end |
Exits pseudowire TLV template configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring Static-to-Dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
When you configure static-to-dynamic pseudowires, you configure the static pseudowire class with the protocol none command, create a dynamic pseudowire class, and then invoke those pseudowire classes with the neighbor commands.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
pseudowire-class
class-name
4.
encapsulation
mpls
5.
control-word
6.
protocol {l2tpv2 | l2tpv3 | none} [l2tp-class-name]
7.
exit
8.
pseudowire-class
class-name
9.
encapsulation
mpls
10.
exit
11.
l2
vfi
name
point-to-point
12.
neighbor
ip-address
vc-id {encapsulation mpls | pw-class pw-class-name}
13.
neighbor
ip-address
vc-id {encapsulation mpls | pw-class pw-class-name}
14.
mpls
label
local-pseudowire-label
remote-pseudowire-label
15.
mpls
control-word
16.
local
interface
pseudowire-type
18.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
pseudowire-class
class-name
Example: Device(config)# pseudowire-class mpls-tp-class1 |
Creates a pseudowire class and enters pseudowire class configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 |
encapsulation
mpls
Example: Device(config-pw-class)# encapsulation mpls |
Specifies the encapsulation type. | ||
| Step 5 |
control-word
Example: Device(config-pw-class)# control-word |
Enables the use of the control word. | ||
| Step 6 |
protocol {l2tpv2 | l2tpv3 | none} [l2tp-class-name] Example: Device(config-pw-class)# protocol none |
Specifies the type of protocol. Use the protocol none command to specify a static pseudowire. | ||
| Step 7 |
exit
Example: Device(config-pw-class)# exit |
Exits pseudowire class configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 8 |
pseudowire-class
class-name
Example: Device(config)# pseudowire-class mpls-tp-class1 |
Creates a pseudowire class and enters pseudowire class configuration mode. | ||
| Step 9 |
encapsulation
mpls
Example: Device(config-pw-class)# encapsulation mpls |
Specifies the encapsulation type. | ||
| Step 10 |
exit
Example: Device(config-pw-class)# exit |
Exits pseudowire class configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 11 |
l2
vfi
name
point-to-point
Example: Device(config)# l2 vfi atom point-to-point |
Creates a point-to-point Layer 2 virtual forwarding interface (VFI) and enters VFI configuration mode. | ||
| Step 12 |
neighbor
ip-address
vc-id {encapsulation mpls | pw-class pw-class-name} Example: Device(config-vfi)# neighbor 10.111.111.111 123 pw-class atom |
Sets up an emulated VC and enters VFI neighbor configuration mode.
| ||
| Step 13 |
neighbor
ip-address
vc-id {encapsulation mpls | pw-class pw-class-name} Example: Device(config-vfi-neighbor)# neighbor 10.111.111.111 123 pw-class atom |
Sets up an emulated VC.
| ||
| Step 14 |
mpls
label
local-pseudowire-label
remote-pseudowire-label
Example: Device(config-vfi-neighbor)# mpls label 101 201 |
Configures the static pseudowire connection by defining local and remote circuit labels. | ||
| Step 15 |
mpls
control-word
Example: Device(config-vfi-neighbor)# mpls control-word |
Specifies the control word. | ||
| Step 16 |
local
interface
pseudowire-type
Example: Device(config-vfi-neighbor)# local interface 4 |
Specifies the pseudowire type. | ||
| Step 17 | Do one of the following:
Example: Device(config-vfi-neighbor)# tlv statictemp 2 4 hexstr 1 |
Specifies the TLV parameters or invokes a previously configured TLV template. | ||
| Step 18 | end Example: Device(config-vfi-neighbor)# end | Ends the session. |
Verifying the MPLS-TP Configuration
Use the following commands to verify and help troubleshoot your MPLS-TP configuration:
- debug mpls tp—Enables the logging of MPLS-TP error messages.
- logging (MPLS-TP)—Displays configuration or state change logging messages.
- show bfd neighbors mpls-tp—Displays the BFD state, which must be up in order for the endpoint LSPs to be up.
- show mpls l2transport static-oam l2transport static-oam—Displays MPLS-TP messages related to pseudowires.
- show mpls tp tunnel-tp number detail—Displays the number and details of the tunnels that are not functioning.
- show mpls tp tunnel-tp lsps—Displays the status of the LSPs, and helps you ensure that both LSPs are up and working from a tunnel endpoint.
- traceroute mpls tp and ping mpls tp—Helps you identify connectivity issues along the MPLS-TP tunnel path.
Configuration Examples for MPLS Transport Profile
Example: Configuring Static-to-dynamic Multisegment Pseudowires for MPLS-TP
The following example shows how to configure static-to-dynamic multisegment pseudowires for Layer 2 VFI.
l2 vfi atom point-to-point (static-dynamic MSPW) neighbor 10.116.116.116 4294967295 pw-class dypw (dynamic) neighbor 10.111.111.111 123 pw-class stpw (static) mpls label 101 201 mpls control-word local interface 4 tlv mtu 1 4 1500 tlv description 3 6 str abcd tlv descr C 4 hexstr 0505
Additional References for MPLS Transport Profile
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
MPLS commands |
Standards and RFCs
|
Standard/RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
draft-ietf-mpls-tp-gach-gal-xx |
MPLS Generic Associated Channel |
|
RFC 5586 |
MPLS Generic Associated Channel |
|
RFC 5885 |
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for the Pseudowire Virtual Circuit Connectivity Verification (VCCV) |
|
RFC 5921 |
A Framework for MPLS in Transport Networks |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for MPLS Transport Profile
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
MPLS Transport Profile
|
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.5S |
MPLS Transport Profile (TP) enables you to create tunnels that provide the transport network service layer over which IP and MPLS traffic traverses. MPLS-TP tunnels enable a transition from SONET and SDH TDM technologies to packet switching to support services with high bandwidth requirements, such as video. In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.5S, support was added for the Cisco ASR 903 Router. The following commands were introduced or modified: debug mpls l2transport static-oam, debug mpls tp, interface tunnel-tp interval local, interface logging (MPLS-TP), medium p2p, mpls tp, mpls tp link, mpls tp lsp ping, notification static timeout refresh, pseudowire-static-oam class, pseudowire-tlv template, show mpls l2transport static-oam, show mpls tp status protocol, tlv, tlv template trace mpls tp. |
MPLS Transport Profile |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S |
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S, support was added for the Cisco ASR 1000 Router. |