- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Restrictions for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Information About QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Benefits of QoS Bandwidth Estimation
QoS Bandwidth Estimation
The QoS Bandwidth Estimation feature uses Corvil Bandwidth technology to allow you, as a network manager, to determine the bandwidth requirements to achieve user-specified quality of service (QoS) targets for networked applications.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Restrictions for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Information About QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- How to Configure QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Configuration Examples for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Additional References
- Feature Information for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Before using this feature, configure a class map and a policy map using the Modular Quality of Service (QoS) Command-Line Interface (CLI) (MQC), and specify the appropriate match criteria.
- This feature requires the purchase of a Cisco IOS software feature license. The right to use this feature is not included in the base Cisco IOS software license for the software image.
Restrictions for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
This feature supports policy maps that are attached to interfaces in an output direction only.
Information About QoS Bandwidth Estimation
Feature Overview of QoS Bandwidth Estimation
Allocating adequate bandwidth is key to ensuring the network performance required for applications. However, allocating too much bandwidth can be costly. The QoS Bandwidth Estimation feature in Cisco IOS software uses Corvil Bandwidth technology to allow you, as a network manager, to determine the bandwidth requirements to achieve user-specified quality of service (QoS) targets for networked applications.
Corvil Bandwidth can determine the minimum bandwidth required to deliver traffic within customer-specified QoS targets with statistical reliability. From a network management perspective, an application's QoS requirements are characterized with respect to its sensitivity to delay and packet loss. Corvil Bandwidth provides a way to specify limits for delay and packet loss, and get a tight estimate of the minimum bandwidth essential to achieve desired application performance.
Corvil Bandwidth achieves its results by taking very short timescale (8-millisecond) snapshots of traffic and summarizing them in traffic descriptors that place very low overhead on the router because each descriptor has fewer than 300 bytes. These traffic descriptors record the exceptional events (bursts) and are input to the Corvil Bandwidth algorithm to calculate the minimum bandwidth required to deliver the user-specified QoS target for the observed traffic. (The QoS target is specified in terms of sensitivity to traffic delay and packet loss. For example, voice over IP [VoIP] traffic is very sensitive to both, whereas e-mail file transfer is sensitive to neither.)
As a result, turning on Corvil Bandwidth in the router allows you to obtain bandwidth values that can be used directly to configure the existing Cisco IOS QoS mechanisms on the router to achieve the required application performance as efficiently as possible.
For example, in the figure below, Corvil Bandwidth is enabled on the router so that the serial interface can deliver the WAN traffic within the customer-specified QoS targets with statistical reliability.
| Figure 1 | Sample Topology Using QoS Bandwidth Estimation |
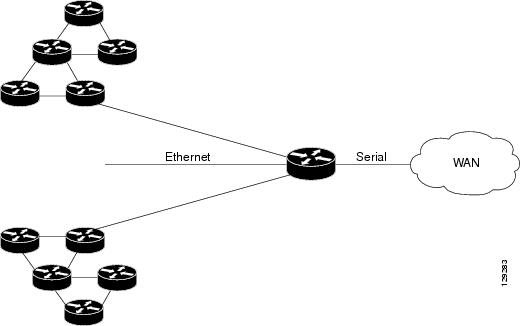
Applying Corvil Bandwidth
The following sections describe how Corvil Bandwidth can be implemented:
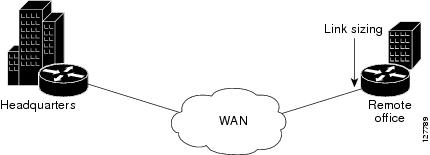
Link Sizing
To use Corvil Bandwidth to establish the overall bandwidth requirement for a link, you start with QoS targets appropriate for the speed of the link and for the applications being carried on the link (see the figure below). The QoS targets are achieved as long as the link capacity is greater than or equal to the computed Corvil Bandwidth value.
| Figure 2 | Link Sizing |
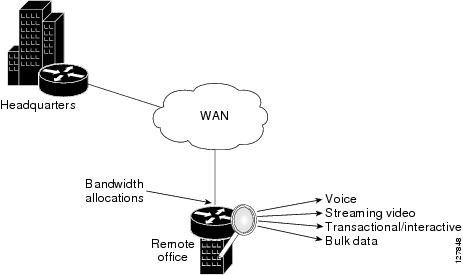
Bandwidth Allocations by Traffic Class
Corvil Bandwidth can be used to size bandwidth allocations for individual traffic classes defined via the MQC (see the figure below). You specify the QoS target for a traffic class, and Corvil Bandwidth reports the minimum amount of bandwidth that must be allocated to meet that target. The Corvil Bandwidth value can be used directly in the corresponding MQC policy. (The bandwidth allocation is not changed automatically.)
| Figure 3 | Bandwidth Allocations |
Benefits of QoS Bandwidth Estimation
The table below shows the features and benefits of QoS Bandwidth Estimation using Corvil Bandwidth technology.
| Table 1 | QoS Bandwidth Estimation |
How to Configure QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Generating a Bandwidth Estimate
- Attaching the Policy Map to an Interface
- Verifying the Configuration
Generating a Bandwidth Estimate
DETAILED STEPS
Attaching the Policy Map to an Interface
 Note |
This feature supports policy maps attached to an interface in the output direction only. > |
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying the Configuration
To verify that bandwidth estimates have been generated, perform the following task.
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
|
|
Example: Router# show policy-map interface fastethernet0/1 |
Displays the packet statistics of all classes that are configured for all service policies either on the specified interface or subinterface or on a specific PVC on the interface.
|
|
|
Example: Router# exit |
(Optional) Exits privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Examples for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
- Example Generating Bandwidth Estimates for QoS Targets
- Example Attaching the Policy Map to an Interface
- Example Verifying the Configuration
Example Generating Bandwidth Estimates for QoS Targets
In the following example, a policy map and a traffic class are configured. Then bandwidth estimates for QoS targets including packet loss rate, delay time and probability, and timeframe in milliseconds are configured.
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# policy-map my-policy
Router(config-pmap)# class my-class
Router(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 20
Router(config-pmap-c)# estimate bandwidth drop-one-in 100 delay-one-in 100 milliseconds 50
Router(config-pmap-c)# end
Example Attaching the Policy Map to an Interface
The following example shows the policy map named my-policy being attached to Fast Ethernet interface 0/1 in the output direction:
Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface f0/1 Router(config-if)# service-policy output my-policy Router(config-if)# exit
Example Verifying the Configuration
The following example from the show policy-map interfacecommand verifies that the policy map named my-policy is attached to Fast Ethernet interface 0/1 in the output direction and that bandwidth estimates have been created:
Router# show policy-map interface fastethernet0/1
FastEthernet0/1
Service-policy output: my-policy
Class-map: icmp (match-all)
199 packets, 22686 bytes
30 second offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: access-group 101
Bandwidth Estimation:
Quality-of-Service targets:
drop no more than one packet in 1000 (Packet loss < 0.10%)
delay no more than one packet in 100 by 40 (or more) milliseconds
(Confidence: 99.0000%)
Corvil Bandwidth: 1 kbits/sec
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
112 packets, 14227 bytes
30 second offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps
Match: any
Bandwidth Estimation:
Quality-of-Service targets:
<none specified, falling back to drop no more than one packet in 500
Corvil Bandwidth: 1 kbits/sec
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the QoS Bandwidth Estimation feature.
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| QoS commands: complete command syntax, command modes, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples |
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference |
| Information about attaching policy maps to interfaces using the MQC |
"Applying QoS Features Using the MQC" module |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified standards are supported, and support for existing standards has not been modified. |
-- |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified RFCs are supported, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified. |
-- |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for QoS Bandwidth Estimation
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 2 | Feature Information for QoS Bandwidth Estimation |
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| QoS Bandwidth Estimation |
12.3(14)T |
The QoS Bandwidth Estimation feature uses Corvil Bandwidth technology to allow you, as a network manager, to determine the bandwidth requirements to achieve user-specified quality of service (QoS) targets for networked applications. The following commands were introduced or modified by this feature: estimate bandwidth, show policy-map interface. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback