- RSVP Aggregation
- RSVP Application ID Support
- RSVP Fast Local Repair
- RSVP Interface-Based Receiver Proxy
- RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- Control Plane DSCP Support for RSVP
- MPLS TE - Tunnel-Based Admission Control
- PfR RSVP Control
- Configuring RSVP Agent
- RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- RSVP Local Policy Support
- RSVP Message Authentication
- RSVP Support for RTP Header Compression Phase 1
- Configuring RSVP
- Configuring RSVP Support for LLQ
- Configuring COPS for RSVP
Configuring RSVP Agent
The RSVP Agent feature implements a Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) agent on Cisco IOS voice gateways that support Cisco Unified Communications Manager Version 5.0.1. The RSVP agent enables Cisco Unified Communications Manager to provide resource reservation for voice and video media to ensure QoS and call admission control (CAC). Cisco Unified Communications Manager controls the RSVP agent through Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP). This signaling is independent of the signaling protocol used for the call so SCCP, SIP, H.323, and MGCP calls can all use the RSVP agent.
Benefits of this feature include the following:
- Improves flexibility and scalability of bandwidth management in a meshed network by decentralizing call admission control
- Provides method of managing unpredictable bandwidth requirements of video media
- Enables RSVP across WAN for Cisco IP phones and other devices that do not support RSVP
Feature History for RSVP Agent
| Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
| 12.4(6)T |
This feature was introduced. |
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn . You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for RSVP Agent
Cisco IOS Voice Gateway
- Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T or a later release.
- Transcoder and MTP services must be configured on the voice gateway. See "Configuring Enhanced Conferencing and Transcoding for Voice Gateway Routers" on page 67 .
- SCCP must be enabled on the local interface that the voice gateway uses to register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager. See the "Enabling SCCP on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interface" section on page 81 .
- The ip rsvp bandwidth command must be enabled on all interfaces.
- The ip rsvp policy preempt command must be enabled.
- The sccp ccm command must use the keyword version 5.0.1.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 5.0.1 or a later release.
- Transcoder and MTP services must be configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager. See the following chapters in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide :
- RSVP policy level must be configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager. See the "Service Parameters Configuration" chapter in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide .
Restrictions for RSVP Agent
- RSVP agent is not supported by conference devices.
- RSVP agent is not supported by a hardware MTP or transcoder device using the NM-HDV.
- RSVP agent is supported by a software MTP using the NM-HDV only if the dsp services dspfarm command is not enabled for the voice card.
- Lip-sync for video calls is not supported.
Information About RSVP Agent
RSVP Agent
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) is the IP service that allows applications to request end-to-end QoS guarantees from the network. Cisco VoIP applications use RSVP for call admission control, limiting the accepted voice load on the IP network to guarantee the QoS levels of calls. In networks that include both voice and video media, bandwidth requirements can vary considerably over any given time. Cisco Unified Communications Manager ensures resource reservation for voice and video media by using RSVP.
The RSVP agent is a transcoding or MTP device on the Cisco IOS gateway that registers with Cisco Unified Communications Manager as RSVP-capable. The RSVP agent is controlled by Cisco Unified Communications Manager which communicates with the RSVP agent using SCCP.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager consults its policy configuration to determine if RSVP is required for a voice or video call. If the configured QoS level for a call is optional or mandatory, and the RSVP agent is enabled on the voice gateway, Cisco Unified Communications Manager inserts a pair of RSVP agents into the media path to provide RSVP support. The RSVP agent on the Cisco IOS gateway creates the RSVP reservation for the two endpoints and bridges the media connection so that resources are reserved for the media path, providing QoS for the call.
The figure below shows where the RSVP agent fits in a Cisco Unified Communications Manager meshed network.
| Figure 1 | RSVP Agent in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Meshed Network |
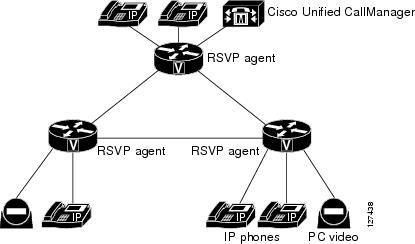
To support video calls, MTP and transcoding resources can process multiple streams in a single session, including audio, video and data, one-way or two-way, using a pass-through mode. In pass-through mode, a SCCP device processes streams using a pure software MTP, regardless of the type of stream, so it can be used for any stream type. Video and data streams are processed using pass-through mode. Audio streams can be processed with or without pass-through mode.
How to Enable the RSVP Agent on the Voice Gateway
 Note |
This document does not contain details about configuring Cisco Unified Communications Manager. See the documentation and online help for Cisco Unified Communications Manager for configuration instructions. |
- Enabling RSVP in a DSP Farm Profile
- Verifying RSVP Agent Configuration
- Troubleshooting the RSVP Agent
Enabling RSVP in a DSP Farm Profile
Perform this procedure to enable the RSVP agent on an MTP or transcoder device.
DETAILED STEPS
What to Do Next
Assign the DSP-farm profile to the appropriate Cisco Unified Communications Manager group. See the "Associating a DSP Farm Profile to a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Group" section on page 85 .
Verifying RSVP Agent Configuration
Perform this procedure to verify the RSVP Agent configuration on the voice gateway.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | show running-config Use the show running-config command to verify that the RSVP agent is enabled on the SCCP device and that the device is assigned to a Cisco Unified Communications Manager group: Example:
Router# show running-config
!
sccp ccm group 1
bind interface FastEthernet0/0
associate ccm 2 priority 3
associate ccm 1 priority 2
associate profile 10 register mtp_A1
associate profile 120 register xcoder_A2
associate profile 110 register mtp_A2
associate profile 20 register xcoder_A1
!
dspfarm profile 20 transcode
codec g711ulaw
codec gsmfr
codec g711alaw
codec g729r8
codec g729ar8
codec g729br8
codec g729abr8
codec pass-through
rsvp
maximum sessions 5
associate application SCCP
! |
| Step 2 | show dspfarm profile profile-number Use the show dspfarm profile command to verify the configuration and status of the resource: Example:
Router# show dspfarm profile 20
Dspfarm Profile Configuration
Profile ID = 20, Service = TRANSCODING, Resource ID = 1
Profile Description :
Profile Admin State : UP
Profile Operation State : ACTIVE
Application : SCCP Status : ASSOCIATED
Resource Provider : FLEX_DSPRM Status : UP
Number of Resource Configured : 5
Number of Resource Available : 5
Codec Configuration
Codec : gsmfr, Maximum Packetization Period : 20
Codec : g729abr8, Maximum Packetization Period : 60
Codec : g711alaw, Maximum Packetization Period : 30
Codec : g711ulaw, Maximum Packetization Period : 30
Codec : g729r8, Maximum Packetization Period : 60
Codec : g729ar8, Maximum Packetization Period : 60
Codec : g729br8, Maximum Packetization Period : 60
Codec : pass-through, Maximum Packetization Period : 0
RSVP : ENABLED
|
| Step 3 | show sccp ccm group group-number Use the show sccp ccm groupcommand to verify the DSP farm profiles that are assigned to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager group and the registration names of the SCCP devices. Example:
Router# show sccp ccm group 1
CCM Group Identifier: 1
Description: None
Binded Interface: NONE, IP Address: NONE
Associated CCM Id: 1, Priority in this CCM Group: 2
Associated CCM Id: 2, Priority in this CCM Group: 3
Associated Profile: 10, Registration Name: mtp_A1
Associated Profile: 20, Registration Name: xcoder_A1
Associated Profile: 110, Registration Name: mtp_A2
Associated Profile: 120, Registration Name: xcoder_A2
Registration Retries: 3, Registration Timeout: 10 sec
Keepalive Retries: 3, Keepalive Timeout: 30 sec
CCM Connect Retries: 3, CCM Connect Interval: 10 sec
Switchover Method: GRACEFUL, Switchback Method: GRACEFUL_GUARD
Switchback Interval: 10 sec, Switchback Timeout: 7200 sec
Signaling DSCP value: default, Audio DSCP value: default
|
Troubleshooting the RSVP Agent
You can troubleshoot the performance of the RSVP agent by performing any of the following steps.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | show sccp Before the start of a call, use the show sccp command to verify that the MTP or transcoder device is successfully registered with Cisco Unified Communications Manager: Example:
Router# show sccp
SCCP Admin State: UP
Gateway IP Address: 192.168.20.1, Port Number: 0
IP Precedence: 5
User Masked Codec list: None
Call Manager: 192.168.20.11, Port Number: 2000
Priority: N/A, Version: 5.0.1, Identifier: 3
Call Manager: 192.168.20.12, Port Number: 2000
Priority: N/A, Version: 5.0.1, Identifier: 1
Call Manager: 192.168.20.13, Port Number: 2000
Priority: N/A, Version: 5.0.1, Identifier: 2
.....
Software MTP Oper State: ACTIVE - Cause Code: NONE
Active Call Manager: 192.168.20.12, Port Number: 2000
TCP Link Status: CONNECTED, Profile Identifier: 10
Reported Max Streams: 1004, Reported Max OOS Streams: 0
Supported Codec: pass-thru, Maximum Packetization Period: N/A
Supported Codec: g711ulaw, Maximum Packetization Period: 30
Supported Codec: rfc2833 dtmf, Maximum Packetization Period: 30
RSVP : ENABLED
|
| Step 2 | show sccp connections During the call, use the show sccp connectionscommand to display information about the active SCCP connections established for the call, the DSP farm service type (MTP or transcoding), codec (for example, pass-through or g711ulaw), and remote end information: Example:
Router# show sccp connections
sess_id conn_id stype mode codec ripaddr rport sport
17537646 19438263 mtp sendrecv pass_th 192.168.20.5 35548 16576
17537646 19438260 mtp sendrecv pass_th 192.168.22.1 16832 19164
Total number of active session(s) 1, and connection(s) 2
|
| Step 3 | show sccp connections details Use the show sccp connections details command to display details about active SCCP connections, including the internal call leg ID: Example:
Router# show sccp connections details
bridge-info(bid, cid) - Normal bridge information(Bridge id, Calleg id)
mmbridge-info(bid, cid) - Mixed mode bridge information(Bridge id, Calleg id)
sess_id conn_id call-id codec pkt-period type bridge-info(bid, cid) mmbridge-info(bid, cid)
17537646 - 326 N/A N/A swmtpmsp All RTPSPI Callegs N/A
17537646 19438263 324 pass_th 20 rtpspi (221,326) N/A
17537646 - 326 N/A N/A swmtpmsp All RTPSPI Callegs N/A
17537646 19438260 325 pass_th 20 rtpspi (222,326) N/A
Total number of active session(s) 1, connection(s) 2, and callegs 4
|
| Step 4 | show sccp connections rsvp Use the show sccp connections rsvp command to display information about the active RSVP reservations for the call: Example:
Router# show sccp connections rsvp
sess_id conn_id rsvp_id dir local ip :port remote ip :port
17537646 19438260 -244 SEND 192.168.20.1 :19164 192.168.22.1 :16832
17537646 19438260 -245 RECV 192.168.20.1 :19164 192.168.22.1 :16832
Total active sessions 1, connections 2, rsvp sessions 2
|
| Step 5 | show ip rsvp installed Use the show ip rsvp installed command to see that the RSVP reservation is successfully made and to display the reserved bandwidth for the call: Example:
Router# show ip rsvp installed
RSVP: Loopback0 has no installed reservations
RSVP: FastEthernet0/0 has no installed reservations
RSVP: Serial0/0
BPS To From Protoc DPort Sport Weight Conversation
80K 192.168.22.1 192.168.20.1 UDP 16832 19164 25 265
RSVP: FastEthernet0/1 has no installed reservations
RSVP: Serial0/1 has no installed reservations
|
| Step 6 | show sccp statistics Use the show sccp statisticscommand to display the SCCP messages exchanged between the RSVP agent and Cisco Unified Communications Manager: Example:
Router# show sccp statistics
SCCP Application Service(s) Statistics:
Profile Identifier: 10, Service Type: Software MTP
TCP packets rx 9, tx 6
Unsupported pkts rx 0, Unrecognized pkts rx 0
Register tx 0, successful 0, rejected 0, failed 0
KeepAlive tx 1, successful 1, failed 0
OpenReceiveChannel rx 2, successful 2, failed 0
CloseReceiveChannel rx 0, successful 0, failed 0
StartMediaTransmission rx 2, successful 2, failed 0
StopMediaTransmission rx 0, successful 0, failed 0
PortReq rx 1
PortRes tx 1, successful 1, failed 0
PortClose rx 0
QosListen rx 1
QosPath rx 1
QosTeardown rx 0, send 0, recv 0, sendrecv 0
QosResvNotify tx 2, send 2, recv 0, sendrecv 0
QosErrorNotify tx 0, send 0, recv 0, sendrecv 0
err0 0, err1 0, err2 0, err3 0, err4 0, err5 0,
err6 0, err7 0, err8 0, err9 0, err10 0, err11 0,
QosModify rx 1, send 0, recv 1, sendrecv 0
UpdateDscp rx 0
Reset rx 0, successful 0, failed 0
MediaStreamingFailure rx 0
Switchover 0, Switchback 0
|
| Step 7 | debug sccp all Use the debug sccp all command to display the sequence of the SCCP messages. The message sequence may be different if the RSVP policy defined in Cisco Unified Communications Manager is not set to mandatory. Example: Router# show sccp statistics Router# show log | incl (rcvd | txed) Feb 4 20:28:41.791: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd KeepAliveAckMessage msg Feb 4 20:28:41.803: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd KeepAliveAckMessage msg Feb 4 20:28:41.815: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd KeepAliveAckMessage msg Feb 4 20:28:55.647: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd PortReq msg : Feb 4 20:28:55.647: sccp_send_port_res: PortRes msg txed in hex(including header) - len 36 Feb 4 20:28:55.651: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd QosPath msg: Feb 4 20:28:55.651: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd QosListen msg: Feb 4 20:28:55.675: sccp_send_qos_resv_notify: QosResvNotify txed in hex(including header) - len 36 Feb 4 20:28:57.706: OpenReceviceChannel msg rcvd in hex - Feb 4 20:28:57.710: sccp_open_receive_chnl_ack: OpenRecvChnlAck msg txed in hex(including header) - len 32 Feb 4 20:28:57.714: OpenReceviceChannel msg rcvd in hex - Feb 4 20:28:57.718: StartMediaTrans msg rcvd in hex - Feb 4 20:28:57.726: sccp_open_receive_chnl_ack: OpenRecvChnlAck msg txed in hex(including header) - len 32 Feb 4 20:28:57.866: StartMediaTrans msg rcvd in hex - Feb 4 20:28:57.870: sccp_parse_control_msg: rcvd QosModify msg: Feb 4 20:28:57.878: sccp_send_qos_resv_notify: QosResvNotify txed in hex(including header) - len 36 |
| Step 8 | debug call rsvp-sync {events | func-trace} Use the debug call rsvp-sync event and debug call rsvp-sync func-trace with the debug sccp all command to show how SCCP messages and RSVP events trigger each other. |
| Step 9 | debug voip ccapi inout Use the debug voip ccapi inoutcommand to trace the execution path through the call control application programming interface (API). |
Configuration Examples for RSVP Agent
RSVP Agent Example
version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 5000000 debugging no logging console enable password lab ! no network-clock-participate slot 2 no network-clock-participate aim 0 no network-clock-participate aim 1 no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! no ip domain lookup no ftp-server write-enable voice-card 2 dspfarm dsp services dspfarm ! ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.26.1 255.255.255.255 max-reserved-bandwidth 100 ip rsvp bandwidth ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 max-reserved-bandwidth 100 duplex auto speed auto fair-queue 64 256 1000 ip rsvp bandwidth ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 192.168.25.2 255.255.255.252 max-reserved-bandwidth 100 fair-queue 64 256 37 ip rsvp bandwidth ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.24.1 255.255.255.0 max-reserved-bandwidth 100 shutdown duplex auto speed auto fair-queue 64 256 1000 ip rsvp bandwidth ! interface Serial0/1 ip address 192.168.25.69 255.255.255.252 max-reserved-bandwidth 100 shutdown fair-queue 64 256 37 ip rsvp bandwidth ! router ospf 10 log-adjacency-changes network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 ! ip classless ip http server ip rsvp policy preempt ! ! ! control-plane ! ! ! voice-port 2/0/0 ! voice-port 2/0/1 ! ! sccp local FastEthernet0/0 sccp ccm 192.168.20.11 identifier 3 version 4.0 sccp ccm 192.168.20.13 identifier 2 version 5.1 sccp ccm 192.168.20.12 identifier 1 version 5.1 sccp ! sccp ccm group 1 bind interface FastEthernet0/0 associate ccm 2 priority 3 associate ccm 1 priority 2 associate profile 10 register mtp_A1 associate profile 120 register xcoder_A2 associate profile 110 register mtp_A2 associate profile 20 register xcoder_A1 ! dspfarm profile 20 transcode codec g711ulaw codec gsmfr codec pass-through codec g711alaw codec g729r8 codec g729ar8 codec g729br8 codec g729abr8 rsvp maximum sessions 5 associate application SCCP ! dspfarm profile 120 transcode codec g729abr8 codec gsmfr codec g711alaw codec g711ulaw codec g729r8 codec g729ar8 codec g729br8 codec pass-through rsvp maximum sessions 5 associate application SCCP ! dspfarm profile 30 conference codec g711ulaw codec g711alaw codec g729ar8 codec g729abr8 codec g729r8 codec g729br8 ! dspfarm profile 10 mtp codec g711ulaw codec pass-through rsvp maximum sessions hardware 2 maximum sessions software 10 associate application SCCP ! dspfarm profile 110 mtp codec pass-through codec g711ulaw rsvp maximum sessions hardware 2 maximum sessions software 10 associate application SCCP ! ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 no login ! ntp clock-period 17175018 ntp server 192.168.20.12 end
Additional References
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide , Release 5.0(1)
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager System Guide , Release 5.0(1)
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager Features and Services Guide , Release 5.0(1)
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback