- Zone-Based Policy Firewalls
- Zone-Based Policy Firewall IPv6 Support
- VRF-Aware Cisco Firewall
- Zone-Based Policy Firewall High Availability
- Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Policy Firewalls
- WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Zone-Based Firewall Logging Export Using NetFlow
- Cisco IOS Firewall-SIP Enhancements ALG and AIC
- Firewall-H.323 V3 V4 Support
- H.323 RAS Support
- Application Inspection and Control for SMTP
- Subscription-Based Cisco IOS Content Filtering
- Cisco IOS Firewall Support for Skinny Local Traffic and CME
- User-Based Firewall Support
- On-Device Management for Security Features
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Information About WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- How to Configure WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Configuration Examples for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Additional References for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Feature Information for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
WAAS Support in
Zone-Based Firewalls
Zone-based firewalls support Wide Area Application Services (WAAS). WAAS allows the firewall to automatically discover optimized traffic by enabling the sequence number to change without compromising the stateful Layer 4 inspection of TCP traffic flows that contain internal firewall TCP state variables.
This module provides more information about the WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls feature.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Information About WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- How to Configure WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Configuration Examples for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Additional References for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
- Feature Information for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
-
In a Wide-Area Application Services (WAAS) and firewall configuration, all packets processed by a Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) must pass through the firewall in both directions to support the Web Cache Coordination Protocol (WCCP). This situation occurs because the Layer 2 redirect is not available in Cisco IOS Release 12.4T. If Layer 2 redirect is configured on the WAE, the system defaults to the generic routing encapsulation (GRE) redirect to continue to function.
-
In a WAAS and firewall configuration, WCCP does not support traffic redirection using policy-based routing (PBR).
Information About WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
WAAS Support for the Cisco Firewall
Depending on your release, the Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) firewall software provides an integrated firewall that optimizes security-compliant WANs and application acceleration solutions with the following benefits:
Integrates WAAS networks transparently.
Protects transparent WAN accelerated traffic.
Optimizes a WAN through full stateful inspection capabilities.
Simplifies Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance.
Supports the Network Management Equipment (NME)-Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) modules or standalone WAAS device deployment.
WAAS has an automatic discovery mechanism that uses TCP options during the initial three-way handshake to identify WAE devices transparently. After automatic discovery, optimized traffic flows (paths) experience a change in the TCP sequence number to allow endpoints to distinguish between optimized and nonoptimized traffic flows.
 Note | Paths are synonymous with connections. |
WAAS allows the Cisco firewall to automatically discover optimized traffic by enabling the sequence number to change without compromising the stateful Layer 4 inspection of TCP traffic flows that contain internal firewall TCP state variables. These variables are adjusted for the presence of WAE devices.
If the Cisco firewall notices that a traffic flow has successfully completed WAAS automatic discovery, it permits the initial sequence number shift for the traffic flow and maintains the Layer 4 state on the optimized traffic flow.
 Note | Stateful Layer 7 inspection on the client side can also be performed on nonoptimized traffic. |
WAAS Traffic Flow Optimization Deployment Scenarios
The following sections describe two different WAAS traffic flow optimization scenarios for branch office deployments. WAAS traffic flow optimization works with the Cisco firewall feature on a Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR).
The figure below shows an example of an end-to-end WAAS traffic flow optimization with the Cisco firewall. In this particular deployment, a Network Management Equipment (NME)-WAE device is on the same device as the Cisco firewall. Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) is used to redirect traffic for interception.
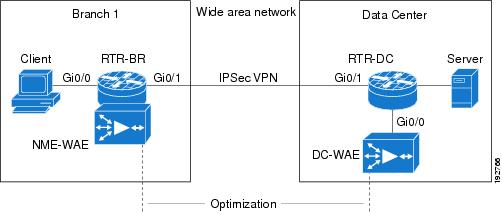
WAAS Branch Deployment with an Off-Path Device
A Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) device can be either a standalone WAE device or an NME-WAE that is installed on an Integrated Services Router (ISR) as an integrated service engine (as shown in the figure Wide Area Application Service [WAAS] Branch Deployment).
The figure below shows a WAAS branch deployment that uses Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) to redirect traffic to an off-path, standalone WAE device for traffic interception. The configuration for this option is the same as the WAAS branch deployment with an NME-WAE.

WAAS Branch Deployment with an Inline Device
The figure below shows a Wide Area Application Service (WAAS) branch deployment that has an inline Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) device that is physically in front of the Integrated Services Router (ISR). Because the WAE device is in front of the device, the Cisco firewall receives WAAS optimized packets, and as a result, Layer 7 inspection on the client side is not supported.
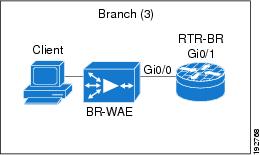
An edge WAAS device with the Cisco firewall is applied at branch office sites that must inspect the traffic moving to and from a WAN connection. The Cisco firewall monitors traffic for optimization indicators (TCP options and subsequent TCP sequence number changes) and allows optimized traffic to pass, while still applying Layer 4 stateful inspection and deep packet inspection to all traffic and maintaining security while accommodating WAAS optimization advantages.
 Note | If the WAE device is in the inline location, the device enters its bypass mode after the automatic discovery process. Although the device is not directly involved in WAAS optimization, the device must be aware that WAAS optimization is applied to the traffic in order to apply the Cisco firewall inspection to network traffic and make allowances for optimization activity if optimization indicators are present. |
WAAS and Firewall Integration Support
The following sections describe three different WAAS traffic flow optimization scenarios for branch office deployments. WAAS traffic flow optimization works with the Cisco IOS XE firewall feature on Cisco Aggregation Services Routers (ASRs).
The figure below shows an example of an end-to-end WAAS traffic flow optimization with the Cisco IOS XE firewall. In this particular deployment, an NME-WAE device is on the Cisco IOS Integrated Services Router (ISR).

WCCP is used to redirect traffic for interception. NME-WAE is not supported on ASR. Therefore, to support NME-WAE in the branch office must be an ISR.
How to Configure WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
Configuring a Parameter Map for WAAS Support
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
ip
wccp
service-id
4.
ip
wccp
service-id
5.
parameter-map
type
inspect
global
6.
waas
enable
7.
log
dropped-packets
enable
8.
max-incomplete
low
9.
max-incomplete
high
10.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Class Maps and Policy Maps for WAAS Support
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
class-map
type
inspect
match-any
class-name
4.
match
protocol
protocol-name
[signature]
5.
match
protocol
protocol-name
[signature]
6.
match
protocol
protocol-name
[signature]
7.
match
protocol
protocol-name [signature]
8.
exit
9.
policy-map
type
inspect
policy-map-name
10.
class-map
type
inspect
class-name
11.
inspect
12.
exit
13.
class
class-default
14.
drop
15.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Zones and Zone-Pairs for WAAS Support
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
zone
security
zone-name
4.
exit
5.
zone
security
zone-name
6.
exit
7.
zone
security
zone-name
8.
exit
9.
zone-pair
security
zone-pair
name
[source
source-zone-name |
self]
destination
[self |
destination-zone-name]
10.
service-policy
type
inspect
policy-map-name
11.
exit
12.
zone-pair
security
zone-pair
name
[source
source-zone-name |
self]
destination
[self |
destination-zone-name]
13.
service-policy
type
inspect
policy-map-name
14.
exit
15.
zone-pair
security
zone-pair
name
[source
source-zone-name |
self]
destination
[self |
destination-zone-name]
16.
service-policy
type
inspect
policy-map-name
17.
exit
18.
zone-pair
security
zone-pair
name
[source
source-zone-name |
self]
destination
[self |
destination-zone-name]
19.
service-policy
type
inspect
p-----
20.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Interfaces for WAAS Support
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4.
description
line-of-description
5.
no
ip
dhcp
client
request
tftp-server-address
6.
no
ip
dhcp
client
request
router
7.
ip
address
dhcp
8.
ip
wccp
service-identifier
redirect
in
9.
ip
wccp
service-identifier
redirect
in
10.
ip
flow
ingress
11.
ip
nat
outside
12.
ip
virtual-reassembly
in
13.
ip
virtual-reassembly
out
14.
zone-member
security
zone-name
15.
load-interval
seconds
16.
delay
throughput-delay
17.
duplex
auto
18.
speed
auto
19.
exit
20.
interface
type
number
21.
description
line-of-description
22.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
23.
ip
pim
spare-mode
24.
ip
nat
inside
25.
ip
virtual-reassembly
in
26.
zone-member
security
zone-name
27.
ip
igmp
version{1
|
2
|
3}
28.
delay
tens-of-microseconds
29.
duplex
auto
30.
speed
auto
31.
exit
32.
interface
type
number
33.
description
line-of-description
34.
ip
address
ip-address
mask
35.
ip
wccp
redirect
exclude
in
36.
ip
nat
inside
37.
ip
virtual-reassembly
in
38.
zone-member
security
zone-name
39.
load-interval
seconds
40.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0 |
Specifies an interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 |
description
line-of-description
Example: Device(config-if)# description WAN connection |
(Optional) Describes an interface. | ||
| Step 5 |
no
ip
dhcp
client
request
tftp-server-address
Example: Device(config-if)# no ip dhcp client request tftp-server-address |
Removes an option from the Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server. | ||
| Step 6 |
no
ip
dhcp
client
request
router
Example: Device(config-if)# no ip dhcp client request router |
Removes the default router option from the DHCP server. | ||
| Step 7 |
ip
address
dhcp
Example: Device(config-if)# ip address dhcp |
Acquires an IP address on an interface from DHCP. | ||
| Step 8 |
ip
wccp
service-identifier
redirect
in
Example: Device(config-if)# ip wccp 62 redirect in |
Redirects inbound packets that have the specified dynamic service identifier to the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) engine. | ||
| Step 9 |
ip
wccp
service-identifier
redirect
in
Example: Device(config-if)# ip wccp 61 redirect out |
Redirects outbound packets that have the specified dynamic service identifier to the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) engine. | ||
| Step 10 |
ip
flow
ingress
Example: Device(config-if)# ip flow ingress |
Enables NetFlow accounting for traffic that is received on an interface. | ||
| Step 11 |
ip
nat
outside
Example: Device(config-if)# ip nat outside |
Specifies that an interface is connected to the outside network. | ||
| Step 12 |
ip
virtual-reassembly
in
Example: Device(config-if)# ip virtual-reassembly in |
| ||
| Step 13 |
ip
virtual-reassembly
out
Example: Device(config-if)# ip virtual-reassembly out |
Enables virtual fragment reassembly (VFR) on outbound interface traffic. | ||
| Step 14 |
zone-member
security
zone-name
Example: Device(config-if)# zone-member security out |
Assigns an interface to a specified security zone.
| ||
| Step 15 |
load-interval
seconds
Example: Device(config-if)# load-interval 30 |
Changes the length of time for which data is used to compute load statistics. | ||
| Step 16 |
delay
throughput-delay
Example: Device(config-if)# delay 30 |
Sets a throughput delay value for an interface. | ||
| Step 17 |
duplex
auto
Example: Device(config-if)# duplex auto |
| ||
| Step 18 |
speed
auto
Example: Device(config-if)# speed auto |
Enables autonegotiation on an interface. | ||
| Step 19 |
exit
Example: Device(config-if)# exit |
Exits interface configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 20 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/1 |
Specifies an interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 21 |
description
line-of-description
Example: Device(config-if)# description clients |
(Optional) Describes an interface. | ||
| Step 22 |
ip
address
ip-address
mask
Example: Device(config-if)# ip address 172.25.50.1 255.255.255.0 |
Specifies an IP address for the interface. | ||
| Step 23 |
ip
pim
spare-mode
Example: Device(config-if)# ip pim sparse-mode |
Enables Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) sparse mode of operation on an interface. | ||
| Step 24 |
ip
nat
inside
Example: Device(config-if)# ip nat inside |
Specifies that an interface is connected to the inside network. | ||
| Step 25 |
ip
virtual-reassembly
in
Example: Device(config-if)# ip virtual-reassembly in |
Enables VFR on inbound interface traffic. | ||
| Step 26 |
zone-member
security
zone-name
Example: Device(config-if)# zone-member security out |
Assigns an interface to a specified security zone. | ||
| Step 27 |
ip
igmp
version{1
|
2
|
3}
Example: Device(config-if)# ip igmp version 3 |
Configure Version 3 of Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) on the router. | ||
| Step 28 |
delay
tens-of-microseconds
Example: Device(config-if)# delay 30 |
Sets a delay value for an interface. | ||
| Step 29 |
duplex
auto
Example: Device(config-if)# duplex auto |
| ||
| Step 30 |
speed
auto
Example: Device(config-if)# speed auto |
Enables autonegotiation on an interface. | ||
| Step 31 |
exit
Example: Device(config-if)# exit |
Exits interface configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 32 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface vlan 1 |
Specifies an interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 33 |
description
line-of-description
Example: Device(config-if)# description WAAS interface |
(Optional) Describes an interface. | ||
| Step 34 |
ip
address
ip-address
mask
Example: Device(config-if)# ip address 172.25.60.1 255.255.255.0 |
Specifies an IP address for an interface. | ||
| Step 35 |
ip
wccp
redirect
exclude
in
Example: Device(config-if)# ip wccp redirect exclude in |
Excludes inbound packets from outbound redirection. | ||
| Step 36 |
ip
nat
inside
Example: Device(config-if)# ip nat inside |
Specifies that an interface is connected to the inside network. | ||
| Step 37 |
ip
virtual-reassembly
in
Example: Device(config-if)# ip virtual-reassembly in |
Enables VFR on inbound interface traffic. | ||
| Step 38 |
zone-member
security
zone-name
Example: Device(config-if)# zone-member security waas |
Assigns an interface to a specified security zone. | ||
| Step 39 |
load-interval
seconds
Example: Device(config-if)# load-interval 30 |
Changes the length of time for which data is used to compute load statistics. | ||
| Step 40 |
end
Example: Device(config-if)# end |
Exits interface configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuring WAAS for Zone-Based Firewalls
 Note | Perform this task on the Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) and not on the router on which zone-based firewall is configured. |
1.
enable
2.
configure
3.
primary-interface
type
number
4.
interface
type
number
5.
ip
address
ip-address
ip-subnet
6.
exit
7.
ip
default-gateway
ip-address
8.
wccp
router-list
number
ip-address
9.
wccp
tcp-promiscuousservice-pair
serviceID
serviceID+1
10.
router-list-num
number
11.
redirect-method
{gre
|
L2}
12.
egress-method
{ip-forwarding
|
generic-gre
|
L2
|
wccp-gre}
13.
enable
14.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
Example: Device# configure |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
primary-interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# primary-interface Virtual 1/0 |
Configures the primary interface for a Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) device. |
| Step 4 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Virtual 1/0 |
Configures an interface and enters interface configuration mode. |
| Step 5 |
ip
address
ip-address
ip-subnet
Example: Device(config-if)# ip address 172.25.60.12 255.255.255.0 |
Configures the IP address for the interface. |
| Step 6 |
exit
Example: Device(config-if)# exit |
Exits interface configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 7 |
ip
default-gateway
ip-address
Example: Device(config)# ip default-gateway 172.25.60.1 |
Specifies the default gateway. |
| Step 8 |
wccp
router-list
number
ip-address
Example: Device(config)# wccp router-list 1 172.25.60.1 |
Configures the IP address and router list number for Web Cache Control Protocol (WCCP) Version 2. |
| Step 9 |
wccp
tcp-promiscuousservice-pair
serviceID
serviceID+1
Example: Device(config)# wccp tcp-promiscuous service-pair 61 62 | Configures the Web Cache Coordination Protocol (WCCP) Version 2 TCP promiscuous mode service and enters WCCP configuration mode. |
| Step 10 |
router-list-num
number
Example: Device(config-wccp-service)# router-list-num 1 |
Associates a configured router list with the WCCP service on a WAE. |
| Step 11 |
redirect-method
{gre
|
L2}
Example: Device(config-wccp-service)# redirect-method gre |
Configures the WAE to use Layer 3 GRE packet redirection. |
| Step 12 |
egress-method
{ip-forwarding
|
generic-gre
|
L2
|
wccp-gre}
Example: Device(config-wccp-service)# egress-method ip-forwarding |
Configures the IP forwarding egress method. |
| Step 13 |
enable
Example: Device(config-wccp-service)# enable |
Enables the WCCP service. |
| Step 14 |
end
Example: Device(config-wccp-service)# end |
Exits WCCP configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Examples for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
Example: Configuring the Cisco Firewall with WAAS
The following is a sample of an end-to-end Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) traffic flow optimization configuration for the firewall that uses Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) to redirect traffic to a Wide Area Application Engine (WAE) device for traffic interception.
The following configuration example prevents traffic from being dropped between security zone members because the integrated-service-engine interface is configured on a different zone and each security zone member is assigned an interface.
! Zone-based firewall configuration on your router. ip wccp 61 ip wccp 62 parameter-map type inspect global WAAS enable log dropped-packets enable max-incomplete low 18000 max-incomplete high 20000 ! class-map type inspect match-any most-traffic match protocol icmp match protocol ftp match protocol tcp match protocol udp ! policy-map type inspect p1 class type inspect most-traffic inspect ! class class-default drop ! zone security in ! zone security out ! zone security waas ! zone-pair security in-out source in destination out service-policy type inspect p1 ! zone-pair security out-in source out destination in service-policy type inspect p1 ! zone-pair security waas-out source waas destination out service-policy type inspect p1 ! zone-pair security in-waas source in destination waas service-policy type inspect p1 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 description WAN Connection no ip dhcp client request tftp-server-address no ip dhcp client request router ip address dhcp ip wccp 62 redirect in ip wccp 61 redirect out ip flow ingress ip nat outside ip virtual-reassembly in ip virtual-reassembly out zone-member security out load-interval 30 delay 30 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 description Clients ip address 172.25.50.1 255.255.255.0 ip pim sparse-mode ip nat inside ip virtual-reassembly in zone-member security in ip igmp version 3 delay 30 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Vlan1 description WAAS Interface ip address 172.25.60.1 255.255.255.0 ip wccp redirect exclude in ip nat inside ip virtual-reassembly in zone-member security waas load-interval 30 !
The following example shows the configuration on the WAE for zone-based firewall support:
 Note | This configuration cannot be done on the router; but only on the WAE. |
!Configuration on the WAE. primary-interface Virtual 1/0 interface Virtual 1/0 ip address 172.25.60.12 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 172.25.60.1 wccp router-list 1 172.25.60.1 wccp tcp-promiscuous service-pair 61 62 router-list-num 1 redirect-method gre egress-method ip-forwarding enable !
 Note | The new configuration, depending on your release, places an integrated service engine in its own zone and need not be part of any zone pair. The zone pairs are configured between zone-hr (zone-out) and zone-eng (zone-output). |
interface Integrated-Service-Engine l/0 ip address 10.70.100.1 255.255.255.252 ip wccp redirect exclude in zone-member security z-waas
Additional References for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Security commands |
|
|
WAAS commands |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
WAAS Support in Zone-Based Firewalls |
12.4(15)T |
Zone-based firewalls support Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) to automatically discover optimized traffic by enabling the sequence number to change without compromising the stateful Layer 4 inspection of TCP traffic flows that contain internal firewall TCP state variables. |
 Feedback
Feedback