- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Information About Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- How to Configure the Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Enabling CTS-SXP
- Configuring a CTS-SXP Peer Connection
- Configuring the Default CTS-SXP Password
- Configuring the Default CTS-SXP Source IP Address
- Configuring the CTS-SXP Reconciliation Period
- Configuring the CTS-SXP Retry Period
- Creating Syslogs to Capture IP-to-SGT Mapping Changes
- Configuring a Class Map for a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
- Creating a Policy Map for a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
- Configuration Examples for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Additional References for TrustSec SGT Handling: L2 SGT Imposition and Forwarding
- Feature Information for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
Cisco TrustSec (CTS) builds secure networks by establishing domains of trusted network devices. Each device in the domain is authenticated by its peers. Communication on the links between devices in the domain is secured with a combination of encryption, message integrity check, and data-path replay protection mechanisms.
The Security Group Tag (SGT) Exchange Protocol (SXP) is one of several protocols that supports CTS and is referred to in this document as CTS-SXP. CTS-SXP is a control protocol for propagating IP-to-SGT binding information across network devices that do not have the capability to tag packets. CTS-SXP passes IP to SGT bindings from authentication points to upstream devices in the network. This process allows security services on switches, routers, or firewalls to learn identity information from access devices.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Information About Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- How to Configure the Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Configuration Examples for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Additional References for TrustSec SGT Handling: L2 SGT Imposition and Forwarding
- Feature Information for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
The CTS-SXP network needs to be established before implementing SXP. The CTS-SXP network has the following prerequisites:
To use the Cisco TrustSec functionality on your existing router, ensure that you have purchased a Cisco TrustSec security license. If the router is being ordered and needs the Cisco TrustSec functionality, ensure that this license is pre-installed on your router before it is shipped to you.
CTS-SXP software runs on all network devices
Connectivity exists between all network devices
The Cisco Identity Services Engine 1.0 is required for authentication. The Secure Access Control Server (ACS) Express Appliance server can also be used for authentication, however not all ACS features are supported by CTS. ACS 5.1 operates with a CTS-SXP license
Configure the retry open timer command to a different value on different routers.
Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
The Cisco TrustSec Support for IOS feature is supported on the Cisco Integrated Services Router Generation 2 (ISR G2) only.
CTS-SXP is supported only on physical interfaces, not on logical interfaces.
CTS-SXP does not support IPv6.
If the default password is configured on a router, the connection on that router should configure the password to use the default password. If the default password is not configured, the connection on that router should configure to not use the password configuration. The configuration of the password option should be consistent across the deployment network.
Information About Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Security Group Tagging
- Using CTS-SXP for SGT Propagation Across Legacy Access Networks
- VRF-Aware CTS-SXP
- Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
Security Group Tagging
CTS-SXP uses the device and user credentials acquired during authentication for classifying the packets by security groups (SGs) as they enter the network. This packet classification is maintained by tagging packets on ingress to the CTS-SXP network so that they can be properly identified for the purpose of applying security and other policy criteria along the data path. The Security Group Tag (SGT) allows the network to enforce the access control policy by enabling the endpoint device to act upon the SGT to filter traffic.
Using CTS-SXP for SGT Propagation Across Legacy Access Networks
Tagging packets with SGTs requires hardware support. There may be devices in the network that can participate in CTS authentication, but lack the hardware capability to tag packets with SGTs. However, if CTS-SXP is used, then these devices can pass IP-to-SGT mappings to a CTS peer device that has CTS-capable hardware.
CTS-SXP typically operates between ingress access layer devices at the CTS domain edge and distribution layer devices within the CTS domain. The access layer device performs CTS authentication of external source devices to determine the appropriate SGTs for ingress packets. The access layer device learns the IP addresses of the source devices using IP device tracking and (optionally) DHCP snooping, then uses CTS-SXP to pass the IP addresses of the source devices along with their SGTs to the distribution switches. Distribution switches with CTS-capable hardware can use this IP-to-SGT mapping information to tag packets appropriately and to enforce Security Group Access Control List (SGACL) policies as shown in the figure below. An SGACL associates an SGT with a policy. The policy is enforced when SGT-tagged traffic egresses the CTS domain.
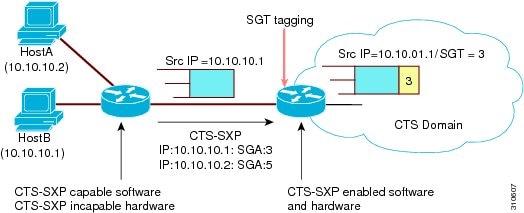
You must manually configure a CTS-SXP connection between a peer without CTS hardware support and a peer with CTS hardware support. The following tasks are required when configuring the CTS-SXP connection:
If CTS-SXP data integrity and authentication are required, the same CTS-SXP password can be configured on both peer devices. The CTS-SXP password can be configured either explicitly for each peer connection or globally for the device. Although a CTS-SXP password is not required it is recommended.
Each peer on the CTS-SXP connection must be configured as either a CTS-SXP speaker or CTS-SXP listener. The speaker device distributes the IP-to-SGT mapping information to the listener device.
A source IP address can be specified to use for each peer relationship or a default source IP address can be configured for peer connections where a specific source IP address is not configured. If no source IP address is specified, then the device uses the interface IP address of the connection to the peer.
CTS-SXP allows multiple hops. That is, if the peer of a device lacking CTS hardware support also lacks CTS hardware support, the second peer can have a CTS-SXP connection to a third peer, continuing the propagation of the IP-to-SGT mapping information until a hardware-capable peer is reached. A device can be configured as a CTS-SXP listener for one CTS-SXP connection as a CTS-SXP speaker for another CTS-SXP connection.
A CTS device maintains connectivity with its CTS-SXP peers by using the TCP keepalive mechanism. To establish or restore a peer connection, the device repeatedly attempts the connection setup by using the configured retry period until the connection is successful or until the connection is removed from the configuration.
VRF-Aware CTS-SXP
The CTS-SXP implementation of Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) binds a CTS-SXP connection with a specific VRF. It is assumed that the network topology is correctly configured for Layer 2 or Layer 3 VPNs, and that all VRFs are configured before enabling CTS-SXP.
CTS-SXP VRF support can be summarized as follows:
Only one CTS-SXP connection can be bound to one VRF.
Different VRFs may have overlapping CTS-SXP peer or source IP addresses.
IP-to-SGT mappings learned (added or deleted) in one VRF can be updated only in the same VRF domain. The CTS-SXP connection cannot update a mapping bound to a different VRF. If no SXP connection exits for a VRF, IP-SGT mappings for that VRF won’t be updated by SXP.
CTS-SXP does not support the establishment of connections with a source IPv6 address. However, multiple address families per VRF are supported where one CTS-SXP connection in a VRF domain can forward both IPv4 and IPv6 IP-to-SGT mappings.
CTS-SXP has no limitation on the number of connections and number of IP-to-SGT mappings per VRF.
Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
CTS-SXP extends the deployment of network devices to additional places on the network by using the Security Group Access (SGA) Zone-Based Policy firewalls (ZBPFs). CTS-SXP is used for Identity distribution through inline devices where the identity information is learned from a primary communication path that exists across networks as shown in the figure below.
The Security Group Tag (SGT) is used by the SGA ZBPF to apply enforcement policy. IP-to-SGT mapping information is learned through CTS-SXP. When a packet arrives, source and destination IP addresses in the packet are used to derive source and destination tags. The Identity firewall applies a policy to the received IP packets based on the configured policy where the SGT is one of the attributes.

How to Configure the Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- Enabling CTS-SXP
- Configuring a CTS-SXP Peer Connection
- Configuring the Default CTS-SXP Password
- Configuring the Default CTS-SXP Source IP Address
- Configuring the CTS-SXP Reconciliation Period
- Configuring the CTS-SXP Retry Period
- Creating Syslogs to Capture IP-to-SGT Mapping Changes
- Configuring a Class Map for a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
- Creating a Policy Map for a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
Enabling CTS-SXP
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
cts
sxp
enable
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a CTS-SXP Peer Connection
The CTS-SXP peer connection must be configured on both devices. One device is the speaker and the other is the listener. When using password protection, make sure to use the same password on both ends.
 Note | If a default CTS-SXP source IP address is not configured and you do not configure a CTS-SXP source address in the connection, the Cisco TrustSec software derives the CTS-SXP source IP address from existing local IP addresses. The CTS-SXP source IP address might be different for each TCP connection initiated from the router. |
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
cts
sxp
connection
peer
ipv4-address {source |
password} {default |
none}
mode {local |
peer} [[listener |
speaker] [vrf
vrf-name]]
4.
exit
5.
show
cts
sxp {connections |
sgt-map} [brief |
vrf
vrf-name]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
cts
sxp
connection
peer
ipv4-address {source |
password} {default |
none}
mode {local |
peer} [[listener |
speaker] [vrf
vrf-name]]
Example: Device(config)# cts sxp connection peer 10.20.2.2 password default mode local speaker |
Configures the CTS-SXP peer address connection. The source keyword specifies the IPv4 address of the source device. If no address is specified, the connection uses the default source address, if configured, or the address of the port. The password keyword specifies the password that CTS-SXP uses for the connection using the following options:
The mode keyword specifies the role of the remote peer device:
The optional vrf keyword specifies the VRF to the peer. The default is the default VRF. |
| Step 4 |
exit Example: Device# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 5 |
show
cts
sxp {connections |
sgt-map} [brief |
vrf
vrf-name]
Example: Device# show cts sxp connections |
(Optional) Displays CTS-SXP status and connections. |
Configuring the Default CTS-SXP Password
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
cts
sxp
default
password
[0 |
6 |
7]
password
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
cts
sxp
default
password
[0 |
6 |
7]
password
Example: Device(config)# cts sxp default password Cisco123 |
Configures the CTS-SXP default password. You can enter either a clear text password (using the 0 or no option) or an encrypted password (using the 6 or 7 option). The maximum password length is 32 characters.
| ||
| Step 4 |
exit Example: Device# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring the Default CTS-SXP Source IP Address
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
cts
sxp
default
source-ip
src-ip-addr
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
cts
sxp
default
source-ip
src-ip-addr
Example: Device(config)# cts sxp default source-ip 10.20.2.2 |
Configures the CTS-SXP default source IP address that is used for all new TCP connections where a source IP address is not specified.
| ||
| Step 4 |
exit Example: Device# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring the CTS-SXP Reconciliation Period
After a peer terminates a CTS-SXP connection, an internal hold-down timer starts. If the peer reconnects before the internal hold-down timer expires, the CTS-SXP reconciliation period timer starts. While the CTS-SXP reconciliation period timer is active, the CTS software retains the SGT mapping entries learned from the previous connection and removes invalid entries. The default value is 120 seconds (2 minutes). Setting the CTS-SXP reconciliation period to 0 seconds disables the timer and causes all entries from the previous connection to be removed.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
cts
sxp
reconciliation
period
seconds
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
cts
sxp
reconciliation
period
seconds
Example: Device(config)# cts sxp reconciliation period 150 |
Sets the CTS-SXP reconciliation timer, in seconds. The range is from 0 to 64000. The default is 120. |
| Step 4 |
exit Example: Device# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring the CTS-SXP Retry Period
The CTS-SXP retry period determines how often the CTS software retries a CTS-SXP connection. If a CTS-SXP connection is not established successfully, then the CTS software makes a new attempt to set up the connection after the CTS-SXP retry period timer expires. The default value is 2 minutes. Setting the CTS-SXP retry period to 0 seconds disables the timer and retries are not attempted.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
cts
sxp
retry
period
seconds
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
cts
sxp
retry
period
seconds
Example: Device(config)# cts sxp retry period 160 |
Sets the CTS-SXP retry timer, in seconds. The range is from 0 to 64000. The default is 120. |
| Step 4 |
exit Example: Device# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Creating Syslogs to Capture IP-to-SGT Mapping Changes
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
cts
sxp
log
binding-changes
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
cts
sxp
log
binding-changes
Example: Device(config)# cts sxp log binding-changes |
Enables logging for IP-to-SGT binding changes causing CTS-SXP syslogs (sev 5 syslog) to be generated whenever a change to IP-to-SGT binding occurs (add, delete, change). These changes are learned and propagated on the CTS-SXP connection.
| ||
| Step 4 |
exit Example: Device# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring a Class Map for a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
Perform this task to configure a class map for classifying Security Group Access (SGA) zone-based policy firewall network traffic.
 Note | You must perform at least one match step. |
The zone-based firewall policy uses the Security Group Tag ID for filtering. In a zone-based firewall policy, only the first packet that creates a session matches the policy. Subsequent packets in this flow do not match the filters in the configured policy, but instead match the session directly. The statistics related to subsequent packets are shown as part of the inspect action.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
object-group security
name
4.
security-group tag-id
sgt-id
5.
group-object
name
6.
description
text
7.
exit
8.
class-map type inspect
[match-any |
match-all]
class-map-name
9.
match group-object security source
name
10.
match group-object security destination
name
11.
end
12.
show object-group [name]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 |
object-group security
name
Example: Device(config)# object-group security myobject1a |
Creates an object group to identify traffic coming from a specific user or endpoint and enters object-group identity mode. |
| Step 4 |
security-group tag-id
sgt-id
Example: Device(config-object-group)# security-group tag-id 120 |
Specifies the membership of a security group by using the SGT ID number. This number can be from 1 to 65535. Multiple security groups can be specified using this command. |
| Step 5 |
group-object
name
Example: Device(config-object-group)# group-object admin |
(Optional) Specifies a nested reference to a type of user group. Multiple nested user groups can be specified using this command. |
| Step 6 |
description
text
Example: Device(config-object-group)# description my sgtinfo |
(Optional) Defines information about the security group. |
| Step 7 |
exit
Example: Device(config-object-group)# exit |
Exits object-group identity mode and enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 8 |
class-map type inspect
[match-any |
match-all]
class-map-name
Example: Device(config)# class-map type inspect match-any myclass1 |
Creates a Layer 3 or Layer 4 inspect type class map and enters class-map configuration mode. |
| Step 9 |
match group-object security source
name
Example: Device(config-cmap)# match group-object security source myobject1 |
Matches traffic from a user in the security group. |
| Step 10 |
match group-object security destination
name
Example: Device(config-cmap)# match group-object security destination myobject1 |
Matches traffic for a user in the security group. |
| Step 11 |
end
Example: Device(config-cmap)# end |
Exits class-map configuration mode and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 12 |
show object-group [name]
Example: Device# show object-group admin |
(Optional) Displays the content of all user groups. Optionally, use the name argument to show information for a single group. |
Creating a Policy Map for a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
Perform this task to create a policy map for a Security Group Access (SGA) zone-based policy firewall that is attached to zone pairs. This task also helps to configure Identity Firewall (IDFW) to work with Security Group Tag (SGT) Exchange Protocol (SXP) or L2-tagged traffic on the interfaces that belong to the security zones.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
policy-map
type
inspect
policy-map-name
4.
class
type
inspect
class-name
5.
inspect
6.
exit
7.
zone-pair security
zone-pair-name
source
source-zone
destination
destination-zone
8.
service-policy type inspect
policy-map-name
9.
end
10.
interface
type
number
11.
zone-member security
zone-name
12.
cts manual
13.
no propagate sgt
14.
policy static sgt
tag [trusted]
15.
exit
16.
show policy-map type inspect zone-pair session
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
policy-map
type
inspect
policy-map-name
Example: Device(config)# policy-map type inspect z1z2-policy |
Creates a Layer 3 or Layer 4 inspect type policy map. | ||
| Step 4 |
class
type
inspect
class-name
Example: Device(config-pmap)# class type inspect cmap-1 |
Specifies the traffic (class) on which an action is to be performed and enters policy-map class configuration mode. | ||
| Step 5 |
inspect Example: Device(config-pmap-c)# inspect |
Enables packet inspection. | ||
| Step 6 |
exit
Example: Device(config-pmap-c)# exit |
Exits policy-map class configuration mode and enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 7 |
zone-pair security
zone-pair-name
source
source-zone
destination
destination-zone
Example: Device(config)# zone-pair security z1z2 source z1 destination z2 |
| ||
| Step 8 |
service-policy type inspect
policy-map-name
Example: Device(config-sec-zone)# service-policy type inspect z1z2-policy2 |
| ||
| Step 9 |
end
Example: Device(config-sec-zone)# end |
Exits security zone configuration mode and enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 10 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 |
Configures an interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 11 |
zone-member security
zone-name
Example: Device(config-if)# zone-member security Inside |
| ||
| Step 12 |
cts manual
Example: Device(config-if)# cts manual |
Enables the interface for Cisco TrustSec Security (CTS) SGT authorization and forwarding, and enters CTS manual interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 13 |
no propagate sgt
Example: Device(config-if-cts-manual)# no propagate sgt |
Disables SGT propagation at Layer 2 on CTS interfaces. | ||
| Step 14 |
policy static sgt
tag [trusted]
Example: Device(config-if-cts-manual)# policy static sgt 100 trusted |
Configures a static authorization policy for a CTS security group with a tagged packet that defines the trustworthiness of the SGT. | ||
| Step 15 |
exit
Example: Device(config-if)# exit |
Exits security zone configuration mode and enters privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 16 |
show policy-map type inspect zone-pair session
Example: Device# show policy-map type inspect zone-pair session |
(Optional) Displays the Cisco IOS stateful packet inspection sessions created because of the policy-map application on the specified zone pair.
|
Example:
The following sample output of the show policy-map type inspect zone-pair session command displays the information about the Cisco IOS stateful packet inspection sessions created because of the policy-map application on the specified zone pair:
Device# show policy-map type inspect zone-pair session
Zone-pair: in-out
Service-policy inspect : test
Class-map: test (match-any)
Match: group-object security source sgt
Inspect
Established Sessions
Session 113EF68C (192.2.2.1:8)=>(198.51.100.252:153) icmp SIS_OPEN
Created 00:00:02, Last heard 00:00:02
Bytes sent (initiator:responder) [360:360]
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
Match: any
Drop (default action)
310 packets, 37380 bytes
Configuration Examples for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
Example: Enabling and Configuring a CTS-SXP Peer Connection
The following example shows how to enable CTS-SXP and configure the CTS-SXP peer connection on Device_A, a speaker, for connection to Device_B, a listener:
Device# configure terminal Device_A(config)# cts sxp enable Device_A(config)# cts sxp default password Cisco123 Device_A(config)# cts sxp default source-ip 10.10.1.1 Device_A(config)# cts sxp connection peer 10.20.2.2 password default mode local speaker
The following example shows how to configure the CTS-SXP peer connection on Device_B, a listener, for connection to Device_A, a speaker:
Device# configure terminal Device_B(config)# cts sxp enable Device_B(config)# cts sxp default password Cisco123 Device_B(config)# cts sxp default source-ip 10.20.2.2 Device_B(config)# cts sxp connection peer 10.10.1.1 password default mode local listener
The following sample output for show cts sxp connections command displays CTS-SXP connections:
Device_B# show cts sxp connections SXP : Enabled Default Password : Set Default Source IP: 10.10.1.1 Connection retry open period: 10 secs Reconcile period: 120 secs Retry open timer is not running ---------------------------------------------- Peer IP : 10.20.2.2 Source IP : 10.10.1.1 Conn status : On Connection mode : SXP Listener Connection inst# : 1 TCP conn fd : 1 TCP conn password: default SXP password Duration since last state change: 0:00:21:25 (dd:hr:mm:sec) Total num of SXP Connections = 1
Example: Configuring a Security Group Access Zone-Based Policy Firewall
The following example shows the configuration of a class map and policy map for an SGA zone-based policy firewall.
Device(config)# object-group security myobject1
Device(config-object-group)# security-group tag-id 1
Device(config-object-group)# exit
Device(config)# object-group security myobject2
Device(config-object-group)# security-group tag-id 2
Device(config-object-group)# exit
Device(config)# object-group security myobject3
Device(config-object-group)# security-group tag-id 3
Device(config-object-group)# exit
Device(config)# object-group security myobject4
Device(config-object-group)# security-group tag-id 4
Device(config-object-group)# exit
Device(config)# class-map type inspect match-any myclass1
Device(config-cmap)# match group-object security source myobject1
Device(config-cmap)# exit
Device(config)# class-map type inspect match-any myclass2
Device(config-cmap)# match group-object security source myobject2
Device(config-cmap)# exit
Device(config)# class-map type inspect match-any myclass3
Device(config-cmap)# match group-object security source myobject3
Device(config-cmap)# exit
Device(config)# class-map type inspect match-any myclass4
Device(config-cmap)# match group-object security source myobject4
Device(config-cmap)# exit
Device(config)# policy-map type inspect InsideOutside
Device(config-pmap)# class type inspect myclass1
Device(config-pmap-c)# pass
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config-pmap)# class type inspect myclass2
Device(config-pmap-c)# drop log
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config)# policy-map type inspect OutsideInside
Device(config-pmap)# class type inspect myclass3
Device(config-pmap-c)# pass
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config-pmap)# class type inspect myclass4
Device(config-pmap-c)# drop
Device(config-pmap-c)# exit
Device(config)# zone-pair security Inside
Device(config-sec-zone)# description Firewall Inside Zone
Device(config-sec-zone)# exit
Device(config)# zone-pair security Outside
Device(config-sec-zone)# description Firewall Outside Zone
Device(config-sec-zone)# exit
Device(config)# zone-pair security InsideOutside source Inside destination Outside
Device(config-sec-zone)# description Firewall ZonePair Inside Outside
Device(config-sec-zone)# service-policy type inspect InsideOutside
Device(config-sec-zone)# exit
Device(config)# zone-pair security OutsideInside source Outside destination Inside
Device(config-sec-zone)# description Firewall ZonePair Outside Inside
Device(config-sec-zone)# service-policy type inspect OutsideInside
Device(config-sec-zone)# exit
Device(config)# interface Gigabit 0/1/1
Device(config-if)# zone-member security Inside
Device(config-if)# exit
Additional References for TrustSec SGT Handling: L2 SGT Imposition and Forwarding
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Security commands |
|
|
Cisco TrustSec switches |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
CISCO-TRUSTSEC-SXP-MIB |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4 |
Cisco IOS 12.2(33)SXI3 Cisco IOS 15.1(3)S Cisco IOS 15.1(2)SY1 |
The Security Group Tag (SGT) Exchange Protocol (SXP) is one of several protocols that supports CTS and is referred to in this document as CTS-SXP. CTS-SXP is a control protocol for propagating IP-to-SGT binding information across network devices that do not have the capability to tag packets. CTS-SXP passes IP-to-SGT bindings from authentication points to upstream devices in the network. This allows security services on switches, routers, or firewalls to learn identity information from access devices. The following commands were introduced or modified: cts sxp enable, cts sxp connection peer, show cts sxp, cts sxp default source-ip, cts sxp reconciliation period, cts sxp retry period, cts sxp log binding-changes. |
|
TrustSec SG Firewall Enforcement IPv4 |
Cisco IOS 15.2(1)S |
This feature helps CTS-SXP extend the deployment of network devices through Security Group Access (SGA) Zone-Based Policy firewalls (ZBPFs). The following commands were introduced or modified: group-object, match group-object security, object-group security, policy static sgt, and security-group. |
 Feedback
Feedback