HGW
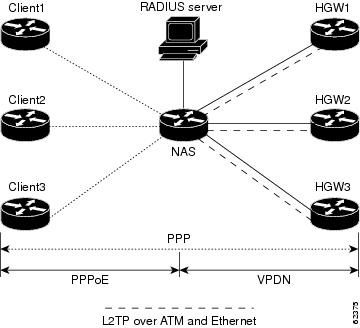
--home gateway. A gateway that terminates Layer 2 tunneling protocols such as L2TP.
home
gateway
--See HGW.
L2TP
--Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol. An Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standards track protocol defined in RFC 2661 that provides
tunneling of PPP. Based upon the best features of L2F and PPTP, L2TP provides an industry-wide interoperable method of implementing
VPDN.
L2TP network server--See LNS.
Layer
2
Tunnel
Protocol
--See L2TP.
LNS
--L2TP network server. A node that acts as one side of an L2TP tunnel endpoint and is a peer to the NAS or L2TP access concentrator
(LAC). The LNS is the logical termination point of a PPP session that is being tunneled from the remote system by the access
server. Analogous to the Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) HGW.
NAS
--network access server. Cisco platform or collection of platforms that interfaces between the packet world (the Internet,
for example) and the circuit world (the public switched telephone network, for example).
network
access
server
--See NAS.
Request
for
Comments
--See RFCs.
RFCs
--Request for Comments. A series of notes about the Internet collected by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). Started
in 1969, the IETF is a large open international community of network designers, operators, vendors, and researchers concerned
with the evolution of the Internet architecture. RFCs define many aspects of computer communication, focusing on networking
protocols, procedures, programs, and concepts.
virtual
private
dialup
network
--See VPDN.
VPDN
--virtual private dialup network. Enables IP traffic to travel securely over a public TCP/IP network by encrypting all traffic
from one network to another.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone
numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown
for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and
coincidental.
© 2001-2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback