- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Layer 2 Local Switching
- Restrictions for Layer 2 Local Switching
- Information About Layer 2 Local Switching
- How to Configure Layer 2 Local Switching
Layer 2 Local Switching
The Layer 2 Local Switching feature allows you to switch Layer 2 data in two ways:
- Between two interfaces on the same router
- Between two circuits on the same interface port, which is called same-port switching
The following interface-to-interface switching combinations are supported by this feature:
The following same-port switching features are supported:
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Layer 2 Local Switching
- Restrictions for Layer 2 Local Switching
- Information About Layer 2 Local Switching
- How to Configure Layer 2 Local Switching
- Configuration Examples for Layer 2 Local Switching
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Layer 2 Local Switching
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Layer 2 Local Switching
You must enable Cisco Express Forwarding for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router.
Restrictions for Layer 2 Local Switching
For Ethernet/Ethernet VLAN circuits, the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router must have Ethernet Adapters.
Information About Layer 2 Local Switching
- Layer 2 Local Switching Overview
- NSF SSO - Local Switching Overview
- Layer 2 Local Switching Applications
Layer 2 Local Switching Overview
Local switching allows you to switch Layer 2 data between two interfaces (for example, Ethernet to Ethernet, Ethernet VLAN to Ethernet VLAN, or Ethernet to Ethernet VLAN) on the same router. The interfaces can be on the same line card or on two different cards. During these kinds of switching, the Layer 2 address is used, not the Layer 3 address.
Additionally, same-port local switching allows you to switch Layer 2 data between two circuits on the same interface.
NSF SSO - Local Switching Overview
Nonstop forwarding (NSF) and stateful switchover (SSO) improve the availability of the network by providing redundant Route Processors and checkpointing of data to ensure minimal packet loss when the primary Route Processor goes down. NSF/SSO support is available for the following locally switched attachment circuits:
- Ethernet/Ethernet VLAN to Ethernet/Ethernet VLAN
Layer 2 Local Switching Applications
Incumbent local exchange carriers (ILECs) that use an interexchange carrier (IXC) to carry traffic between two local exchange carriers can use the Layer 2 Local Switching feature. Telecom regulations require the ILECs to pay the IXCs to carry that traffic. At times, the ILECs cannot terminate customer connections that are in different local access and transport areas (LATAs). In other cases, customer connections terminate in the same LATA, which may also be on the same router.
For example, company A has more than 50 LATAs across the country and uses three routers for each LATA. Company A uses companies B and C to carry traffic between local exchange carriers. Local switching of Layer 2 frames on the same router might be required.
Similarly, if a router is using, for example, a channelized interface, it might need to switch incoming and outgoing traffic across two logical interfaces that reside on a single physical port. The same-port local switching feature addresses that implementation.
How to Configure Layer 2 Local Switching
- Configuring Ethernet VLAN Same-Port Switching
- Configuring Ethernet Port Mode to Ethernet VLAN Local Switching
- Configuring ATM-to-ATM PVC Local Switching and Same-Port Switching
- Configuring ATM-to-ATM PVP Local Switching
- Configuring ATM PVP Same-Port Switching
- Verifying Layer 2 Local Switching
Configuring Ethernet VLAN Same-Port Switching
Perform this task to configure Ethernet VLAN same-port switching.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Ethernet Port Mode to Ethernet VLAN Local Switching
Perform this task to configure local switching for Ethernet (port mode) to Ethernet VLAN.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring ATM-to-ATM PVC Local Switching and Same-Port Switching
You can configure local switching for both ATM AAL5 and ATM AAL0 encapsulation types.
Creating the ATM PVC is not required. If you do not create a PVC, one is created for you. For ATM-to-ATM local switching, the autoprovisioned PVC is given the default encapsulation type AAL0 cell relay.
Perform this task to configure ATM-to-ATM PVC local switching and same-port switching.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring ATM-to-ATM PVP Local Switching
Perform this task to configure ATM-to-ATM PVP local switching.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring ATM PVP Same-Port Switching
Perform this task to configure ATM PVP switching on an ATM interface.
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying Layer 2 Local Switching
- Verifying Layer 2 Local Switching Configuration
- Verifying the NSF SSO Local Switching Configuration
- Troubleshooting Tips
Verifying Layer 2 Local Switching Configuration
To verify configuration of the Layer 2 local switching feature, use the show connection command on the provider edge (PE) router.
DETAILED STEPS
|
The show connectioncommand displays the local connection between a Gigabit Ethernet interface and another local Gigabit Ethernet interface: Example: Router# show connection name ethconn1 Connection: 1 - ethconn1 Current State: UP Segment 1: GigabitEthernet0/0/0.1 up Segment 2: GigabitEthernet0/0/0.2 up |
Verifying the NSF SSO Local Switching Configuration
Layer 2 local switching provides NSF/SSO support for Local Switching of the following attachment circuits on the same router:
For information about configuring NSF/SSO on the Route Processors, see the " Stateful Switchover " module in the Cisco IOS XE High Availability Configuration Guide . Perform this task to verify that the NSF/SSO: Layer 2 Local Switching feature is working correctly.
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
You can troubleshoot Layer 2 local switching using the following commands on the PE router:
- debug conn
- show connection
Configuration Examples for Layer 2 Local Switching
- Example Ethernet VLAN Same-Port Switching
- Example NSF SSO Ethernet Port Mode to Ethernet VLAN Local Switching
- Example ATM-to-ATM Local Switching
- Example ATM PVC Same-Port Switching
- Example ATM PVP Same-Port Switching
Example Ethernet VLAN Same-Port Switching
The following example shows same-port switching between two VLANs on one Ethernet interface:
interface fastethernet 0/0.1 encapsulation dot1q 1 interface fastethernet 0/0.2 encapsulation dot1q 2 connect conn FastEthernet 0/0.1 FastEthernet 0/0.2
Example NSF SSO Ethernet Port Mode to Ethernet VLAN Local Switching
The following configuration uses the network topology shown in the figure below.
| Figure 1 | NSF/SSO: Layer 2 Local Switching: Ethernet to Ethernet VLAN |
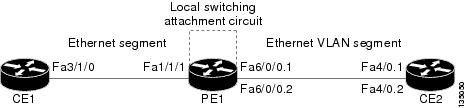
The following example shows the configuration of the CE interfaces to connect to the PE1 router:
| CE1 |
CE2 |
|---|---|
ip routing ! interface fa3/1/0 description: connection to PE fa1/1/1 no shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 |
ip routing ! interface fa4/0 no shutdown ! interface fa4/0.1 description: connection to PE1 fa6/0/0.1 encapsulation dot1Q 10 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface fa4/0.2 description - connection to PE1 fa6/0/0.2 encapsulation dot1Q 20 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 |
The following example shows the configuration of the PE1 router with NSF/SSO and the PE interfaces to the CE routers:
PE1
redundancy
no keepalive-enable
mode sso
!
!
ip routing
ip cef distributed
!
interface fa1/1/1
description - connection to CE1 fa3/1/0
no shutdown
no ip address
!
!
interface fa6/0/0
no shutdown
no ip address
!
interface fa6/0/0.1
description - connection to CE2 fa4/0.1
encapsulation dot1Q 10
no ip address
!
interface fa6/0/0.2
description - connection to CE2 fa4/0.2
encapsulation dot1Q 20
no ip address
Example ATM-to-ATM Local Switching
The following example shows local switching on ATM interfaces configured for AAL5:
interface atm1/0/0 pvc 0/100 l2transport encapsulation aal5 interface atm2/0/0 pvc 0/100 l2transport encapsulation aal5 connect aal5-conn atm1/0/0 0/100 atm2/0/0 0/100
Example ATM PVC Same-Port Switching
The following example shows same-port switching between two PVCs on one ATM interface:
interface atm1/0/0 pvc 0/100 l2transport encapsulation aal5 pvc 0/200 l2transport encapsulation aal5 connect conn atm1/0/0 0/100 atm1/0/0 0/200
Example ATM PVP Same-Port Switching
The following example shows same-port switching between two PVPs on one ATM interface:
interface atm1/0/0 atm pvp 100 l2transport atm pvp 200 l2transport connect conn atm1/0/0 100 atm1/0/0 200
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS commands |
|
| WAN Commands |
Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Command Reference |
| Stateful switchover configuration information |
"Stateful Switchover " module in the Cisco IOS XE High Availability Configuration Guide |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| draft-ietf-l2tpext-l2tp-base-03.txt |
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (Version 3) 'L2TPv3' |
| draft-martini-l2circuit-trans-mpls-09.txt |
Transport of Layer 2 Frames Over MPLS |
| draft-martini-l2circuit-encap-mpls-04.txt |
Encapsulation Methods for Transport of Layer 2 Frames Over IP and MPLS Networks |
| draft-ietf-ppvpn-l2vpn-00.txt |
An Architecture for L2VPNs |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS XE software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| None |
-- |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Layer 2 Local Switching
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for Layer 2 Local Switching |
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| Layer 2 Local Switching |
Cisco IOS XE Release 2.5 |
The Layer 2 Local Switching feature allows you to switch Layer 2 data between two interfaces on the same router, and in some cases to switch Layer 2 data between two circuits on the same interface port. In Cisco IOS XE Release 2.5, this feature was introduced on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. The following commands were introduced or modified: connect (L2VPN local switching), show connection. |
| Layer 2 Local Switching - ATM to ATM |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3S |
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3S, this feature was introduced on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. The following commands were introduced or modified: connect (L2VPN local switching), show connection. |
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback