Cisco ASR 9902 Router Fixed Ports
The Cisco ASR 9902 router has 48 ports that are grouped into slice 0 and slice 1. The slice 0 is color coded in blue, and slice 1 in purple:
-
2 ports that support QSFP-DD-based 100GE pluggables
-
6 ports that support QSFP28-based 100GE pluggables
-
16 ports that support SFP28-based 25GE/10GE dual-rate pluggables
-
24 ports that support SFP+- based LAN/WAN (OTN) pluggables
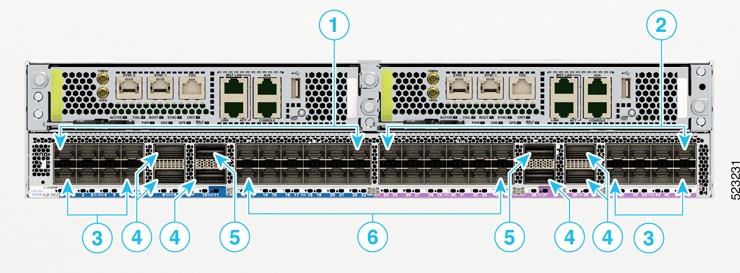
|
1 |
Slice 0 |
4 |
QSFP28 ports; three on each slice. |
|
2 |
Slice 1 |
5 |
QSFP-DD ports; one on each slice. |
|
3 |
SFP28 ports; eight on each slice. |
6 |
SFP+ ports; twelve on each slice. |
Port Mode Configurations
The Cisco ASR 9902 router has 48 ports with maximum of 800G data bandwidth capacity. By default, these ports are in 10GE mode. You can configure the 48 ports in various port modes (100GE, 25GE, and 10GE) using the hw-module location <node> slice <number> config-mode command.
For more information, see Configuring Port Modes in Cisco ASR 9902 Router in System Management Configuration Guide for Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers.











































 Feedback
Feedback