Information About Implementing Secure Shell
To implement SSH, you should understand the following concepts:
SSH Server
The SSH server feature enables an SSH client to make a secure, encrypted connection to a Cisco router. This connection provides functionality that is similar to that of an inbound Telnet connection. Before SSH, security was limited to Telnet security. SSH allows a strong encryption to be used with the Cisco IOS XR software authentication. The SSH server in Cisco IOS XR software works with publicly and commercially available SSH clients.
SSH Client
The SSH client feature is an application running over the SSH protocol to provide device authentication and encryption. The SSH client enables a Cisco router to make a secure, encrypted connection to another Cisco router or to any other device running the SSH server. This connection provides functionality that is similar to that of an outbound Telnet connection except that the connection is encrypted. With authentication and encryption, the SSH client allows for a secure communication over an insecure network.
The SSH client in the Cisco IOS XR software works with publicly and commercially available SSH servers. The SSH client supports the ciphers of AES, 3DES, the hash algorithm SHA1, and password authentication. The user authentication mechanisms supported for SSH are RADIUS, TACACS+, and the use of locally stored usernames and passwords.
The SSH client supports setting DSCP value in the outgoing packets using this command:
ssh client dscp dscp-value
The dscp-value ranges from 0 to 63. If not configured, 16 is set as the default DSCP value in the packets (for both client and server).
You can use the ssh client command in the XR Config mode to configure various SSH client options.
Router#ssh 192.0.2.1 username admin command "show redundancy sum"
Password:
Wed Jan 9 07:05:27.997 PST
Active Node Standby Node
----------- ------------
0/4/CPU0 0/5/CPU0 (Node Ready, NSR: Not Configured)
Router#
SFTP Feature Overview
SSH includes support for secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) , a new standard file transfer protocol introduced in SSHv2. This feature provides a secure and authenticated method for copying router configuration or router image files.
The SFTP client functionality is provided as part of the SSH component and is always enabled on the router. Therefore, a user with the appropriate level can copy files to and from the router. Like the copy command, the sftp command can be used only in XR EXEC mode.
The SFTP client is VRF-aware, and you may configure the secure FTP client to use the VRF associated with a particular source interface during connections attempts. The SFTP client also supports interactive mode, where the user can log on to the server to perform specific tasks via the Unix server.
The SFTP Server is a sub-system of the SSH server. In other words, when an SSH server receives an SFTP server request, the SFTP API creates the SFTP server as a child process to the SSH server. A new SFTP server instance is created with each new request.
The SFTP requests for a new SFTP server in the following steps:
-
The user runs the sftp command with the required arguments
-
The SFTP API internally creates a child session that interacts with the SSH server
-
The SSH server creates the SFTP server child process
-
The SFTP server and client interact with each other in an encrypted format
-
The SFTP transfer is subject to LPTS policer "SSH-Known". Low policer values will affect SFTP transfer speeds
 Note |
The default policer value for SSH-Known is set to 300pps. Slower transfers are expected due to this. You can adjust the lpts policer value for this punt cause to higher values that allows faster transfers. |
You can increase the throughput of SCP or SFTP over inband using the ssh server tcp-window-scale command.
When the SSH server establishes a new connection with the SSH client, the server daemon creates a new SSH server child process. The child server process builds a secure communications channel between the SSH client and server via key exchange and user authentication processes. If the SSH server receives a request for the sub-system to be an SFTP server, the SSH server daemon creates the SFTP server child process. For each incoming SFTP server subsystem request, a new SSH server child and SFTP server instances are created. The SSH server authenticates the user session and initiates a connection. It sets the environment for the client and the default directory for the user.
Once the initialization occurs, the SFTP server waits for the SSH_FXP_INIT message from the client, which is essential to start the file communication session. This message may then be followed by any message based on the client request. Here, the protocol adopts a 'request-response' model, where the client sends a request to the server; the server processes this request and sends a response.
The SFTP server displays the following responses:
-
Status Response
-
Handle Response
-
Data Response
-
Name Response
 Note |
The server must be running in order to accept incoming SFTP connections. |
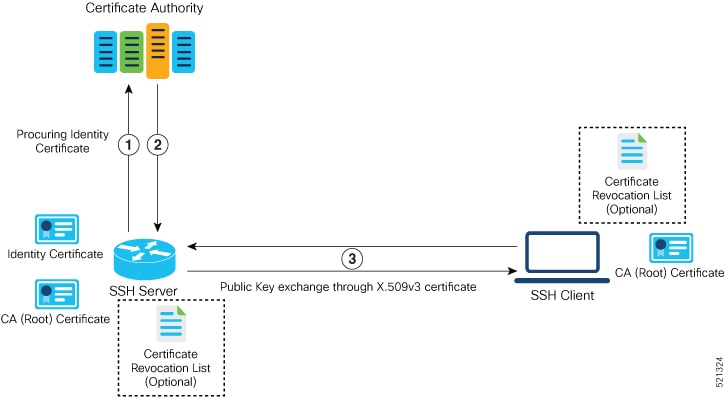
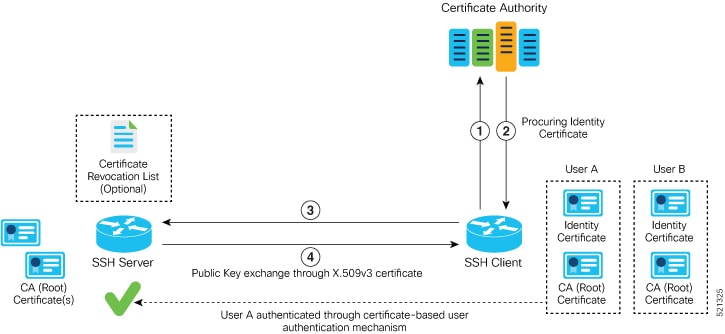
RSA Based Host Authentication
Verifying the authenticity of a server is the first step to a secure SSH connection. This process is called the host authentication, and is conducted to ensure that a client connects to a valid server.
The host authentication is performed using the public key of a server. The server, during the key-exchange phase, provides its public key to the client. The client checks its database for known hosts of this server and the corresponding public-key. If the client fails to find the server's IP address, it displays a warning message to the user, offering an option to either save the public key or discard it. If the server’s IP address is found, but the public-key does not match, the client closes the connection. If the public key is valid, the server is verified and a secure SSH connection is established.
The IOS XR SSH server and client had support for DSA based host authentication. But for compatibility with other products, like IOS, RSA based host authentication support is also added.
RSA Based User Authentication
One of the method for authenticating the user in SSH protocol is RSA public-key based user authentication. The possession of a private key serves as the authentication of the user. This method works by sending a signature created with a private key of the user. Each user has a RSA key pair on the client machine. The private key of the RSA key pair remains on the client machine.
The user generates an RSA public-private key pair on a unix client using a standard key generation mechanism such as ssh-keygen. The max length of the keys supported is 4096 bits, and the minimum length is 512 bits. The following example displays a typical key generation activity:
bash-2.05b$ ssh-keygen –b 1024 –t rsa
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
The public key must be in base64 encoded (binary) format for it to be imported correctly into the box. You can use third party tools available on the Internet to convert the key to the binary format.
Once the public key is imported to the router, the SSH client can choose to use the public key authentication method by specifying the request using the “-o” option in the SSH client. For example:
client$ ssh -o PreferredAuthentications=publickey 1.2.3.4
If a public key is not imported to a router using the RSA method, the SSH server initiates the password based authentication. If a public key is imported, the server proposes the use of both the methods. The SSH client then chooses to use either method to establish the connection. The system allows only 10 outgoing SSH client connections.
Currently, only SSH version 2 supports the RSA based authentication. For more information on how to import the public key to the router, see the Implementing Certification Authority Interoperability chapter in this guide.
 Note |
The preferred method of authentication would be as stated in the SSH RFC. The RSA based authentication support is only for local authentication, and not for TACACS/RADIUS servers. |
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) is a suite of network security services that provides the primary framework through which access control can be set up on your Cisco router or access server. For more information on AAA, the Configuring AAA Services chapter in this guide.
SSHv2 Client Keyboard-Interactive Authentication
An authentication method in which the authentication information is entered using a keyboard is known as keyboard-interactive authentication. This method is an interactive authentication method in the SSH protocol. This type of authentication allows the SSH client to support different methods of authentication without having to be aware of their underlying mechanisms.
Currently, the SSHv2 client supports the keyboard-interactive authentication. This type of authentication works only for interactive applications.
 Note |
The password authentication is the default authentication method. The keyboard-interactive authentication method is selected if the server is configured to support only the keyboard-interactive authentication. |
SSH and SFTP in Baseline Cisco IOS XR Software Image
The SSH and SFTP components are present in the baseline Cisco IOS XR software image. The management and control plane components (such as the IPSec control plane) are also present in the base package. However, the data plane components (such as the MACSec and the IPSec data plane) are part of the security package as per the export compliance regulations. This segregation of package components makes the software more modular. It also gives you the flexibility of including or excluding the security package as per your requirements.
The base package and the security package allow FIPS, so that the control plane can negotiate FIPS-approved algorithms.
CiscoSSH
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CiscoSSH |
Release 7.3.2 |
This release introduces CiscoSSH, a newer implementation of SSH on this platform. CiscoSSH leverages OpenSSH implementation, by using the Linux TCP/IP stack to transmit and receive SSH packets over the management Ethernet interface and line card interfaces on the router. CiscoSSH provides additional security features like FIPS compliance and X.509 digital certification. It supports packet path features like MPP, ACL and VRF support, and ensures interoperability with various existing SSH implementations.
|
 Note |
Any reference to CiscoSSH in this chapter implies OpenSSH-based implementation of SSH that is available on this platform from Cisco IOS XR Software Release 7.3.2 and later. CiscoSSH replaces Cisco IOS XR SSH, which is the older SSH implementation that existed prior to this release. |
OpenSSH is a stable, widely deployed open-source implementation of SSH. CiscoSSH implementation leverages the key features of openSSH such as strong authentication, cryptography, encryption, port forwarding, and so on, to provide secured management access to the router. CiscoSSH provides additional security features like FIPS compliance and support for X.509 digital certificate.
For more details on SSH in general, see Information About Implementing Secure Shell and How to Implement Secure Shell.
The CiscoSSH implementation also ensures backward compatibility for all the existing Cisco IOS XR SSH configuration and management. You can continue to use SSH the way it was existing before. The functionality and configuration commands of CiscoSSH and Cisco IOS XR SSH remain the same for majority of the part. However, certain behavioral changes exist between CiscoSSH and Cisco IOS XR SSH. For details, see the subsequent sections.
This table lists the behavioral changes introduced by CiscoSSH as compared to Cisco IOS XR SSH. Also, see Guidelines for Using CiscoSSH.
| Functionality |
CiscoSSH |
Cisco IOS XR SSH |
|---|---|---|
|
Port number for Netconf server |
The system uses the port numbers 830 (the default IANA-assigned TCP port number for Netconf over SSH) or 22 (the default port number for SSH) for the Netconf server. You cannot configure this value. |
You can explicitly configure the desired port number for Netconf server using the ssh server netconf port command. |
|
Username syntax |
Because CiscoSSH considers ':' (colon ) as a delimiter in certain types of user authentication, it does not support authentication of usernames having ':' (colon ) in it. |
No restriction for using ':' (colon ) in username syntax. |
|
Configuring unsupported algorithms |
You cannot enable unsupported algorithms using any configuration command. |
You can explicitly enable unsupported algorithms using the ssh server enable cipher command. |
|
SSH session timeout |
The SSH session initiated from the router to an unreachable host times out after 120 seconds. |
The SSH session initiated from the router to an unreachable host times out after 60 seconds. |
|
SSH session timeout criteria |
The SSH timeout configuration considers the total timeout value for the maximum number of login attempts allowed. |
The SSH timeout configuration considers the timeout value for individual login attempt. |
|
Time-based rekey of SSH sessions |
The router triggers time-based rekey of SSH sessions only when it receives a packet after the timer expiry. |
The router triggers time-based rekey of SSH sessions immediately after the timer expiry. |
|
LPTS policer rate for port-forwarded SSH sessions |
When using SSH port forwarding feature, the router considers the traffic flows corresponding to port-forwarded SSH sessions as third party applications. Hence, the LPTS polices those traffic flows at a medium rate. |
The LPTS polices the traffic flows corresponding to port-forwarded SSH sessions at a high rate. |
|
Port-forwarded channels |
No limit to the number of port-forwarded channels supported with CiscoSSH. But, the show ssh command displays a maximum of only 16 entries. | Supports a maximum of 16 port-forwarded channels. |
|
File transfer through SCP |
While using SCP with CiscoSSH, the router checks for the presence of system files after authentication. |
The router checks for the presence of system files before authentication. |
|
File transfer through SFTP |
With non-interactive SFTP session initiated from the router, you can transfer files from an external device to the router; not from the router to external device. |
You can transfer files from an external device to the router, and the other way round. |
Restrictions for Cisco SSH
-
Does not support SSH version 1
-
Does not support back up SSH server
-
Does not support management access to the router over the standby management Ethernet interface.
-
Does not allow to use secondary IPv4 addresses because they are not currently synchronized to Linux (prior to Cisco IOS XR Software Release 7.7.1)
-
Does not support BVI interfaces as source or destination for the SSH connections (prior to Cisco IOS XR Software Release 7.7.1)
-
Does not support these algorithms:
-
The cipher algorithms, aes128-cbc , aes192-cbc, aes256-cbc, and 3des-cbc
-
The key-exchange algorithm, diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
-
-
Does not support these commands:
-
show ssh history
-
show ssh history details
-
clear ssh stale sessions
-
Guidelines for Using CiscoSSH
The following section lists certain functionality aspects and guidelines for using CiscoSSH.
-
Netconf Request: You must follow a specific syntax when you send Netconf request over CLI. Add the subsystem (netconf or sftp ) name as the last argument while issuing an SSH command.
For example,
ssh username@ipaddress -p 830 -s netconf ---> Correct usagessh username@ipaddress netconf -p 830 -s ---> Incorrect usage -
Configuring unsupported algorithms: Configuring CiscoSSH server only with unsupported algorithms (3des-cbc or diffie-hellman-group1-sha1 ) results in commit failure. Hence, you must remove such configurations on your router as a part of the pre-upgrade procedure.
For example,
Router(config)#ssh server algorithms cipher 3des-cbc !!% Operation not permitted: 3des-cbc is not supported in ciscossh, SSH cannot work with this option onlySimilarly, if you configure CiscoSSH server with both supported and unsupported algorithms, then the router issues the following warning and removes the unsupported algorithm:
Router(config)#ssh server algorithms cipher aes128-ctr aes192-ctr 3des-cbc ssh_conf_proxy[1193]: %SECURITY-SSHD_CONF_PRX-3-ERR_GENERAL : 3des-cbc is not supported, will be removed -
SSH session keep alive: By default, the SSH session keep alive functionality is enabled in CiscoSSH, to detect and terminate unresponsive sessions. The default keep alive time is 60 seconds, with a maximum of three attempts allowed, so that the detection time for unresponsive sessions is 180 seconds. These keep alive parameters are not configurable.
-
TCP window scale: Although the router accepts the configuration to change the TCP window scale parameter, the configuration does not have any effect with CiscoSSH. This is because, CiscoSSH uses Linux TCP/IP stack that has dynamic window scaling, and hence it does not require applications to specify the window scale.
-
SSH session limit and rate limit: Although the configuration for SSH session limit and rate limit applies to all VRFs where SSH is enabled, the router enforces the limit for each VRF. However, the maximum number of virtual teletype (VTY) sessions across all VRFs still remains as 200. This in turn limits the total number of SSH sessions that require a VTY interface, across all VRFs. As a result, when upgrading from a release version having Cisco IOS XR SSH to a version having CiscoSSH, the system applies the session limit and rate limit configurations to all VRFs where SSH is enabled. Hence, as part of the post-upgrade procedure, you must reconfigure these limits to achieve the same limit as that of Cisco IOS XR SSH.
-
SSH session limit enforcement: Information on the number of active SSH sessions on the router is not persistent across SSH server process restarts. Hence, SSH session limit enforcement does not consider the existing sessions after an SSH server restart.
-
SSH with ACL or MPP configuration: With SSH ACL or MPP configured on the router, the attempt for client connection that is now allowed as per that configuration times out. The router does not send TCP reset for such blocked SSH connections. This implementation is to enhance security.
-
Default VRFs: Configuring the default SSH VRF using the ssh vrf default command enables only version 2 of CiscoSSH, because version 1 is not supported.
-
Non-default VRFs: If SSH service is enabled on any of the non-default VRFs that is configured on the router, and if you restart the ssh_conf_proxy process, there might be a delay in allowing incoming SSH sessions on that non-default VRF. The session establishment might even timeout in such a scenario. This behavior is due to the delay in programming the LPTS entries for those sessions.
-
Public key-based authentication: In CiscoSSH, the router negotiates public key-based authentication even if there is no public key imported on to the router. So, the authentication attempt from the client using public key fails in such scenarios. The router displays a syslog on the console for this authentication failure. However, the client and server proceed with subsequent authentication methods like keyboard-interactive and password methods. If the router does not have a public key imported, you may choose to disable public key-based authentication from the client side. For details on public key-based authentication, see the Implementing Certification Authority Interoperability chapter in this guide.
-
Modifying SSH configuration: Any change to the SSH configuration results in process restart of SSH server process. However, it does not impact the existing SSH, SCP, SFTP, or Netconf sessions.
-
Clearing SSH sessions: The clear ssh all command clears all incoming sessions.
-
Line-feed option: Adding a line-feed option for Gossh-based clients results in SSH session establishment failure. This is because, the SSH client checks for non-zero window size for session establishment. Whereas CiscoSSH sends window size as 0. The workaround for this issue is to use the option to ignore the window size while initiating an SSH connection from such clients.
-
Virtual IP addresses: After a process restart of xlncd or ip_smiap , there might be a delay in restoring the virtual IP addresses.
-
More-specific Routes: Routes that are more specific than a connected route will not be available through Linux.
For example:
XR routing table: 10.0.0.0/24 via 10.0.0.2 (connected route) 10.0.0.192/28 via 20.0.0.1 (static route)The expected behavior is as follows:
Table 3. Expected Behavior of More-specific Routes with CiscoSSH Destination IP Range
Cisco IOS XR OS Sends to:
Linux Sends to:
Match
(Yes/No)
10.0.0.1 - 10.0.0.191
10.0.0.2
10.0.0.2
Yes
10.0.0.193 - 10.0.0.206
20.0.0.1
10.0.0.2
No
10.0.0.207 - 10.0.0.255
10.0.0.2
10.0.0.2
Yes
-
Verification commands: During stress test on the router, certain show commands like show ssh , show ssh session details , and show ssh rekey might time out. The console displays the following error message in such cases:
"Error: Timed out to obtain information about one or more incoming/outgoing session. please retry." -
Process restart:
-
You cannot restart the CiscoSSH server process using the process restart ssh_server command, because it is a Linux process. Use the kill command on the Linux shell to restart the process.
-
CiscoSSH has ssh_conf_proxy and ssh_syslog_proxy processes that are responsible for processing the SSH configuration and logging syslog messages respectively. You can restart these processes using the process restart command.
-
A restart of XR-TCP process does not have any impact on CiscoSSH functionality, because CiscoSSH uses Linux TCP.
-
-
Debuggability:
-
You can enable 3 levels of debugs for CiscoSSH using the debug ssh server l1/l2/l3 command. Similarly, you can use the debug ssh client l1/l2/l3 command for CiscoSSH client.
-
The SSH server process restarts every time you enable or disable the debugs, because enabling the debugs results in updating the LOGLEVEL in the internal sshd_config file.
-
Syslogs for CiscoSSH
CiscoSSH introduces new syslogs for various SSH session events. The following table gives a comparison of syslogs between CiscoSSH and Cisco IOS XR SSH:
|
Session Event |
Syslogs on CiscoSSH |
Syslogs on Cisco IOS XR SSH |
|---|---|---|
|
Session login |
|
|
|
Session logout |
|
|
|
Session login failure |
|
|
|
Session rekey |
|
|




 Feedback
Feedback