Running a Telemetry Receiver in a Linux Container (LXC)
For telemetry to work on Cisco IOS XR, it must use GPB (Google Protocol Buffer) over UDP, instead of TCP.
The procedure consists of the following steps:
-
Create a telemetry policy file.
-
Generate and compile a .proto file.
-
Configure the GPB encoder.
-
Launch a third-party container (LXC).
-
Configure the telemetry receiver.
Creating a Telemetry Policy File
A telemetry policy file is used to specify the kind of data to be generated and pushed to the telemetry receiver. The following steps describe how you can create the policy file for telemetry:
-
Determine the schema paths to stream data.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# schema-describe show interface Wed Aug 26 02:24:40.556 PDT RootOper.InfraStatistics.Interface(*).Latest.GenericCounters -
Create a policy file that contains these paths:
{ "Name": "Test", "Metadata": { "Version": 25, "Description": "This is a sample policy", "Comment": "This is the first draft", "Identifier": "<data that may be sent by the encoder to the mgmt stn" }, "CollectionGroups": { "FirstGroup": { "Period": 30, "Paths": [ "RootOper.InfraStatistics.Interface(*).Latest.GenericCounters" ] } } } -
Enter the XR Linux bash shell, and copy the policy file to IOS XR by using Secure Copy Protocol (SCP).
/* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.0, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# run ip netns exec tpnns bash /* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.2, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# bash [XR-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ scp Test.policy cisco@10.0.0.1:/telemetry/policies cisco@10.0.0.1's password: Test.policy 100% 779 0.8KB/s 00:00 Connection to 10.0.0.1 closed by remote host.Where 10.0.0.1 is the IP address of the device on which you are copying the policy file.
-
Navigate to the IOS XR prompt and verify if the policy file has been successfully installed.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# show telemetry policies brief Wed Aug 26 02:24:40.556 PDT Name |Active?| Version | Description ----------------------------|-------|---------|------------------------------ Test N 1 This is a sample policy
Generating and Compiling a .proto File
The path in a policy file that you created needs a.proto file associated with it. The .proto file describes the GPB message format used to stream data. The following steps describe
how you can generate and compile a .proto file for a telemetry receiver:
The .proto file is complied into a .map file. The compilation is done on a server.
-
Generate a .proto file.
telemetry generate gpb-encoding path "RootOper.InfraStatistics.Interface(*).Latest.GenericCounters" file disk0:generic_counters.protoThe .proto file is generated by an on-box tool. The tool ignores naming parameters, and are hence optional.

Note
The tool ignores text within quotes; therefore, the path should not contain quotes.
-
Compile the .proto file off the box.
-
Cisco provides a telemetry compiler on Dev Hub. You can copy the directory to your Linux box, and run it, as shown here:
telemetry_protoc -f generic_counters.proto -o generic_counters.map -
Access the copy of the .proto file from Dev Hub, and run the standard compiler on your Linux box, as shown here:
protoc python_out . -I=/ sw/packages/protoc/current/google/include/:. generic_counters.proto ipv4_counters.proto
-
-
Copy the map file to IOS XR at
/telemetry/gpb/maps.
Configuring the GPB Encoder
Configure the GPB encoder to activate the telemetry policy and stream data as outlined in the following steps:
-
Configure a loopback interface address for mapping the telemetry receiver to IOS XR, as shown here:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# interface Loopback2 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# ipv4 address 2.2.2.2/32 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# no shut RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# commit Fri Oct 30 07:51:14.785 UTC RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# exit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# exit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# show ipv4 interface brief Fri Oct 30 07:51:48.996 UTC Interface IP-Address Status Protocol Loopback0 1.1.1.1 Up Up Loopback1 8.8.8.8 Up Up Loopback2 2.2.2.2 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 192.164.168.10 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 192.57.43.10 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2 unassigned Shutdown Down MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 192.168.122.197 Up Up RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# -
Configure the encoder to stream the policy to the loopback interface of IOS XR that was just configured.
telemetry encoder gpb policy group alpha policy demo destination ipv4 2.2.2.2 port 5555 ! ! !
Launching a Third-Party Container (LXC)
This section describes how you can launch a third-party container (LXC) on IOS XR.
-
Log into IOS XR.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# run [xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ -
Launch the third-party container.
[xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ virsh -c lxc+tcp://10.11.12.15:16509/ -e ^Q console demo1 -
Log into the container when prompted.
Connected to domain demo Escape character is ^Q Kernel 3.14.23-WR7.0.0.2_standard on an x86_64 host login: Password:
You have successfully launched a third-party container.
Configuring the Telemetry Receiver
A telemetry
receiver listens for streamed data on the specified interface IP address and
port number, and it prints the header of the received packets. If .proto files
are provided, they are compiled using the protoc compiler and the message
contents are also printed. By default, only the first row of each table is
printed, though the
print-all option can be used to print the complete
output.
To run a telemetry receiver within the container you launched, use the following steps:
-
Download all the receiver files to the third-party container. The receiver files are available on IOS XR at
https://github.com/cisco/bigmuddy-network-telemetry-collector. -
Run the receiver to stream and print data.
python gpb_receiver.py ipaddress 2.2.2.2 port 5555 proto generic_counters.proto ipv4_counters.protoYou can see data on the telemetry receiver, as shown here:
Waiting for message Got message of length:1036bytes from address:('10.1.1.1', 5555) Encoding:2271560481 Policy Name:demo Version:25 Identifier:<data that may be sent by the encoder to the mgmt stn> Start Time:Wed Jan 21 09:54:33 1970 End Time:Wed Aug 26 09:28:37 2015 # Tables:1 Schema Path:RootOper.InfraStatistics.Interface.Latest.GenericCounters # Rows:6 Row 0: applique:0 availability_flag:0 broadcast_packets_received:0 broadcast_packets_sent:0 bytes_received:0 bytes_sent:0 carrier_transitions:0 crc_errors:0 framing_errors_received:0 giant_packets_received:0 input_aborts:0 input_drops:0 input_errors:0 input_ignored_packets:0 input_overruns:0 input_queue_drops:0 interface_name:Null0 last_data_time:1440606516 last_discontinuity_time:1440498130 multicast_packets_received:0 multicast_packets_sent:0 output_buffer_failures:0 output_buffers_swapped_out:0 output_drops:0 output_errors:0 output_queue_drops:0 output_underruns:0 packets_received:0 packets_sent:0 parity_packets_received:0 resets:0 runt_packets_received:0 seconds_since_last_clear_counters:0 seconds_since_packet_received:4294967295 seconds_since_packet_sent:4294967295 throttled_packets_received:0 unknown_protocol_packets_received:0 Waiting for message Got message of length:510bytes from address:('2.2.2.2', 5555) Encoding:2271560481 Policy Name:demo Version:25 Identifier:<data that may be sent by the encoder to the mgmt stn> Start Time:Wed Jan 21 09:54:33 1970 End Time:Wed Aug 26 09:28:38 2015 # Tables:1 Schema Path:RootOper.InfraStatistics.Interface.Latest.Protocol # Rows:5 Row 0: bytes_received:0 bytes_sent:0 input_data_rate:0 input_packet_rate:0 interface_name:Loopback2 last_data_time:1440606517 output_data_rate:0 output_packet_rate:0 packets_received:0 packets_sent:0 protocol:24 protocol_name:IPV4_UNICAST
The telemetry receiver runs successfully within the third-party container (LXC).
Use Cases on Vagrant: Container Application Hosting
This section describes how you can use vagrant to run use cases for container application hosting.
Pre-requisites for Using Vagrant
Before you can start using vagrant, ensure that you have fulfilled the following requirements on your host device.
-
Latest version of Vagrant for your operating system. We recommend Version 1.8.6.
-
Latest version of a virtual box for your operating system. We recommend Version 5.1+.
-
Minimum of 5 GB of RAM with two cores.
-
(Optional) If you are using the Windows Operating System, we recommend that you download the Git bash utility for running the commands.
OSPF Path Failover by Running iPerf with Netconf on Vagrant
This section describes a use case for solving a path remediation problem by using iPerf and Netconf applications on vagrant.
Topology
The topology used for OSPF path remediation is illustrated in the following figure.
The router on the left is rtr1 and is the source of traffic. We run the pathchecker application inside an LXC on this router. Pathchecker uses an iPerf client to determine the health of the path.
The router on the right is rtr2 and is the destination for traffic. We run the pathchecker application inside an LXC on this router. Pathchecker uses an iPerf server that talks to the iPerf client on rtr1.
devbox serves two
purposes in this topology:
-
To create an LXC tar ball with pathchecker before being deployed to the routers.
-
To bridge the two networks between the two routers over the parallel paths.
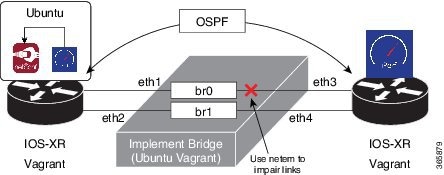
This example uses the following process for OSPF path failover:
-
Configure and establish OSPF neighbor relationship between two routers over two parallel paths.
-
Increase the cost of one path so that the other path is the preferred active path.
-
Use the pathchecker python application to monitor the OSPF active path by determining the bandwidth, jitter, packet loss and other parameters. Pathchecker uses the iPerf application to measure health of the active traffic path.
-
Use pathchecker to simulate network degradation by changing the OSPF active path cost during a Netconf session.
Procedure
Use the following steps to use iPerf with Netconf for OSPF path failover.
-
Generate an API key and a CCO ID by using the steps described on Github.
-
Download the latest stable version of the IOS-XRv vagrant box.
$ curl <cco-id>:<API-KEY> $ BOXURL --output ~/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box $ vagrant box add --name IOS-XRv ~/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box -
Verify if the vagrant box has been successfully installed.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$ vagrant box list IOS-XRv (virtualbox, 0) -
Create a working directory.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$ mkdir ~/iosxrv AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$cd ~/iosxrv -
Initialize the vagrant file with the new vagrant box.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$ vagrant init IOS-XRv A `Vagrantfile` has been placed in this directory. You are now ready to `vagrant up` your first virtual environment! Please read the comments in the Vagrantfile as well as documentation on `vagrantup.com` for more information on using Vagrant. -
Clone the repository containing the pathchecker code.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$ git clone https://github.com/ios-xr/pathchecker.git Cloning into 'pathchecker'... remote: Counting objects: 46, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (28/28), done. remote: Total 46 (delta 8), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 18 Unpacking objects: 100% (46/46), done. Checking connectivity... done. -
Navigate to the
pathchecker/vagrantdirectory and launchdevbox.AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$ cd pathchecker/ AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:pathchecker akshshar$ cd vagrant/ AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ pwd /Users/akshshar/pathchecker/vagrant AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant up devbox Bringing machine 'devbox' up with 'virtualbox' provider... ==> devbox: Importing base box 'ubuntu/trusty64'... ---------------------------- snip output --------------------------------- ==> devbox: Running provisioner: file... AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant status Current machine states: rtr1 not created (virtualbox) devbox running (virtualbox) rtr2 not created (virtualbox) This environment represents multiple VMs. The VMs are all listed above with their current state. For more information about a specific VM, run `vagrant status NAME`. -
Launch an LXC within
devbox.AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant ssh devbox vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo lxc-create -t ubuntu --name pathchecker Checking cache download in /var/cache/lxc/trusty/rootfs-amd64 ... Installing packages in template: ssh,vim,language-pack-en Downloading ubuntu trusty minimal ... I: Retrieving Release I: Retrieving Release.gpg I: Checking Release signature ... vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo lxc-start --name pathchecker <4>init: hostname main process (3) terminated with status 1 <4>init: plymouth-upstart-bridge main process (5) terminated with status 1 <4>init: plymouth-upstart-bridge main process ended, respawning Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS nc_iperf console pathchecker login: ubuntu Password: Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-87-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/ The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. ... -
Install all the required iPerf and Netconf application dependencies within the LXC.
ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ sudo apt-get -y install python-pip python-lxml python-dev libffi-dev libssl-dev iperf git ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ sudo pip install ncclient jinja2 cryptography==1.2.1 -
Retrieve the iPerf and Netconf application code from Github.
ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ git clone https://github.com/ios-xr/pathchecker.git Cloning into 'pathchecker'... remote: Counting objects: 46, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (28/28), done. remote: Total 46 (delta 8), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 18 Unpacking objects: 100% (46/46), done. Checking connectivity... done. ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ -
Change the SSH port inside the LXC.
When a container is deployed on XR, it shares the network namespace of XR. Since XR uses ports 22 and 57722 for internal processes, we change the port number to 58822 in this example.
ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ sudo sed -i s/Port\ 22/Port\ 58822/ /etc/ssh/sshd_config ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep Port Port 58822 -
Create the LXC tar ball.
-
Shut down the LXC.
ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ sudo shutdown -h now ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ Broadcast message from ubuntu@pathchecker (/dev/lxc/console) at 10:24 ... The system is going down for halt NOW! -
Assume the root user role.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo -s root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~# whoami root -
Navigate to the
/var/lib/lxc/pathchecker/rootfs/directory and package therootfsinto a tar ball.root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~# cd /var/lib/lxc/pathchecker/rootfs/ root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:/var/lib/lxc/pathchecker/rootfs/# tar -czvf /vagrant/pathchecker_rootfs.tar.gz * tar: dev/log: socket ignored root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:/var/lib/lxc/pathchecker/rootfs/# exit vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ exit logout Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed. AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ pwd /Users/akshshar/pathchecker/vagrant AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ ls -l pathchecker_rootfs.tar.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 akshshar staff 301262995 Jul 18 07:57 pathchecker_rootfs.tar.gz AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$
-
-
Launch the two router topology.
-
Navigate to the
pathchecker/vagrantdirectory and launch the vagrant instance.AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ pwd /Users/akshshar/pathchecker/vagrant AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant up Bringing machine 'rtr1' up with 'virtualbox' provider... Bringing machine 'devbox' up with 'virtualbox' provider... Bringing machine 'rtr2' up with 'virtualbox' provider... -
Verify if the topology has been launched.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant status Current machine states: rtr1 running (virtualbox) devbox running (virtualbox) rtr2 running (virtualbox) This environment represents multiple VMs. The VMs are all listed above with their current state. For more information about a specific VM, run `vagrant status NAME`.
-
-
Verify if OSPF is running on rtr1 and check the path state.
You can also see the cost of the OSPF path.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant port rtr1 The forwarded ports for the machine are listed below. Please note that these values may differ from values configured in the Vagrantfile if the provider supports automatic port collision detection and resolution. 22 (guest) => 2223 (host) 57722 (guest) => 2200 (host) 58822 (guest) => 58822 (host) AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ ssh -p 2223 vagrant@localhost The authenticity of host '[localhost]:2223 ([127.0.0.1]:2223)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is b1:c1:5e:a5:7e:e7:c0:4f:32:ef:85:f9:3d:27:36:0f. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '[localhost]:2223' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. vagrant@localhost's password: RP/0/RP0/CPU0:rtr1# show running-config router ospf Mon Jul 18 15:25:53.875 UTC router ospf apphost area 0 interface Loopback0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 cost 20 ! ! ! RP/0/RP0/CPU0:rtr1# show route 2.2.2.2 Mon Jul 18 15:26:03.576 UTC Routing entry for 2.2.2.2/32 Known via "ospf apphost", distance 110, metric 2, type intra area Installed Jul 18 15:18:28.218 for 00:07:35 Routing Descriptor Blocks 10.1.1.20, from 2.2.2.2, via GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 Route metric is 2 No advertising protos. RP/0/RP0/CPU0:rtr1# -
Start the iPerf server on
rtr2and configure it for receiving packets fromrtr1.
Note
iPerf was launched as a native application on
rtr2while launching the vagrant instance.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant ssh rtr2 Last login: Mon Jul 18 15:57:05 2016 from 10.0.2.2 xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$ xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$ iperf -s -u ------------------------------------------------------------ Server listening on UDP port 5001 Receiving 1470 byte datagrams UDP buffer size: 64.0 MByte (default) -
Launch the pathchecker application within the LXC on
rtr1.-
Log in to the LXC on
rtr1.Password for user
ubuntuis ubuntu.AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ ssh -p 58822 ubuntu@localhost The authenticity of host '[localhost]:58822 ([127.0.0.1]:58822)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 19:54:83:a9:7a:9f:0a:18:62:d1:f3:91:87:3c:e9:0b. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '[localhost]:58822' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. ubuntu@localhost's password: Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.14.23-WR7.0.0.2_standard x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/ Last login: Mon Jul 18 15:19:45 2016 from 10.0.2.2 ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ -
Navigate to the pathchecker repository within the LXC, and check the contents of the pathchecker script.
ubuntu@pathchecker:~$ cd pathchecker/ ubuntu@pathchecker:~/pathchecker$ cat pc_run.sh #!/bin/bash ./pathchecker.py --host 6.6.6.6 -u vagrant -p vagrant --port 830 -c 10 -o apphost -a 0 -i GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 -s 2.2.2.2 -j 4 -l 5 -f -t 10-Irepresents the threshold for packet loss and has been set to 5% for this run.-jrepresents the jitter threshold that has a value of 4. -
Start the pathchecker application by running the script.
ubuntu@pathchecker:~/pathchecker$ ./pc_run.sh Error while opening state file, let's assume low cost state Currently, on reference link GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 Starting an iperf run..... 20160718162513,1.1.1.1,62786,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1311240,1048992 20160718162513,1.1.1.1,62786,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1312710,1048474 20160718162513,2.2.2.2,5001,1.1.1.1,62786,6,0.0-10.0,1312710,1048679,2.453,0,892,0.000,1 bw is 1025.5546875 jitter is 2.453 pkt_loss is 0.000 verdict is False Currently, on reference link GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 Starting an iperf run.....The pathchecker application is running on the path from
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0interface.
-
-
Open a parallel Git bash window and simulate impairment on the active path.
-
Access
devboxthrough SSH.AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ cd pathchecker/vagrant AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ vagrant ssh devbox Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-87-generic x86_64) ... -
View the impairment script and run it on
devbox.vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ ls impair_backup.sh impair_reference.sh stop_impair.sh vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ cat impair_reference.sh #!/bin/bash echo "Stopping all current impairments" sudo tc qdisc del dev eth3 root &> /dev/null sudo tc qdisc del dev eth4 root &> /dev/null echo "Starting packet loss on reference link" sudo tc qdisc add dev eth3 root netem loss 7% vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ ./impair_reference.sh Stopping all current impairments Starting packet loss on reference linkThe script creates a packet loss of 7% on the reference link.
-
-
Open the first Git bash window to view the pathchecker application running on
rtr1.Currently, on reference link GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 Starting an iperf run..... 20160718164745,1.1.1.1,60318,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1311240,1048992 20160718164745,1.1.1.1,60318,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1312710,1048516 20160718164745,2.2.2.2,5001,1.1.1.1,60318,6,0.0-573.0,1312710,18328,5.215,0,892,0.000,1 bw is 1025.5546875 jitter is 5.215 pkt_loss is 0.000 verdict is True Woah! iperf run reported discrepancy, increase cost of reference link ! Increasing cost of the reference link GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 Currently, on backup link Starting an iperf run..... 20160718164755,1.1.1.1,61649,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1311240,1048992 20160718164755,1.1.1.1,61649,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1312710,1048577 20160718164755,2.2.2.2,5001,1.1.1.1,61649,6,0.0-583.3,1312710,18002,1.627,0,893,0.000,0 bw is 1025.5546875 jitter is 1.627 pkt_loss is 0.000 verdict is False Currently, on backup link Starting an iperf run..... 20160718164805,1.1.1.1,59343,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1311240,1048992 20160718164805,1.1.1.1,59343,2.2.2.2,5001,6,0.0-10.0,1312710,1048520 20160718164805,2.2.2.2,5001,1.1.1.1,59343,6,0.0-593.4,1312710,17697,2.038,0,893,0.000,0Pathchecker has initiated a failover from primary to secondary link.
-
Verify if the failover was successful on
rtr1.AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant akshshar$ ssh -p 2223 vagrant@localhost vagrant@localhost's password: RP/0/RP0/CPU0:rtr1# show running-config router ospf Mon Jul 18 17:50:47.851 UTC router ospf apphost area 0 interface Loopback0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 cost 30 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 cost 20 ! ! !The path cost from the GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 interface is greater than that from the GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 interface. Hence, failover takes place to the GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 interface for traffic from
rt1tortr2. -
Verify the OSPF path failover on rtr1.
The Loopback 0 interface IP address of
rtr1in this example is 2.2.2.2RP/0/RP0/CPU0:rtr1# show route 2.2.2.2 Mon Jul 18 18:01:49.297 UTC Routing entry for 2.2.2.2/32 Known via "ospf apphost", distance 110, metric 21, type intra area Installed Jul 18 16:47:45.705 for 01:14:03 Routing Descriptor Blocks 11.1.1.20, from 2.2.2.2, via GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 Route metric is 21 No advertising protos. RP/0/RP0/CPU0:rtr1#The next hop for
rtr1is 11.1.1.20 through the backup reference link: GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
You have successfully configured OSPF path failover by using iPerf and Netconf on vagrant.
Using Solenoid with exaBGP on Vagrant
Solenoid is an application that can be used to bridge route updates between an exaBGP application instance and the RIB table on Cisco IOS XR. This section explains how you can install and use the Solenoid application with the exaBGP application for route filtering on vagrant.
Topology
The following topology is used to demonstrate the hosting of Solenoid and exaBGP applications on XR.
Two instances of Ubuntu on Vagrant are used in this topology. The vagrant instance on the right is the devbox that uses exaBGP to generate BGP route updates. The route updates are sent to the vagrant instance (on the left) running a light version of the Cisco IOS XR router image.
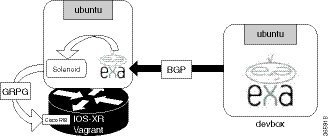
The following workflow is used for BGP route filtering by Solenoid:
-
Solenoid receives the route updates from exaBGP.
-
Solenoid filters the required routes to create Cisco YANG data models for static routes.
-
Solenoid uses gRPC to send the data models to the RIB table on XR.
Procedure
Use the following steps to host and use Solenoid and exaBGP applications for BGP route filtering.
-
Generate an API key and a CCO ID by using the steps described on Github.
-
Download the latest stable version of the IOS-XRv vagrant box.
$ curl <cco-id>:<API-KEY> $ BOXURL --output ~/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box $ vagrant box add --name IOS-XRv ~/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box -
Verify if the vagrant box has been successfully installed.
lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/X/S/vagrant> vagrant box list IOS XRv (virtualbox, 0) -
Create a working directory.
LISROACH-M-J0AY:~ lisroach$ mkdir ~/iosxrv LISROACH-M-J0AY:~ lisroach$cd ~/iosxrv -
Initialize the vagrant file with the new vagrant box.
LISROACH-M-J0AY:~ lisroach$ vagrant init IOS-XRv A `Vagrantfile` has been placed in this directory. You are now ready to `vagrant up` your first virtual environment! Please read the comments in the Vagrantfile as well as documentation on `vagrantup.com` for more information on using Vagrant. -
Clone the repository containing the Solenoid application source code.
lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/Workspace> git clone https://github.com/ios-xr/Solenoid.git Cloning into 'Solenoid'... remote: Counting objects: 1539, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (623/623), done. remote: Total 1539 (delta 884), reused 1508 (delta 866), pack-reused 0 Receiving objects: 100% (1539/1539), 713.76 KiB | 317.00 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (884/884), done. Checking connectivity... done. lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/Workspace> -
Launch the vagrant instance running devbox.
lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/Workspace> cd Solenoid/vagrant lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> vagrant up devbox -
Verify if the exaBGP application is running successfully on devbox.
-
Launch the exaBGP screen.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo screen -ls There is a screen on: 1762.exabgp (09/27/2016 10:43:34 PM) (Detached) 1 Socket in /var/run/screen/S-root. vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo screen -r exabgp Tue, 27 Sep 2016 23:43:25 | INFO | 1764 | processes | Command from process add-routes : announce route 2.2.2.0/24 next-hop self Tue, 27 Sep 2016 23:43:25 | INFO | 1764 | reactor | Route added to neighbor 11.1.1.10 local-ip 11.1.1.20 local-as 65000 peer-as 65000 router-id 11.1.1.20 family-allowed in-open : 2.2.2.0/24 next-hop 11.1.1.20 -
Detach from the exaBGP screen without killing the processes or destroying the screen by pressing CTRL+a,d.
-
Verify if the screen has been successfully detached.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo screen -r exabgp [detached from 1762.exabgp]
-
-
Create the LXC (container) to host the Solenoid application.
-
Access devbox through SSH.
lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> vagrant ssh devbox Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-92-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/ ... -
Install the LXC tools for creating the LXC for Solenoid.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo apt-get update vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo apt -y install lxc -
Create the Solenoid LXC.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo lxc-create -t ubuntu --name solenoid -
Launch the Solenoid LXC.
The password for user ubuntu is ubuntu.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo lxc-start --name solenoid solenoid login: init: setvtrgb main process (428) terminated with status 1 init: plymouth-upstart-bridge main process ended, respawning ubuntu Password:
-
-
Install the exaBGP application dependencies inside the LXC.
ubuntu@solenoid:~$ sudo apt-get -y install git curl screen python-dev python-setuptools [sudo] password for ubuntu: ubuntu ubuntu@solenoid:~$ sudo easy_install pip ubuntu@solenoid:~$ sudo pip install virtualenv exabgp -
Install the Solenoid application code dependencies inside the LXC.
-
Clone the Solenoid application code from github.
ubuntu@solenoid:~$ git clone https://github.com/ios-xr/Solenoid.git -
Activate the virtual environment inside the Solenoid directory.
ubuntu@solenoid:~$ cd Solenoid ubuntu@solenoid:~$ virtualenv venv ubuntu@solenoid:~$ source venv/bin/activate
Note
You cannot activate Solenoid without activating the virtual environment.
-
Install the Solenoid application code dependencies in the virtual environment.
(venv) ubuntu@solenoid:~$ pip install grpcio (venv) ubuntu@solenoid:~$ python setup.py install
-
-
Create the configuration file for Solenoid,
solenoid.config, in the Solenoid directory with the following contents.[default] # Name you choose for the node transport: gRPC # Either gRPC or RESTconf ip: 11.1.1.10 # IP address of the destination RIB table (the XR device you intend to control) port: 57777 # Depends on what is configured for your gRPC or RESTconf servers username: vagrant # Username for the XR device password: vagrant # Password for the XR device -
Create the configuration file for exaBGP,
router.ini, in your home directory with the following contents.group demo { router-id 11.1.1.10; process monitor-neighbors { encoder json; receive { parsed; updates; neighbor-changes; } run /usr/bin/env python /home/ubuntu/Solenoid/solenoid/edit_rib.py -f '/home/ubuntu/Solenoid/filter.txt'; } neighbor 11.1.1.20 { local-address 11.1.1.10; local-as 65000; peer-as 65000; } } -
Change the SSH port inside the LXC.
(venv) ubuntu@solenoid:~$ sudo sed -i s/Port\ 22/Port\ 58822/ /etc/ssh/sshd_config (venv) ubuntu@solenoid:~$ cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep Port Port 58822 -
Shut down the LXC.
(venv) ubuntu@solenoid:~$ sudo shutdown -h now (venv) ubuntu@solenoid:~$ Broadcast message from ubuntu@solenoid (/dev/lxc/console) at 23:00 ... The system is going down for halt NOW! ... -
Package the LXC tar ball as the root user.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ sudo -s root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~# cd /var/lib/lxc/solenoid/rootfs/ root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~# tar -czvf /vagrant/solenoid.tgz * root@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~# exit exit vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ exit logout Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed. lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> pwd /Users/lisroach/Workspace/Solenoid/vagrant lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> ls -la solenoid.tgz -rw-r--r-- 1 lisroach staff 252417007 Aug 2 11:27 solenoid.tgz -
Launch the topology by launching the vagrant instance in the
Solenoid/vagrant/directory.lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> pwd /Users/lisroach/Workspace/Solenoid/vagrant lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> vagrant up Bringing machine 'xrv' up with 'virtualbox' provider... Bringing machine 'devbox' up with 'virtualbox' provider... ... ==> xrv: Importing base box 'IOS XRv'... ==> xrv: Machine 'xrv' has a post `vagrant up` message. This is a message ==> xrv: from the creator of the Vagrantfile, and not from Vagrant itself: ==> xrv: ==> xrv: ==> xrv: Welcome to the IOS XRv (64-bit) VirtualBox. lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> vagrant status Current machine states: xrv running (virtualbox) devbox running (virtualbox) This environment represents multiple VMs. The VMs are all listed above with their current state. For more information about a specific VM, run `vagrant status NAME`. -
Launch the solenoid GUI on your host machine by entering
localhost:57780in your web browser.Figure 3. Solenoid GUI on Host Machine 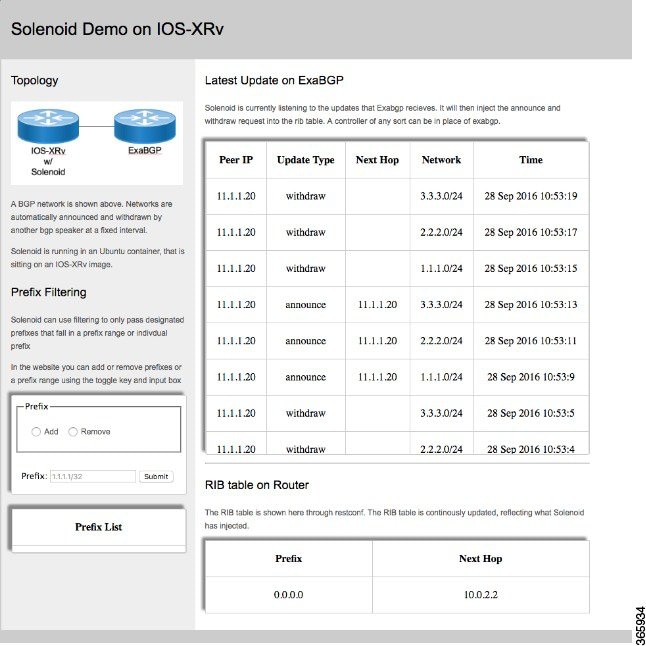
The GUI displays the IOS XR RIB table. You can see the exaBGP routes that were added and withdrawn by Solenoid.
You can enable filtering of prefixes, by adding the prefixes to the filtering file as shown. The file acts as an allowed list by allowing the entered prefixes and dropping all other prefixes.
Figure 4. Prefix Filter Creation on Solenoid GUI 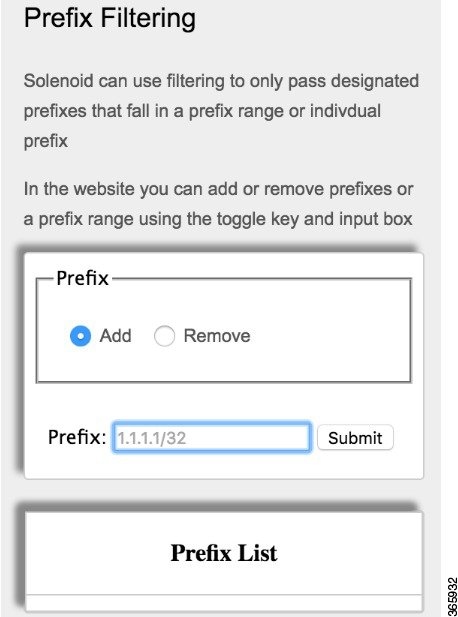
For the sake of illustration, we add the prefix range: 1.1.1.0/24 to 2.2.2.0/24 to the allowed list filter. Because of this configuration, the 3.3.3.0/24 prefix gets filtered out and is not added to the RIB table, as shown.
Figure 5. Prefix Filtering on Solenoid GUI 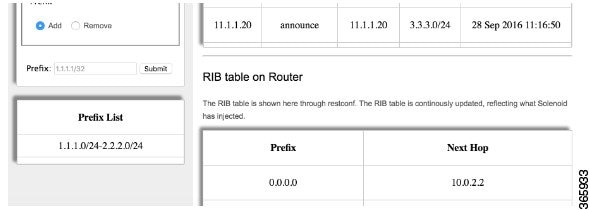
-
Verify the RIB table on XR.
lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> vagrant port xrv The forwarded ports for the machine are listed below. Please note that these values may differ from values configured in the Vagrantfile if the provider supports automatic port collision detection and resolution. 22 (guest) => 2223 (host) 57722 (guest) => 2222 (host) 57780 (guest) => 57780 (host) 58822 (guest) => 58822 (host) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- (venv) lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> ssh -p 2223 vagrant@localhost vagrant@localhost's password: RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# show ip route Wed Sep 28 18:33:18.266 UTC Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, (>) - Diversion path D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - ISIS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, su - IS-IS summary null, * - candidate default U - per-user static route, o - ODR, L - local, G - DAGR, l - LISP A - access/subscriber, a - Application route M - mobile route, r - RPL, (!) - FRR Backup path Gateway of last resort is 10.0.2.2 to network 0.0.0.0 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.2, 01:01:34 C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, 01:03:27, MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 L 10.0.2.15/32 is directly connected, 01:03:27, MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 L 10.1.1.5/32 is directly connected, 01:01:34, Loopback1 C 11.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, 01:01:34, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 L 11.1.1.10/32 is directly connected, 01:01:34, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#Notice that the default route of 0.0.0.0 is the only static route in the RIB table, prior to running the Solenoid application on XR.
-
Open a second Git bash window in parallel and access the Solenoid LXC.
lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> vagrant port xrv The forwarded ports for the machine are listed below. Please note that these values may differ from values configured in the Vagrantfile if the provider supports automatic port collision detection and resolution. 22 (guest) => 2223 (host) 57722 (guest) => 2222 (host) 57780 (guest) => 57780 (host) 58822 (guest) => 58822 (host) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- lisroach@LISROACH-M-J0AY ~/W/S/vagrant> ssh -p 58822 ubuntu@localhost The authenticity of host '[localhost]:58822 ([127.0.0.1]:58822)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Swie3V2VIYDNCACaRLbSjQa7417yIM6hpbeimNwZr1o. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '[localhost]:58822' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. ubuntu@localhost's password: Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.5 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.14.23-WR7.0.0.2_standard x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/ Last login: Thu Sep 22 21:31:13 2016 ubuntu@solenoid:~$ -
Launch the exaBGP screen to verify that Solenoid is in operation.
ubuntu@solenoid:~$ screen -ls There are screens on: 1423.website (09/28/2016 05:38:22 PM) (Detached) 1421.exabgp (09/28/2016 05:38:22 PM) (Detached) 2 Sockets in /var/run/screen/S-ubuntu. ubuntu@solenoid:~$ ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- ubuntu@solenoid:~$ screen -r exabgp Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:04 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:06 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:11 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | ANNOUNCE | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:13 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | ANNOUNCE | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:17 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:19 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:25 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | ANNOUNCE | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:27 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | ANNOUNCE | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:37 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:37 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:38 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | ANNOUNCE | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:40 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | ANNOUNCE | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:44 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OK Wed, 28 Sep 2016 18:35:46 | INFO | 1436 | solenoid | WITHDRAW | OKThe OK messages verify that the Solenoid application is running as desired.
-
Open the first Gitbash window, and view the RIB table on XR with Solenoid in operation.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#show ip route Wed Sep 28 18:49:22.165 UTC Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, (>) - Diversion path D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - ISIS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, su - IS-IS summary null, * - candidate default U - per-user static route, o - ODR, L - local, G - DAGR, l - LISP A - access/subscriber, a - Application route M - mobile route, r - RPL, (!) - FRR Backup path Gateway of last resort is 10.0.2.2 to network 0.0.0.0 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.2, 01:17:38 S 1.1.1.0/24 [1/0] via 11.1.1.20, 00:00:00 C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, 01:19:31, MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 L 10.0.2.15/32 is directly connected, 01:19:31, MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 L 10.1.1.5/32 is directly connected, 01:17:38, Loopback1 C 11.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, 01:17:38, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 L 11.1.1.10/32 is directly connected, 01:17:38, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#show ip route Wed Sep 28 18:49:25.660 UTC Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, (>) - Diversion path D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - ISIS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, su - IS-IS summary null, * - candidate default U - per-user static route, o - ODR, L - local, G - DAGR, l - LISP A - access/subscriber, a - Application route M - mobile route, r - RPL, (!) - FRR Backup path Gateway of last resort is 10.0.2.2 to network 0.0.0.0 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.2, 01:17:42 S 1.1.1.0/24 [1/0] via 11.1.1.20, 00:00:03 S 2.2.2.0/24 [1/0] via 11.1.1.20, 00:00:01 C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, 01:19:35, MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 L 10.0.2.15/32 is directly connected, 01:19:35, MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 L 10.1.1.5/32 is directly connected, 01:17:42, Loopback1 C 11.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, 01:17:42, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 L 11.1.1.10/32 is directly connected, 01:17:42, GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#The RIB table clearly shows that because we added the 1.1.1.0/24 and 2.2.2.0/24 prefixes to the Solenoid GUI, these prefixes are added to the RIB table on XR when Solenoid is launched on XR (through exaBGP screen).
This verifies the successful hosting and operation of Solenoid application on XR for filtering BGP routes, by using exaBGP and the Solenoid GUI on vagrant.
 Feedback
Feedback