Table 3. Feature History Table
|
Feature Name
|
Release Information
|
Description
|
|
Enhanced Golden ISO Build Tool
|
Release 7.5.1
|
This enhancement provides you with the flexibility to use the gisobuild.py tool to build GISO images using Cisco IOS XR software commands, YAML-based template file, or docker capability to suit your
customized install requirements. When you build a GISO, you can also specify Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) initialization
file, script initialization file, Cisco IOS XR configuration file, and SMUs in addition to using the base image and optional
RPMs to automatically provision the router.
|
To build GISO, provide the following input parameters to the script:
-
Base mini-x.iso (mandatory)
-
XR configuration file (optional)
-
one or more Cisco-specific SMUs for host, XR and System admin (optional)
-
one or more third-party SMUs for host, XR and System admin (optional)
-
Label for golden ISO (optional)
-
Optional RPMs
-
ZTP initialization ztp.ini file (optional)
-
Script initialization script.ini file (optional)
The GISO script does not support verification of XR configuration.

Note
|
To
successfully add k9sec RPM to GISO, change the permission of the file to
644 using the
chmod
command.
chmod 644 [k9 sec rpm]
|
Cisco IOS XR, Release 7.5.1 introduces enhancements to the gisobuild.py GISO build tool. You can also add a ztp.ini ZTP initialization and script.ini Script initialization file. The ZTP configuration is applied on the router when the current software version is replaced
or rolled back to a version with GISO image, and is used whenever ZTP is run to automatically provision the router. The tool
supports more than one repository. You can use CLI command, docker, or a YAML file to build GISO.

Note
|
-
For Cisco NCS 5500 and Cisco NCS 5000 series routers, set the migration value to false.
-
Set the clean option to true if you use the same build directory after the first GISO is created. Ensure that you set the option to true for every successive GISO build.
-
Set the docker option to true if you are building GISO using docker.
-
Ensure that the format and syntax of the YAML file is intact to avoid errors when building a GISO. For example, if the : symbol is missing, or if an unsupported symbol is used in the template, the GISO build displays errors.
|
The gisobuild.py tool can be run either natively or on systems where docker service is enabled and has the ability to pull published docker
images. Prefer building the image using the docker as it does not require additional privileges:.

Note
|
The full-iso option is used to build a full ISO image xrv9k-full-x-7.5.1.iso specific to Cisco IOS XRv 9000 routers. Starting Cisco IOS XR, Release 7.8.1, the full ISO image must not be used to build
GISO.
|
To build GISO,
perform the following steps:
Example: Build Docker-Based GISO Image
In this example, a GISO image is built using docker.
View that the GISO file is created succesfully.[root@xr src]# ls
exrmod gisobuild.py lntmod output_gisobuild utils
[root@xr src]# cd output_gisobuild/
[root@xr output_gisobuild]# ls
img_built_name.txt logs -golden-x-7.5.1-dockerbasedgiso.iso
rpms_packaged_in_giso.txt
Example: Build YAML-Based GISO Image
YAML is a markup file that serves as a template to provide the package list and manage the build options.
The following example shows a sample YAML template:# Options below correspond to the tool input options.
# --iso ISO Path to Mini.iso/golden.iso file
# --repo REPO [REPO ...]
# Path to list of RPM repositories. RPMs are only used if already
# included in the ISO, or specified by the user via the --pkglist option.
# --pkglist PKGLIST [PKGLIST ...]
# Optional list of rpm or smu to add to the ISO.
# --remove-packages REMOVE_PACKAGES [REMOVE_PACKAGES ...]
# Remove named RPMs, specified in a space separated list. Valid build
# option for LNT only. eXR builds simply ignores this option.
# --bridging-fixes BRIDGE_FIXES [BRIDGE_FIXES ...]
# Bridging rpms to package. Takes from-release (supported for eXR)
# or rpm names.
# --xrconfig XRCONFIG Path to XR config file
# --ztp-ini ZTP_INI Path to user ztp ini file
# --script SCRIPT Path to user executable script executed as part of
# bootup post activate. Valid build option for eXR only.
# LNT builds simply ignores.
# --label LABEL Golden ISO Label
# --out-directory OUT_DIRECTORY
# Output Directory. Built GISO and logs will be available post gisobuild.
# --copy-directory COPY_DIRECTORY
# Copy built artefacts to specified directory if provided. Valid build
# option for LNT only. eXR build ignores this option.
# --yamlfile CLI_YAML Cli arguments via yaml.
# --clean Delete output dir before proceeding.
# --migration To build Migration tar only for ASR9k. Valid build option for eXR only.
# LNT builds simply ignore this option.
# --docker Load and run pre-built docker image. Valid build option for eXR only.
# LNT builds simply ignore this option.
# --x86-only Use only x86_64 rpms even if other architectures are applicable. Valid build
# option for eXR only. LNT builds simply ignore this option.
# --version Print version of this script and exit
packages:
iso: <path-to-iso>
repo:
- <path-to-repo1>
- <path-to-repo2>
pkglist:
- <pkg1>
- <pkg2>
bridge-fixes:
upgrade-from-release:
- <dotted-release-1>
- <dotted-release-2>
rpms:
- <pkg1>
- <pkg2>
remove_packages:
- <pkg1>
- <pkg2>
user-content:
script: <path-to-script-sh>
xrconfig: <path-to-router.cfg>
ztp-ini: <path-to-ztp.ini>
output:
label: <giso-label>
out-directory: <path-to-output-directory>
clean: <true/false>
options:
docker: <true/false>
migration: <true/false>
x86-only: <true/false>
In this example, you configure a YAML file with the required files:
If you do not want to specify the list of packages and parameters via CLI, you can use the YAML file template. [directory-path]$ ./src/gisobuild.py --yamlfile <input-yaml-cfg>
To override any input in the YAML configuration file, use the corresponding CLI options.[directory-path]$ ./src/gisobuild.py --yamlfile <input-yaml-cfg> --label <new-label>
This new label overrides the label specified in the YAML file.
When the host machine does not have its package dependencies met, but allows pulling and running docker images, enable the
docker option in YAML file to true and run the command:[directory-path]$ ./src/gisobuild.py --yamlfile <input-yaml-cfg>
where, the input-yaml-cfg has the docker option set to true.
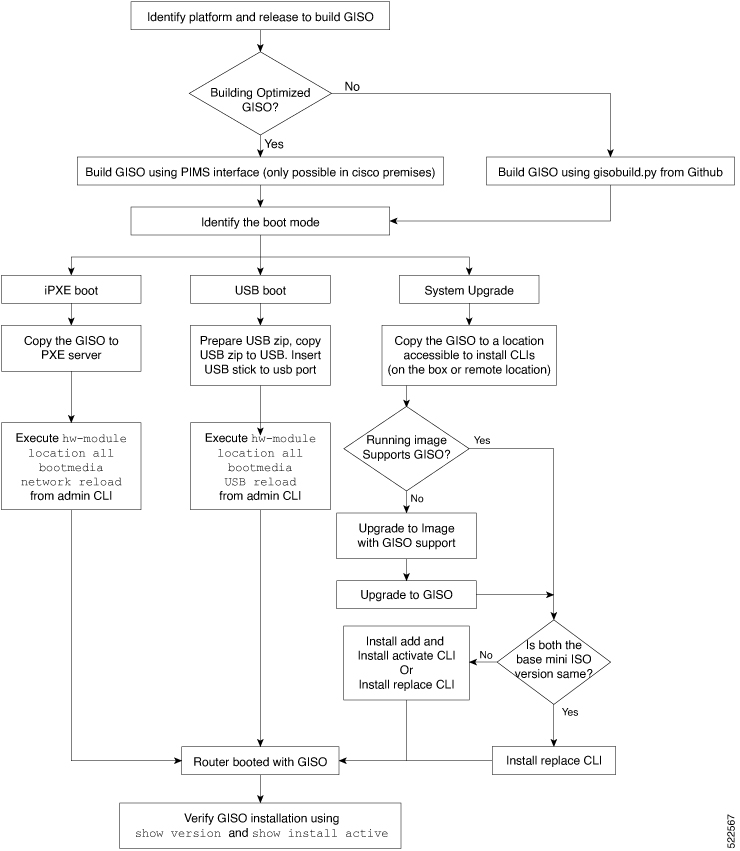
Install the GISO image on the router.

 Feedback
Feedback