WAN and Application Optimization Overview
This chapter presents the Cisco WAN and application optimization framework, provides an overview of the solution, and introduces Cisco WAN and application optimization products and technologies. It also briefly discusses the solution deployed in different places in the network.
3.1 The Cisco Vision
In modern enterprises, the network is an essential component of application performance. Cisco Systems empowers network managers to deploy critical business applications on integrated networks to increase productivity and gain competitive advantages. Cisco delivers advanced, integrated WAN and application optimization solutions to support a broad set of applications with different requirements, from IP communications to transaction-oriented applications. Cisco continues to add optimization techniques and delivers the "network as the platform."
Security directly affects network and application performance. A complete, holistic solution delivers more than comprehensive WAN and application optimization capabilities, but also cooperates with security components to protect business against disruption. Cisco offers a network-based, end-to-end systems approach that evolves with business needs and enables the opportunities generated from future technical innovations.
Figure 3-1 WAN and Application Optimization in the Network

Cisco WAN and application optimization is an architectural solution consisting of a set of tools and techniques working together to improve the reliability, performance, and delivery of applications securely across your network. A strategic systems approach uses the network to identify applications running in the network, gains end-to-end visibility, optimizes the network and applications, and controls and protects business critical traffic.
The Cisco WAN and application optimization solution comprises five critical components for effective application delivery. The following sections are brief descriptions of the five architectural components and the associated techniques and technologies. Subsequent chapters provide more details of each of the components.
3.1.1 Classification
An intelligent network must evolve to become an active participant in application delivery. The network must be application-aware to assess and control application performance to ensure that valuable shared network resources are used efficiently. Prior to controlling traffic, the network needs to learn the requirements of and automatically discover applications running on the network. Techniques must go beyond simple IP address or TCP port recognition by supporting dynamic and migration port assignments using deep packet inspection technologies.
3.1.2 Optimization
Several techniques, when applied to network traffic, dramatically improve application performance and availability/reliability, decrease latency, improve bandwidth utilization, and bolster security:
•![]() TCP Flow Optimization (TFO) - Improves the TCP stack and brings uniformity to TCP sessions. Mitigates the inherent lack of performance in TCP slow start and general flow control, which can slow data transfers. TFO techniques fill the pipe and reduce latency, resulting in faster transfers and optimal bandwidth use.
TCP Flow Optimization (TFO) - Improves the TCP stack and brings uniformity to TCP sessions. Mitigates the inherent lack of performance in TCP slow start and general flow control, which can slow data transfers. TFO techniques fill the pipe and reduce latency, resulting in faster transfers and optimal bandwidth use.
•![]() Advanced Compression - Data redundancy elimination (DRE) replaces matching byte streams with a signature to significantly reduce the amount of data sent over the WAN. Signatures are maintained in libraries on opposite sides of the peering devices and enable up to 100:1 compression ratios. Standard (LZ) compression further compresses nonredundant data for maximum compression.
Advanced Compression - Data redundancy elimination (DRE) replaces matching byte streams with a signature to significantly reduce the amount of data sent over the WAN. Signatures are maintained in libraries on opposite sides of the peering devices and enable up to 100:1 compression ratios. Standard (LZ) compression further compresses nonredundant data for maximum compression.
•![]() Path Optimization - Each networked application is matched to the best path, ensuring application availability.
Path Optimization - Each networked application is matched to the best path, ensuring application availability.
•![]() Server Optimization - Reduces server workloads using techniques such as server load balancing (SLB), connection management, and offloading Secure Socket Layer (SSL).
Server Optimization - Reduces server workloads using techniques such as server load balancing (SLB), connection management, and offloading Secure Socket Layer (SSL).
•![]() Secure WAN - Firewalls, SSL encryption, and techniques that minimize denial-of-service and other threats protect applications and critical business information assets.
Secure WAN - Firewalls, SSL encryption, and techniques that minimize denial-of-service and other threats protect applications and critical business information assets.
•![]() Secure VPN - Technologies promote low-latency paths by enabling direct spoke-to-spoke communications.
Secure VPN - Technologies promote low-latency paths by enabling direct spoke-to-spoke communications.
•![]() DNS Optimization - Accelerating DNS lookups helps to ensure speedy application delivery.
DNS Optimization - Accelerating DNS lookups helps to ensure speedy application delivery.
•![]() Enterprise Content Delivery Network (ECDN) - Improves the performance and reliability of content and application delivery across the WAN. ECDN typically comprises caching, policy-based distribution, redirection, and content management. Together, these components enable enterprises to efficiently distribute content to its remote branch offices.
Enterprise Content Delivery Network (ECDN) - Improves the performance and reliability of content and application delivery across the WAN. ECDN typically comprises caching, policy-based distribution, redirection, and content management. Together, these components enable enterprises to efficiently distribute content to its remote branch offices.
3.1.3 Control
Quality of service (QoS) techniques ensure that business-critical traffic is not negatively affected by less important traffic, and that controls conform with established business policies and priorities.
3.1.4 Monitoring
Successful application delivery requires IT organizations to continuously identify applications on the network, ensuring acceptable business-critical application performance while controlling or eliminating non-critical applications.
Controlling performance requires visibility into network and application behavior. Not only does monitoring verify that policies are correctly implemented, but data acquired through monitoring can drive the generation and enforcement of new dynamic policies.
3.1.5 Network Management
Management tools gather network application- and network-performance information, which is integrated into a series of comprehensive reports to provide visibility into the network and applications. Configuration management tools also centrally define policies and perform system-based change and configuration management.
3.2 Solution Components
Cisco WAN and application optimization provides a comprehensive solution comprising several products and technologies. This section lists the Cisco products and technologies that implement the five architectural components described in the preceding sections. These architectural components are implemented in dedicated appliances and blades, and in network router features.
3.2.1 Classification
•![]() IOS Network Based Application Recognition (NBAR)
IOS Network Based Application Recognition (NBAR)
3.2.2 Optimization
•![]() Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) or Wide Area Application Engine (WAE)
Cisco Wide Area Application Services (WAAS) or Wide Area Application Engine (WAE)
•![]() IOS Performance Routing (PfR)
IOS Performance Routing (PfR)
•![]() Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE)
Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE)
•![]() IOS Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network (DMVPN)
IOS Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network (DMVPN)
3.2.3 Control
•![]() IOS QoS
IOS QoS
3.2.4 Monitoring
•![]() IOS NetFlow
IOS NetFlow
•![]() IOS IP Service Level Agreement (SLA)
IOS IP Service Level Agreement (SLA)
•![]() Cisco WAAS Flow Agent
Cisco WAAS Flow Agent
3.2.5 Network Management
•![]() Cisco Network Analysis Module-2 (NAM-2) for Cisco Catalyst 6000 Series
Cisco Network Analysis Module-2 (NAM-2) for Cisco Catalyst 6000 Series
•![]() NetQoS SuperAgent
NetQoS SuperAgent
•![]() NetQoS ReporterAnalyzer
NetQoS ReporterAnalyzer
3.3 Deploying WAN and Application Optimization
WAN and application optimization solutions are primarily deployed in the data center and branch. As the Cisco WAN and application optimization solution evolves, it will touch more places in the network.
A "network as a platform" approach uses the network to identify applications on the network, gains end-to-end visibility, optimizes applications, and controls and protects business-critical traffic.
Figure 3-2 End-to-End WAN and Application Optimization
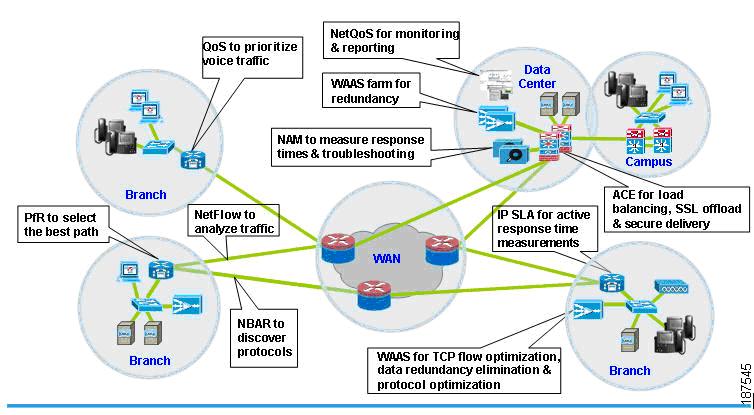
As discussed in the preceding sections, WAN and application optimization is not a single technique. It is a collection of techniques and tools working cooperatively to improve application performance. For example, in Figure 3-2 various techniques and tools are enabled in different places in the network.
Inside the branch, NetFlow and NBAR are enabled in the branch access router to provide extensive visibility into the network and applications. With visibility into the applications and their utilization, IT operations can apply QoS policies in the branch router to establish transmission priorities of the application mix. A WAAS appliance can be deployed to apply a suite of WAN optimization and application acceleration technologies to dramatically improve application performance. When the branch has dual links, performance can be further enhanced by selecting the optimal path by using PfR.
Inside the data center, ACE is deployed to improve application performance, from SSL acceleration to load balancers. For example, ACE can make intelligently decide which server can send requests to yield further performance improvement. SSL acceleration is also enabled to handle the processing required to decrypt or encrypt traffic in order to offload the server.
In addition, performance management tools are deployed to support and protect business goals and objectives on an ongoing basis. NAM is deployed in the data center to measure application response times and troubleshooting. NetQoS Performance Center is used for centralized monitoring and reporting.
 Feedback
Feedback