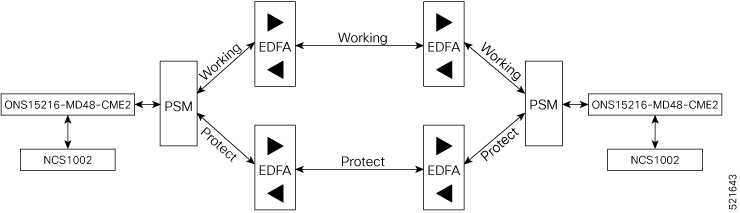
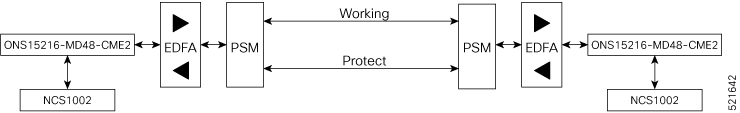
Optical Amplifier Module
The optical amplifier module (NCS1K-EDFA) has pre-amplifier and booster amplifier.
The optical amplifier module provides the following functionality.
-
Preamplifier (LINE-RX to COM-TX) - Single preamplifier variant, with switchable gain ranges, according to link loss:
-
Range # 1: 0 to 24 dB gain, Tilt control: 24 to 27 gain, with tilt uncontrolled
-
Range # 2: 20 to 34 dB gain, Tilt control: 34 to 37 dB gain, with tilt uncontrolled
-
23dBm output power @ COM-TX port
-
-
Booster amplifier (COM-RX to LINE-TX) - True variable gain booster amplifier
-
Gain range: 1 to 20. 20 to 25 uncontrolled tilt.
-
23dBm output power @ LINE-TX port
-
-
ADD/DROP OSC channel supports both 1510nm and 1610nm +/-10nm
-
OCM assesses channel presence and Gain regulation and per channel power monitoring.
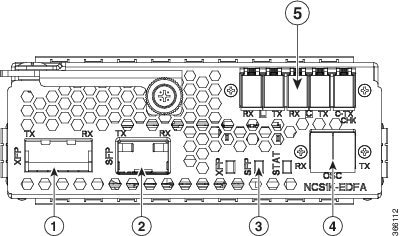
|
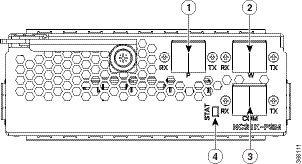
1 |
XFP for OSC and additional OTDR feature |
|
2 |
SFP for OSC (Optical Service Channel) |
|
3 |
Status LED |
|
4 |
Service Channel input and output port [OSC - RX, TX] |
|
5 |
PRE and BST amplifier inputs and output ports [L (LINE) - RX, TX] [C (COM) - RX, TX] [COM - TX CHECK] |
The following table describes the mapping of controllers and optical ports for the optical amplifier module.
|
Controller |
Optical Ports |
|---|---|
|
Ots 0/slot/0/0 |
|
|
Ots 0/slot/0/1 |
|
|
Ots 0/slot/0/2 |
|
|
Ots 0/slot/0/3 |
COM-CHECK |

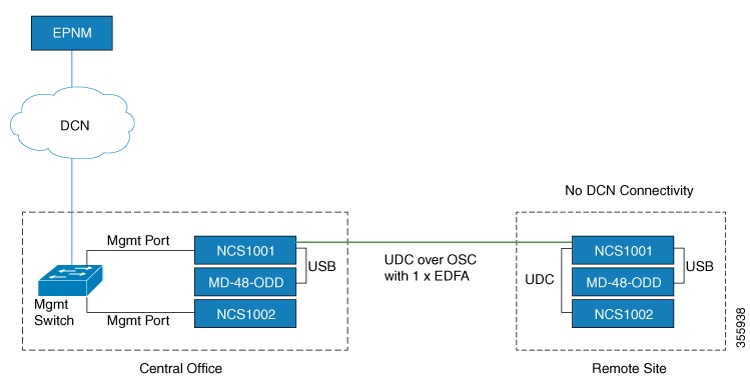
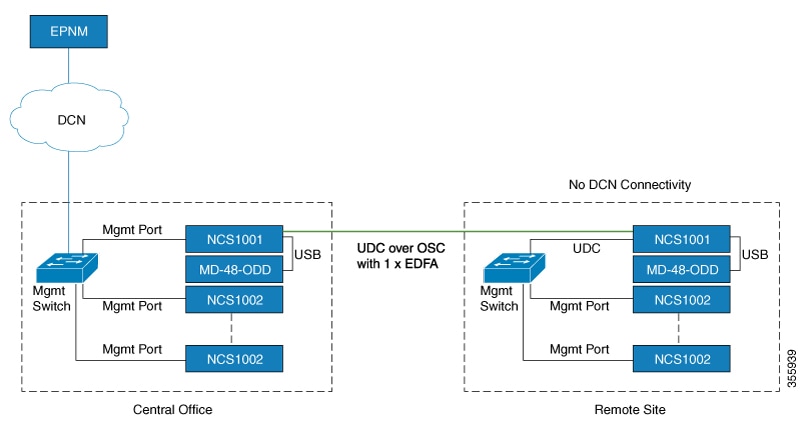
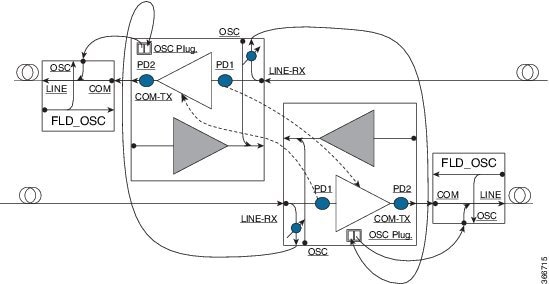

 Feedback
Feedback