Create Binding to BFD Peer
Procedure
|
When you configure High Availability with IOS XE releases 17.4 and later, you can create a binding to a BFD peer by executing the following command: Example: |
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
High Availability is supported for Cisco Catalyst 8000V on Cisco IOS XE 17.4 release and later.
|
When you configure High Availability with IOS XE releases 17.4 and later, you can create a binding to a BFD peer by executing the following command: Example: |
The following table specifies the redundancy parameters that are specific to Microsoft Azure:
|
Parameter Switch |
Switch |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Node Index |
-i |
The index that is used to uniquely identify this node. Valid values: 1–255. |
|
Cloud Provider |
-p |
Specifies the type of Azure cloud: azure, azusgov, or azchina. |
|
Subscription ID |
-s |
The Azure subscription id. |
|
Resource Group Name |
-g |
The name of the route table to be updated. |
| Route Table Name | -t | The name of the route table to be updated. |
|
Route |
-r |
IP address of the route to be updated in CIDR format. Can be IPv4 or IPv6 address. If a route is unspecified, then the redundancy node is considered to apply to all routes in the routing table of type “virtual appliance”. |
|
Next Hop Address |
-n |
The IP address of the next hop router. Use the IP address that is assigned to this Cisco Catalyst 8000V on the subnet which utilizes this route table. Can be an IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Mode |
-m |
Indicates whether this router is the primary or secondary router for servicing this route. Default value is secondary. |
|
Run the following script to create a redundancy node and add it to the database: You must configure the following parameters for a valid redundancy node:
If the configuration is successful, the script returns a value of zero. |
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
To change the value of parameters in an existing redundancy node, run the following script: Example: |
The index parameter (-i) is mandatory. This command sets the values of the specified parameters. If the specified parameter is already defined for the redundancy node, the value of the parameter is updated. In this example, the next hop address and mode will be updated for the redundancy node with index 10. If this configuration is successful, the script returns a value of zero. |
|
If you want to clear the value of specified parameters for an existing redundancy node, run the following script: Example:In this example, the clear_params script clears both the route and next hop address parameters. Specify only the switch parameter when you clear an associated value. Do not include the current value of the parameter.
|
To update a routing table in the Azure network, you must first authenticate the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router. This is accomplished by creating an application which represents the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router in the Azure Active Directory. You can use the application that is granted permissions, to access the Azure network resources.
You can create the application by using the following two mechanisms:
System-assigned managed identity - Azure automatically creates an application and binds it to the router. This mechanism was previously called as Managed Service Identity by Azure.
Manual application registration in Azure Active Directory - Here, the user creates an application in the Azure Active Directory, which represents the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router.
You can manually create a managed identity in Azure Active Directory by creating an application which represents the router. The application is assigned a set of identifiers; tenant ID, application ID, and application key. These application identifiers must be configured in the high availability feature either as the default AAD application or within an individual redundancy node.
Alternatively, when you create the Cisco Catalyst 8000V, you can configure Azure to create a system-assigned managed identity for the Cisco Catalyst 8000V instance. In this case, you need not configure any application identifiers in the high availability feature. That is, in the absence of the configuration of an application’s tenant ID, application ID, and application key, the high availability feature assumes that the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router is using a system-assigned managed identity.
When you create the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router, you can enable for it to be assigned a system managed identity by Azure. There are two ways in which you can create a Cisco Catalyst 8000V router from the Azure marketplace:
Solution template – A Cisco Catalyst 8000V router is created along with other Azure resources to create a networking solution in a single step.
Standalone – A standalone Cisco Catalyst 8000V is created, usually within an existing virtual network, with the base Cisco Catalyst 8000V image.
If you create a Cisco Catalyst 8000V router by using one of the solution template offerings in the Azure marketplace, a system-assigned managed identify for the Cisco Catalyst 8000V is enabled by default. If you create a standalone Cisco Catalyst 8000V by using a base Cisco Catalyst 8000V image, a system-managed identity is enabled as shown in the following image:
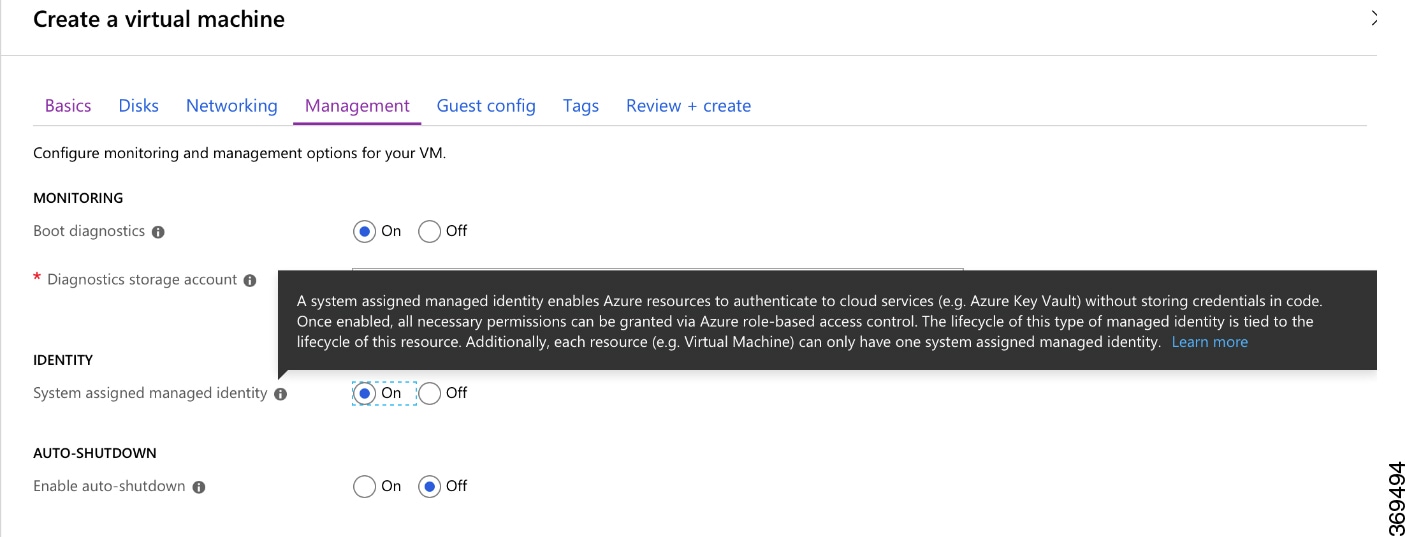
This section explains how to create an application in a Microsoft Azure Active Directory with permissions to access Microsoft Azure Resource Manager APIs.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
See the latest instructions on registering an application with Azure Active Directory in Microsoft Azure documentation. See also: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/quickstart-v1-add-azure-ad-app. |
|
|
Step 2 |
Go to the portal for Microsoft Azure by visiting https://portal.azure.com. |
|
|
Step 3 |
Choose your account name and sign in using your Microsoft Azure password. |
|
|
Step 4 |
In the left navigation, click Azure Active Directory and select an Active Directory in the main pane. Click Switch Directory at the top of the pane to select the active directory. |
|
|
Step 5 |
Verify whether you are authorized to create a new application. See the following Microsoft Azure documentation for creating an application in the Azure Active Directory: Use portal to create an Azure Active Directory application and service principal that can access resources. |
|
|
Step 6 |
Navigate to the Active Directory that you want to use. |
|
|
Step 7 |
To create a new application, select Create > New Application Registration. |
|
|
Step 8 |
Specify the name of the application and ensure that Web App / API is selected as the Application type |
|
|
Step 9 |
Specify the Sign-on URL. Use a name for the sign-on URL which is in the URI format, but it does not have to be reachable. You can use a string in the following format: http://<your_directory_domain_name>/<app_name>. For example, if your application name is myapp, and the domain name of your directory is \mydir.onmicrosoft.com, use the following is the sign-on URL: http://mydir.onmicrosoft.com/myapp. |
|
|
Step 10 |
Click Create. |
|
|
Step 11 |
Navigate to the Azure Active Directory page. Search for the application that you created. Make a note of the assigned Application ID. |
Create an application in the Microsoft Azure Active Directory.
|
Step 1 |
After you create the application, the registered app should appear on the screen as shown in the following image:  |
|
Step 2 |
Use the portal to create an Azure Active Directory application and service principal that can access resources. Make a note of the Application ID. See step 2 in the Get application ID and authentication key section in the Microsoft Documentation. |
|
Step 3 |
Select Azure Active Directory. |
|
Step 4 |
Select Properties. Make a note of the value in the Directory ID field. This is your tenant ID. |
|
Step 1 |
From the Microsoft Azure portal, select the Azure Active Directory. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Select App Registrations. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Select the application that you previously created in the Obtain the Application ID and Tenant ID section. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Settings. |
||
|
Step 5 |
To create a key for API access, select Keys and specify a value for Duration. Duration is the length of time after which the key becomes invalid. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Make a note of the API key from the Value field.
|
||
|
Step 7 |
You must convert the API key to URL unencoded format. To find a suitable conversion tool, enter URL encoder into an Internet search engine. You might need the unencoded API key for procedures such as Configure Failure Detection for the Cisco Catalyst 8000V on Microsoft Azure. Example: |
There are a set of utility scripts that can be run in the guestshell environment to manage applications in the Azure Active Directory, whether they were created manually as user-assigned identities or system-assigned identities. The following sections describe the use of these scripts and how to configure the binding between a redundancy node and the application used to authenticate the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router.
Managing user-defined applications: If you have chosen to use a user-assigned identity for the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router, the application that was created in Azure Active Directory must be configured in the high availability feature. The application can be configured as the default application used for all the redundancy nodes, or for individual redundancy nodes.
Set the default application: If you configure a user-assigned application as the default application using the set_default_aad_app script, all the redundancy nodes use the specified application for authentication, unless a redundancy node has an individual
application configured.
Set the default application by running the set_default_aad_app.py{ switch value } […[{ switch value }] script. See the following table for the AAD Redundancy Node Parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Switch |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Cloud Provider |
-p |
Specifies which Azure cloud is in use {azure | azusgov | azchina} |
|
Tenant ID |
-d |
Identifies the AAD instance. |
|
Application ID |
-a |
Identifies the application in AAD. |
|
Application Key |
-k |
Access key that is created for the application. Key should be specified in unencoded URL format. |
[guestshell@guestshell]$ set_default_aad_app.py -p azure -d c4426c0b-036f-4bfb-b2d4-5c910c5389d6 -a 3d6e2ef4-8160-4092-911d-53c8f68ba808 -k hZFvMGfzJuwFiukez27e/duyztom1bj7QL0Yix+KY9c=[guestshell@guestshell]$ set_default_aad_app.py -h
usage: set_default_aad_app.py [-h] -p {azure,azusgov,azchina} -a A -d D -k K
AAD Application
required arguments:
-p {azure,azusgov,azchina} <cloud_provider> {azure | azusgov | azchina}
-a A to add the applicationId
-d D to add the tenantId
-k K to add the applicationKey
You can clear the default user-assigned application configuration by using the clear_default_aad_app script.
[guestshell@guestshell]$ clear_default_aad_app.pyIf you create a user-assigned application and associate the application with individual redundancy nodes, information about
these applications is cached in memory. You can display the list of known applications by using the show_auth_applications.py script. Clear the cache using the clear_aad_application_list script.
[guestshell@guestshell]$ clear_aad_application_list.pyUse the following scripts to manage all the applications - user-assigned or system-assigned.
Cisco Catalyst 8000V router maintains a list of configured applications. You can view this list by using the show_auth_applications script.
[guestshell@guestshell]$ show_auth_applications.pyWhen an event is triggered on a redundancy node, the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router uses the configured application to obtain an authentication token from the Azure network. This token is cached up
to five minutes in the router. You can clear the cached token by using the clear_token script.
This script clears either the default user-assigned application or the system-assigned application. The script does not clear the token on any user assigned application which is explicitly configured on an individual redundancy node.
[guestshell@guestshell]$ clear_token.pyThe Cisco Catalyst 8000V router can be forced to obtain a new token for the active application by using the refresh_token script.
This script refreshes either the default user-assigned application or the system-assigned application. This script does not refresh the token on any user-assigned application which is explicitly configured on an individual redundancy node.
[guestshell@guestshell]$ refresh_token.pyYou can choose either system-assigned or user-assigned applications to identify a Cisco Catalyst 8000V router for the purpose of authentication. You can use the same mechanism for all the applications within a single Cisco Catalyst 8000V router. You can also have multiple user-assigned applications across multiple redundancy nodes.
The following table summarizes which application is used by the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router when processing a redundancy node:
|
Is A Default Application Configured? |
Does Node Have a User Assigned Application Configured? |
Will Cisco Catalyst 8000V Use This Application? |
|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
System assigned application |
|
No |
Yes |
User assigned application configured on this redundancy node |
|
Yes |
No |
User assigned application configured as the default by set_default_aad_app.py |
|
Yes |
No |
User assigned application configured on this redundancy node |
|
Step 1 |
To add an application into an existing network, in the All Resources pane, choose a private side subnet from the left pane. For example, noeem-sub1-RouteTable.  |
|
Step 2 |
In the center pane, select Access control (IAM). Select the plus icon to add a role assignment.  |
|
Step 3 |
In the Add Role Assignment screen, set the Role to Network Contributor. |
|
Step 4 |
Select the Assign Access to Pulldown menu. If you are using system-assigned managed identity, select the Virtual Machine sub option and go to Step 6. If you are using user-assigned managed identity, select the option and go to step 5. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Select field, enter the name of the user-assigned application that you created in Azure Active Directory. Click Save. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Select field, enter the name given to the Cisco Catalyst 8000V instance. If you have configured the Cisco Catalyst 8000V instance properly for system-assigned identity, the Cisco Catalyst 8000V instance appears in the search results. |
|
Step 7 |
Select the Cisco Catalyst 8000V instance by name, and click Save. |
The route tables in Microsoft Azure support different entry types. The entry type for a route can be one of the following: Virtual network gateway, Internet, or Virtual Appliance. The next hop address identifies a resource in the Azure network.
Routes with an entry type of Virtual network gateway or Internet do not have an explicit IP address for the next hop and are not supported by the High Availability feature.
When you configure High Availability on a Cisco Catalyst 8000V instance, you can specify individual routes to be updated in the case of failure. Ensure that you configure each individual route as having an entry type of Virtual Appliance. If you configure a redundancy node that represents all the entries in the route table, ensure that all the routes have an entry type of Virtual Appliance.
If you have a network security group attached to NIC0 of the router, you must allow the BFD protocol to pass the interface. Configure an inbound and outbound security rule that allows ports 4789 and 4790 to be passed.
When you start an SSH session to the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router, ensure that you do not configure the terminal VTY timeout as infinite. That is, do not configure: exec-timeout 0 0. Use a non-zero value for the timeout; for example, exec-timeout 4 0. This command specifies a timeout of four minutes and zero seconds. The exec-timeout 0 0 command causes an issue as Azure enforces a timeout for the console idle period of 4 to 30 minutes. When the idle timer expires, Azure disconnects the SSH session. However, the session is not cleared from the point of view of the Cisco Catalyst 8000V as the timeout was set to infinite (by the exec-timeout 0 0 configuration command). The disconnection causes a terminal session to be orphaned. The session in the Cisco Catalyst 8000V remains open indefinitely. If you try to establish a new SSH session, a new virtual terminal session is used. If this pattern continues, the maximum number of simultaneous terminal sessions allowed is reached and no new sessions can be established. In addition to configuring the exec-timeout command correctly, it is also a good practice to delete idle virtual terminal sessions using the commands that are shown in the following example:
RouterA# show users
Line User Host(s) Idle Location
2 vty 0 cisco idle 00:07:40 128.107.241.177
* 3 vty 1 cisco idle 00:00:00 128.107.241.177
RouterA# clear line 2
 Note |
If the workaround in the preceding scenarios are ineffective, as a last resort, you can restart the Cisco Catalyst 8000V router in the Azure portal. |