SLP Overview
Smart Licensing Using Policy (SLP), previously known as Smart Licensing Enhanced (SLE), is the default mode for IoT routers. SLE replaced Smart Software Licensing.
This guide supports all IoT routers, and replaces individual chapters in each of the software configuration guides.
The following sections show the features and software differences between the IoT routers.
IR1800
The IR1800 series only supports SLP. Some of the feature differences are:
-
Support started with IOS-XE release 17.3.2
-
An Authorization Code is required only for export control requirement
-
Throughput greater than 250MB requires an HSEC license
-
No more EVAL licenses. Authorized status has changed to In Use or Not In Use with an Enforcement Type class.
-
Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) is a new tool interfacing between the devices and Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) in specific customer topologies.
IR1101
The IR1100 series only supports SLP. Some of the feature differences are:
-
Support started with IOS-XE release 17.3.2
-
An Authorization Code is required only for export control requirement
-
No more EVAL licenses. Authorized status has changed to In Use or Not In Use with an Enforcement Type class.
-
Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) is a new tool interfacing between the devices and Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) in specific customer topologies.
-
Throughput is defaulted and capped at 250MB.
IR8100
The IR8100 series only supports SLP. Some of the feature differences are:
-
Support started with IOS-XE release 17.3.2
-
An Authorization Code is required only for export control requirement
-
Throughput greater than 250 Mbps requires an HSEC license
-
No more EVAL licenses. Authorized status has changed to In Use or Not In Use with an Enforcement Type class.
-
Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) is a new tool interfacing between the devices and Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) in specific customer topologies.
IR8300
The IR8300 series only supports SLP. Some of the feature differences are:
-
Support started with IOS-XE release 17.3.2
-
An Authorization Code is required only for export control requirement
-
Throughput greater than 250 Mbps requires an HSEC license
-
No more EVAL licenses. Authorized status has changed to In Use or Not In Use with an Enforcement Type class.
-
Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) is a new tool interfacing between the devices and Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) in specific customer topologies.
ESR6300
The ESR6300 embedded router operates slightly different than the other IoT routers. Some of the feature differences are:
-
Support started with IOS-XE release 17.4.1
-
An Authorization Code is required only for export control requirement
-
Throughput greater than 250 Mbps requires an HSEC license
-
No more EVAL licenses. Authorized status has changed to In Use or Not In Use with an Enforcement Type class.
-
Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU) is a new tool interfacing between the devices and Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) in specific customer topologies.
License Enforcement Types
A given license belongs to one of three enforcement types. The enforcement type indicates if the license requires authorization before use, or not.
-
Unenforced or Not Enforced
The vast majority of licenses belong to this enforcement type. Unenforced licenses do not require authorization before use in air-gapped networks, or registration, in connected networks. The terms of use for such licenses are as per the end user license agreement (EULA).
-
Enforced
Licenses that belong to this enforcement type require authorization before use. The required authorization is in the form of an authorization code, which must be installed in the corresponding product instance.
An example of an enforced license is the Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) Client license, which is available on Industrial Ethernet Switches.
-
Export-Controlled
Licenses that belong to this enforcement type are export-restricted by U.S. trade-control laws and these licenses require authorization before use. The required authorization code must be installed in the corresponding product instance for these licenses as well. Cisco may pre-install export-controlled licenses when ordered with hardware purchase.
An example of an export-controlled license is the High Security (HSEC) license, which is available on certain Cisco Routers.
High Security (HSEC) License
HSEC (High Security) license is a feature license that can be configured in addition to the network license (NE/NA). An HSEC license provides export controls for strong levels of encryption. HSEC is available to customers in all currently non-embargoed countries as listed by the U.S. Department of Commerce. Without an HSEC license, SEC performance is limited to a total of 250 Mbps of IPsec throughput in each direction. An HSEC license removes this limitation.
Command Line Interface
The configuration mode CLI to enable HSEC on the IR1101 is the following:
IR1101(config)# license feature hsec9To benefit from the HSEC license, a new bandwidth will be available. The new bandwidth is called uncapped, and it is available with the following CLI from configuration mode:
IR1101(config)# platform hardware throughput level ?
250M throughput in bps
uncapped throughput in bps
IR1101# platform hardware throughput level uncappedAfter performing the above commands, write mem and reload the router. The configuration will take effect when the router comes back up.
License Types
With this new feature, the IR1101 will support the following bandwidth/license types:
-
Network-essentials 250 Mbps
-
Network-advantage 250 Mbps
-
Network-essentials uncapped
-
Network-advantage uncapped
-
HSEC
Ordering
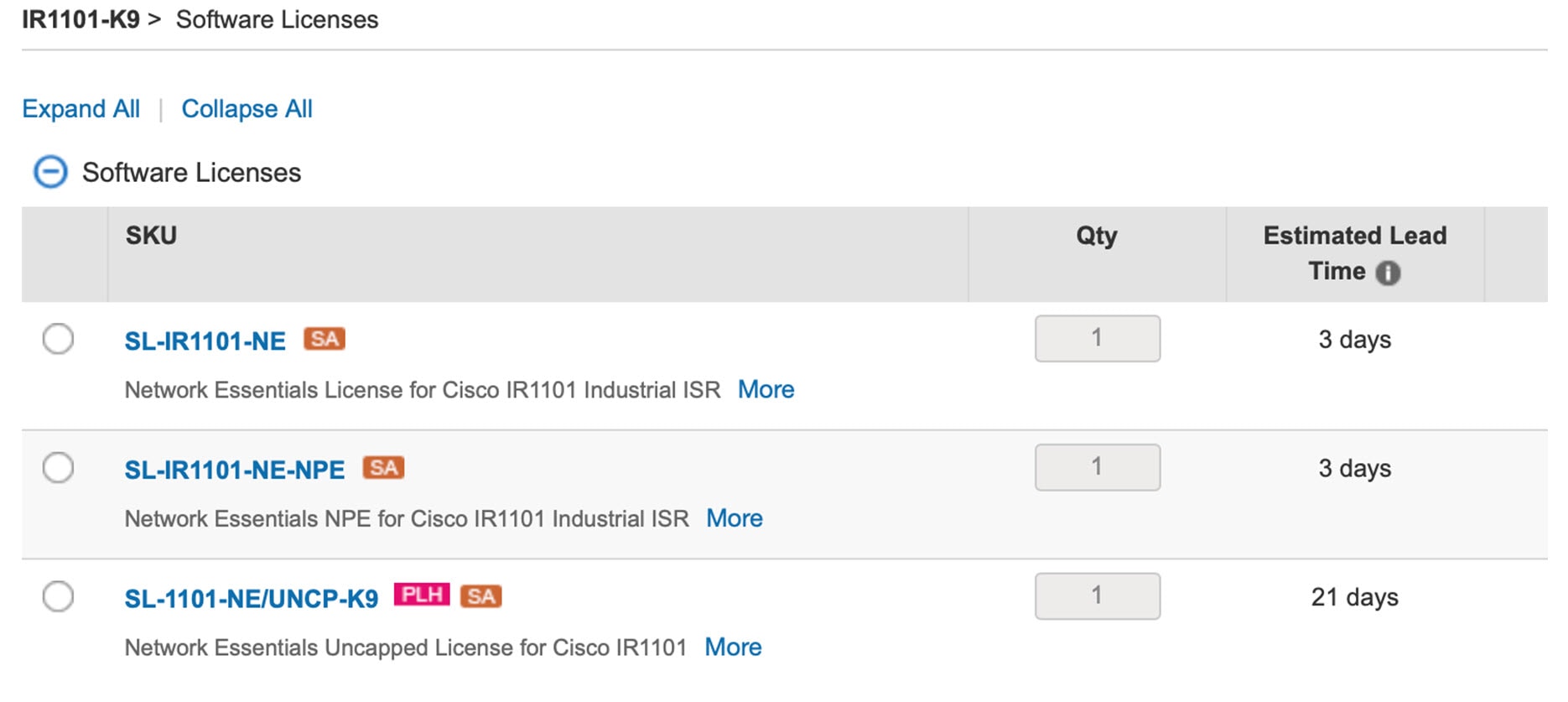
The following is an example from the IR1101-K9. The license will be available on the IR1101-A-K9 as well.
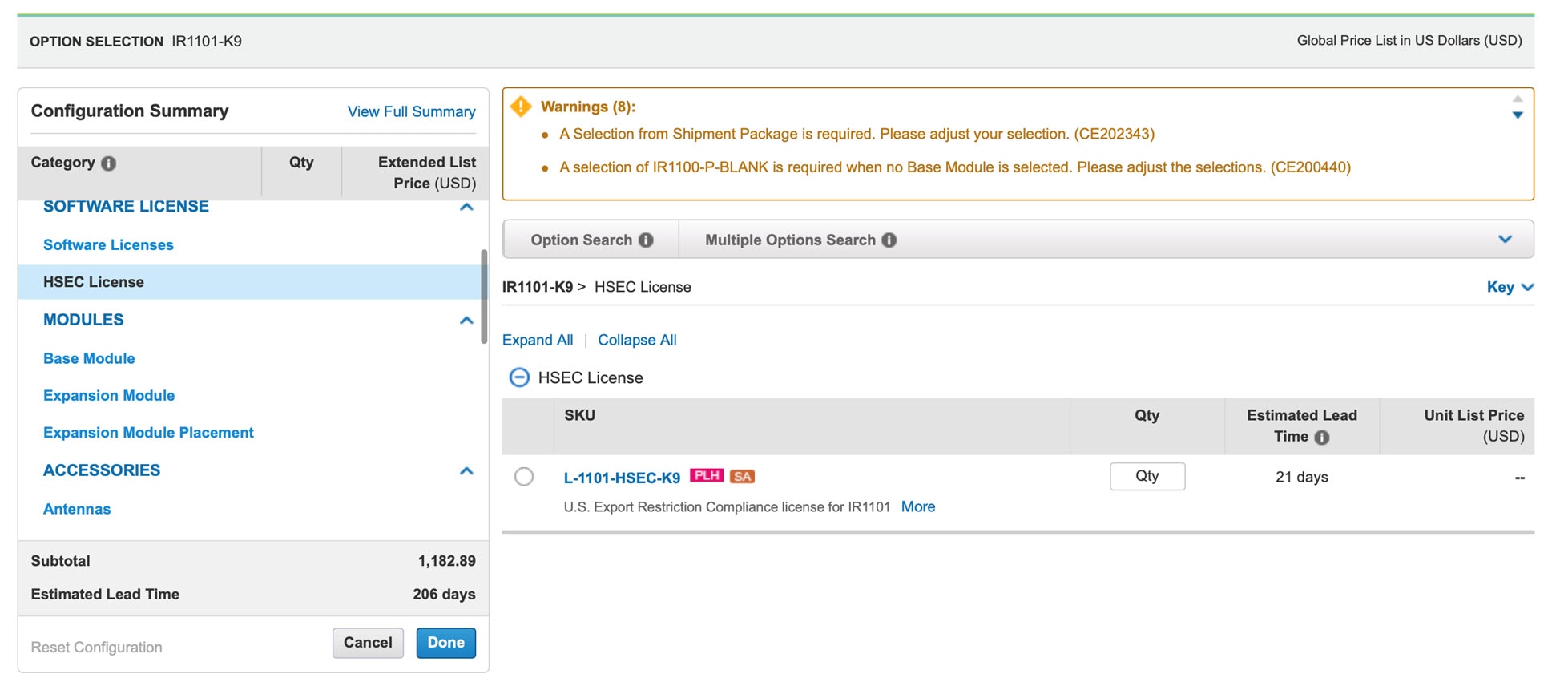
In the following example, select the SL-1101-NE/UNCP-K9 (Network Essentials Uncapped License):
The L-1101-HSEC-K9 license will get auto included when you select the uncapped license, as shown in the following:
Cisco Software Central
This guide provides information on how to order, activate, and manage your Cisco Smart Licenses.
https://software.cisco.com/software/csws/ws/platform/home?locale=en_US&locale=en_US&locale=en_US#
SLP Architecture
This section explains the various components that can be part of your SLP implementation.
Product Instance
A product instance is a single instance of a Cisco product, identified by a Unique Device Identifier (UDI).
A product instance records and reports license usage (RUM reports), and provides alerts and system messages about overdue reports, communication failures, etc. The RUM reports and usage data are also stored securely in the product instance.
A Resource Utilization Measurement report (RUM report) is a license usage report, which fulfils reporting requirements as specified by the policy. RUM reports are generated by the product instance and consumed by CSSM. The product instance records license usage information and all license usage changes in an open RUM report. At system-determined intervals, open RUM reports are closed and new RUM reports are opened to continue recording license usage. A closed RUM report is ready to be sent to CSSM.
A RUM acknowledgement (RUM ACK or ACK) is a response from CSSM and provides information about the status of a RUM report. Once the ACK for a report is available on the product instance, it indicates that the corresponding RUM report is no longer required and can be deleted.
CSSM displays license usage information as per the last received RUM report.
Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM)
CSSM is a portal that enables you to manage all your Cisco software licenses from a centralized location. CSSM helps you manage current requirements and review usage trends to plan for future license requirements.
You can access CSSM at https://software.cisco.com. Under the License tab, click the Smart Software Licensing link.
In CSSM you can:
-
Create, manage, or view virtual accounts.
-
Create and manage Product Instance Registration Tokens.
-
Transfer licenses between virtual accounts or view licenses.
-
Transfer, remove, or view product instances.
-
Run reports against your virtual accounts.
-
Modify your email notification settings.
-
View overall account information.
Prior to using CSSM, please view a short video about how to use the portal found here:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/buy/smart-accounts/software-manager.html
Click on the View Video button.
Cisco Smart Licensing Utility (CSLU)
CSLU is a Windows-based reporting utility that provides aggregate licensing work-flows. It helps you administer all your licenses and their associated product instances from your premises instead of having to connect to CSSM.
This utility performs the following key functions:
-
Provides the options relating to how work-flows are triggered. The work-flows can be triggered by CSLU or by the product instance,
-
Collects usage reports from the product instance and upload these usage reports to the corresponding smart account or virtual account – online, or offline, using files. Similarly, the RUM report ACK is collected online, or offline, and provided back to the product instance.
-
Sends authorization code requests to CSSM and receives authorization codes1 from CSSM.
CSLU can be part of your SLP topology in the following ways:
-
Install the windows application, to use CSLU as a standalone tool and connect it to CSSM.
-
Install the windows application, to use CSLU as a standalone tool and not connect it to CSSM. With this option, the required usage information is downloaded to a file and then uploaded to CSSM. This is suited to air-gapped networks.
-
Embed it in a controller such as Cisco DNA Center.

































 Feedback
Feedback