Features and Benefits
The Cisco Voice Gateway provides VoIP connectivity to analog devices such as analog desk phones, analog conference room phones, fax machines, and modems. This voice gateway provides several improvements from the previous high-density analog and digital extension modules (EVMs) in the following ways:
-
On-board Digital Signal Processor (DSP): The FXO and FXS service modules contain an onboard DSP and don’t require the router to have a dedicated packet voice DSP module (PVDM) on the motherboard. The DSP on the voice module is necessary for the voice features. It also provides for echo cancellation of up to 128-ms echo-tail length for demanding network conditions.
-
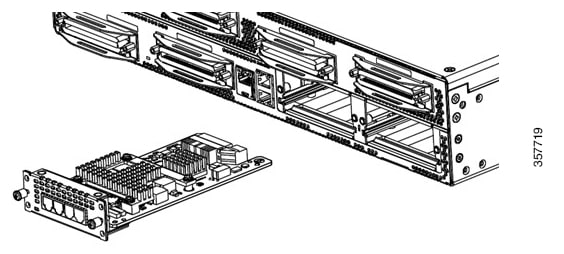
Support for Online Insertion and Removal (OIR): The FXS and FXO service modules support Online Insertion and Removal (OIR), reducing the downtime required for new or replacement modules. The service modules can be inserted into the NIM slot on the device without powering off the voice gateway.
-
FXS-E (extended loops) support: FXS ports on the new modules support FXS-E with the following details:
-
Higher loop current (35 mA) to accommodate specialty phones
-
Longer loop length for loops with 26 AWG wire, up to 11,000 feet (3400 meters)
-
Higher ringing voltage (65 Vrms, no load)
-
In addition to these features, the following are also supported:
-
Caller line ID
-
G.711, G.729a, and G.726
-
G722, iLBC
-
Fax detection, pass-through, and relay (T.38)
-
Modem pass-through
-
DTMF detection
-
Echo cancellation
-
Voice activity detection
-
Comfort noise generation
-
Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP)
-
Acoustic shock protection
-
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)
-
RFC 4733 Digit Relay
-
Noise reduction
The FXS features include:
-
Support for either FXS or DID functionality
-
Message-Waiting Indicator (MWI)
-
Cable detection: GR909 line test
The FXO features include:
-
Support for both ground-start and loop-start modes
-
Call Detail Record (CDR) information
-
Support for interworking with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Skinny Client Control Protocol [SCCP]), Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), and Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) 0.1
-
Cable detection
-
Overload protection
-
Analog phone connectivity
-
Fax and modem connectivity





 Feedback
Feedback