|
CABLE-16TDM-R1EL1
|
T1/E1-Cable S-3
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T1/E1 Cable S-2
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 7.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T1/E1 Cable S-1
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 6.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R1EL2
|
T1/E1-Cable M-3
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T1/E1-Cable M-2
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 7.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T1/E1-Cable M-1
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 6.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R1EL3
|
T1/E1-Cable L-3
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T1/E1-Cable L-2
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 7.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T1/E1-Cable L-1
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 6.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R3EL1
|
T3/E3-Cable S-3
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T3/E3-Cable S-2
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 7.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T3/E3-Cable S-1
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 6.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R3EL2
|
T3/E3-Cable M-3
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T3/E3-Cable M-2
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 7.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T3/E3-Cable M-1
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 6.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R3EL3
|
T3/E3-Cable L-3
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T3/E3-Cable L-2
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 7.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
T3/E3-Cable L-1
|
16-port cable for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 6.5 inches stub length, even slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R1OL1
|
T1/E1-Cable S-3
|
3 x 16-port cables for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, odd slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R1OL2
|
T1/E1-Cable M-3
|
3 x 16-port cables for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, odd slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R1OL3
|
T1/E1-Cable L-3
|
3 x 16-port cables for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, odd slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R3OL1
|
T3/E3-Cable S-3
|
3 x 16-port cables for TDM CEM Interface Module, 42 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, odd slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R3OL2
|
T3/E3-Cable M-3
|
3 x 16-port cables for TDM CEM Interface Module, 62 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, odd slot
|
|
CABLE-16TDM-R3OL3
|
T3/E3-Cable L-3
|
3 x 16-port cables for TDM CEM Interface Module, 78 inches cable length and 10 inches stub length, odd slot
|
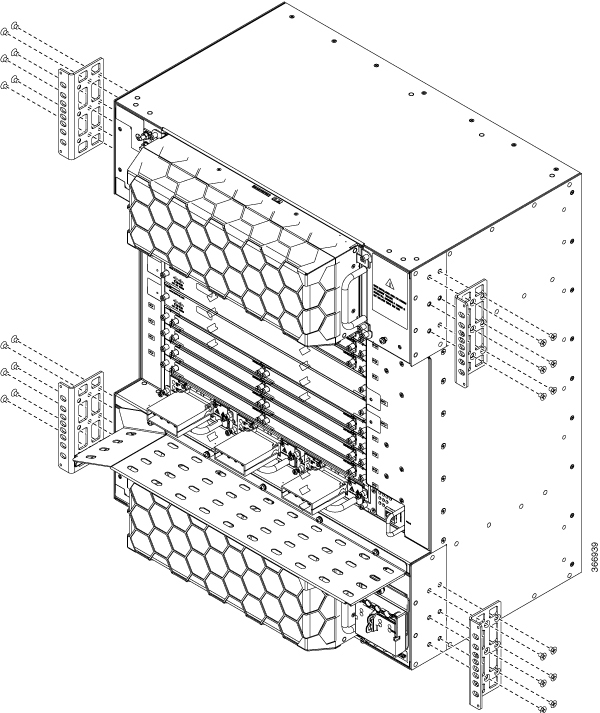
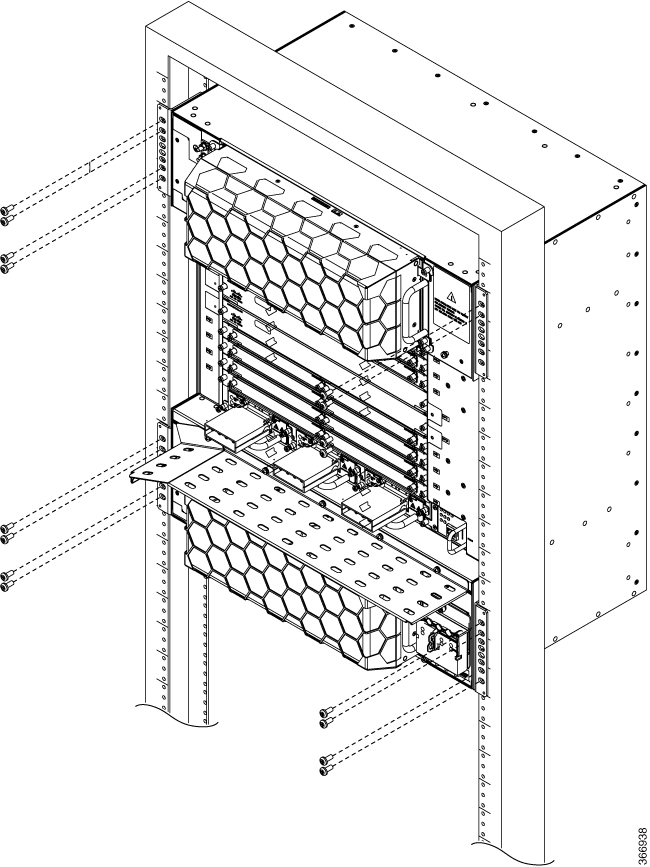
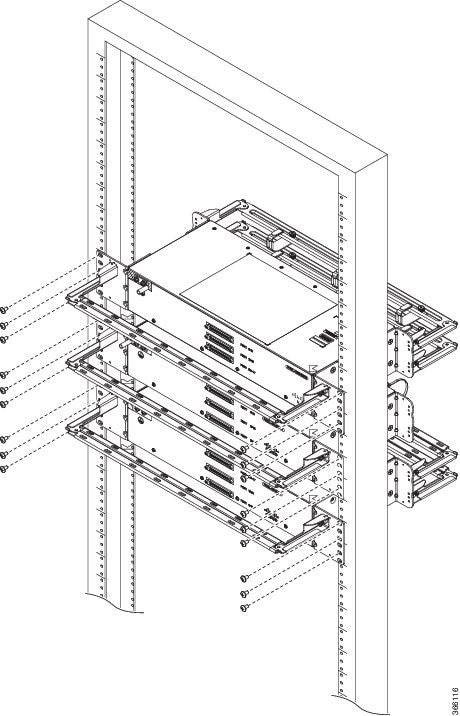

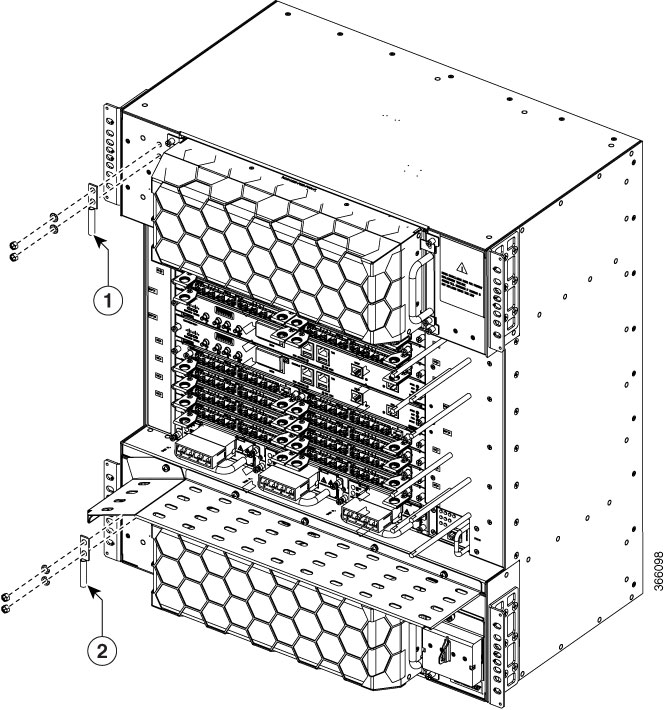




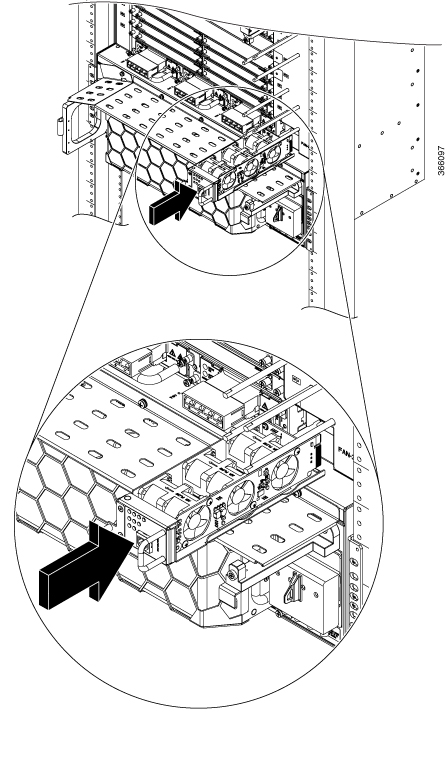
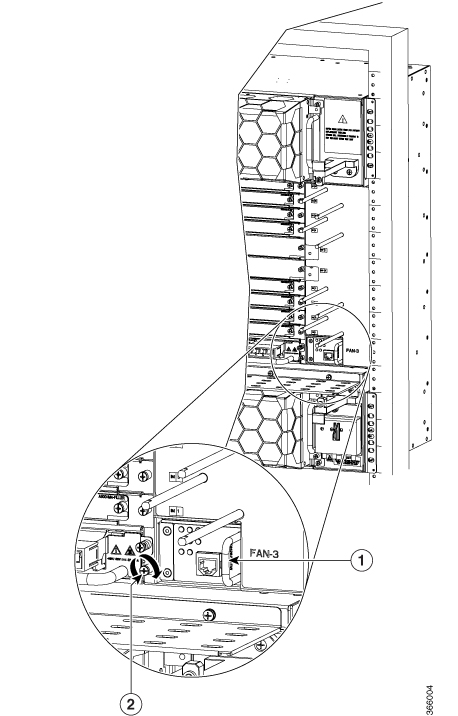
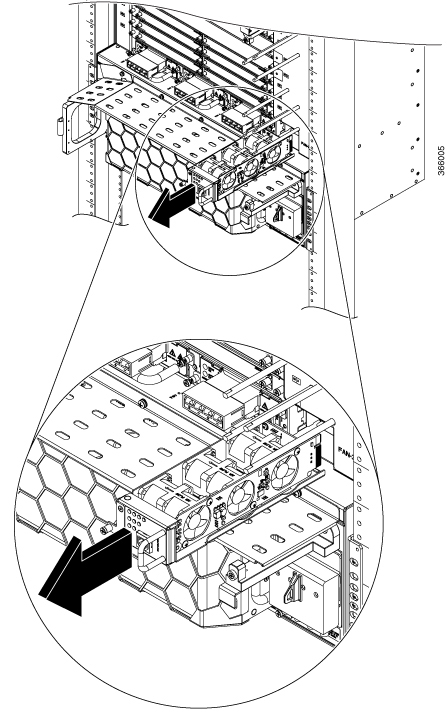
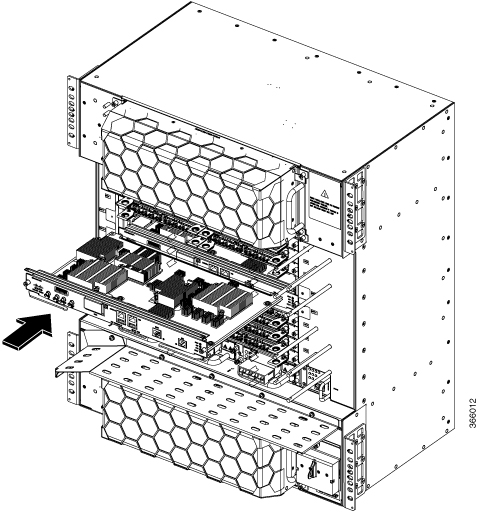
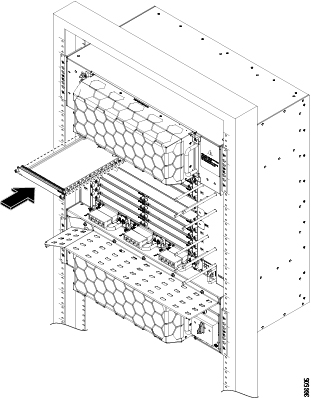


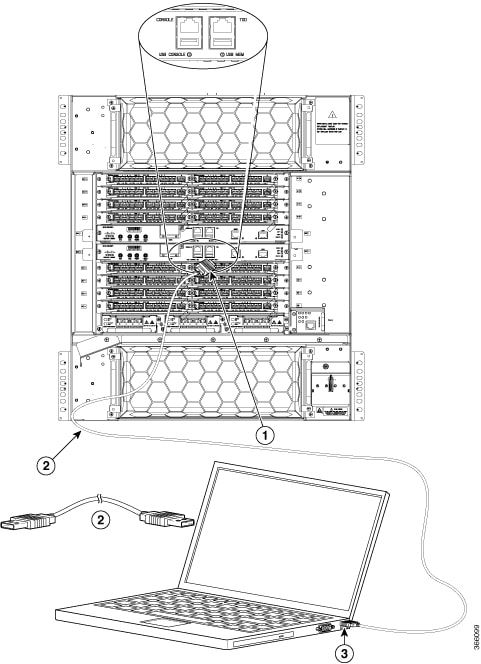
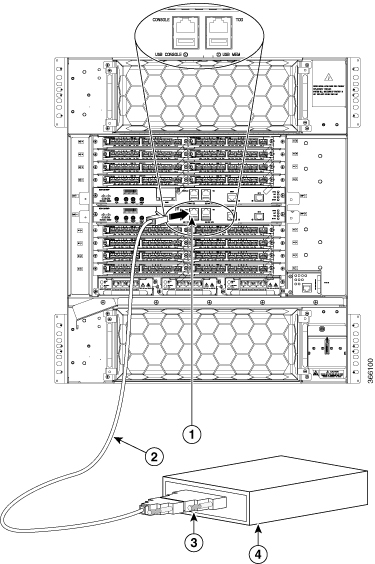

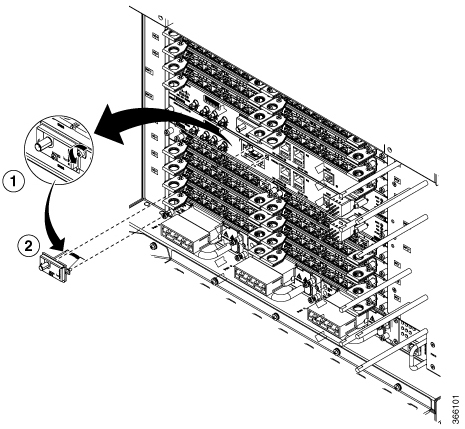














































 Feedback
Feedback