Information About ICMP for IPv6 Redirect
IPv6 Neighbor Redirect Message
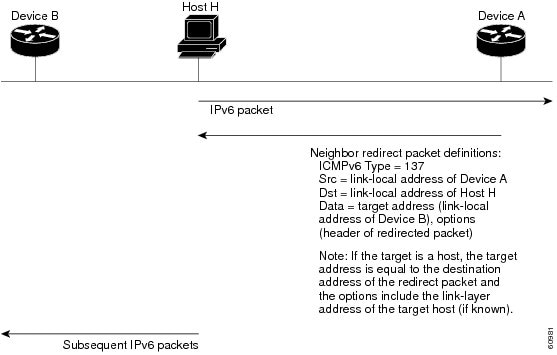
A value of 137 in the type field of the ICMP packet header identifies an IPv6 neighbor redirect message. Devices send neighbor redirect messages to inform hosts of better first-hop nodes on the path to a destination (see the figure below).
 Note |
A device must be able to determine the link-local address for each of its neighboring devices in order to ensure that the target address (the final destination) in a redirect message identifies the neighbor device by its link-local address. For static routing, the address of the next-hop device should be specified using the link-local address of the device; for dynamic routing, all IPv6 routing protocols must exchange the link-local addresses of neighboring devices. |
After forwarding a packet, a device should send a redirect message to the source of the packet under the following circumstances:
-
The destination address of the packet is not a multicast address.
-
The packet was not addressed to the device.
-
The packet is about to be sent out the interface on which it was received.
-
The device determines that a better first-hop node for the packet resides on the same link as the source of the packet.
-
The source address of the packet is a global IPv6 address of a neighbor on the same link, or a link-local address.
Use the ipv6 icmp error-interval command to limit the rate at which the device generates all IPv6 ICMP error messages, including neighbor redirect messages, which ultimately reduces link-layer congestion.
 Note |
A device must not update its routing tables after receiving a neighbor redirect message, and hosts must not originate neighbor redirect messages. |
 Feedback
Feedback