Table of Contents
Cisco Connected Grid Cellular 3G GSM Module for CGR 1000 Series Installation and Configuration Guide (Cisco IOS)
Kit Contents
Features
Hardware Overview
Front Panel
Ports and LEDs
Supported Cisco Antennas
Supported Cisco Cables
Interfaces
Radio Frequency Interface
Environmental Specifications
Power Specifications
Modem
SIM Interface
Voltage Monitoring State Machine
Temperature Monitoring State Machine
Data Rate
Memory Specifications
Module Power States
Installing and Removing the SIM Card
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Installing the SIM Card
Removing the SIM Card
Installing and Removing the 3G GSM Module
Before You Begin Installation
Installation Warning Statements
Installing the 3G Module
Removing the Module
Regulatory and Compliance Information
UMTS/GSM Data Network Overview
3G Cellular WAN MIB
ciscoWan3gMIBObjects
ciscoWan3gMIBNotifs
Configuring the 3G GSM Module
Prerequisites
Restrictions and Limitations
Data Account Provisioning
Verifying Signal Strength and Service Availability
Configuring a Modem Data Profile
Data Call Setup
Configuring the Cellular Interface
Configuring DDR
Configuring DDR Backup
Configuring Dual SIM
Configuration Examples
Basic Cellular Interface Configuration
Tunnel over Cellular Interface Configuration
Troubleshooting
Verifying Data Call Setup
Checking Signal Strength
Verifying Service Availability
Successful Call Setup
Modem Settings for North America and Carriers Operating on 850 MHz and 1900 MHz Bands
Additional References
Release Notes
Hardware Overview and Installation Documents
Supported Cisco Antennas and Accessories Documents
Cisco System Software Commands Documents
Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information
Retrieving the Electronic Serial Number
Converting Hexadecimal ESN to Decimal Notation
Command Reference
cellular gsm band
cellular gsm mep unlock
cellular gsm plmn search
cellular gsm plmn select
cellular gsm profile create
cellular gsm sim change-pin
cellular gsm sim lock
cellular gsm sim unblock
cellular gsm sim unlock
debug cellular messages all
debug cellular messages async
debug cellular messages callcontrol
debug cellular messages data
debug cellular messages management
gsm radio off
gsm sim authenticate
show cellular all
show cellular connection
show cellular hardware
show cellular network
show cellular profile
show cellular radio
show cellular security
show controllers cellular
show interfaces cellular
show run interface cellular
Technical Assistance
Cisco Connected Grid Cellular 3G GSM Module for CGR 1000 Series Installation and Configuration Guide (Cisco IOS)
First Published: January 2014
Last Updated: July 2014
OL-31237-02
This document provides an overview of hardware and Cisco IOS configuration information for the 3G GSM single-wide, high-speed, connected grid router WAN interface card (GRWIC).
The 3rd Generation (3G) GSM module is a multiband, multiservice WAN card for use over Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) networks. You can use the 3G GSM module as the backup for critical applications as well as the primary WAN connection.
You can install the 3G GSM module in both versions of the Cisco 1000 Series Connected Grid Routers: the CGR 1240 and the CGR 1120.
This document contains the following topics:
Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Kit Contents
Your 3G module kit contains the 3G GSM module (see Figure 1). Refer to the information shown in Table 1 when ordering parts.
Note The Cisco Connected Grid 3G GSM Module is a field-replaceable unit.
The Cisco Connected Grid 3G GSM Module is a field-replaceable unit.
Figure 1 Cisco Connected Grid 3G GSM Wireless Connected Grid Module
|
|
CGM-3G-HSPA-A and CGM-3G-HSPA-G |
|
CGM-3G-HSPA-AB-G (all band) |
Table 1 Kit Contents for the 3G GSM Module
|
|
|
|
|
CGM-3G-HSPA-A |
AT&T (MC8705), Connected Grid Module - 3G AT&T HSPA+/UMTS/ GSM/GPRS/EDGE |
North America |
- GSM/GPRS/EDGE: 850/1800/1900 MHz
- UMTS/HSPA+: 850/900/1900/2100 MHz
|
CGM-3G-HSPA-G |
ROW (Rest of World) (MC8705), Connected Grid Module - 3G (Global) HSPA+/UMTS/ GSM/GPRS/EDGE |
Global |
- GSM/GPRS/EDGE: 850/1800/1900 MHz
- UMTS/HSPA+: 850/900/1900/2100 MHz
|
CGM-3G-HSPA-AB-G (all band) |
All bands (MC8705), Connected Grid Module - 3G (All band) HSPA+/UMTS/ GSM/EDGE |
Global |
- GSM/GPRS/EDGE: 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
- UMTS/HSPA+: 850/900/1900/2100 MHz
|
For system requirements, important notes, limitations, open and resolved bugs, and last-minute documentation updates, see the Release Notes on Cisco.com. For translations of the warnings that appear in this document, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco Connected Grid Router 1000 Series Routers .
When using the online publications, see the documents that match the Cisco system software version running on the 2G/3G wireless module. (To display the software version, run the show version command.)
Features
The Cisco Connected Grid 3G GSM module offers the following features:
- 3G wireless WAN support on Cisco Connected Grid Router 1000 Series platforms
- MC8705 PCI Express Mini Card wireless data modem:
– GSM data connectivity
GSM data connectivity
– GSM Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)-card interface
GSM Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)-card interface
– Supports 850 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequencies for CGM-3G-HSPA-A and CGM-3G-HSPA.
Supports 850 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequencies for CGM-3G-HSPA-A and CGM-3G-HSPA.
– Supports 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequencies for CGM-3G-HSPA-AB-G.
Supports 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequencies for CGM-3G-HSPA-AB-G.
– PCI Express chip-set interface
PCI Express chip-set interface
– Input/output hub component for embedded applications
Input/output hub component for embedded applications
- Plug-in SIM card—ISO 7816 compliant, (U)SAT commands, USIM, 3G phone book, flash memory 8/6/128-1024 MB
- Multiple antenna and cable options:
– Diversity antenna
Diversity antenna
– Indoor and outdoor external antennas
Indoor and outdoor external antennas
– Radio Frequency Ultra Low Loss coaxial cable
Radio Frequency Ultra Low Loss coaxial cable
- Support for the following technologies:
– High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA and HSPA+)
High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA and HSPA+)
– High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
– Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)
Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)
– Enhanced Data-Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE)
Enhanced Data-Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE)
– General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
- Automatic best network selection
- Always-on capability
- Auto-detect—3G WAN for fixed and modular routers automatically detects and uses the best available service
- Dynamic IP addressing
- Cellular modem upgrade over wireless link—Enables you to upgrade the firmware on the modem by using Cisco commands
- Modem management—Enables you to access modem software and hardware information, radio and network status, and data profile information by using Cisco IOS commands
- Profile Configuration—Enables you to configure the Access-Point Name (APN) profile.
- Dual SIM— Provides a failover mechanism in case the active SIM loses connectivity to the network.
Hardware Overview
The 3G GSM module is a wireless module with a mini-card cellular modem (PCI-e mini-card form factor). The module connects to the host router board of the CGR 1120 or CGR 1240.
This section covers the following topics:
Front Panel
The front panel of the 3G GSM module has the following components:
- Auxiliary port—QMA connector for the RX diversity antenna. (The connector is not used for GPS because the GPS of the host router is used.)
- QMA connector for antenna—transmits and receives RF.
- Mini-USB port—Can be used as a diagnostic port.
- LEDs:
– Wireless WAN (WWAN)
Wireless WAN (WWAN)
– Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI)
Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI)
– Service (SVC)
Service (SVC)
– SIM0 and SIM1
SIM0 and SIM1
Figure 2 shows the front panel components of the 3G GSM module.
Figure 2 Front Panel of the 3G GSM module
|
|
Captive screws (2) |
|
Auxiliary port—QMA connector for RX diversity antenna. (Connector is not used for GPS because the GPS of host router is used). |
|
|
Main port—QMA connector for antenna—transmits and receives RF. |
|
SIM card slots—Only one slot is active at any given time. |
|
|
RSVD—Mini-USB port (can be diagnostic port). |
|
LEDs—WWAN, RSSI, SVC, SIM0, and SIM1. |
Ports and LEDs
Figure 3 shows the LEDs of the 3G GSM module.
Figure 3 3G GSM module LEDs
|
|
WWAN LED |
|
RSSI LED |
|
|
SVC LED |
|
GPS LED (not used) |
|
|
SIM0 LED |
|
SIM1 LED |
Table 2 lists the ports and the LED indicators and describes their behavior. The LEDs provide a visual indication of the available services.
Table 2 LED Definitions
|
|
|
|
WWAN |
Green |
Indicates the modem status. Driven by the modem; not under software control except for diagnostic purposes. Functionality may be changed by configuring modem.
- Off : Module not powered
- On : Module is powered on and connected but not transmitting or receiving
- Slow blink : Module is powered on and searching for connection
- Fast blink : Module is transmitting or receiving
For information on modem settings, see Modem. |
RSSI |
Bi-color, green/amber |
Indicates the level of signal strength received by the software:
- Off : RSSI ≤ –110
- Solid amber : –110 < RSSI ≤ –90
- Fast green blink: –90 < RSSI ≤ –75
- Slow green blink : –75 < RSSI ≤ –60
- Solid green : RSSI > –60
|
SVC |
Bi-color, green/amber |
Service LED indicates the following:
- Off : No service
- Solid amber : GPRS/EDGE mode is in use
- Green slow blink : UMTS mode is in use
- Solid green : HSDPA/HSUPA/HSPA+ mode is in use
|
SIMx |
Bi-color, green/amber |
SIM0 and SIM1 LEDs are controlled by hardware under normal operation. SIM insertion/removal and software setting of the SIM Socket Select bit are decoded by the CPLD to control the LEDs.
- Off : No SIM
- Amber : SIM installed but not active
- Green : SIM installed and active
|
Supported Cisco Antennas
The antenna is connected to the QMA, panel-mount, 50-ohm connector located on the faceplate of the module. The modem mini-card antenna connector is a U.FL, 50-ohm, with a short 50-ohm coaxial cable to the QMA connector.
Note The antennas have either N or TNC connectors (not QMA connectors). This means that either an adapter (ANT-4G-SR-OUT-TNC) or lightning arrestor (omni or panel) is required.
The antennas have either N or TNC connectors (not QMA connectors). This means that either an adapter (ANT-4G-SR-OUT-TNC) or lightning arrestor (omni or panel) is required.
For more information about antennas, including installation procedures, see the Connected Grid Antennas Installation Guide .
Table 3 lists the Cisco antennas that are supported for use with the 3G module and the Cisco 1120 Connected Grid Router.
Table 3 CGR 1120—Supported Antennas and Cables for Use With the 3G module
Cisco 1120 Connected Grid Router
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Case 1: 2G/3G Connected Grid Module, 10’, 15’ or 20’ cable through conduit or building entry panel passthrough, Stick Omni or Directional Flat Panel antenna, 2 QMA(f) on faceplate |
RA-QMA(m) to N(m), LMR-240-DB, 10’, qty 2
|
None |
Same cable as indoor cable, that is, a single cable runs from inside to outside, through conduit. |
4G omni stick, N(f), qty 2
|
RA-QMA(m) to N(m), LMR-240-DB, 15’, qty 2
|
3G, 806-960 MHz, 1710-2170 MHz, flat panel antenna, 10/11 dBi, qty 1
|
RA-QMA(m) to N(m), LMR-240-DB, 20’, qty 2
|
| Case 2: 2G/3G Connected Grid Module, Indoor Cable, Lightning Arrestor, Outdoor Cable, Stick Omni or Directional Flat Panel antenna, 2 QMA(f) on faceplate |
RA-QMA(m) to N(m), LMR-240-DB, 10’, qty 2
|
Lightning Arrestor, N(f)-N(f), qty 2
|
RA-N(m) to N(m), LMR-400-DB, 20’, qty 2
|
4G omni stick, N(f), qty 2
|
RA-N(m)-N(m), LMR-600-DB, 30’
|
3G, 806-960 MHz, 1710-2170 MHz, flat panel antenna, 10/11 dBi, qty 2
|
Case 3. 2G/3G Connected Grid Module, Low Profile Antenna with Integrated 15” coax cable, Mounted to top of Utility Cabinet Roof, 2 QMA(f) on faceplate |
None |
Connector Adaptor, QMA(m)-TNC(f), qty 2
|
None |
4G Low Profile, Integrated, 15’ LMR-195 cable with TNC(m), qty 2
|
(f) denotes female connector
(m) denotes male connector
Table 4 lists the Cisco antennas that are supported for use with the 3G module and the Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router.
Table 4 CGR 1240—Supported Antennas and Cables for Use With the 3G Module
Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router
|
|
|
|
Adapter or Lightning Arrestor
|
|
|
Case 1: Integrated Antenna, 2G/3G Connected Grid Module, 2 QMA(f) on faceplate |
RA-QMA(m) to RA-MCX(m), LMR-100, 10.5”, qty 2
|
None |
None |
900 MHz, 3G, 806-960 MHz, 1710-2700 MHz, Monopole Antenna, Chassis Mounted, Omni-directional, qty 2
|
| Case 2: External Antenna, 2G/3G Connected Grid Module, 2 QMA(f) on faceplate |
RA-QMA(m) to RA-MCX(m), LMR-100, 10.5”, qty 2
|
Bulkhead Adapter, MCX(f) receptacle – N(f), qty 2
and Lightning Arrestor, DC Pass, N(m)-N(f), qty 2
|
RA-N(m)-N(m), LMR-400-DB, 20’, qty 2
|
4G omni stick, N(f), qty 2
|
RA-N(m)-N(m), LMR-600-DB, 30’, qty 2
|
3G, 806-960 MHz, 1710-2170 MHz, flat panel antenna, qty 2
|
Supported Cisco Cables
Table 5 lists insertion loss information and operating frequency levels for the Ultra Low Loss (ULL) LMR cables and LMR 400 cables available from Cisco for use with the 3G GSM Connected Grid module.
You can use the RG-174/U type cables to adapt the modem external antenna connection to any of the modules cables and antennas.
Table 5 Cisco Extension Cable Assemblies for 3G GSM Module
|
|
|
|
|
CAB-L240-10-Q-N |
10 ft (3.1 m) |
1.3 dB max. at 2000 MHz |
700 to 2700 MHz |
CAB-L240-15-Q-N |
15 ft (4.6 m) |
1.9 dB max. at 2000 MHz |
700 to 2700 MHz |
CAB-L240-20-Q-N |
20 ft (6.1 m) |
2.5 dB max. at 2000 MHz |
700 to 2700 MHz |
CAB-L400-20-N-N |
20 ft (6.1 m) |
1.4 dB max. at 2000 MHz |
700 to 2700 MHz |
CAB-L400-30-N-N |
30 ft (9.1 m) |
1.0 dB max. at 2000 MHz |
700 to 2700 MHz |
Interfaces
The module includes the following physical interfaces to the host:
- Power —Supplied to the module by the host.
- Wireless disable —As described in the PCI-Express Mini Card specification.
- LED output —As described in the PCI-Express Mini Card specification.
- Antenna —QMA (f) RF connector for the Rx/Tx path.
- USIM —Supported through the interface connector. The USIM cavity/connector needs to be placed on the host device for this feature.
- USB —Only communication interface to the host for data, control, and status information.
Radio Frequency Interface
The Radio Frequency (RF) interface consists of two QMA connectors on the faceplate labeled MAIN and AUX . The main antenna is mandatory; it both transmits and receives RF. The AUX QMA connector is for the RX Diversity.
Environmental Specifications
Table 6 lists the environmental specifications for the 3G GSM module.
Table 6 Module Environmental Specifications
Environmental—Operational
|
|
Operating temperature (CGR 1120) |
-13°F to 140°F (-25°C to 60°C) |
Operating temperature (CGR 1240) |
-40 to +158°F (-40 to +70°C) |
Altitude |
Up to 1500 meters |
Humidity |
RH95% non condensed |
Vibration |
1.0 g from 1.0 to 150 Hz |
Shock |
30 G half sine 6 ms and 11 ms |
Seismic |
GR63-Core, Zone 4 |
Power Specifications
There are two switching DC-DC power supplies on the 3G GSM module. The module 12V-to-3.3V DC-DC switcher and modem 12V-to-3.3V DC-DC switcher can both be power margined through CLI commands.
Note Power cables are self-shielded; no additional shielding is required.
Power cables are self-shielded; no additional shielding is required.
The 3G GSM module has a 12V power rail and 3.3V stand-by power provided by the host system. It has two 3.3V DC-DC converters on the 12V power rail: one for the module and the other for the modem.
Table 7 Power Specifications
|
|
|
12V power rail |
Max 1A (based on current draw from 2 DC-DC converters below) |
3.3V modem |
Peak current 3.75A, average power: 3W (based on average current of ~0.8A) |
3.3V module |
Peak current 500mA typical: 200mA (for LEDs and integrated circuitry) |
3.3V standby |
Peak current 500mA (for quack2/temp sensor) |
Modem
The MC8705 PCI Express mini-card modem provides EDGE, GPRS, GSM, WCDMA, HSDPA, HSUPA, and HSPA+ wireless radio connectivity technologies over the following frequency bands:
Table 8 Frequency Bands
|
|
|
GSM, GPRS, EDGE |
850 MHz, 1800 MHz, 1900 MHz |
UMTS/WCDMA/HSDPA/HSUPA/HSPA+ |
800 MHz, 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1900 MHz, 2100 MHz |
Receive diversity |
Optimized for diversity on 800, 850, 900, 1900 and 2100 MHz |
MC8705 includes an RF connector jack for use with host antennas (it does not have integrated antennas) which is used for the main Rx/Tx path.
The MC8705 modem supports the following GSM features:
- Cellular packet data profile
- Traditional modem COM port support for CSD and AT commands (concurrent with NDIS)
- Suspend/resume
- SIM application tool kit with proactive SIM commands
- Static and Dynamic IP address. The network may assign a fixed IP address or dynamically assign one using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
SIM Interface
The 3G GSM module has two GSM SIM card sockets for storing critical subscriber authentication information. The SIM card can be installed in either of the two available sockets accessible on the front panel of the 3G module. Only one slot is active at any given time—if both slots SIM0 and SIM1 are occupied by a card, then the system activates SIM0.
When the Dual SIM feature is enabled (the default), SIM0 is the primary slot and SIM1 is the secondary (failover) slot. If SIM0 loses connectivity to the network, the system automatically switches to SIM1.
- The SIM card stores critical GSM subscriber authentication information.
- The two SIM cards are powered by the modem and operate at 5 MHz.
- The SIM card is a 3.3 V device, and it has 2.8 V power applied to its power pin.
Through the software you can control which SIM is connected to the modem. Only one SIM can be connected to the modem at any time. The SIM switching circuit also provides the option of disconnecting both SIMs from the modem. The 3G Debug and SIM Control register controls the SIM connections.
By setting the SIM Socket Enable and the SIM Socket Select bit, you can control the signal and power connections from the modem to the SIM card.
Table 9 shows the options used to connect to SIM0 and SIM1 cards:
Table 9 Options to Connect to the SIM Sockets
|
|
|
|
0 |
— |
No SIM connected |
1 |
0 |
SIM0 connected |
1 |
1 |
SIM1 connected |
For information on installing and removing the SIM card, see Installing and Removing the SIM Card. See Configuring Dual SIM for information about configuring the Dual SIM feature.
Voltage Monitoring State Machine
A state machine in the 3G GSM module monitors the VCC supply and the voltage conditions that trigger state changes.
Temperature Monitoring State Machine
The state machine in the 3G GSM module monitors the embedded module temperature.
Data Rate
The actual throughput rate depends on many different factors, but the theoretical data rate for HSPA+ is 21.1 Mbps down; 5.76 Mbps up.
Memory Specifications
The memory specifications for the module are listed in Table 10 .
Table 10 Memory Specifications for the 3G GSM Module
|
|
|
|
DDR2 SDRAM |
1Gb (128 Mb) |
Not applicable (1Gb is sufficient for the Linux SDK design and modem firmware upgrade) |
DDR2 SDRAM for fixed platforms |
512 Mb (384 Mb for IOS and 128 Mb for the Linux) |
— |
Module Power States
The module has the following power states:
- Normal mode (default mode)—Module is active. Receive and Transmit modes are possible. In this state:
– The module is fully powered.
The module is fully powered.
– The module is capable of placing/receiving calls or establishing data connections on the wireless network.
The module is capable of placing/receiving calls or establishing data connections on the wireless network.
– The USB interface is fully active.
The USB interface is fully active.
Note The module unit defaults to the Normal state when VCC is first applied.
- Low power mode (airplane mode)—The module is active, but RF is disabled. In this state, RF (both Rx and Tx) is disabled on the module, but the USB interface is still active. This state is controlled though the host interface by the following software commands:
– +CFUN=0 command (AT Command Set for User Equipment (UE) (Release 6))
+CFUN=0 command (AT Command Set for User Equipment (UE) (Release 6))
– CNS_RADIO_POWER [0x1075] (MC87XX Modem CnS Reference (Document 2130602))
CNS_RADIO_POWER [0x1075] (MC87XX Modem CnS Reference (Document 2130602))
– Disable Modem command (MC87XX Modem CnS Reference (Document 2130602))
Disable Modem command (MC87XX Modem CnS Reference (Document 2130602))
Note The module goes from normal mode into low-power mode to suspend RF activity. This occurs when the module’s supply voltage exceeds either the high or low limits. The module returns to normal mode to resume RF activity. It occurs when the module’s supply voltage returns from critical to normal limits.
- Disconnected mode —No power to the module. The host power source is disconnected from the module and all voltages associated with the module are at 0 V.
CGR 1120 and CGR 1240 control the power to the module, therefore the host can stay powered on and cut the power in order to put the module into the disconnected state.
The module begins a shutdown sequence and powers off if it has been in a powered-on state for more than 10.5 seconds and the host device drives the W_Disable# signal low for:
- MC8775/MC8775V: > 50 ms
- Other devices: > 500 ms
Installing and Removing the SIM Card
For more information on the SIM interface, see SIM Interface.
Note You must reload the system after installing or changing the SIM card.
You must reload the system after installing or changing the SIM card.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) damage can occur when electronic cards or components are handled improperly, which can result in complete or intermittent failures.
To prevent ESD damage:
- Always use an ESD wrist or ankle strap and ensure that it makes good skin contact.
- Connect the equipment end of the strap to an unfinished chassis surface.
- Place a removed compact SIM card on an antistatic surface or in a static shielding bag. If the card will be returned to the factory, immediately place it in a static shielding bag.
- Avoid contact between the card and clothing. The wrist strap protects the card from ESD voltages on the body only; ESD voltages on clothing can still cause damage.
- Do not remove the wrist strap until the installation is complete.
Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Statement 1030
Caution For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. The measurement should be between 1 and 10 megohms (Mohms).
Installing the SIM Card
To install the SIM card:
Step 1 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, loosen the screw that secures the SIM slot cover in place. Rotate the cover downward so it exposes the SIM slot.
Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, loosen the screw that secures the SIM slot cover in place. Rotate the cover downward so it exposes the SIM slot.
Step 2 Insert the SIM card with the key (notch) positioned on the right-hand side. The SIM card will come in contact with the metal contacts in the socket.
Insert the SIM card with the key (notch) positioned on the right-hand side. The SIM card will come in contact with the metal contacts in the socket.
Figure 4 Installing the SIM Card
Step 3 Firmly insert the card until it clicks into place.
Firmly insert the card until it clicks into place.
Step 4 Rotate the cover back in place and secure it by tightening the screw.
Rotate the cover back in place and secure it by tightening the screw.
Removing the SIM Card
To remove the SIM card, open the cover and press the card to eject it. Remove the card and replace the cover.
Installing and Removing the 3G GSM Module
Some Cisco Connected Grid 3G Wireless Connected Grid Modules are installed into the host router at the factory.
Before You Begin Installation
Before installing the module, verify that the following guidelines have been met:
- Clearance to the I/O-side view is such that the LEDs can be easily read.
- Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise, such as radios, power lines, and fluorescent lighting fixtures. Make sure that the cabling is away from other devices that might damage the cables.
- Airflow around the module and through the vents is unrestricted.
- Temperature around the unit does not exceed 140°F (60° C). If the module is installed in a closed or multi-rack assembly, the temperature around it might be higher than normal room temperature.
- Relative humidity around the module does not exceed 95 percent (non-condensing).
- Altitude at the installation site is not higher than 4921 feet (1500 meters).
- For 10/100 and 10/100/1000 fixed ports, cable lengths from the module to connected devices are not longer than 328 feet (100 meters).
Installation Warning Statements
This section includes the basic installation warning statements. Translations of these warning statements appear in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco Connected Grid Router 1000 Series Routers .
Warning This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security. Statement 1017
Warning Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Warning To prevent the system from overheating, do not operate it in an area that exceeds the maximum recommended ambient temperature of:
140°F (60°C) Statement 1047
Warning This equipment is intended to be grounded to comply with emission and immunity requirements. Ensure that the switch functional ground lug is connected to earth ground during normal use. Statement 1064
Warning To prevent airflow restriction, allow clearance around the ventilation openings to be at least: 1.75 in. (4.4 cm) Statement 1076
Installing the 3G Module
Install the 3G module into slot 3 of the Cisco 1120 Connected Grid Router and the Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router.
To install the module into the router:
Caution The module cannot be hot swapped—to install the module, you must first power down the host router.
Step 1 Before you install the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module into the host router, read the instructions about installing and removing modules in the Hardware Installation Guide of your router.
Before you install the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module into the host router, read the instructions about installing and removing modules in the Hardware Installation Guide of your router.
Step 2 Insert the module into the slot. (CGR 1120 and CGR 1240 shown.)
Insert the module into the slot. (CGR 1120 and CGR 1240 shown.)
Step 3 Using a screwdriver, secure the two captive screws. Tighten to 5 to 8 pound-force inches (lbf-in.).
Using a screwdriver, secure the two captive screws. Tighten to 5 to 8 pound-force inches (lbf-in.).
Removing the Module
To remove the module from a router:
Caution The module cannot be hot swapped—to remove the module, you must first power down the host router.
Step 1 Before you remove the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module from the host router, power down the router as described in the Hardware Installation Guide of your router.
Before you remove the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module from the host router, power down the router as described in the Hardware Installation Guide of your router.
Step 2 Using a screwdriver, loosen the two captive screws on the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module.
Using a screwdriver, loosen the two captive screws on the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module.
Step 3 Gently pull the module out of the slot.
Gently pull the module out of the slot.
UMTS/GSM Data Network Overview
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is the most widely deployed cellular network in the world. It is based on the specification from the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). GSM was primarily designed for voice and was circuit switched but due to the popularity of cellular networks and the great demand for data services, GPRS was introduced as a packet switched data overlay over the GSM radio network. The radio and network resources of GPRS are accessed only when data actually needs to be transmitted between the GPRS mobile user and the GPRS network.
GPRS introduced several new network nodes into the GSM architecture for packet switching; they form the Mobile Packet Core. The Mobile Packet Core includes the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and the GPRS Gateway Support Node (GGSN). The SGSN tunnels IP packets towards the GGSN and detunnels packets back from the GGSN. It also carries out mobility management and billing. The GGSN provides the connectivity to the IP network and the SGSN. It is responsible for IP address assignment and is the default router for the connected User Equipment (UE).
Figure 5 shows a GSM network and the network elements it contains.
Figure 5 GSM Network Overview
The Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC) are located at the Cell site and are the common nodes for both voice and data services. They provide the radio or the physical layer connectivity between the mobile user and the mobile network. As the BSC voice and data traffic get segregated, the voice traffic goes to the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), while the data traffic is sent to the GGSN. From the GGSN, the data packets either go directly to the internet or they can be backhauled to the customer data center for a VPN connection.
UMTS is a 3G wireless system that delivers high-bandwidth data and voice services to mobile users.UMTS evolved from GSM. UMTS has an air interface based on Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (W-CDMA) and an IP core network based on general-packet radio service (GPRS). The nodes in a UMTS network are almost the same as in a GSM/GPRS network. BTS and BSC renamed as Node B and Radio Network Controller (RNC), respectively. UMTS addresses the growing demand of mobile and Internet applications for new capacity in the overcrowded mobile communications sky. The UMTS network increases transmission speed to 2 Mbps per mobile user and establishes a global roaming standard.
High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is a collection of two mobile protocols - High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High-Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA), that extends and improves the performance of existing WCDMA/UMTS protocols. HSDPA and HSUPA provide increased performance by using improved modulation schemes and by refining the protocols by which 3G modem and base stations communicate. These improvements lead to a better utilization of the existing radio bandwidth provided by WCDMA. HSPA improves the end-user experience by increasing peak data rates of up to 14 Mbit/s in the downlink and 5.76 Mbit/s in the uplink. It also reduces latency and provides up to five times more system capacity in the downlink and up to twice as much system capacity in the uplink, reducing the production cost per bit compared to original WCDMA protocols.
3G Cellular WAN MIB
This section describes the MIB definition and implementation support for Cisco cellular 3G WAN products on the customer premises equipment (CPE) end.
The 3G Cellular WAN MIB supports both CDMA and GSM set of cellular standards and includes the following technologies:
- GSM—GPRS/EDGE/UMTS/HSPA
- CDMA—1xRTT/EVDO Rev0/RevA
The 3G cellular MIB uses indexes from the cellular interface and from the modem. You can obtain the interface index using IF-MIBs and the modem index using the ENTITY MIBs.
The 3G MIB definition includes the following major sub-trees:
- Common objects
- CDMA objects
- GSM objects
- Traps or notifications
You can use MIB object c3gStandard defined in the c3gWanCommonTable to distinguish between CDMA or GSM and implementing MIB for CDMA or GSM.
Note Cisco 3G MIB supports all SNMP versions including V1, V2, V2C, and V3. For more information about SNMP, see theSNMP Software Configuration Guide for Cisco 1000 Series Connected Grid Routers (Cisco IOS).
Cisco 3G MIB supports all SNMP versions including V1, V2, V2C, and V3. For more information about SNMP, see theSNMP Software Configuration Guide for Cisco 1000 Series Connected Grid Routers (Cisco IOS).
At a high level architecture, the Cisco 3G WAN MIBs are divided into two groups and have the following structure:
1. ciscoWan3gMIBNotifs—this group defines all the trap events for Cisco 3G WAN MIBs
ciscoWan3gMIBNotifs—this group defines all the trap events for Cisco 3G WAN MIBs
2. ciscoWan3gMIBObjects—this group defines all the MIB objects for Cisco 3G WAN MIBs
ciscoWan3gMIBObjects—this group defines all the MIB objects for Cisco 3G WAN MIBs
ciscoWan3gMIBObjects
The ciscoWan3gMIBObjects group has three sub-groups:
– c3gWanCommonTable—defines the common MIB objects for both CDMA and GSM.
c3gWanCommonTable—defines the common MIB objects for both CDMA and GSM.
– c3gWanCdma—defines the MIB objects specific for CDMA set of standards (3GPP2).
c3gWanCdma—defines the MIB objects specific for CDMA set of standards (3GPP2).
– c3gWanGsm—defines the MIB objects specific for GSM set of standards (3GPP).
c3gWanGsm—defines the MIB objects specific for GSM set of standards (3GPP).
Under c3gWanGsm, there are five sub-groups:
- c3gGsmIdentityTable for GSM user identity related objects.
- c3gGsmNetworkTable for GSM network related objects.
- c3gGsmPdpProfile for GSM PDP profile related objects.
- c3gGsmRadio for GSM radio related objects.
- c3gGsmSecurityTable for GSM security related objects.
ciscoWan3gMIBNotifs
Cisco Cellular 3G WAN MIB implementation supports SNMP GET (read operation) for all MIB objects, and SNMP SET (write operation) for the following RW (read-write) objects, including:
- c3gRssiOnsetNotifThreshold
- c3gRssiAbateNotifThreshold
- c3gEcIoOnsetNotifThreshold
- c3gEcIoAbateNotifThreshold
- c3gModemTemperOnsetNotifThreshold
- c3gModemTemperAbateNotifThreshold
- c3gModemReset
- c3gModemUpNotifEnabled
- c3gModemDownNotifEnabled
- c3gServiceChangedNotifEnabled
- c3gNetworkChangedNotifEnabled
- c3gConnectionStatusChangedNotifFlag
- c3gRssiOnsetNotifFlag
- c3gRssiAbateNotifFlag
- c3gEcIoOnsetNotifFlag
- c3gEcIoAbateNotifFlag
- c3gModemTemperOnsetNotifEnabled
- c3gModemTemperAbateNotifEnabled
Note By default, all notifications are disabled. To view notifications, you must enable these notifications (seeTable 12).
By default, all notifications are disabled. To view notifications, you must enable these notifications (seeTable 12).
Note The IF MIBs also have notifications for the cellular interface objects that are used in conjunction with the notification type. When you get a notification, you must check the associated objects.
The IF MIBs also have notifications for the cellular interface objects that are used in conjunction with the notification type. When you get a notification, you must check the associated objects.
Table 11 shows various notifications and what they mean.
Table 11 Notifications
|
|
|
ModemUpNotification |
The modem was successfully recognized. |
ModemDown |
A crash or power-cycle occurred. |
Change Notification |
Notifies about changes in service objects related to this notification—previous service type to current service type. |
ConnectionStatus |
Shows the connection status. Service type is included in this notification. |
Table 12 lists the commands to enable CISCO-WAN-3G-MIB notifications for GSM events. Use these commands in controller configuration mode. To disable a notification, use the no form of the command.
Table 12 Commands for CISCO-WAN-3G-MIB GSM Event Notifications
|
|
|
gsm event connection-status mib-trap { all-gsm | active | inactive } |
Enables the generation of c3gConnectionStatusChangedNotif traps when connection changes occur.
- all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services
- active –Active state
- inactive –Inactive state
|
gsm event ecio abate { mib-trap mibtrap | threshold threshold-value } |
Enables generation of the ECIO abate trap (c3gEcIoAbateNotif) for a particular GSM service. The trap is sent when the current ECIO value goes above the abate threshold.
- mibtrap –Specifies the mib-trap technology:
– all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services – edge –EDGE Service edge –EDGE Service – gprs –GPRS Service gprs –GPRS Service – hsdpa –HSDPA Service hsdpa –HSDPA Service – hspa –HSPA Service hspa –HSPA Service – hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service – hsupa –HSUPA Service hsupa –HSUPA Service – umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service
- threshold threshold-value –Sets the threshold for sending MIB trap events to the specified value.
When the ECIO abate value is greater than the specified threshold, a MIB trap event is sent to the administrator. The range of the threshold value is from -150 to 0 dBm. |
gsm event ecio onset mib-trap { mib-trap mibtrap | threshold threshold-value } |
Enables generation of the ECIO onset trap (c3gEcIoOnsetNotif) for a particular GSM service. The trap is sent when the current ECIO value goes below the onset threshold.
- mibtrap –Specifies the mib-trap technology:
– all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services – edge –EDGE Service edge –EDGE Service – gprs –GPRS Service gprs –GPRS Service – hsdpa –HSDPA Service hsdpa –HSDPA Service – hspa –HSPA Service hspa –HSPA Service – hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service – hsupa –HSUPA Service hsupa –HSUPA Service – umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service
- threshold threshold-value –Sets the threshold for sending MIB trap events to the specified value.
When the ECIO value is less than the specified onset threshold, a MIB trap event is sent to the administrator. The range of the threshold value is from -150 to 0 dBm. |
gsm event modem-state mib-trap { all | up | down } |
Enables the generation of trap events for modem states.
- all –Enables the generation of traps for modem up and down states.
- up –Enables the generation of traps for modem up state.
- down –Enables the generation of traps for modem down state.
|
gsm event network mib-trap |
Enables generation of trap c3gNetworkChangedNotif when network changes occur. |
gsm event service mib-trap |
Enables generation of trap c3gServiceChangedNotif when service changes occur. |
gsm event temperature abate { mib-trap | threshold threshold-value } |
Sets the temperature abate threshold value for sending the c3gModemTemperAbateNotif trap.
- mib-trap –Enables or disables temperature abate MIB trap events.
- threshold threshold-value –Sets the threshold in Celsius for sending MIB trap events to the specified value.
When the temperature abate value is less than the specified threshold (lower temperature), a MIB trap event is sent to the administrator. The range of the threshold value is from -58 to 212°F (-50 to 100°C). |
gsm event temperature onset { mib-trap | threshold threshold-value } |
Sets the temperature onset threshold value for sending the c3gModemTemperOnsetNotif trap.
- mib-trap –Enables or disables temperature onset MIB trap events.
- threshold threshold-value –Sets the threshold in Celsius for sending MIB trap events to the specified value.
When the temperature onset value is greater than the specified threshold (higher temperature), a MIB trap event is sent to the administrator. The range of the threshold value is from -58 to 212°F (-50 to 100°C). |
gsm event rssi abate { mib-trap mibtrap | threshold threshold-value } |
Enables generation of the RSSI abate trap (c3gRssiAbateNotif) for a particular GSM service. The trap is sent when the current RSSI value goes above the abate threshold.
- mibtrap –Specifies the mib-trap technology:
– all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services – edge –EDGE Service edge –EDGE Service – gprs –GPRS Service gprs –GPRS Service – hsdpa –HSDPA Service hsdpa –HSDPA Service – hspa –HSPA Service hspa –HSPA Service – hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service – hsupa –HSUPA Service hsupa –HSUPA Service – umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service
- threshold threshold-value –Sets the threshold for sending MIB trap events to the specified value.
When the RSSI abate value is greater than the specified threshold (signal getting weaker), a MIB trap event is sent to the administrator. The range of the threshold value is from -150 to 0 dBm. |
gsm event rssi onset { mib-trap mibtrap | threshold threshold-value } |
Enables generation of the RSSI onset trap (c3gRssiAbateNotif) for a particular GSM service . The trap is sent when the current RSSI value goes below the onset threshold.
- mibtrap –Specifies the mib-trap technology:
– all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services all-gsm –All the GSM/UMTS Services – edge –EDGE Service edge –EDGE Service – gprs –GPRS Service gprs –GPRS Service – hsdpa –HSDPA Service hsdpa –HSDPA Service – hspa –HSPA Service hspa –HSPA Service – hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service hspa-plus –HSPA Plus Service – hsupa –HSUPA Service hsupa –HSUPA Service – umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service umts/wcdma –UMTS/WDMA Service
- threshold threshold-value –Sets the threshold for sending MIB trap events to the specified value.
When the RSSI onset value is less than the specified threshold (signal getting stronger), a MIB trap event is sent to the administrator. The range of the threshold value is from -150 to 0 dBm. |
Configuring the 3G GSM Module
The module is configured using the system software.
This section covers the following topics:
Note The 3G module can be plugged into slot 3 of the Cisco 1120 Connected Grid Router and Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router. Therefore, the interface name used to configure the module can be 3/1. Interface 3/1 is used in the configuration examples in this section.
The 3G module can be plugged into slot 3 of the Cisco 1120 Connected Grid Router and Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router. Therefore, the interface name used to configure the module can be 3/1. Interface 3/1 is used in the configuration examples in this section.
Prerequisites
To configure the 3G GSM module, you must meet the following requirements:
- Have 2G/3G network coverage where your router will be physically located. For a complete list of supported carriers, see the product data sheet.
- Subscribe to a service plan with a wireless service provider and obtain a SIM card.
- Install the SIM card before configuring the 3G GSM module. For instructions on how to install the SIM card, see the section, Installing the SIM Card.
- You must install the required antennas before you configure the 3G GSM module. See the Connected Grid Antennas Installation Guide for instructions on how to install the antennas.
- You must check your LEDs for signal reception as described in Table 2 .
- When installing within a Verizon network, be sure that you register the 3G Verizon modem as CGR 1240.
- Contact your ISP to get your access point name.
- You should be familiar with Cisco IOS.
Restrictions and Limitations
The following restrictions apply to configuring the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module:
- Data connection can be originated only by the module.
- Throughput: Due to the shared nature of wireless communications, the experienced throughput varies depending on the number of active users or congestion in a given network.
- Cellular networks have higher latency compared to wired networks. Latency rates depend on the technology and carrier. Latency may be higher because of network congestion.
- Any restrictions that are a part of the terms of service from your carrier.
Data Account Provisioning
To provision your data account, follow these procedures:
Verifying Signal Strength and Service Availability
To verify the signal strength and service availability on your modem, use the following commands in privileged EXEC mode.
DETAILED STEPS
| |
|
|
Step 1 |
show cellular interface-id network |
Displays information about the carrier network, cell site, and available service. |
Step 2 |
show cellular interface-id radio |
Shows the radio signal strength. Note The RSSI should be better than -90 dBm for steady and reliable connection. |
Step 3 |
show cellular interface-id profile |
Shows information about the modem data profiles created. |
Step 4 |
show cellular interface-id security |
Shows the security information for the modem, such as SIM and modem lock status. |
Step 5 |
show cellular interface-id all |
Shows consolidated information about the modem, profiles created, radio signal strength, network security, and so on. |
EXAMPLE
Router# show cellular 3/1 network
Router# show cellular 3/1 radio
Router# show cellular 3/1 profile
Router# show cellular 3/1 security
Router# show cellular 3/1 all
Configuring a Modem Data Profile
To configure or create a new modem data profile, enter the following command in privileged EXEC mode.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
cellular interface-id gsm profile create profile number apn authentication username password |
Creates a new modem data profile.
- interface-id —Interface name of the 3G GSM module.
- profile number— Number for the profile you are creating. You can create up to 16 profiles.
- apn— Access Point Name. You must get this information from the service provider.
- authentication— The type of authentication. For example, CHAP, PAP.
- Username— The username provided by your service provider
- Password— The password provided by your service provider.
|
EXAMPLE
Router# cellular 3/1 gsm profile create 3 apn.com chap GSM GSMPassword
Data Call Setup
To set up a data call, use the following procedures:
Figure 6 shows a typical data call setup with the 3G GSM module.
Figure 6 Data Call Setup with 3G GSM Module
Configuring the Cellular Interface
To configure the cellular interface, enter the following commands in the cellular interface mode.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
When a static IP address is required for the cellular interface, the address may be configured as ip address negotiated . During IPCP, the network ensures that the correct static IP address is allocated to the device. If a tunnel interface is configured with ip address unnumbered type number , it is necessary to configure the actual static IP address under the cellular interface, in place of ip address negotiated . For a sample cellular interface configuration, see the “Basic Cellular Interface Configuration” section.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode from the terminal. |
Step 2 |
interface cellular interface-id |
Specifies the cellular interface. |
Step 3 |
async mode interactive |
Returns a line that has been placed into dedicated asynchronous network mode to interactive mode, thereby enabling the SLIP and PPP commands in privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 4 |
ip address negotiated |
Specifies that the IP address for a particular interface is obtained via PPP/IPCP address negotiation. |
EXAMPLE
Router# configure terminal
Router (config)# interface cellular 3/1
Router (config-if)# async mode interactive
Router (config-if)# ip address negotiated
Configuring DDR
To configure dial-on-demand routing (DDR) for the cellular interface, follow this procedure.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode from the terminal. |
Step 2 |
interface cellular interface-id |
Specifies the cellular interface. |
Step 3 |
dialer in-band |
Enables DDR and configures the specified serial interface to use in-band dialing. |
Step 4 |
dialer idle-timeout seconds |
Specifies the duration of idle time, in seconds, after which a line will be disconnected. |
Step 5 |
dialer string string |
Specifies the number or string to dial. Use the name of the CHAT script here. |
Step 6 |
dialer-group number |
Specifies the number of the dialer access group to which the specific interface belongs. |
Step 7 |
exit |
Enters the global configuration mode. |
Step 8 |
dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name { permit | deny | list access-list-number | access-group } |
Creates a dialer list for traffic of interest and permits access to an entire protocol. |
Step 9 |
ip access-list access list number permit ip source address |
Defines traffic of interest. |
Step 10 |
line number |
Specifies the line configuration mode. |
Step 11 |
script dialer regexp |
Specifies a default modem chat script. |
Step 12 |
exit |
Exits line configuration mode. |
Step 13 |
chat-script hspa-R7 "" "AT!SCACT=1,1" TIMEOUT 60 "OK" or chat-script < script-name > "" "AT!SCACT=1,1" TIMEOUT < time > "OK" |
Defines the AT commands when the dialer is initiated.
- script-name —Name of the chat script
- time —Sets the time to wait for input, in seconds. The default is 5 seconds.
Note You can use the auto generated chat-script hspa-R7 or configure your own chat-script. |
Step 14 |
ip route prefix mask interface-type interface-number |
Establishes a static route through the interface. |
EXAMPLE
Router# configure terminal
Router (config)# interface cellular 3/1
Router (config-if)# dialer in-band
Router (config-if)# dialer idle-timeout 30
Router (config-if)# dialer string hspa-R7
Router (config-if)# dialer-group 1
Router (config)# dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 1
Router (config)# ip access list 1 permit any
Router (config-line)# line 3/1
Router (config-line)# script-dialer hspa-R7
Router (config-line)# exit
Router (config)# chat-script hspa-R7 "" "AT!SCACT=1,1" TIMEOUT 60 "OK"
Router (config)# ip route 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 cellular 3/1
Configuring DDR Backup
To monitor the primary connection and initiate the backup connection when needed, the router can use one of the following methods:
- Backup Interface—The backup interface that stays in standby mode until the primary interface line protocol is detected as down and then is brought up.
- Floating Static Route—The route through the backup interface has an administrative distance that is greater than the administrative distance of the primary connection route and therefore would not be in the routing table until the primary interface goes down.
- Dialer Watch—Dialer watch is a backup feature that integrates dial backup with routing capabilities.
Configuring Interfaces to Use a Backup Interface
To configure one or more interfaces to use a backup interface, use the following commands, beginning in global configuration mode.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
You cannot configure a backup interface for the cellular interface and any other asynchronous serial interface.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
interface type number |
Specifies the interface to be backed up and begins interface configuration mode. |
Step 2 |
backup interface cellular number |
Specifies the cellular interface as backup. |
Step 3 |
backup delay enable-delay-period disable-delay-period |
Specifies delay between the physical interface going down and the backup interface being enabled, and between the physical interface coming back up and the backup being disabled. |
EXAMPLE
Router(config)# interface Gi 2/1
Router(config-if)# backup interface cellular 3/1
Router(config-if)# backup delay 0 10
Configuring DDR Backup Using Dialer Watch
To enable dialer watch on the backup interface and create a dialer list, perform the following procedure in interface configuration mode.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Configure the interface to perform DDR and backup as described in the Configuring DDR and Configuring DDR Backup. Use traditional DDR configuration commands, such as dialer maps, for DDR capabilities.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode from the terminal. |
Step 2 |
interface type number |
Specifies the interface. |
Step 3 |
dialer watch-group group-number |
Enables dialer watch on the backup interface. |
Step 4 |
dialer watch-list group-number ip ip-address address-mask |
Defines a list of all IP addresses to be watched. |
Step 5 |
dialer-list dialer-group protocol protocol-name { permit | deny | list access-list-number | access-group } |
Creates dialer list for traffic of interest and permits access to an entire protocol. |
Step 6 |
ip access-list access list number permit ip source address |
Defines traffic of interest. Note Do not use the access list permit all command to avoid sending traffic to the IP network. This may result in call termination. |
Step 7 |
interface cellular interface-id |
Specifies the cellular interface. |
Step 8 |
dialer-group dialer group number |
Maps a dialer list to the dialer interface. |
EXAMPLE
Router# configure terminal
Router (config)# interface Gi 2/1
Router(config-if)# dialer watch-group 2
Router(config-if)# dialer watch-list 2 ip 10.4.0.254 255.255.0.0
Router(config)# dialer-list 2 protocol ip permit
Router(config)# access list 2 permit 10.4.0.0
Router (config)# interface cellular 3/1
Router(config-if)# dialer-group 2
Configuring DDR Backup Using Floating Static Route
To configure a floating static default route on the secondary interface beginning in the global configuration mode, perform the following tasks.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Make sure that you have ip classless enabled on your router.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode from the terminal. |
Step 2 |
ip route network-number network-mask { ip-address | interface } [ administrative distance ] [ name name ] |
Establishes a floating static route with the configured administrative distance through the specified interface. Note A higher administrative distance should be configured for the route through the backup interface, so that it is used only when the primary interface is down. |
EXAMPLE
Router# configure terminal
Router (config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 Dialer 2 track 234
Configuring Dual SIM
The Dual SIM feature implements auto-switch and failover between two cellular networks on the CGR 1000. This feature is enabled by default with SIM slot 0 being the primary slot and slot 1 being the secondary (failover) slot. Follow this procedure to configure the Dual SIM feature.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
- For auto-switch and failover to work, configure the SIM profile for slots 0 and 1 using the gsm sim profile command.
- For auto-switch and failover to work, configure the chat script without a specific profile number.
- If no SIM profile is configured, profile #1 is used by default.
- If no GSM failover timer is configured, the default failover timeout is 2 minutes.
- If no GSM SIM primary slot is configured, the default primary SIM is slot 0.
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
Step 1 |
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode from the terminal. |
Step 2 |
gsm failovertimer minutes |
Sets the timeout period, in minutes, before the 3G GSM module with dual SIMs fails over to the secondary SIM. The range is from 1 to 7. The default timeout period is 2 minutes. |
Step 3 |
gsm sim authenticate { 0 | 7 } pin slot number |
Stores the SIM CHV1 code for verification.
– 0 —Specifies an unencrypted (cleartext) PIN that follows this parameter. 0 —Specifies an unencrypted (cleartext) PIN that follows this parameter. – 7 —Specifies a hidden PIN that follows this parameter. 7 —Specifies a hidden PIN that follows this parameter.
- pin —A 4 to 8 character code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card.
- number —Slot number. Either 0 or 1.
Note This command works only when the SIM is locked. If you enter it incorrectly several times, the SIM is blocked. To avoid this, when CHV1 verification fails, you must re-enter the CHV1 code to initiate verification. |
Step 4 |
gsm sim max-retry retries |
Specifies the maximum number of times the switchover between the two SIM cards can occur. The range for retries is 0-65535. Every time a SIM switchover occurs, a counter is incremented until it reaches the maximum number of switchover attempts. Then, service is tied to one SIM (the primary SIM) and automatic SIM switchover is stopped. To see the number of switchover attempts, use the show cellular 0 security command. Setting the number of retries to 0 disables the automatic switchover and keeps the service tied to one SIM (the primary SIM). The default is 10. |
Step 5 |
gsm sim primary slot number |
Sets a SIM slot to be the primary slot.
- number —Slot number. Either 0 or 1.
By default, slot 0 is the primary slot. |
Step 6 |
gsm sim profile profile-id slot number |
Configures the SIM profile.
- profile-id —Profile number (a value from 1 to 16).
- number —Slot number. Either 0 or 1.
To create a profile, use the cellular gsm profile create command. For more information, see Configuring a Modem Data Profile. |
EXAMPLE
This example shows how to set the SIM switchover timeout period to 3 minutes:
router# configure terminal
router(config-controller)# gsm failovertimer 3
This example shows how to authenticate using an unencrypted pin:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim authenticate 0 1234 slot 0
This example shows how to set the maximum number of SIM switchover retries to 20:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim max-retry 20
This example shows how to set SIM slot 1 as the primary slot:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim primary slot 1
This example shows how to configure the SIM card in slot 0 to use profile 10:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim profile 10 slot 0
Configuration Examples
This section provides the following configuration examples:
Basic Cellular Interface Configuration
The following example shows how to configure the cellular interface to be used as a primary and is configured as the default route:
no peer default ip address
ip route 173.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Cellular3/1
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
Tunnel over Cellular Interface Configuration
The following example shows how to configure a tunnel over the cellular interface:
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
tunnel source Cellular3/1
tunnel destination <ip_address>
tunnel path-mtu-discovery
tunnel protection ipsec profile <ipsec_profile>
no peer default ip address
Troubleshooting
This section provides the necessary background information and resources available for troubleshooting the Cisco 3G module.
Verifying Data Call Setup
To verify the data call setup, follow these steps:
Step 1

After you create a modem data profile
cellular profile create command and configuring DDR on the cellular interface, send a ping from the router to a host across the wireless network.
Step 2 If the ping fails, debug the failure by using the following debug and show commands:
If the ping fails, debug the failure by using the following debug and show commands:
- debug chat
- debug dialer
- debug cellular interface-id messages callcontrol
- show cellular interface-id all
- show interface cellular
- show running-config
- show ip route
Step 3 Save the output from these commands and contact your system administrator.
Save the output from these commands and contact your system administrator.
Checking Signal Strength
If the Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) level is very low (for example, if it is less than -110 dBm) follow these steps:
Step 1

Check the antenna connection. Make sure the TNC connector is correctly threaded and tightened.
Step 2 If you are using a remote antenna, move the antenna cradle and check if the RSSI has improved.
If you are using a remote antenna, move the antenna cradle and check if the RSSI has improved.
Step 3 Contact your wireless service provider to verify if there is service availability in your area.
Contact your wireless service provider to verify if there is service availability in your area.
Verifying Service Availability
The following is a sample output for the show cellular interface-id all command for a scenario where the antenna is disconnected and a modem data profile has not been created. The errors in this case have been highlighted with >>>>>>> :
3825_GSM_3#show cellular 3/1 all
Load for five secs: 0%/0%; one minute: 0%; five minutes: 1%
Time source is hardware calendar, 19:40:43.239 UTC Wed Nov 8 2013
Modem Firmware Version = H1_0_0_7MCAP G:/WS/
Modem Firmware built = 10/26/13
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) = <specific sim number>
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) = <specific modem number>
Factory Serial Number (FSN) = X2819460388100D
Current Modem Temperature = 38 deg C, State = Normal
* - Default profile >>>>>>>> Indicates that no profile is present.
Data Connection Information
===========================
Profile 1, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 2, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 3, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 4, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 5, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 6, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 7, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 8, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 9, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 10, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 11, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 12, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 13, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 14, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 15, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 16, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Current Service Status = No service, Service Error = None >>>>>>> no service means not connected to the network.
Current Service = Combined
Packet Session Status = Inactive
Current Roaming Status = Home
Network Selection Mode = Automatic
Country = USA, Network = Cinglr
Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 310
Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 380
Location Area Code (LAC) = 6042
Routing Area Code (RAC) = 255
Primary Scrambling Code = 0
PLMN Selection = Automatic
Current Band = None, Channel Number = 0
Current RSSI = -110 dBm >>>>>>> either no antenna, or bad antenna or out of network.
Modem Security Information
==========================
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
Successful Call Setup
The following is a sample output when a call is set up using a CHAT script. It shows a received IP address from the network. Call setup is successful, and data path is open.
debug cellular 3/1 message callcontrol
*Apr 16 09:10:29.777 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: re-enable timeout
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: place call
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: Dialing cause ip (s=1.1.1.1, d=192.168.168.170)
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: Attempting to dial hspa-R7
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: CHAT3/1: Attempting async line dialer script
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: CHAT3/1: Dialing using Modem script: hspa-R7 & System script: none
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: CHAT3/1: process started
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: CHAT3/1: Asserting DTR
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: CHAT3/1: Chat script hspa-R7 started >>>>> chat script invoked
*Apr 16 09:10:31.257 PDT: CHAT3/1: Sending string: AT!SCACT=1,1
*Apr 16 09:10:31.259 PDT: CHAT3/1: Expecting string: OK...
*Apr 16 09:10:36.363 PDT: CHAT3/1: Completed match for expect: OK
*Apr 16 09:10:36.363 PDT: CHAT3/1: Chat script hspa-R7 finished, status = Success >>>> successful communication with modem
*Apr 16 09:10:36.367 PDT: [Cellular3/1]:CALLCTRL RX Link Status Indication (218 bytes):
00 DA 78 00 01 01 00 D6 07 0A 00 31 00 20 00 2D
00 20 00 31 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 04 4C 49 4E 4B 20 55 50 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 04 C0 A8 A8 13 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 04 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 04 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 54 60 16 80 04 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
*Apr 16 09:10:36.369 PDT: Incoming LSI msg: profile_id = 1, session_state = 4, pdp_context_no = 0
*Apr 16 09:10:36.369 PDT: ip address for profile id 1
*Apr 16 09:10:38.363 PDT: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Cellular3/1, changed state to up
*Apr 16 09:10:38.363 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: Dialer statechange to up
*Apr 16 09:10:38.363 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: Dialer call has been placed
*Apr 16 09:10:38.363 PDT: Cellular3/1 DirectIP: Install negotiated IP interface address 192.168.168.19
*Apr 16 09:10:38.365 PDT: Ce3/1 DDR: dialer protocol up
*Apr 16 09:10:39.363 PDT: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Cellular3/1, changed state to up
Modem Settings for North America and Carriers Operating on 850 MHz and 1900 MHz Bands
For 3G GSM module deployments in North America and for carriers operating in the 850MHz and 1900 MHz bands, the following changes to the modem settings are required to prevent long network attach times.
The output of show cellular x/x all command shows the following:
- No network attach
- RSSI value is -110 dB
- Band selection is set to AUTO
Changing Modem Settings
To change the modem settings to force the modem to scan NA (North American) bands only, follow these steps:
Step 1 Change the PRL region to '2' (the default is 1). To do this, follow the procedure in “Changing the PRL Region on the Modem” section.
Change the PRL region to '2' (the default is 1). To do this, follow the procedure in “Changing the PRL Region on the Modem” section.
Step 2 Set the band to WCDMA/GSM NA using the following Cisco IOS command:
Set the band to WCDMA/GSM NA using the following Cisco IOS command:
router# cellular 3/1 gsm band wcdma-gsm-na
Prerequisites
Before you change the PRL region, you must ensure that:
- The interface is in a shutdown mode before the chat-script is executed.
- Interface is un-shut for normal operation after the chat-script is executed.
- You must run the chat-script only once.
Changing the PRL Region on the Modem
To change the PRL region on the modem, follow these steps:
Step 1

Go to the configuration mode of the router and configure the PRL change chat-script. The following is an example using “prl” as the name of the chat script and “02” specifying the PRL region:
Router(config)# chat-script prl "" "at" TIMEOUT 5 "OK" AT!ENTERCND="A710" TIMEOUT 5 "OK" AT!CUSTOM="PRLREGION",02 TIMEOUT 5 "OK" "AT!RESET"
Note The entire chat script command must be entered in one line. Copy and paste it from this document to avoid typing errors.
Step 2 Shut down the cellular interface by entering the shut command in the configuration mode:
Shut down the cellular interface by entering the shut command in the configuration mode:
In the following example, 3/1 is a sample interface number. Replace it with the correct interface number based on the slot in which the 3G GSM module is plugged in.
Router(config)#interface cellular 3/1
Step 3 Exit the configuration mode.
Exit the configuration mode.
Step 4 To execute the chat-script, enter the start-chat prl command. In the following example, “prl” is the name of the chat script and 3/1 is the corresponding slot/port number that the cellular 3G module is plugged into.
To execute the chat-script, enter the start-chat prl command. In the following example, “prl” is the name of the chat script and 3/1 is the corresponding slot/port number that the cellular 3G module is plugged into.
Router#start-chat prl 3/1
Enabling "debug chat" and monitoring the console logs will indicate whether the chat-script executed successfully. For example,
Router(config)#logging enable
Step 5 Un-shut the cellular interface once the chat-script is over by entering the no shut command in the configuration mode:
Un-shut the cellular interface once the chat-script is over by entering the no shut command in the configuration mode:
Router(config)#interface cellular 3/1
Router(config-if)#no shut
Below is a sample output after the debugs are enabled for a successful PRL change after invoking the chat-script:
Router#start-chat prl 3/1
*May 8 11:01:04.598: CHAT3/1: Matched chat script prl to string prl
*May 8 11:01:04.598: CHAT3/1: Asserting DTR
*May 8 11:01:04.598: CHAT3/1: Chat script prl started
*May 8 11:01:04.598: CHAT3/1: Sending string: at
*May 8 11:01:04.598: CHAT3/1: Expecting string: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.638: CHAT3/1: Completed match for expect: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.638: CHAT3/1: Sending string: AT!ENTERCND="A710"
*May 8 11:01:04.638: CHAT3/1: Expecting string: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.650: CHAT3/1: Completed match for expect: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.650: CHAT3/1: Sending string: AT!CUSTOM="PRLREGION",02
*May 8 11:01:04.650: CHAT3/1: Expecting string: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.682: CHAT3/1: Completed match for expect: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.682: CHAT3/1: Sending string: AT!RESET
*May 8 11:01:04.682: CHAT3/1: Expecting string: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.690: CHAT3/1: Completed match for expect: OK
*May 8 11:01:04.690: CHAT3/1: Chat script prl finished, status = Success
*May 8 11:01:05.374: %CELLWAN-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular3/1 modem is DOWN
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface cellular 3/1
Router(config-if)#no shut
*May 9 01:48:58.398: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Cellular3/1, changed state to up
Additional References
Consult the following resources for related information about the 3G module or for technical assistance.
Hardware Overview and Installation Documents
Supported Cisco Antennas and Accessories Documents
Cisco System Software Commands Documents
Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information
Retrieving the Electronic Serial Number
If your network provider requests the 11-digit decimal equivalent of your Electronic Serial Number (ESN), you must retrieve your ESN, then convert it to decimal notation. See Converting Hexadecimal ESN to Decimal Notation.
The ESN number is located directly on the modem label in hexadecimal notation. It can also be retrieved using the Cisco IOS CLI using the show cellular 3/1 all command.
The sample output below shows the IMEI number:
CGR1K# show cellular 3/1 all
Modem Firmware Version = T1_0_3_2AP R361 CNSZ
Modem Firmware built = 04/15/11
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) = 001012345678901
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) = 357115040188141<-- Unique identifier for module
Integrated Circuit Card ID (ICCID) = 89600112051700021362
Mobile Subscriber International Subscriber
IDentity Number (MSISDN) =
Factory Serial Number (FSN) = CC3059208731007
Current Modem Temperature = 30 deg C, State = Normal
PRI SKU ID = 9900198, SKU Rev. = 1.2
Converting Hexadecimal ESN to Decimal Notation
If your network provider requests the 11-digit decimal equivalent of your Electronic Serial Number (ESN), you must retrieve your ESN, then convert it to decimal notation. See Retrieving the Electronic Serial Number.
To convert the ESN number from hexadecimal notation to decimal notation, follow this procedure:
Step 1

Start with the 8-digit HEX ESN # obtained from the label or using CLI, for example 0x603C9854. This number consists of two parts:
- 0x60—Serial number
- 3C9854—Manufacturer’s code
Step 2 Convert manufacturer’s code to decimal as shown:
Convert manufacturer’s code to decimal as shown:
Hexadecimal 0x60 equals decimal 96.
If decimal value is two digits only, prepend it with a zero to expand it to three digits.
Manufacturer’s code is thus 096.
Step 3 Convert the serial number to decimal, as shown in the example below:
Convert the serial number to decimal, as shown in the example below:
Hexadecimal 0x3C9854 equals decimal 3971156.
If decimal value is less than 8 digits, add enough zeros to make it into an 8 digit number.
Serial number is thus 03971156.
Step 4 To obtain complete 11-digit decimal ESN notation, combine manufacturer code and serial number:
To obtain complete 11-digit decimal ESN notation, combine manufacturer code and serial number:
Manufacturer code: 096
Serial #: 03971156
Decimal ESN: 09603971156
Command Reference
This reference contains Cisco IOS commands for the 3G GSM module.
For commands to enable GSM event notifications, see Table 12 .
cellular gsm band
To select a particular band manually, use the cellular gsm band command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular slot/port gsm band < band >
Note Only the bands that can be selected by the modem are listed.
Only the bands that can be selected by the modem are listed.
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
band |
GSM frequency band. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(15)T1 |
This command was introduced. |
cellular gsm mep unlock
If your modem is locked by Mobile Equipment Personalization (MEP), in order to submit the unlocking code to your service provider, use the cellular gsm mep unlock command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular < unit> gsm mep unlock < puk> < pin>
Syntax Description
unit |
Cellular modem. |
puk |
Unblocking CHV1 code to be obtained from the carrier. |
pin |
A 4 to 8 character code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
15.0(1)XA |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
- Check the modem status by using the show cellular security command.
- Entering the command will result in modem reset automatically if you have entered the correct MEP code. If the code is incorrect, the modem pauses and resends notification to enter MEP code.
Examples
To verify if the modem MEP is locked, use the show cellular security command. The following output is an example when the modem MEP is locked:
Router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = Enter MEP code
Number of Retries remaining = 255
The following example shows output for this command when you enter a correct MEP PIN:
Router#cellular 3/1 gsm mep unlock 12348765
!!!WARNING: Modem will be MEP unlocked with PIN:12348765(8).
Interface will be shutdown for MEP unlock.
This will terminate any active data connection.Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
MEP unlock code has been sent to modem for verification
Resetting modem, please wait...
*Sep 26 01:36:04.103: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 26 01:36:04.103: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
*Sep 26 01:36:05.391: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Cellular0, changed state to administratively down
*Sep 26 01:36:10.443: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 26 01:36:10.443: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 26 01:36:17.551: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Cellular0, changed state to down
*Sep 26 01:36:45.867: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
Router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
cellular gsm plmn search
To search for the available public land mobile networks (PLMNs), use the cellular gsm plmn search command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular slot/port gsm plmn search
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
This command searches for the available PLMNs or carrier networks at your location. After you issue this command, you must wait for the search completion message and then use the show cellular network command to view the list of the PLMNs available. It may take up to 5 minutes for the search to be completed.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command:
router# cellular 3/1 gsm plmn search
Dec 12 07:37:15.147: Searching for available PLMNS...Please wait...
Dec 12 07:37:45.095: PLMN search done. Please use "show cellular x/x/x network" to see available PLMNS
c2800#sh cellular 3/1 network
PLMN Name = <carrier name>
Status = Registered,, Network = Unknown
PLMN Name = <carrier name>
Status = Registered,Supports GPRS, Network = GSM
PLMN Name = <carrier name>
Status = Supports GPRS, Network = GSM
cellular gsm plmn select
To manually or automatically select from the available public land mobile network (PLMN) in an area to attach the modem to, use the cellular gsm plmn select command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular slot/port gsm plmn select { manual < mcc > < mnc > | auto }
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
manual |
Allows manual selection of the PLMN for the modem. |
mcc |
Mobile country code—a number between 0 and 65535. |
mnc |
Mobile network code—a number between 0 and 65535. |
auto |
Automatically selects the PLMN available in the area. |
Command Default
By default, PLMN is set to automatic.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Examples
The following example shows output for the cellular gsm plmn select manual command. In this example, the user selects PLMN with MCC=310, MNC=17. The show cellular x/x/x network ", shows the modem attached to the EDGE network.
Dec 12 07:38:43.799: Selecting PLMN mode to Manual...Please wait...
Dec 12 07:38:43.811: PLMN Selection Successful
router# show cellular 3/1 network
Current Service Status = Normal, Service Error = None
Current Service = Combined
Packet Service = EDGE (Attached)
Packet Session Status = Inactive
Current Roaming Status = Roaming
Network Selection Mode = Manual
Country = USA, Network = Cinglr
Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 310
Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 17
Location Area Code (LAC) = 230
Routing Area Code (RAC) = 1
Primary Scrambling Code = 0
Registered PLMN = Cingular , Abbreviated = Cinglr
Service Provider = ROGERS
The following example shows output for the cellular gsm plmn select auto command.
router# cellular 3/1 gsm plmn select auto
Dec 12 07:46:42.751: Selecting PLMN mode to Auto...Please wait...
Dec 12 07:46:42.763: PLMN Selection Successful
router#sh cellular 3/1 network
Current Service Status = Normal, Service Error = None
Current Service = Combined
Packet Service = UMTS/WCDMA (Attached)
Packet Session Status = Inactive
Current Roaming Status = Roaming
Network Selection Mode = Automatic
Country = USA, Network = CINGULAR
Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 310
Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 380
Location Area Code (LAC) = 56997
Routing Area Code (RAC) = 253
Primary Scrambling Code = 169
PLMN Selection = Automatic
Registered PLMN = CINGULAR , Abbreviated = CINGULAR
Service Provider = ROGERS
cellular gsm profile create
To create a new modem data profile, use the cellular gsm profile create command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular slot/port gsm profile create < profile number > < apn > < pdp type > < authentication > < username > < password >
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
profile number |
Number for the profile you are creating. You can create up to 16 profiles. |
apn |
Access point name. You must get this information from the service provider. |
pdp type |
PDP type. Can be set to IPv4 or ppp. Default is IPv4. |
authentication |
The type of authentication. For example, CHAP or PAP. |
username |
The username provided by your service provider. |
password |
The password provided by your service provider. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
15.1(4)M4 |
This command was modified to increase the lengths of the username and password from 32 to 128 B. |
Usage Guidelines
Some of the command parameters, such as username, password, and authentication, are optional, and do not need specification. When multiple profiles are created, you can select the profile used to set up the data call by including the profile number in the AT command ( AT!SCACT=1, < profile number >). If you do not include a profile number in the AT command ( AT!SCACT=1 ), profile 1 is used. The show cellular < cellular id > profile command indicates the default profile number.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command:
router# cellular 3/1 gsm profile create 3 apn.com ipv4 chap GSM GSMPassword
Profile 3 will be created with the following values:
Profile 3 written to modem
cellular gsm sim change-pin
To change CHV1 pin for the SIM, use the cellular gsm sim change-pin command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular < unit > gsm sim change-pin < old pin > < new pin >
Syntax Description
unit |
Cellular modem. |
pin |
A 4 to 8 digit numeric code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
15.0(1)XA |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
Typically, you can attempt to change pin only 3 times consecutively after which the SIM will get blocked, but the number of attempts will vary depending on your carrier. Using this command resets the modem.
If the old PIN is entered incorrectly, your PIN will not be changed.
You can verify the SIM status using the show cellular security command.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command:
change SIM's PIN with SIM is not locked:
----------------------------------------
#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin ?
WORD Old PIN (Length 4 to 8 digits)
#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678 ?
#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678
!!!WARNING: SIM PIN will be changed from:1234(4) to:5678(4)
Call will be disconnected. If old PIN is entered incorrectly in 3 attempt(s), SIM will be blocked!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Change CHV1 failed: CHV1 verification not enabled <<<=== SIM needs to be locked first
Change SIM PIN with authentication in IOS:
----------------------------------
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678
!!!WARNING: SIM PIN will be changed from:1234(4) to:5678(4)
Call will be disconnected. If old PIN is entered incorrectly in 3 attempt(s), SIM will be blocked!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Change CHV1 failed: Please remove 'gsm sim authenticate' from controller configuration and then retry this command
* User needs to remove Auth from IOS first before can change PIN
(config)#controller cellular 3/1
(config-controller)#no gsm sim authenticate 0 1234 <<<=== this needs to be done first before can change PIN
WARNING!!!This command will not unlock SIM. Please execute 'cellular <unit> gsm sim unlock <pin>' to unlock SIM.
Resetting modem. Call will be disconnected.
*Sep 28 18:00:44.999: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 18:00:44.999: %CISCO800-2-CELLULAR_INTERFACE_NOT_SHUTDOWN: WARNING: Cellular0 interface should be shutdown before removing modem. Reload Required to reset interface
*Sep 28 18:00:44.999: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
*Sep 28 18:00:48.167: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
*Sep 28 18:00:51.191: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 18:00:51.191: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 18:01:26.535: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 18:01:26.655: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678
!!!WARNING: SIM PIN will be changed from:1234(4) to:5678(4)
Call will be disconnected. If old PIN is entered incorrectly in 3 attempt(s), SIM will be blocked!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Resetting modem, please wait...
CHV1 code change has been completed. Please enter the new PIN in controller configuration for verfication
*Sep 28 18:02:32.051: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 18:02:32.051: %CISCO800-2-CELLULAR_INTERFACE_NOT_SHUTDOWN: WARNING: Cellular0 interface should be shutdown before removing modem. Reload Required to reset interface
*Sep 28 18:02:38.159: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 18:02:38.159: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 18:02:51.655: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
Note PIN must be numeric, not letters or any other characters.
PIN must be numeric, not letters or any other characters.
cellular gsm sim lock
To lock or unlock the SIM card provided by your service provider, use the cellular gsm sim lock command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular slot/port gsm sim lock < pin >
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
pin |
The numeric code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card.
Note The code is only numeric and cannot be alphabets or other marks.
|
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(15)T |
This command was introduced. |
15.0(1)XA |
This command was modified. |
Usage Guidelines
To verify the SIM lock, use the show cellular slot/port security command.
To change the PIN, use the cellular gsm sim change-pin command.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command:
Router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
Router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim lock 1234
!!!WARNING: SIM will be locked with pin=1234(4).
Do not enter new PIN to lock SIM. Enter PIN that the SIM is configured with.
Call will be disconnected!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
*Sep 28 17:33:04.052: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 17:33:04.056: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
*Sep 28 17:33:10.724: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 17:33:10.724: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 17:33:46.032: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 17:33:46.140: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
Router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled <<<=== lock sim is enabled
SIM Status = Locked <<<=== no authentication, user can not use SIM
SIM User Operation Required = Enter CHV1 <<<=== enter "gsm sim authentication <0|7> <PIN>
Number of Retries remaining = 3
If the modem is not ready, you will see the following output:
Router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim unlock 1234
Cellular0 Modem is still in reset, we recommend to re-execute this cmd after 60 seconds
Router(config)#controller cellular 3/1
Router(config-controller)#gsm sim authenticate ?
0 Specifies an UNENCRYPTED (cleartext) PIN will follow
7 Specifies a HIDDEN PIN will follow
Router(config-controller)#gsm sim authenticate 0 1234
CHV1 configured and sent to modem for verification
Router(config-controller)#
Router(config-controller)#end
*Sep 28 17:38:02.516: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled <<<=== SIM locked is enabled
SIM Status = OK <<<=== authentication is correct, user may use SIM
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
Output for show cellular slot/port security to verify lock:
Router#show cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled
SIM User Operation Required = Enter CHV1
Number of Retries remaining = 3
Removing authentication with SIM still in locked state:
router(config)#controller cellular 3/1
router(config-controller)#no gsm sim authenticate 0 1234
WARNING!!!This command will not unlock SIM. Please execute 'cellular <unit> gsm sim unlock <pin>' to unlock SIM.
Resetting modem. Call will be disconnected.
router(config-controller)#
router(config-controller)#
*Sep 28 17:40:07.808: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 17:40:07.808: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN
router(config-controller)#
router(config-controller)#end
*Sep 28 17:40:11.256: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
*Sep 28 17:40:14.700: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 17:40:14.700: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 17:40:50.040: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 17:40:50.148: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP
Note You will see high CPU usage when modem is not up and ready.
You will see high CPU usage when modem is not up and ready.
You will see the following output if you enter the wrong authentication:
router(config)#controller cellular 3/1
router(config-controller)#gsm sim authenticate 0 45689
CHV1 configured and sent to modem for verification
router(config-controller)#end
*Sep 28 17:42:14.700: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 17:42:14.700: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_CHV1_CONFIG_REMOVED: [Cellular0]: CHV1 verfication failed: Incorrect PIN configured. Erased the CHV1 code from router running configuration to avoid SIM blocking during modem reset/powercycle.
!!!WARNING: If the incorrect PIN is saved in router start-up configuration, please remove it manually to avoid SIM blocking during router reload
*Sep 28 17:42:15.468: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Booting up router with locked SIM without authentication configured in Cisco IOS:
*Sep 28 21:47:08.411: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 21:47:08.531: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
*Sep 28 21:47:16.675: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled
SIM User Operation Required = Enter CHV1
Number of Retries remaining = 3 <<<=== no lost to retries
Booting up router with unlock SIM with authentication configured in Cisco IOS:
*Sep 28 21:14:42.575: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
*Sep 28 21:14:45.575: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_SECURITY_SHUTDOWN: [Cellular0/0]: CHV1 PIN is configured while SIM is unlocked. Shutting down all PDP interfaces
*Sep 28 21:14:47.771: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_SECURITY_SHUTDOWN: [Cellular0/0]: CHV1 PIN is configured while SIM is unlocked. Shutting down all PDP interfaces
*Sep 28 21:14:50.611: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_SECURITY_SHUTDOWN: [Cellular0/0]: CHV1 PIN is configured while SIM is unlocked. Shutting down all PDP interfaces
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 2057 bytes
gsm sim authenticate 0 1234 <<<=== config remains with show run
shutdown <<<=== PDP context should be shut down
router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3 <<<=== no loss of retries
The following is a sample output if you lock a locked SIM:
router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim lock 1234
!!!WARNING: SIM will be locked with pin=1234(4).
Do not enter new PIN to lock SIM. Enter PIN that the SIM is configured with.
Call will be disconnected!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Lock CHV1 failed: SIM status = Locked
The following is a sample output for changing the SIM PIN when SIM is not locked:
router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin ?
WORD Old PIN (Length 4 to 8 digits)
router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678 ?
router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678
!!!WARNING: SIM PIN will be changed from:1234(4) to:5678(4)
Call will be disconnected. If old PIN is entered incorrectly in 3 attempt(s), SIM will be blocked!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Change CHV1 failed: CHV1 verfication not enabled <<<=== SIM needs to be locked first
Change SIM's PIN with authentication in Cisco IOS:
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of Retries remaining = 3
router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678
!!!WARNING: SIM PIN will be changed from:1234(4) to:5678(4)
Call will be disconnected. If old PIN is entered incorrectly in 3 attempt(s), SIM will be blocked!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Change CHV1 failed: Please remove 'gsm sim authenticate' from controller configuration and then retry this command
Note You must remove authentication from IOS first before you can change the PIN.
You must remove authentication from IOS first before you can change the PIN.
router(config)#controller cellular 3/1
router(config-controller)#no gsm sim authenticate 0 1234 <<<=== this needs to be done first before can change PIN
WARNING!!!This command will not unlock SIM. Please execute 'cellular <unit> gsm sim unlock <pin>' to unlock SIM.
Resetting modem. Call will be disconnected.
router(config-controller)#
*Sep 28 18:00:44.999: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 18:00:44.999: %CISCO800-2-CELLULAR_INTERFACE_NOT_SHUTDOWN: WARNING: Cellular0 interface should be shutdown before removing modem. Reload Required to reset interface
*Sep 28 18:00:44.999: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
router(config-controller)#end
*Sep 28 18:00:48.167: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
*Sep 28 18:00:51.191: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 18:00:51.191: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 18:01:26.535: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 18:01:26.655: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim change-pin 1234 5678
!!!WARNING: SIM PIN will be changed from:1234(4) to:5678(4)
Call will be disconnected. If old PIN is entered incorrectly in 3 attempt(s), SIM will be blocked!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Resetting modem, please wait...
CHV1 code change has been completed. Please enter the new PIN in controller configuration for verfication
*Sep 28 18:02:32.051: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 18:02:32.051: %CISCO800-2-CELLULAR_INTERFACE_NOT_SHUTDOWN: WARNING: Cellular0 interface should be shutdown before removing modem. Reload Required to reset interface
*Sep 28 18:02:38.159: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 18:02:38.159: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 18:02:51.655: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
cellular gsm sim unblock
To unblock the SIM card provided by your service provider if the CHV1 has been blocked, use the cellular gsm sim unblock command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular < unit > gsm sim unblock < puk > < pin >
Syntax Description
unit |
The cellular device for which SIM is to be unblocked. |
puk |
Unblocking 8-digit CHV1 code to be obtained from the carrier. |
pin |
A 4 to 8 character code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
15.0(1)XA |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
You can verify the unlocked mode by using the show cellular slot/port security command.
Note The device will become permanently blocked and the SIM completely unusable if the unlocking code is not entered correctly after, usually, 10 attempts. The permitted number of attempts can vary depending on the SIM.
The device will become permanently blocked and the SIM completely unusable if the unlocking code is not entered correctly after, usually, 10 attempts. The permitted number of attempts can vary depending on the SIM.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command:
Router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim unblock 60265772 1234
!!!WARNING: SIM will be unblocked with PUK=60265772(8).
If successful, SIM will be locked with new PIN:1234(4)!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
Resetting modem, please wait...
CHV1 unblock has been completed. Please enter the new PIN in controller configuration for verfication
*Sep 28 18:11:37.263: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_REMOVAL_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now REMOVED
*Sep 28 18:11:37.263: %CISCO800-2-CELLULAR_INTERFACE_NOT_SHUTDOWN: WARNING: Cellular0 interface should be shutdown before removing modem. Reload Required to reset interface
*Sep 28 18:11:37.263: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_DOWN: Cellular0 modem is now DOWN.
*Sep 28 18:11:44.183: Sierra Wireless 501modem is detected
*Sep 28 18:11:44.183: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_INSERTED_DETECTED: Cellular0 modem is now INSERTED
*Sep 28 18:12:19.467: %CELLWAN-2-SIM_LOCKED: [Cellular0]: SIM is locked
*Sep 28 18:12:19.575: %CISCO800-2-MODEM_UP: Cellular0 modem is now UP.
router#sh cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Enabled
SIM User Operation Required = Enter CHV1
Number of Retries remaining = 3
cellular gsm sim unlock
To unlock the SIM card provided by your service provider, use the cellular gsm sim unlock command in privileged EXEC mode.
cellular slot/por t gsm sim unlock < pin >
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
pin |
A 4 to 8 digit numeric code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(15)T1 |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
You can verify the unlocked mode by using the show cellular slot/port security command.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command:
Router#cellular 3/1 gsm sim unlock 1234
!!!WARNING: SIM will be unlocked with pin=1234(4), call will be disconnected!!!
Are you sure you want to proceed?[confirm]
debug cellular messages all
To print all Cisco IOS driver debug messages, use the debug cellular messages all command in EXEC mode.
debug cellular slot/port messages all
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command for debugging purposes only.
debug cellular messages async
To debug cellular async, use the debug cellular messages async command in EXEC mode.
debug cellular slot/port messages async
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command for debugging purposes only.
debug cellular messages callcontrol
To debug cellular direct IP call control, use the debug cellular messages callcontrol command in privileged EXEC mode.
debug cellular slot/port messages callcontrol
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command for debugging purposes only.
debug cellular messages data
To print Cisco IOS data path debug messages, use the debug cellular messages data command in EXEC mode.
debug cellular slot/port messages data
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command for debugging purposes only.
debug cellular messages management
To print management path messages, such as CnS, use the debug cellular messages management command in EXEC mode.
debug cellular slot/port messages management
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command for debugging purposes only.
gsm radio off
To shutdown the radio hardware resources when none of the PDP contexts are in use, particularly in areas where wireless user density is huge, and to turn on power save mode, use the gsm radio off command in the configuration mode.
gsm radio off
Use the no form of this command to turn power save mode off, or to turn radio on. When you use the no form of this command, you also must enter a no shut command on the cellular interface.
Command Modes
Configuration
Command History
|
|
|
15.1(1)T |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
To check whether power save mode is ON or OFF on a 3G GSM module, use the show controllers cellular slot/port command or the show run command and check for the relevant information.
Examples
The following example shows output for this command when you enter a correct MEP PIN:
Router(config-controller)#gsm radio off
Warning: Not all PDP contexts are in shutdown state
Please shutdown all the interfaces manually and re-enter this command.
Router(config-controller)#
Router(config-controller)#int c0
Router(config)#controller cellular 3/1
Router(config-controller)#gsm radio off
WARNING(Controller cellular 3/1): Radio power OFF setting will NOT persists if router
or modem resets. Save to startup configuration.Use "no gsm radio off" to turn radio power ON
Router(config-controller)#end
To verify, use the show run , show controller or the show cellular radio commands. The following examples shows the sample output when the radio is turned off for the three commands:
Building configuration...
Router#sh controller cellular 3/1
3G Modem-HSPA/UMTS/EDGE/GPRS-850/900/1800/1900/2100MHz / Global,
Power save mode is ON <<<====
Router#sh cellular 3/1 radio
Radio power mode = OFF <<<===, Reason = User request
Current Band = None, Channel Number = 0
Number of nearby cells = 1
Primary Scrambling Code = 0xA9
RSCP = -100 dBm, ECIO = -12 dBm
gsm sim authenticate
To store the SIM CHV1 code for verification, use the gsm sim authenticate command in configuration mode.
gsm sim authenticate auth-type pin slot number
Syntax Description
auth-type |
Authentication type: 0—Specifies an unencrypted (cleartext) PIN that follows this parameter. 7—Specifies a hidden PIN that follows this parameter. |
pin |
A 4 to 8 character code provided by your carrier to lock or unlock the SIM card. |
number |
Slot number. Either 0 or 1. |
Command Modes
Controller configuration (config-controller)
Command History
|
|
|
15.1(1)T |
This command was introduced. |
15.1(4)M |
This command was modified. |
Usage Guidelines
This command works only when the SIM is locked. If you enter it incorrectly several times, the SIM is blocked. To avoid this, when CHV1 verification fails, you must re-enter the CHV1 code to initiate verification.
Examples
The following example shows how to authenticate using an unencrypted PIN:
router(config-controller)# gsm sim authenticate 0 1234 slot 0
show cellular all
To display all the modem information in one listing, use the show cellular < interface-id > all command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular < interface-id > all
Syntax Description
< interface-id > |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the output is different for each.
Examples
The following example shows output from the show cellular < interface-id > all command.
CGR1K# show cellular 3/1 all
Modem Firmware Version = T1_0_3_2AP R361 CNSZ
Modem Firmware built = 04/15/11
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) = 001012345678901
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) = 357115040188141
Integrated Circuit Card ID (ICCID) = 89600112051700021362
Mobile Subscriber International Subscriber
IDentity Number (MSISDN) =
Factory Serial Number (FSN) = CC3059208731007
Current Modem Temperature = 30 deg C, State = Normal
PRI SKU ID = 9900198, SKU Rev. = 1.2
Access Point Name (APN) = isp.cingular
Access Point Name (APN) = isp.cingular
Access Point Name (APN) = isp.cingular
Configured default profile for active SIM 0 is profile 1.
Data Connection Information
===========================
Data Transmitted = 0 bytes, Received = 0 bytes
Profile 1, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 2, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 3, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 4, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 5, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 6, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 7, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 8, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 9, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 10, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 11, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 12, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 13, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 14, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 15, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Profile 16, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Current Service Status = Normal, Service Error = None
Current Service = Combined
Packet Service = HSPA (Attached)
Packet Session Status = Inactive
Current Roaming Status = Home
Network Selection Mode = Automatic
Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 1
Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 1
Location Area Code (LAC) = 1
Routing Area Code (RAC) = 1
Primary Scrambling Code = 0
PLMN Selection = Automatic
Registered PLMN = , Abbreviated =
Service Provider = Agilent TS34.108
Current Band = WCDMA 2100, Channel Number = 10700
Number of nearby cells = 1
Primary Scrambling Code = 0x0
RSCP = -67 dBm, ECIO = -2 dBm
Modem Security Information
==========================
SIM switchover attempts = 0
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) = Disabled
SIM User Operation Required = None
Number of CHV1 Retries remaining = 1
==========================
Incoming Message Information
----------------------------
SMS archived since booting up = 0
Total SMS deleted since booting up = 0
Storage records allocated = 30
Number of callbacks triggered by SMS = 0
Number of successful archive since booting up = 0
Number of failed archive since booting up = 0
Outgoing Message Information
----------------------------
Total SMS sent successfully = 0
Total SMS send failure = 0
Number of outgoing SMS pending = 0
Number of successful archive since booting up = 0
Number of failed archive since booting up = 0
Last Outgoing SMS Status = SUCCESS
Send-to-Network Status = 0x0
Report-Outgoing-Message-Number:
Diag Code = 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0
00 F 01 dsumtsp 10472 00 01 hsu_conf_sel_nv 00572
01 F 02 drx 07085 01 01 hsu_conf_sel_nv 00616
02 F 01 mdsp_de 00599 02 02 timer 03552
Modem Crashdump Information
===========================
Modem crashdump logging: off
show cellular connection
To display the current active connection state and data statistics, use the show cellular connection command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular slot/port connection
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the output is different for each.
Examples
The following is sample output for the 3G GSM module.
router# show cellular 3/1 connection
Data Transmitted = 1066807500 bytes, Received = 1066807500 bytes
Profile 1, Packet Session Status = ACTIVE
Profile 2, Packet Session Status = INACTIVE
Inactivity Reason = Normal inactivate state
Table 13 describes each output field.
Table 13 Output Description
|
|
|
Data Transmitted |
Total data transmitted by the modem. Can be cleared by the clear counters command. |
Data Received |
Total data received by the modem. Can be cleared by the clear counters command. |
Profile <profile number> |
Indicates the profiles configured in the modem. A total of 16 profiles can be configured. |
Packet Session Status |
Packet Data Protocol (PDP) session status of the profile. Active when the call is made and PDP context has become active in the modem. |
IP Address |
IP address of the cellular interface received during IPCP negotiation. |
Inactivity Reason |
Reason why the profile is inactive. |
show cellular hardware
To display the cellular modem hardware information, use the show cellular hardware command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular slot/port hardware
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the output is different for each.
Examples
The following example shows output for the 3G GSM module:
router# show cellular 3/1 hardware
Modem Firmware Version = H1_0_0_1MCAP C:/WS/
Modem Firmware built = 09/08/06
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) = <number>
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) = <number>
Factory Serial Number (FSN) = X2819460254100D
Current Modem Temperature = 33 deg Celsius, State = Normal
Table 14 Output Description for show cellular hardware command
|
|
|
Modem Firmware Version |
Firmware version of the modem. |
Modem Firmware Built |
Date firmware was built in mm-dd-yy format. |
Hardware Version |
Modem hardware version. |
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) |
IMSI is stored in the SIM. IMSI consists of MCC (mobile country code, 3 digits), MNC (mobile network code, 3 digits for N. America and 2 digits for rest of the world) and MSIN (mobile station identification number). The MCC and MNC in the IMSI identify the subscribers in the PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network). |
International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) |
Number that uniquely identifies the modem in a GSM/UMTS network. |
Factory Serial Number (FSN) |
Unique serial number of the modem. |
Modem Status |
Will be online if the modem has booted up correctly; otherwise will be offline and the modem will not be usable. |
Current Modem Temperature |
Radio temperature of the modem in degrees Celsius. State is normal when temperature is between 5 to 185°F (-15° to 85°C). If state reaches critical 226.4°F (108°C), the modem will be shut down. |
show cellular network
To display information about the carrier network and service, use the show cellular network command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular slot/port network
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the outputs differ.
Examples
The following example shows output for the 3G GSM module:
router# show cellular 3/1 network
Current Service Status = Normal, Service Error = None
Current Service = Combined
Packet Service = UMTS/WCDMA (Attached)
Packet Session Status = Inactive
Current Roaming Status = Roaming
Network Selection Mode = Automatic
Country = USA, Network = CINGULAR
Mobile Country Code (MCC) = 310
Mobile Network Code (MNC) = 380
Location Area Code (LAC) = 56997
Routing Area Code (RAC) = 253
Primary Scrambling Code = 169
PLMN Selection = Automatic
Registered PLMN = Cingular , Abbreviated =
Table 15 describes each output field.
Table 15 Output Description for show cellular hardware command for GSM
|
|
|
Current Service Status |
Indicates whether service is available. |
Current Service Error |
Shows the error in case there is no service |
Current Idle Digital Mode |
Idle mode of the modem. |
Packet Service |
Indicates the type of service available. For normal operation, the modem should be attached. |
Packet Session Status |
Status of PDP session. When data transfer is taking place, packet session will be active. |
Current Roaming Status |
Indicates whether the modem is in the home network or is roaming. |
Network Selection Mode |
Can be manual selection mode or automatic selection mode. Set to automatic by default. |
Country |
Country string given by the base station. |
Network |
Network string given by the base station. |
Mobile Country Code |
Country code given by the base station. The modem will be in the home network only if the country code given by the base station matches the MCC of the IMSI and the network code given by the base station matches the MNC of the IMSI. |
Mobile Network Code |
Network code given by the base station. The modem will be in the home network only if the country code given by the base station matches the MCC of the IMSI and the network code given by the base station matches the MNC of the IMSI. |
Location Area Code |
LAC given by the base station. |
Routing Area Code |
RAC given by the base station. |
Cell ID |
Cell ID given by the base station. |
PLMN Selection |
Default is automatic. |
show cellular profile
To display the cellular profile information, use the show cellular profile command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular slot/port profile
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the output is different for each.
Examples
The following example shows output for the 3G GSM module:
router# show cellular 3/1 profile
PDP Type = IPv4, Header Compression = ON
Access Point Name (APN) = enzo.cisco.com
Username: cisco, Password: lab
Primary DNS address = 127.0.2.1
Source Address = 127.0.2.1 255.255.255.0
PDP Type = IPv4, Header Compression = ON
Access Point Name (APN) = enzo.cingular.com
Username: cisco, Password: lab
Primary DNS address = 127.0.2.1
Source Address = 127.0.2.2 255.255.255.0
Table 16 Field Descriptions for show cellular profile command
|
|
|
Profile <number> |
Shows whether a particular profile is ACTIVE or INACTIVE. The profile is ACTIVE when the PDP context is active. This happens when a data call is successfully established. |
PDP Type |
Indicates the packet data protocol (PDP) type. Supported type is IPv4. |
PDP Address |
Shows the IP address assigned for the PDP context. |
Access Point Name |
Access Point Name for the profile. This information is provided by the service provider. |
Authentication |
PPP authentication supported. CHAP and PAP are supported. The type of authentication to be used is provided by the service provider. |
Username |
Username to be used for PPP authentication. This information is provided by the service provider. |
Password |
Password to be used for PPP authentication. This information is provided by the service provider. |
show cellular radio
To display the cellular modem radio statistics, use the show cellular radio command in user privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular slot/port radio [history <all | per-hour | per-min | per-sec>]
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
history |
Displays the RSSI history. |
all |
Complete RSSI history. |
per-hour |
Per-hour RSSI history. |
per-min |
Per-minute RSSI history. |
per-sec |
Per-second RSSI history. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the output is different for each.
Examples
The following example shows output for the 3G GSM module:
router# show cellular 3/1 radio
Current Band = WCDMA 1900, Channel Number = 9721
Current RSSI(RSCP) = -91 dBm
Table 17 Output Description for show cellular radio command for GSM
|
|
|
Current Band |
GPRS/UMTS band to which the modem is attached. |
Channel Number |
Channel number to which the modem is attached. |
Current RSSI |
Current radio signal strength on the modem. (-125 dbm indicates no signal.) |
show cellular security
To display the SIM status and modem lock state, use the show cellular security command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cellular slot/port security
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
15.1(1)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)T. |
Usage Guidelines
The command usage is the same for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and code division multiple access (CDMA), although the output is different for each.
Examples
The following example shows output for a 3G GSM module:
router# show cellular 3/1 security
Card Holder Verification (CHV1) ENABLED
SIM User Operation Required = CHV1
Number of Retries remaining = 3
Table 18 describes the output from this command:
Table 18 Output Description
|
|
|
Card Holder Verification |
If enabled, access to the SIM is restricted. |
SIM Status |
Indicates whether the SIM is present or removed from the SIM socket. |
SIM User Operation Required |
If the SIM is protected (for example, because of CHV1 enabled), it will indicate the type of user operation required. |
Number of Retries Remaining |
Indicates the number of attempts remaining in case the SIM is locked. If the number of retries becomes zero, the SIM is blocked and becomes unusable. |
show controllers cellular
To display 3G GSM module hardware and driver-specific information, use the show controllers cellular command in privilege EXEC mode.
show controllers cellular slot/port
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Default
There is no default for this command.
Command Modes
Privilege EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to capture the output for debugging or troubleshooting purposes only.
show interfaces cellular
To display statistics for the cellular interface, use the show interfaces cellular command in EXEC mode.
show interfaces cellular slot/port
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Default
There is no default for this command.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Usage Guidelines
When you enter this command, encapsulation should be SLIP and all signals, such as DCD, DSR, DTR, RTS, and CTS, should be up during normal operation.
Examples
The following example shows the cellular interface statistics for a 3G GSM module:
router# show interfaces cellular 3/1
Cellular3/1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is HSDPA/UMTS/EDGE/GPRS-850/900/1800/1900/2100MHz
Internet address is 1.5.97.2/32
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 384 Kbit, RxBW 2400000 Kbit, DLY 100000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Open: IPCP, loopback not set
Time to interface disconnect: idle 3w3d
Last input 00:20:21, output 00:20:21, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:00:01
Input queue: 1/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 0/16/16 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 288 kilobits/sec
30 second input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
30 second output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
*Feb 7 22:55:33.985: %CLEAR-5-COUNTERS: Clear counter on all interfaces by consoleroadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
DCD=up DSR=up DTR=up RTS=up CTS=up
show run interface cellular
To see the current running configuration for the cellular interface, use the show run interface cellular command in privileged EXEC mode.
show run interface cellular slot/port
Syntax Description
slot/port |
Numeric values that indicate the router slot and port. |
Command Default
There is no default for this command.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.4(11)XV |
This command was introduced. |
12.4(15)T |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T. |
Examples
The following example shows the output of the command for a 3G GSM module:
router#show running-config interface cellular 3/1
dialer idle-timeout 2147483
no peer default ip address
Technical Assistance
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks . Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
No combinations are authorized or intended under this document.
© 2014 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.


The Cisco Connected Grid 3G GSM Module is a field-replaceable unit.

GSM Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)-card interface
Supports 850 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequencies for CGM-3G-HSPA-A and CGM-3G-HSPA.
Supports 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz frequencies for CGM-3G-HSPA-AB-G.
PCI Express chip-set interface
Input/output hub component for embedded applications
Indoor and outdoor external antennas
Radio Frequency Ultra Low Loss coaxial cable
High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA and HSPA+)
High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)
Enhanced Data-Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE)
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI)



The antennas have either N or TNC connectors (not QMA connectors). This means that either an adapter (ANT-4G-SR-OUT-TNC) or lightning arrestor (omni or panel) is required.

Power cables are self-shielded; no additional shielding is required.
The module is fully powered.
The module is capable of placing/receiving calls or establishing data connections on the wireless network.
The USB interface is fully active.

+CFUN=0 command (AT Command Set for User Equipment (UE) (Release 6))
CNS_RADIO_POWER [0x1075] (MC87XX Modem CnS Reference (Document 2130602))
Disable Modem command (MC87XX Modem CnS Reference (Document 2130602))


You must reload the system after installing or changing the SIM card.


Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, loosen the screw that secures the SIM slot cover in place. Rotate the cover downward so it exposes the SIM slot.
Insert the SIM card with the key (notch) positioned on the right-hand side. The SIM card will come in contact with the metal contacts in the socket.

Firmly insert the card until it clicks into place.
Rotate the cover back in place and secure it by tightening the screw.






Before you install the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module into the host router, read the instructions about installing and removing modules in the Hardware Installation Guide of your router.
Insert the module into the slot. (CGR 1120 and CGR 1240 shown.)
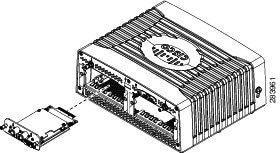

Using a screwdriver, secure the two captive screws. Tighten to 5 to 8 pound-force inches (lbf-in.).

Before you remove the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module from the host router, power down the router as described in the Hardware Installation Guide of your router.
Using a screwdriver, loosen the two captive screws on the Cisco Connected Grid 3G Module.
Gently pull the module out of the slot.


Cisco 3G MIB supports all SNMP versions including V1, V2, V2C, and V3. For more information about SNMP, see theSNMP Software Configuration Guide for Cisco 1000 Series Connected Grid Routers (Cisco IOS).
ciscoWan3gMIBNotifs—this group defines all the trap events for Cisco 3G WAN MIBs
ciscoWan3gMIBObjects—this group defines all the MIB objects for Cisco 3G WAN MIBs
c3gWanCommonTable—defines the common MIB objects for both CDMA and GSM.
c3gWanCdma—defines the MIB objects specific for CDMA set of standards (3GPP2).
c3gWanGsm—defines the MIB objects specific for GSM set of standards (3GPP).

By default, all notifications are disabled. To view notifications, you must enable these notifications (seeTable 12).

The IF MIBs also have notifications for the cellular interface objects that are used in conjunction with the notification type. When you get a notification, you must check the associated objects.

The 3G module can be plugged into slot 3 of the Cisco 1120 Connected Grid Router and Cisco 1240 Connected Grid Router. Therefore, the interface name used to configure the module can be 3/1. Interface 3/1 is used in the configuration examples in this section.

0 —Specifies an unencrypted (cleartext) PIN that follows this parameter.
7 —Specifies a hidden PIN that follows this parameter.
After you create a modem data profile cellular profile create command and configuring DDR on the cellular interface, send a ping from the router to a host across the wireless network.
If the ping fails, debug the failure by using the following debug and show commands:
Save the output from these commands and contact your system administrator.
Check the antenna connection. Make sure the TNC connector is correctly threaded and tightened.
If you are using a remote antenna, move the antenna cradle and check if the RSSI has improved.
Contact your wireless service provider to verify if there is service availability in your area.
Change the PRL region to '2' (the default is 1). To do this, follow the procedure in “Changing the PRL Region on the Modem” section.
Set the band to WCDMA/GSM NA using the following Cisco IOS command:
Go to the configuration mode of the router and configure the PRL change chat-script. The following is an example using “prl” as the name of the chat script and “02” specifying the PRL region:
Router(config)# chat-script prl "" "at" TIMEOUT 5 "OK" AT!ENTERCND="A710" TIMEOUT 5 "OK" AT!CUSTOM="PRLREGION",02 TIMEOUT 5 "OK" "AT!RESET"
Shut down the cellular interface by entering the shut command in the configuration mode:
Exit the configuration mode.
To execute the chat-script, enter the start-chat prl command. In the following example, “prl” is the name of the chat script and 3/1 is the corresponding slot/port number that the cellular 3G module is plugged into.
Un-shut the cellular interface once the chat-script is over by entering the no shut command in the configuration mode:
Start with the 8-digit HEX ESN # obtained from the label or using CLI, for example 0x603C9854. This number consists of two parts:
Convert manufacturer’s code to decimal as shown:
Convert the serial number to decimal, as shown in the example below:
To obtain complete 11-digit decimal ESN notation, combine manufacturer code and serial number:

Only the bands that can be selected by the modem are listed.

PIN must be numeric, not letters or any other characters.

You will see high CPU usage when modem is not up and ready.

You must remove authentication from IOS first before you can change the PIN.

The device will become permanently blocked and the SIM completely unusable if the unlocking code is not entered correctly after, usually, 10 attempts. The permitted number of attempts can vary depending on the SIM.

 Feedback
Feedback