Information About the AWS Integration
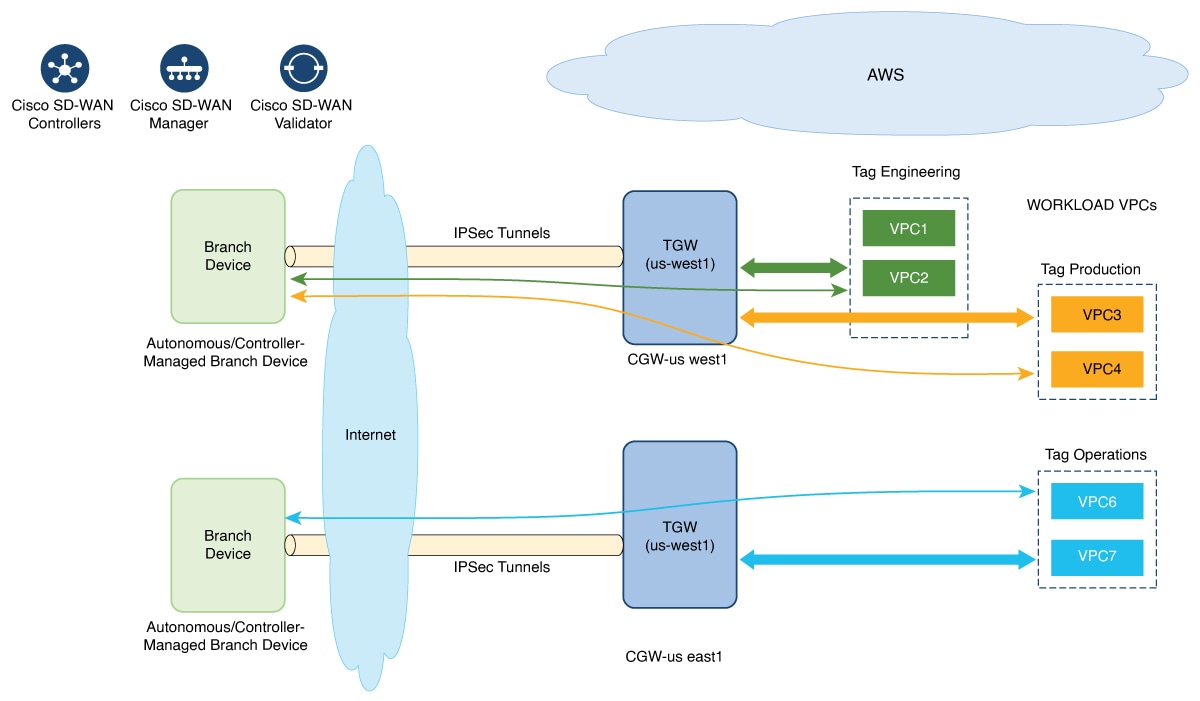
A transit gateway is a network transit hub that you can use to interconnect your VPC and on-premises networks. You can attach a VPC, or a VPN connection to a transit gateway. It acts as a virtual router for traffic flowing between your VPC and VPN connections.
You can configure and manage Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud environments through the Cisco SD-WAN Manager controller. A configuration wizard in Cisco SD-WAN Manager automates the bring-up of the transit gateway to your public cloud account and automates the connections between public-cloud applications and the users of those applications at branches in the overlay network. This feature works with AWS virtual private clouds (VPCs) on Cisco cloud routers.
Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud supports integration with multiple AWS accounts.
AWS Branch Connect with SD-Routing Devices
When you deploy SD-Routing Cloud OnRamp through SD-Routing based branch, it should be deployed though the SD-Routing based Config group. Also, you should set the bootup license level manually through the respective CG device CLI template for the tunnel-based config to work during Cloud OnRamp connectivity.
The edge/branch devices connect to the host VPCs in the cloud over secure point-to-point tunnels. IPSec tunnels are set up between edge devices and the AWS Transit Gateway (TGW). These tunnels carry the branch VPNs or VRFs traffic and BGP routing traffic. Using BGP, the devices and the transit gateway exchange the routing information and build routing tables.
The SD-Routing branch device can have only the default VRF. You can use this default VRF to mapping through the SD-Routing Cloud OnRamp branch connect. You cannot use any other VPN/VRF for mapping. Along with SD-Routing soluction, you can have multiple VPN mapping for SD-WAN solution. Both the Cisco SD-WAN and Cisco SD-Routing connection can co-exist.
 Note |
A branch site can have more than one branch endpoint connecting to the cloud. |
Benefits of Cloud OnRamp for SD-Routing Devices
SD-Routing Cloud OnRamp supports secure cloud connectivity for the cloud workloads deployed in AWS or Azure using SD-Routing devices through Multicloud workflows.
Prerequisites for Cloud onRamp
The following are the prerequisites for Cloud onRamp:
-
The branch site should be in reachable state and the status should be In-Sync.
-
The branch site should have one of these boot level licenses:
-
network-advantage
-
network-essentials
-
network-premier
Otherwise, when you attach the site, the IPSec tunnel configurations will not get applied.
-
-
Interface should have a public IP address assigned that is reachable from AWS TGW or Azure vHub, or NAT on the branch device. Otherwise, the tunnel will not be formed between the branch site and AWS TGW or Azure vHub.
-
SD-routing branch should be deployed using or ported to Config-Group.
-
Refer to Onboarding the Existing Devices and Onboarding the New SD-Routing Device Using Config Group Automated Workflow sections to On-board or to get SD-Routing device compatible to use the Cloud onRamp feature.
-
Limitations
-
Cloud OnRamp does not support peering between the TGWs in different regions.
Configure AWS Integration on SD-Routing Devices
This section explains the workflows to onboard the SD-Routing devices for features:
-
Onboarding the existing devices:
-
Converting the existing Autonomous Device to SD-Routing device and use the Cloud onRamp feature
-
Converting the existing Non-config group based SD-Routing devices to use Cloud onRamp feature
-
-
Onboarding new SD-Routing device using Config Group Automated Workflow
Onboarding the Existing Devices
To onboard the existing devices, perform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
To deploy or convert the existing autonomous device to SD-Routing device manually, follow the instruction provided in the section Onboarding the Devices Manually. Or |
||
|
Step 2 |
To deploy SD-Routing device using the Quick Connect Workflow follow the instruction provided in the section Onboarding the SD-Routing Devices Using Bootstrap. Pre-requisities: |
||
|
Step 3 |
To port the SD-Routing device to Configuration Group, do the following:
|
||
|
Step 4 |
To add the Configuration Group on the SD-routing device, do the following:
|
||
|
Step 5 |
Click on Associate Devices and selct the Site ID for the SD-routing device and proceed with associtation. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Click on the deployment status link and ensure that the deployent is successful. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Check the following details in the Configuration > Devices page.
|
||
|
Step 8 |
To verify the status, use the show sd-routing connections summary command. |
Onboarding the New SD-Routing Device Using Config Group Automated Workflow
To onboard the new SD-Routing device using Config Group automated workflow, perform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration > Configuration Groups > Add Configuration Group > Create SD-Routing Config . |
|
Step 2 |
In the Name field, enter a name for the configuration group. |
|
Step 3 |
In the Description field, enter the description. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Create SD-Routing Config. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Configuration Group Created pop-up dialog box, click the No, I will Do It Later option. |
|
Step 6 |
From the What's Next? section, click Go to Configuration Groups. |
|
Step 7 |
Click (…) adjacent to the configuration group name and choose Edit. |
|
Step 8 |
Click on the Cli profile under Feature Profiles and select Unconfigured. |
|
Step 9 |
Click Create New. |
|
Step 10 |
Configure the basic Configuration Group. This example shows the minimum CLIs for the Config Group. |
|
Step 11 |
Click Save. |
|
Step 12 |
Click on Associate Devices > Associate Devices. |
|
Step 13 |
Choose Unassigned and select one UUID . |
|
Step 14 |
Click Save. |
|
Step 15 |
You can provision the device with the respective Sytem IP, Site ID, and Host name. |
|
Step 16 |
Click Next . |
|
Step 17 |
Click Deploy, |
|
Step 18 |
Click on the deployment status link and ensure that the deployent is successful. |
|
Step 19 |
Go to Configuration > Devices > against the uuid three dots click "generate bootstrap " enter the wan interface name (eg: GigabitEthernet1) and genreta the bootstrap |
|
Step 20 |
Click (…) adjacent to the UUID name and click Generate bootstrap . |
|
Step 21 |
In the WAN Interface field, enter interface name a GigabitEthernet1 and generatethe bootstrap. |
|
Step 22 |
Use the bootstrap to deploy the Cisco 8000v instance against the respective AMI in AWS console and assign the public IP to the WAN interface. |
|
Step 23 |
Click on the deployment status link and ensure that the deployment is successful. |
|
Step 24 |
Check the following details in the Configuration > Devices page.
|
|
Step 25 |
To verify the status, use the show sd-routing connections summary command. |
Create AWS Cloud Account
To create the AWS cloud account, follow these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration > Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud. The Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud dashboard displays. |
||||||||
|
Step 2 |
Click Associate Cloud Account in the Setup pane. Note the external Id from the Associate Cloud Account page. |
||||||||
|
Step 3 |
In the Cloud Provider field, choose Amazon Web Services from the drop-down list. |
||||||||
|
Step 4 |
Enter the account name in the Cloud Account Name field. |
||||||||
|
Step 5 |
(Optional) Enter the description in the Description field. |
||||||||
|
Step 6 |
In Use for Cloud Gateway, choose Yes if you want to create cloud gateway in your account, or choose No. |
||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Choose the authentication model you want to use in the field Login in to AWS With.
If you choose the Key model, then provide API Key and Secret Key in the respective fileds. OrIf you choose the IAM Role model, then create an IAM role with Cisco SD-WAN Manager provided External ID. Note the displayed external Id from the window and provide the Role ARN value that is available when creating an IAM role. Starting from Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.4.1a, to create an IAM role, you must enter the External Id provided by Cisco SD-WAN Manager into a policy by using the AWS Management Console. Do the following:
|
||||||||
|
Step 8 |
Click Add.To view or update cloud account details, click ... on the Cloud Account Management page. You can also remove the cloud account if there are no associated host VPC tags or cloud gateways. |
Configure Cloud Global Settings
To configure cloud global settings for AWS, peform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose . Click Cloud Global Settings in the Setup pane. The Cloud Global Settings window appears. |
|
Step 2 |
In the Cloud Provider field, choose Amazon Web Services. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Cloud Gateway Solution drop-down list to choose the Transit Gateway–Branch-connect.
|
|
Step 4 |
In the Cloud Gateway BGP ASN Offset field, enter the value. |
|
Step 5 |
Choose the Intra Tag Communication. The options are Enabled or Disabled |
|
Step 6 |
Choose the Program Default Route in VPCs towards TGW/Core. The options are Enabled or Disabled. |
|
Step 7 |
Enable or disable the Enable Periodic Audit field by clicking Enabled or Disabled. If you the enable periodic audit, Cisco SD-WAN Manager triggers an automatic audit every two hours. This automatic audit takes place in the background, and a discrepancies report is generated. |
|
Step 8 |
Enable or disable the Enable Auto Correct field by clicking Enabled or Disabled. If you enable the auto correct option, after every periodic audit is triggered, all the recoverable issues that are discovered are auto corrected. |
|
Step 9 |
Click Add or Update. |
Discover Host Private Networks
You can discover host VPCs in all the accounts across all the respective regions of the account that are available. When the Host VPC Discovery is invoked, the discovery of the VPCs is performed without any cache.
To discover the host private networks, peform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose . Click Host Private Networks under Discover. The Discover Host Private Networks window appears with the list of available VPCs. The host VPC table includes the following columns:
Click a column to sort the VPCs, as required. |
|
Step 2 |
Click the Region drop-down list to select the VPCs based on particular region. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Tag Actions to perform the following actions:
A number of host VPCs can be grouped under a tag. All VPCs under the same tag are considered as a singular unit. |
Create a Cloud Gateway
Cloud gateway is an instantiation of Transit VPC (TVPC)and transit gateway in the cloud. To create a cloud gateway, perform the following steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration > Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud. Click Create Cloud Gateway under Manage. The Manage Cloud Gateway - Create window appears. |
|
Step 2 |
In the Cloud Provider field, choose Amazon Web Services from the drop-down list. |
|
Step 3 |
In the Cloud Gateway Name field, enter the cloud gateway name. |
|
Step 4 |
(Optional) In the Description, enter the description. |
|
Step 5 |
Choose the account name from the Account Name drop-down list. |
|
Step 6 |
Choose the region from the Region drop-down list. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Add to create a new cloud gateway. |
Attaching Sites
To attach sites to a cloud gateway, perform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration > Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud > Gateway Management under Manage. The Cloud Gateway window appears. A table displays the list of cloud gateways with cloud account name, ID, cloud type, transit gateway. For each of the cloud gateways, you can view, delete, or attach more sites. |
|
Step 2 |
For the desired cloud gateway, click (…) and choose Cloud Gateway. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Attach SD-Routing. |
|
Step 4 |
Click Attach Sites. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Next. The Attach Sites - Select Sites window appears. The table shows the sites with the selected WAN interface. |
|
Step 6 |
Choose one or more sites from Available Sites and move them to Selected Sites. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Next. |
|
Step 8 |
On the Attach Sites - Site Configuration window, enter the Tunnel Count. The tunnel count ranges from 1 to 8 and each tunnel gives a bandwidth of 2.5 Gbps. |
|
Step 9 |
On Attach Sites - Select Interface window, enter the details of the Interface . This interface is used to form the tunnel to TGW. |
|
Step 10 |
For the Accelerated VPN option, choose Enabled or Disabled. AWS Global Accelerator helps in optimized connectivity to the cloud. |
|
Step 11 |
For the Use selected interface as Preferred Path option, chose Enabled or Disabled. Multicloud workflow will configure the selected WAN interface as the default path. |
|
Step 12 |
Click Next. |
|
Step 13 |
Click Save and Exit. If the configuration is successful, you see a message that indicates that the branch devices are successfully attached. |
|
Step 14 |
To verify the status of the device, use the show running config command. |
|
Step 15 |
To view the status of the configuration, from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration> Configuration Groups> Feature Profile and click View Details. |
Detaching Sites
To detach sites to a cloud gateway, perform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration > Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud >Cloud Gateways. A table displays the list of cloud gateways with cloud account name, ID, cloud type, transit gateway. |
|
Step 2 |
For the desired cloud gateway, click ... and choose Cloud Gateway. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Attach SD-Routing. |
|
Step 4 |
Choose one or more sites from Available Sites and click Detach Sites. The Are you sure you want to detach sites from cloud gateway? window appears. |
|
Step 5 |
Click OK. The sites attached to a cloud gateway are detached. |
|
Step 6 |
To view the status of the configuration, from the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration> Configuration Groups> Feature Profile and click View Details. |
Editing a Site
To edit a site, perform these steps:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
From the Cisco SD-WAN Manager menu, choose Configuration > Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud >Cloud Gateways. A table displays the list of cloud gateways with cloud account name, ID, cloud type, transit gateway. |
|
Step 2 |
For the desired cloud gateway, click ... and choose Cloud Gateway. |
|
Step 3 |
Click Edit Site Details. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Edit Site Details dialog box, enter the tunnel count. |
|
Step 5 |
Enable or disable the Accelerated VPN field. By default, this field is Enabled. |
|
Step 6 |
Enable or disable the Use Select Interface as Preferred path field. By default, this field is Enabled. |
|
Step 7 |
Click Submit. |
Intent Management - Connectivity
Mapping workflow in Cisco SD-WAN Manager enables connectivity between Cisco Catalyst SD-Routing VPNs (segment) and VPCs, and VPCs to VPCs. VPCs are represented based on the tags.
 Note |
The SD-Routing branch device can have only the Default VRF. You can use this default VRF to mapping through the SD-Routing Cloud OnRamp branch connect. You cannot use any other VPN/VRF for mapping. Along with SD-Routing solution, you can have multiple VPN mapping for SD-WAN solution. Both the Cisco SD-WAN and Cisco SD-Routing connection can co-exist. |
When the system records the intent for connectivity, mapping is realized in cloud in regions where cloud gateway is present. Mapping intents can be entered without cloud gateways being present in different regions. The user mapping intent is preserved and realized when a new cloud gateway or mapping change is discovered. As and when cloud gateways get instantiated in different regions, the mapping intents are realized in those regions. Similarly, tagging operations can influence the mapping in different regions as well and mappings as per the tags are realized in the cloud.
In the Cloud OnRamp for Multicloud dashboard, click Connectivity under Management. The Intent Management - Connectivity window appears. The window displays the connectivity status with the following legends:
-
Blank - Editable
-
Grey color - System Defined
-
Blue color - Intent Defined
-
Green color - Intent Realized
-
Red color - Intent Realized With Errors
On the Connectivity window, you can:
-
View the changes in connectivity as required.
-
Filter and sort.
-
Define the connectivity independent of cloud gateways in different regions.
-
Realize the connectivity in regions wherever cloud gateways are present.
 Feedback
Feedback