Information About Lawful Intercept
Lawful intercept is a process that enables a Law Enforcement Agency (LEA) to perform electronic surveillance on an individual (a target) as authorized by a judicial or administrative order. To facilitate the lawful intercept process, certain legislation and regulations require service providers (SPs) and Internet service providers (ISPs) to implement their networks to explicitly support authorized electronic surveillance.
Lawful Intercept Process
When triggering a lawful intercept for communications from Site A to Site B, the edge platform duplicates the traffic and sends an unencrypted copy of the traffic to a target server, which hosted in the customer network designed for Lawful Intercept. Cisco SD-WAN Manager ensures that Cisco SD-WAN Manager users (non-Lawful Intercept users), who have access to Site A and Site B for any information, are unaware of the duplicated flow of information.
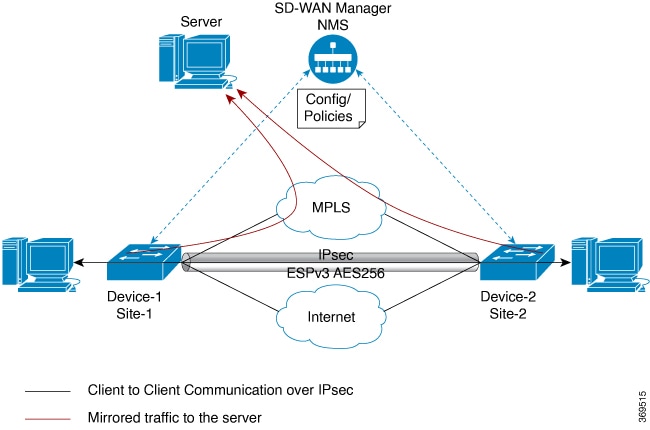

Licence-based Lawful Intercept
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN solution is a term-based licensed feature. This feature license enables the Cisco SD-WAN Manager component of the Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN solution and allows the customer to access the Lawful Intercept function. Once the Lawful Intercept license is enabled on the solution, Cisco SD-WAN Manager provides a new privilege in the Manage Users menu of the Cisco SD-WAN Manager UI. By default, this privilege is available to all admin users. In addition, administrators can assign the Lawful Intercept privilege to any other user.
Any user with Lawful Intercept privilege would be able to enable Lawful Intercept function on an edge device in the WAN network. All changes made by any user with Lawful Intercept function would be audit logged and changes will be recorded just like any other change made by any user in the system.
After acquiring a court order or warrant to perform surveillance, any user with Lawful Intercept privilege will be able to make Lawful Intercept related changes on sites with a warrant.
-
Install license for Lawful Intercept on Cisco SD-WAN Manager.
-
Create an lawful intercept admin (liadmin) user on Cisco SD-WAN Manager. The liadmin user must be associated with the user group, Basic.
-
Login to Cisco SD-WAN Manager as liadmin user and configure Lawful Intercept specific templates.
-
Cisco SD-WAN Manager automatically pushes templates to all Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN devices with Lawful Intercept compatible images.
-
Configuration is pushed to device from Cisco SD-WAN Manager using the following:
-
SNMP TAP MIB configuration
-
SNMP Access list (li-acl keyword)
-
MD List
-
-
SNMP SET is sent to device to achieve the following goals:
-
To setup and activate MD entry on Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN devices.
-
To setup and activate stream to be intercepted.
-
To activate or deactivate intercept
-
-
Mediation Device receives the intercepted or mirrored traffic.
VRF-Aware Lawful Intercept
VRF Aware Lawful Intercept is the ability to provision a Lawful Intercept wiretap on IPv4 data in a particular VPN. This feature allows a LEA to lawfully intercept targeted data within that VPN. Only IPv4 data within that VPN is subject to the VRF-based Lawful Intercept tap.
To provision a VPN-based IPv4 tap, the LI administrative function (running on the mediation device) uses the CISCO-IP-TAP-MIB to identify the name of the VRF table that the targeted VPN uses. The VRF name is used to select the VPN interfaces on which to enable LI in order to execute the tap. The device determines which traffic to intercept and which mediation device to send the intercepted packets based on the VRF name (along with the source and destination address, source and destination port, and protocol).

 Feedback
Feedback