Overview of Cisco SD-WAN Multitenancy
With Cisco SD-WAN multitenancy, a service provider can manage multiple customers, called tenants, from Cisco vManage. The tenants share Cisco vManage instances, Cisco vBond Orchestrators, and Cisco vSmart Controllers. The domain name of the service provider has subdomains for each tenant. For example, the multitenancy.com service provider can manage the tenants Customer1 (Customer1.multitenancy.com) and Customer2 (Customer2.multitenancy.com).
Following are the key features of Cisco SD-WAN multitenancy:
-
Full enterprise multitenancy: Cisco SD-WAN supports multitenancy and offers enterprises the flexibility of segregated roles such as service provider and tenants. Service providers can use multitenancy to provide Cisco SD-WAN service offerings to their customers.
-
Multi-tenant Cisco vManage:
-
Cisco vManage is deployed and configured by the service provider. The provider enables multitenancy and creates a Cisco vManage cluster to serve tenants. Only the provider can access a Cisco vManage instance through the SSH terminal.

Note
To connect to a device through SSH, use the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface; this IP address is assigned by Cisco vManage. Do not use a user-configured system IP address to connect to a device through SSH.You can find the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface from the output of the show interface description command. Alternatively, you can launch the device SSH terminal from Cisco vManage and find the vmanage_system IP address from the first line of the log-in prompt.
-
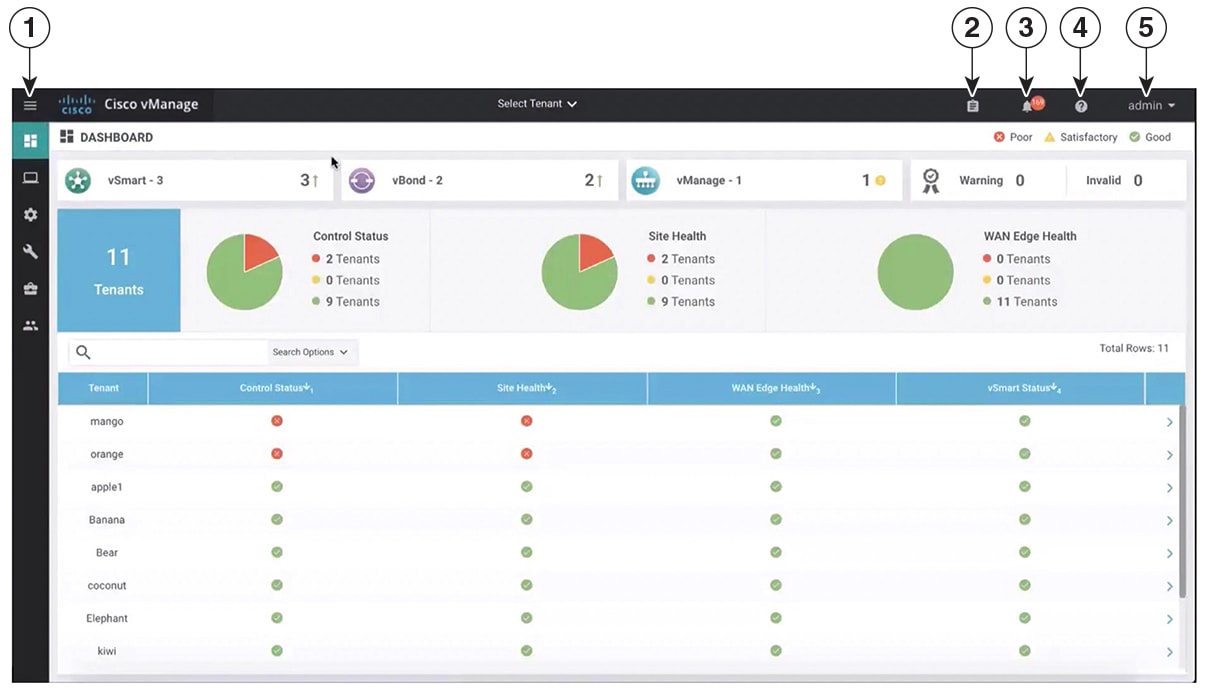
Cisco vManage offers service providers an overall view of the SD-WAN multi-tenant deployment and allows a provider to manage the shared Cisco vBond Orchestrator and Cisco vSmart Controller devices. Cisco vManage also allows service providers to monitor and manage the deployments of each tenant.
-
Cisco vManage allows tenants to monitor and manage their deployment. Through Cisco vManage, tenants can deploy and configure WAN edge devices. Tenants can also configure custom policies on assigned Cisco vSmart Controllers.
-
-
Multi-tenant Cisco vBond Orchestrators:
-
Cisco vBond Orchestrators are deployed and configured by the service provider. Only the provider can access a Cisco vBond Orchestrator through the SSH terminal.

Note
To connect to a device through SSH, use the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface; this IP address is assigned by Cisco vManage. Do not use a user-configured system IP address to connect to a device through SSH.You can find the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface from the output of the show interface description command. Alternatively, you can launch the device SSH terminal from Cisco vManage and find the vmanage_system IP address from the first line of the log-in prompt.
-
Cisco vBond Orchestrators serve WAN edge devices of multiple tenants as the devices are added to the overlay network.
-
-
Multi-tenant Cisco vSmart Controllers:
-
Cisco vSmart Controllers are deployed by the service provider. Only the provider can create and attach device and feature templates to Cisco vSmart Controllers, and can access a Cisco vSmart Controller through the SSH terminal.

Note
To connect to a device through SSH, use the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface; this IP address is assigned by Cisco vManage. Do not use a user-configured system IP address to connect to a device through SSH.You can find the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface from the output of the show interface description command. Alternatively, you can launch the device SSH terminal from Cisco vManage and find the vmanage_system IP address from the first line of the log-in prompt.
-
When a tenant is created, Cisco vManage assigns two Cisco vSmart Controllers for the tenant. The Cisco vSmart Controllers form an active-active cluster.
Each tenant is assigned only two Cisco vSmart Controllers. Before a tenant is created, two Cisco vSmart Controllers must be available to serve the tenant.
-
Each pair of Cisco vSmart Controllers can serve a maximum of 24 tenants.
-
Tenants can configure custom policies on the Cisco vSmart Controllers assigned to them. Cisco vManage notifies the Cisco vSmart Controllers to pull the policy templates. Cisco vSmart Controllers pull the templates and deploy the policy configuration for the specific tenant.
-
Only the provider can view events, audit logs, and OMP alarms for a Cisco vSmart Controller on Cisco vManage.
-
-
WAN Edge Devices:
-
A tenant or the provider acting on behalf of a tenant can add WAN edge devices to the tenant network, configure the devices, and remove the devices from the tenant network, or access the device through the SSH terminal.

Note
To connect to a device through SSH, use the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface; this IP address is assigned by Cisco vManage. Do not use a user-configured system IP address to connect to a device through SSH.You can find the IP address of the
vmanage_systeminterface from the output of the show interface description command. Alternatively, you can launch the device SSH terminal from Cisco vManage and find the vmanage_system IP address from the first line of the log-in prompt.
-
A provider can manage the WAN edge devices only from provider-as-tenant view. In the provider view, Cisco vManage does not present any WAN edge device information.
-
Cisco vManage reports WAN edge device events, logs, and alarms only in the tenant and the provider-as-tenant views.
-
-
Overlapping VPN numbers: A particular VPN or a set of common VPNs is assigned to a specific tenant, with their own configurations and monitoring dashboard environment. These VPN numbers can overlap where they are used by other tenants.
-
On-prem and cloud deployment models: Cisco SD-WAN controllers can be deployed in an organization data center on servers running the VMware vSphere ESXi or the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) hypervisor. Cisco SD-WAN controllers can also be deployed in the cloud on Amazon Web Services (AWS) servers.
 Feedback
Feedback