Deploy the ASAv Using KVM
You can deploy the ASAv using the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM).
- About ASAv Deployment Using KVM
- Prerequisites for the ASAv and KVM
- Prepare the Day 0 Configuration File
- Prepare the Virtual Bridge XML Files
- Launch the ASAv
- Hotplug Interface Provisioning
- SR-IOV Interface Provisioning
- Increasing Performance on KVM Configurations
About ASAv Deployment Using KVM
Sample ASAv Deployment Using KVM shows a sample network topology with ASAv and KVM. The procedures described in this chapter are based on the sample topology. You requirements will dictate the exact procedures you need. The ASAv acts as the firewall between the inside and outside networks. A separate management network is also configured.
Figure 1 Sample ASAv Deployment Using KVM

Prerequisites for the ASAv and KVM
http://www.cisco.com/go/asa-software
Note: A Cisco.com login and Cisco service contract are required.
- For the purpose of the sample deployment in this document, we are assuming you are using Ubuntu 14.04 LTS. Install the following packages on top of the Ubuntu 14.04 LTS host:
- Performance is affected by the host and its configuration. You can maximize the throughput of the ASAv on KVM by tuning your host. For generic host-tuning concepts, see Network Function Virtualization Packet Processing Performance of Virtualized Platforms with Linux and Intel Architecture.
- Useful optimizations for Ubuntu 14.04 include the following:
–![]() macvtap—High performance Linux bridge; you can use macvtap instead of a Linux bridge. Note that you must configure specific settings to use macvtap instead of the Linux bridge.
macvtap—High performance Linux bridge; you can use macvtap instead of a Linux bridge. Note that you must configure specific settings to use macvtap instead of the Linux bridge.
–![]() Transparent Huge Pages—Increases memory page size and is on by default in Ubuntu 14.04.
Transparent Huge Pages—Increases memory page size and is on by default in Ubuntu 14.04.
–![]() Hyperthread disabled—Reduces two vCPUs to one single core.
Hyperthread disabled—Reduces two vCPUs to one single core.
–![]() txqueuelength—Increases the default txqueuelength to 4000 packets and reduces drop rate.
txqueuelength—Increases the default txqueuelength to 4000 packets and reduces drop rate.
–![]() pinning—Pins qemu and vhost processes to specific CPU cores; under certain conditions, pinning is a significant boost to performance.
pinning—Pins qemu and vhost processes to specific CPU cores; under certain conditions, pinning is a significant boost to performance.
- For information on optimizing a RHEL-based distribution, see Red Hat Enterprise Linux6 Virtualization Tuning and Optimization Guide.
- For KVM system requirements, see Cisco ASA Compatibility.
Prepare the Day 0 Configuration File
You can prepare a Day 0 configuration file before you launch the ASAv. This file is a text file that contains the ASAv configuration that will be applied when the ASAv is launched. This initial configuration is placed into a text file named “day0-config” in a working directory you chose, and is manipulated into a day0.iso file that is mounted and read on first boot. At the minimum, the Day 0 configuration file must contain commands that will activate the management interface and set up the SSH server for public key authentication, but it can also contain a complete ASA configuration.
The day0.iso file (either your custom day0.iso or the default day0.iso) must be available during first boot:
- To automatically license the ASAv during initial deployment, place the Smart Licensing Identity (ID) Token that you downloaded from the Cisco Smart Software Manager in a text file named ‘idtoken’ in the same directory as the Day 0 configuration file.
- If you want to access and configure the ASAv from the serial port on the hypervisor instead of the virtual VGA console, you should include the console serial setting in the Day 0 configuration file to use the serial port on first boot.
- If you want to deploy the ASAv in transparent mode, you must use a known running ASA config file in transparent mode as the Day 0 configuration file. This does not apply to a Day 0 configuration file for a routed firewall.
Note: We are using Linux in this example, but there are similar utilities for Windows.
1.![]() Enter the CLI configuration for the ASAv in a text file called “day0-config”. Add interface configurations for the three interfaces and any other configuration you want.
Enter the CLI configuration for the ASAv in a text file called “day0-config”. Add interface configurations for the three interfaces and any other configuration you want.
The fist line should begin with the ASA version. The day0-config should be a valid ASA configuration. The best way to generate the day0-config is to copy the desired parts of a running config from an existing ASA or ASAv. The order of the lines in the day0-config is important and should match the order seen in an existing show run command output.
2.![]() (Optional) Download the Smart License identity token file issued by the Cisco Smart Software Manager to your computer.
(Optional) Download the Smart License identity token file issued by the Cisco Smart Software Manager to your computer.
3.![]() (Optional) Copy the ID token from the download file and put it a text file named ‘idtoken’ that only contains the ID token.
(Optional) Copy the ID token from the download file and put it a text file named ‘idtoken’ that only contains the ID token.
4.![]() (Optional) For automated licensing during initial ASAv deployment, make sure the following information is in the day0-config file:
(Optional) For automated licensing during initial ASAv deployment, make sure the following information is in the day0-config file:
–![]() Management interface IP address
Management interface IP address
–![]() (Optional) HTTP proxy to use for Smart Licensing
(Optional) HTTP proxy to use for Smart Licensing
–![]() A route command that enables connectivity to the HTTP proxy (if specified) or to tools.cisco.com
A route command that enables connectivity to the HTTP proxy (if specified) or to tools.cisco.com
–![]() A DNS server that resolves tools.cisco.com to an IP address
A DNS server that resolves tools.cisco.com to an IP address
–![]() Smart Licensing configuration specifying the ASAv license you are requesting
Smart Licensing configuration specifying the ASAv license you are requesting
–![]() (Optional) A unique host name to make the ASAv easier to find in CSSM
(Optional) A unique host name to make the ASAv easier to find in CSSM
5.![]() Generate the virtual CD-ROM by converting the text file to an ISO file:
Generate the virtual CD-ROM by converting the text file to an ISO file:
The Identity Token automatically registers the ASAv with the Smart Licensing server.
6.![]() Repeat Steps 1 through 5 to create separate default configuration files with the appropriate IP addresses for each ASAv you want to deploy.
Repeat Steps 1 through 5 to create separate default configuration files with the appropriate IP addresses for each ASAv you want to deploy.
Prepare the Virtual Bridge XML Files
You need to set up virtual networks that connect the ASAv guests to the KVM host and that connect the guests to each other.
Note: This procedure does not establish connectivity to the external world outside the KVM host.
Prepare the virtual bridge XML files on the KVM host. For the sample virtual network topology described in Prepare the Day 0 Configuration File, you need the following three virtual bridge files: virbr1.xml, virbr2.xml, and virbr3.xml (you must use these three filenames; for example, virbr0 is not allowed because it already exists). Each file has the information needed to set up the virtual bridges. You must give the virtual bridge a name and a unique MAC address. Providing an IP address is optional.
1.![]() Create three virtual networks bridge XML files:
Create three virtual networks bridge XML files:
2.![]() Create a script that contains the following (in our example, we will name the script virt_network_setup.sh):
Create a script that contains the following (in our example, we will name the script virt_network_setup.sh):
3.![]() Run this script to setup the virtual network. The script brings the virtual networks up. The networks stay up as long as the KVM host is running.
Run this script to setup the virtual network. The script brings the virtual networks up. The networks stay up as long as the KVM host is running.
Note: If you reload the Linux host, you must re-run the virt_network_setup.sh script. It does not persist over reboots.
4.![]() Verify that the virtual networks were created:
Verify that the virtual networks were created:
5.![]() Display the IP address assigned to the virbr1 bridge. This is the IP address that you assigned in the XML file.
Display the IP address assigned to the virbr1 bridge. This is the IP address that you assigned in the XML file.
Launch the ASAv
Use a virt-install based deployment script to launch the ASAv.
1.![]() Create a virt-install script called “virt_install_asav.sh”.
Create a virt-install script called “virt_install_asav.sh”.
The name of the ASAv VM must be unique across all other virtual machines (VMs) on this KVM host. The ASAv can support up to 10 networks. This example uses three networks. The order of the network bridge clauses is important. The first one listed is always the management interface of the ASAv (Management 0/0), the second one listed is GigabitEthernet 0/0 of the ASAv, and the third one listed is GigabitEthernet 0/1 of the ASAv, and so on up through GigabitEthernet0/8. The virtual NIC must be Virtio.
Note:![]() The watchdog element is a virtual hardware watchdog device for KVM guests. If the ASAv becomes unresponsive for any reason, the watchdog can initiate a restart of the KVM guest.
The watchdog element is a virtual hardware watchdog device for KVM guests. If the ASAv becomes unresponsive for any reason, the watchdog can initiate a restart of the KVM guest.
Note:![]() Each KVM guest disk interface can have one of the following cache modes specified: writethrough, writeback, none, directsync, or unsafe. A cache=writethrough will help reduce file corruption on KVM guest machines when the host experiences abrupt losses of power. However, cache=writethrough can also affect disk performance due to more disk I/O writes than cache=none.
Each KVM guest disk interface can have one of the following cache modes specified: writethrough, writeback, none, directsync, or unsafe. A cache=writethrough will help reduce file corruption on KVM guest machines when the host experiences abrupt losses of power. However, cache=writethrough can also affect disk performance due to more disk I/O writes than cache=none.
cache=writethrough
2.![]() Run the virt_install script:
Run the virt_install script:
A window appears displaying the console of the VM. You can see that the VM is booting. It takes a few minutes for the VM to boot. Once the VM stops booting you can issue CLI commands from the console screen.
Hotplug Interface Provisioning
You can add and remove interfaces dynamically without the need to stop and restart the ASAv. When you add a new interface to the ASAv virtual machine, the ASAv should be able to detect and provision it as a regular interface. Similarly, when you remove an existing interface via hotplug provisioning, the ASAv should remove the interface and release any resource associated with it.
Guidelines for Hotplug Interface Provisioning
Interface Mapping and Numbering
- When you add a hotplug interface, its interface number is the number of the current last interface plus one.
- When you remove a hotplug interface, a gap in the interface numbering is created, unless the interface you removed is the last one.
- When a gap exists in the interface numbering, the next hotplug-provisioned interface will fill that gap.
- When you use a hotplug interface as a failover link, the link must be provisioned on both units designated as the failover ASAv pair.
–![]() You first add a hotplug interface to the active ASAv in the hypervisor, then add a hotplug interface to the standby ASAv in the hypervisor.
You first add a hotplug interface to the active ASAv in the hypervisor, then add a hotplug interface to the standby ASAv in the hypervisor.
–![]() You configure the newly added failover interface in the active ASAv; the configuration will be synchronized to the standby unit.
You configure the newly added failover interface in the active ASAv; the configuration will be synchronized to the standby unit.
–![]() You enable failover on the primary unit.
You enable failover on the primary unit.
–![]() You first remove the failover configuration in the active ASAv.
You first remove the failover configuration in the active ASAv.
–![]() You remove the failover interface from the active ASAv in the hypervisor, then immediately remove the corresponding interface from the standby ASAv in the hypervisor.
You remove the failover interface from the active ASAv in the hypervisor, then immediately remove the corresponding interface from the standby ASAv in the hypervisor.
- Hotplug interface provisioning is limited to Virtio virtual NICs.
- The maximum number of interfaces supported is 10. You will receive an error message if you attempt to add more than 10 interfaces.
- You cannot open the interface card (media_ethernet/port/id/10).
- Hotplug interface provisioning requires ACPI. Do not include the --noacpi flag in your virt-install script.
You can use the virsh command line to add and remove interfaces in the KVM hypervisor.
1.![]() Open a virsh command line session:
Open a virsh command line session:
2.![]() Use the attach-interface command to add an interface:
Use the attach-interface command to add an interface:
The domain can be specified as a short integer, a name, or a full UUID. The type parameter can be either network to indicate a physical network device or bridge to indicate a bridge to a device. The source parameter indicates the type of connection. The model parameter indicates the virtial NIC type. The mac parameter specifies the MAC address of the network interface. The live parameter indicates that the command affects the running domain.
Note:![]() Use the interface configuration mode on the ASAv to configure and enable the interface for transmitting and receiving traffic; see Navigating the Cisco ASA Series Documentation for more information.
Use the interface configuration mode on the ASAv to configure and enable the interface for transmitting and receiving traffic; see Navigating the Cisco ASA Series Documentation for more information.
3.![]() Use the detach-interface command to remove an interface:
Use the detach-interface command to remove an interface:
SR-IOV Interface Provisioning
SR-IOV allows multiple VMs to share a single PCIe network adapter inside a host. SR-IOV defines these functions:
- Physical function (PF) - PFs are full PCIe functions that include the SR-IOV capabilities. These appear as regular static NICs on the host server.
- Virtual function (VF) - VFs are lightweight PCIe functions that help in data transfer. A VF is derived from, and managed through, a PF.
VFs are capable of providing up to 10 Gbps connectivity to ASAv virtual machines within a virtualized operating system framework. This section explains how to configure VFs in a KVM environment. SR-IOV support on the ASAv is explained in ASAv and SR-IOV Interface Provisioning.
Guidelines for SR-IOV Interface Provisioning
If you have a physical NIC that supports SR-IOV, you can attach SR-IOV-enabled VFs, or Virtual NICs (vNICs), to the ASAv instance. SR-IOV also requires support in the BIOS as well as in the operating system instance or hypervisor that is running on the hardware. The following is a list of general guidelines for SR-IOV interface provisioning for the ASAv running in a KVM environment:
- You need an SR-IOV-capable physical NIC in the host server; see Supported NICs for SR-IOV.
- You need virtualization enabled in the BIOS on your host server. See your vendor documentation for details.
- You need IOMMU global support for SR-IOV enabled in the BIOS on your host server. See your vendor documentation for details.
Modify the KVM Host BIOS and Host OS
This section shows various setup and configuration steps for provisioning SR-IOV interfaces on a KVM system. The information in this section was created from devices in a specific lab environment, using Ubuntu 14.04 on a Cisco UCS C Series server with an Intel Ethernet Server Adapter X520 - DA2.
- Make sure you have an SR-IOV-compatible network interface card (NIC) installed.
- Make sure that the Intel Virtualization Technology (VT-x) and VT-d features are enabled.
Note:![]() Some system manufacturers disable these extensions by default. We recommend that you verify the process with the vendor documentation because different systems have different methods to access and change BIOS settings.
Some system manufacturers disable these extensions by default. We recommend that you verify the process with the vendor documentation because different systems have different methods to access and change BIOS settings.
- Make sure all Linux KVM modules, libraries, user tools, and utilities have been installed during the operation system installation; see Prerequisites for the ASAv and KVM.
- Make sure that the physical interface is in the UP state. Verify with ifconfig <ethname>.
1.![]() Log in to your system using the “root” user account and password.
Log in to your system using the “root” user account and password.
2.![]() Verify that Intel VT-d is enabled.
Verify that Intel VT-d is enabled.
The last line indicates that VT-d is enabled.
3.![]() Activate Intel VT-d in the kernel by appending the intel_iommu=on parameter to the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX entry in the /etc/default/grub configuration file.
Activate Intel VT-d in the kernel by appending the intel_iommu=on parameter to the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX entry in the /etc/default/grub configuration file.
Note:![]() If you are using an AMD processor, you should append amd_iommu=on to the boot parameters instead.
If you are using an AMD processor, you should append amd_iommu=on to the boot parameters instead.
4.![]() Reboot the server for the iommu change to take effect.
Reboot the server for the iommu change to take effect.
5.![]() Create VFs by writing an appropriate value to the sriov_numvfs parameter via the sysfs interface using the following format:
Create VFs by writing an appropriate value to the sriov_numvfs parameter via the sysfs interface using the following format:
To ensure that the desired number of VFs are created each time the server is power-cycled, you append the above command to the rc.local file, which is located in the /etc/rc.d/ directory. The Linux OS executes the rc.local script at the end of the boot process.
For example, the following shows the creation of one VF per port. The interfaces for your particular setup will vary.
7.![]() Verify that the VFs have been created using lspci.
Verify that the VFs have been created using lspci.
Note:![]() You will see additional interfaces using the ifconfig command.
You will see additional interfaces using the ifconfig command.
Assign PCI Devices to the ASAv
Once you create VFs, you can add them to the ASAv just as you would add any PCI device. The following example explains how to add an Ethernet VF controller to an ASAv using the graphical virt-manager tool.
1.![]() Open the ASAv click the Add Hardware button to add a new device to the virtual machine.
Open the ASAv click the Add Hardware button to add a new device to the virtual machine.
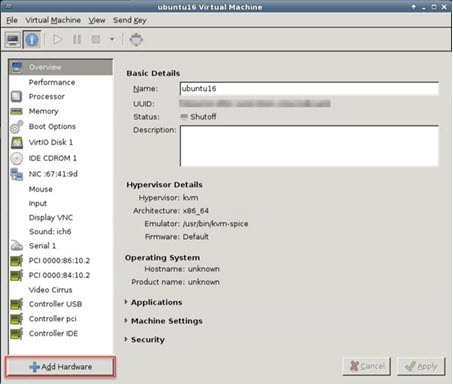
2.![]() Click PCI Host Device from the Hardware list in the left pane.
Click PCI Host Device from the Hardware list in the left pane.
The list of PCI devices, including VFs, appears in the center pane.
Figure 3 List of Virtual Functions

3.![]() Select one of the available Virtual Functions and click Finish.
Select one of the available Virtual Functions and click Finish.
The PCI Device shows up in the Hardware List; note the description of the device as Ethernet Controller Virtual Function.
Figure 4 Virtual Function added

- Use the show interface command from the ASAv command line to verify newly configured interfaces.
- Use the interface configuration mode on the ASAv to configure and enable the interface for transmitting and receiving traffic; see Navigating the Cisco ASA Series Documentation for more information.
Increasing Performance on KVM Configurations
You can increase the performance for an ASAv in the KVM environment by changing settings on the KVM host. These settings are independent of the configuration settings on the host server. This option is available in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0 KVM.
You can improve performance on KVM configurations by enabling CPU pinning.
Enabling CPU Pinning
To increase the performance of the ASAv in KVM environments, you can use the KVM CPU affinity option to assign a virtual machine to a specific processor. To use this option, configure CPU pinning on the KVM host.
1.![]() In the KVM host environment, verify the host topology to find out how many vCPUs are available for pinning:
In the KVM host environment, verify the host topology to find out how many vCPUs are available for pinning:
2.![]() Verify the available vCPU numbers:
Verify the available vCPU numbers:
3.![]() Pin the vCPUs to sets of processor cores:
Pin the vCPUs to sets of processor cores:
The virsh vcpupin command must be executed for each vCPU on your ASAv. The following example shows the KVM commands needed if you have an ASAv configuration with four vCPUs and the host has eight cores:
The host core number can be any number from 0 to 7. For more information, see the KVM documentation.
Note:![]() When configuring CPU pinning, carefully consider the CPU topology of the host server. If using a server configured with multiple cores, do not configure CPU pinning across multiple sockets.
When configuring CPU pinning, carefully consider the CPU topology of the host server. If using a server configured with multiple cores, do not configure CPU pinning across multiple sockets.
The downside of improving performance on KVM configuration is that it requires dedicated system resources.
 Feedback
Feedback