Net-SNMP
Net-SNMP Version 5.1.2 provides the following tools and libraries:
-
An extensible agent
-
An SNMP library
-
Tools to request or set information from SNMP agents
-
Tools to generate and handle SNMP traps
You can download the Net-SNMP network management tool from the following URL: http://sourceforge.net/projects/net-snmp/
This section includes the following topics:
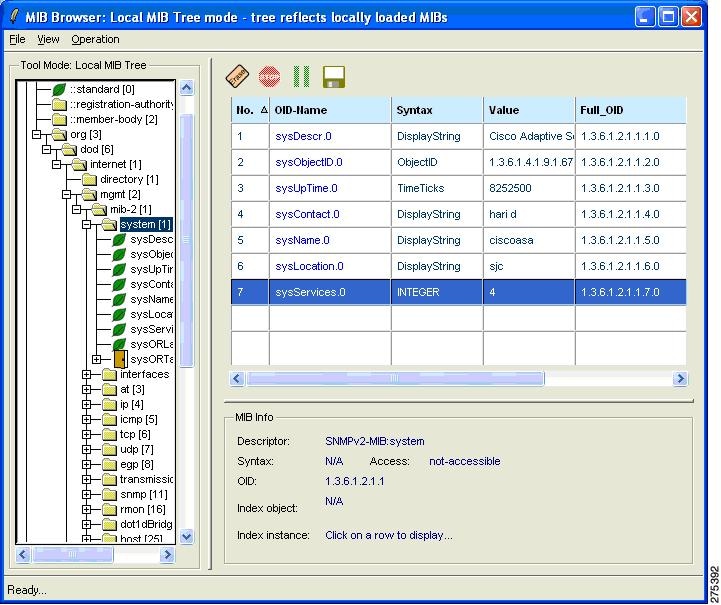
Polling a MIB
Procedure
|
To poll a MIB, after you have finished configuring the ASA, run the snmpwalk command from the NMS to the ASA:
|
SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Version 8.2(0)227
SNMPv2-MIB::sysObjectID.0 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.9.1.915
SNMPv2-MIB::sysUpTime.0 = Timeticks: (486600) 1:21:06.00
SNMPv2-MIB::sysContact.0 = STRING: admin admin
SNMPv2-MIB::sysName.0 = STRING: ciscoasa
SNMPv2-MIB::sysLocation.0 = STRING: sjc - 190 W Tasman Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
USA
SNMPv2-MIB::sysServices.0 = INTEGER: 4Sending a Trap
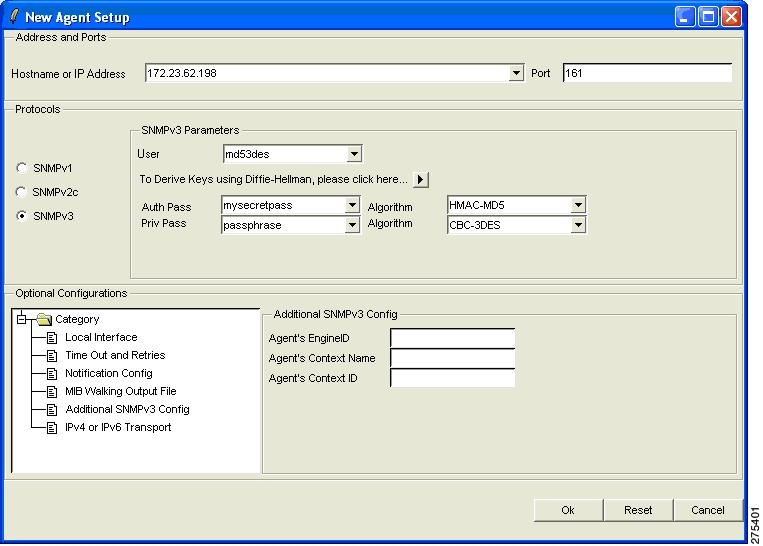
When the ASA sends a trap, it is authoritative, which means that the user created within the snmptrapd command must be associated with the EngineID sending the trap.
To establish this association, perform the following steps:
Procedure
| Step 1 |
In the /var/net-snmp/snmptrapd.conf file, enter the following statement: For this statement, define the listed parameters, which include the following:
|
||
| Step 2 |
In the /tmp/snmptrapd.conf file, enter the following statement: |
||
| Step 3 |
Run the snmptrapd command, pointing to that file.
|
||
| Step 4 |
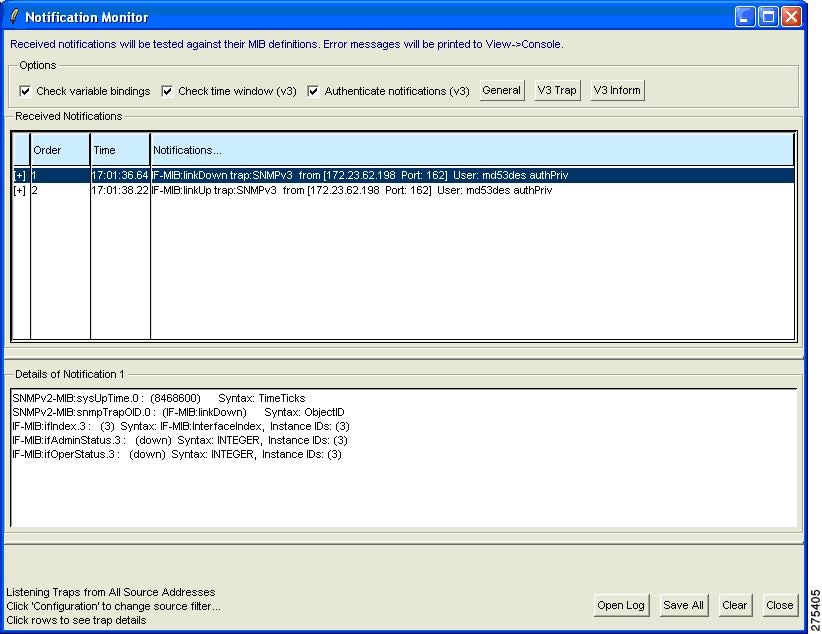
Run the snmptrap command from the ASA to send a linkdown or linkup trap by entering the following commands: |
2009-03-18 23:52:06 NET-SNMP version 5.1.2 Started.
2009-03-18 23:52:20 10.31.8.254 [10.31.8.254]:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysUpTime.0 = Timeticks: (938700) 2:36:27.00 SNMPv2-MIB::snmp
TrapOID.0 = OID: IF-MIB::linkDown IF-MIB::ifIndex.1 = INTEGER: 1 IF-MIB::
ifAdminStatus.1 = INTEGER: down(2) IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.1 = INTEGER: down(2
)
2009-03-18 23:52:22 10.31.8.254 [10.31.8.254]:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysUpTime.0 = Timeticks: (939000) 2:36:30.00 SNMPv2-MIB::snmp
TrapOID.0 = OID: IF-MIB::linkUp IF-MIB::ifIndex.1 = INTEGER: 1 IF-MIB::ifAdminS
tatus.1 = INTEGER: up(1) IF-MIB::ifOperStatus.1 = INTEGER: up(1)













































 Feedback
Feedback