Complete the CLI setup script for the Management interface settings.
You must accept the EULA to continue.
Press <ENTER> to display the EULA:
Cisco General Terms
[...]
Please enter 'YES' or press <ENTER> to AGREE to the EULA:
System initialization in progress. Please stand by.
You must configure the network to continue.
Configure at least one of IPv4 or IPv6 unless managing via data interfaces.
Do you want to configure IPv4? (y/n) [y]:
Do you want to configure IPv6? (y/n) [y]: n
Guidance: Enter y for at least one of these
types of addresses. Although you
do not plan to use the Management interface, you must set an IP address,
for example, a private address.
Configure IPv4 via DHCP or manually? (dhcp/manual) [manual]:
Guidance: Choose
manual. DHCP is not supported when using the
outside interface for manager access. Make sure this interface is on a
different subnet from the manager access interface to prevent routing
issues.
Enter an IPv4 address for the management interface [192.168.45.61]: 10.89.5.17
Enter an IPv4 netmask for the management interface [255.255.255.0]: 255.255.255.192
Enter the IPv4 default gateway for the management interface [data-interfaces]:
Guidance: Set the gateway to
be data-interfaces. This setting forwards management
traffic over the backplane so it can be routed through the outside
interface.
Enter a fully qualified hostname for this system [firepower]: 1010-3
Enter a comma-separated list of DNS servers or 'none' [208.67.222.222,208.67.220.220,2620:119:35::35]:
Enter a comma-separated list of search domains or 'none' []: cisco.com
If your networking information has changed, you will need to reconnect.
Disabling IPv6 configuration: management0
Setting DNS servers: 208.67.222.222,208.67.220.220,2620:119:35::35
Setting DNS domains:cisco.com
Guidance: Set the Management
interface DNS servers. These will probably match the outside interface DNS
servers you set later, since they are both accessed from the outside
interface.
Setting hostname as 1010-3
Setting static IPv4: 10.89.5.17 netmask: 255.255.255.192 gateway: data on management0
Updating routing tables, please wait...
All configurations applied to the system. Took 3 Seconds.
Saving a copy of running network configuration to local disk.
For HTTP Proxy configuration, run 'configure network http-proxy'
Setting hostname as 1010-3
Setting static IPv4: 10.89.5.17 netmask: 255.255.255.192 gateway: data on management0
Updating routing tables, please wait...
All configurations applied to the system. Took 3 Seconds.
Saving a copy of running network configuration to local disk.
For HTTP Proxy configuration, run 'configure network http-proxy'
Guidance: Enter routed.
Outside manager access is only supported in routed firewall mode.
Configuring firewall mode ...
Device is in OffBox mode - disabling/removing port 443 from iptables.
Update policy deployment information
- add device configuration
- add network discovery
- add system policy
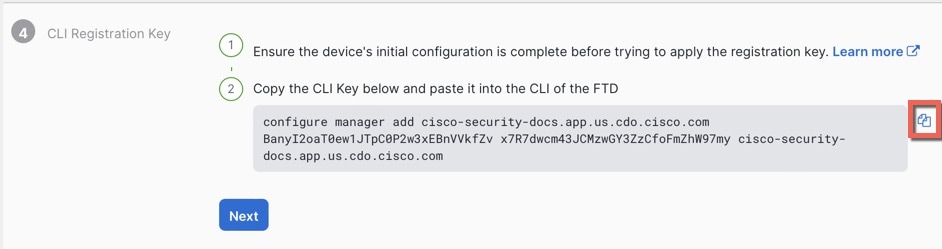
You can register the sensor to a Firepower Management Center and use the
Firepower Management Center to manage it. Note that registering the sensor
to a Firepower Management Center disables on-sensor Firepower Services
management capabilities.
When registering the sensor to a Firepower Management Center, a unique
alphanumeric registration key is always required. In most cases, to register
a sensor to a Firepower Management Center, you must provide the hostname or
the IP address along with the registration key.
'configure manager add [hostname | ip address ] [registration key ]'
However, if the sensor and the Firepower Management Center are separated by a
NAT device, you must enter a unique NAT ID, along with the unique registration
key.
'configure manager add DONTRESOLVE [registration key ] [ NAT ID ]'
Later, using the web interface on the Firepower Management Center, you must
use the same registration key and, if necessary, the same NAT ID when you add
this sensor to the Firepower Management Center.
>
 Feedback
Feedback