Configure Hub Site and Settings
This section describes setting up the network environment, which provides resources for routers at hub and branch sites. Later, you can provision branch routers using “Setup Branch Sites”.
Select each of the tabs below and complete the configuration tasks:
- System
- Certified IOS Releases
- IP Address Pools
- Service Providers
- IWAN Aggregation Site
- Configure LAN Settings for the Data Center

Note![]() The generic IP pool is used for overlay and loopback addresses. The generic IP pool is divided according to the number of remote sites and service providers as specified in the “IP Address Pools” tab. Please plan by understanding your future requirements by specifying the maximum number of service providers and remote sites they you plan to deploy. The IP address pool settings cannot be changed once specified.
The generic IP pool is used for overlay and loopback addresses. The generic IP pool is divided according to the number of remote sites and service providers as specified in the “IP Address Pools” tab. Please plan by understanding your future requirements by specifying the maximum number of service providers and remote sites they you plan to deploy. The IP address pool settings cannot be changed once specified.
System

Enter the global system settings in preparation for enabling both IWAN hubs and spokes.
Select each of the menu options within the “System” menu option to define settings for TACACS, SNMP, DNS, NTP, and Syslog servers.
Netflow Collector
Enter an IP address for the Netflow collector. This is the IP address of a Netflow collector such as the LiveAction application. Application visibility and performance metrics are sent to the collector.
|
|
|
|---|---|
IP address of the NetFlow collector (server). Traffic is sent from the network devices to the Netflow collector; for example, Cisco Prime, or LiveAction. |
|
DNS
Enter a domain name and the IP address of a DNS primary server, used by network devices for SSH. The ip domain-name command is used to generate RSA keys. A secondary server can be specified for redundancy.
|
|
|
|---|---|
(Optional) Secondary server IP address. |
SNMP
Enter SNMP server details. Either the APIC-EM controller can act as an SNMP manager for managed network devices or a separate SNMP server can be specified to handle SNMP traps. SNMP settings determine the inventory from hub and remote site devices and these values are reflected in the configuration.
Click Show more for SNMP Retries and Timeout, to change the values for number of retries and timeout period.
|
|
|
|---|---|
(Optional) IP address of the SNMP server. (If you do not enter an IP address, the Cisco IWAN application is used as an SNMP server.) |
|
Syslog
You may enter the IP address of a third party syslog server, to which network devices send syslog messages.
|
|
|
|---|---|
(Optional) Syslog server’s destination IP address. The router will be configured to send Syslog messages to this server. |
Authorization, Authentication, Accounting
TACACS is the only supported centralized Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) service for Cisco IWAN. If a TACACS server is provided, spoke devices will utilize TACACS for all management access to the spoke devices (SSH & HTTPS). Whether or not a TACACS service is provided, a local AAA user database is created on the spoke device, which can be used when TACACS is not available.
Cisco APIC-EM global credentials, if present, are used as default values for the local AAA user credentials, else local user credentials default to the username and password specified in global device credentials for branch routers or to the username and password entered while provisioning the hub. The enable password for device configuration mode is cisco123.
Enter an IP address and key for the AAA server.
|
|
|
|---|---|
DHCP
Enter the IP address of a DHCP server that provides client computers and other TCP/IP-based network devices with valid IP addresses.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Certified IOS Releases

Note![]() If the routers already have the correct image loaded, selecting an image in Certified IOS Releases is optional.
If the routers already have the correct image loaded, selecting an image in Certified IOS Releases is optional.
For each of the router types (such as “ISR4431”) displayed in the window, you can specify a Cisco IOS image. To update the image for a router, click on the small “Up” icon of the router. After an image is uploaded it is ready to be pushed to the branch router later.
IP Address Pools
Overview of IP Address Pools
IWAN application will automatically utilize IP addresses carved from the global enterprise IP Pool space. To support this functionality, one generic global IP pool must be defined for the IWAN application. Allocated out of this generic IP pool will be all the IPs required to provision hub and spoke device needs. This includes interface, LAN, VPN overlay and routing needs.
Optionally, one or more LAN IP pools may be defined to further refine the branch LAN side IP address space. These LAN IP pools will be used for LAN needs until exhausted and then if required, generic IP pool is leveraged.

Note![]() It is important to size the generic IP pool correctly for the long term needs of the IWAN site. VPN requirements dictate that subnets must be defined and allocated internally (up front) before any sites are provisioned. Therefore, once the site and service provider sizing is set, it is frozen for the life of the controller. Please plan accordingly for long term IWAN site requirements. For instance, it is best if you specify the service provider, keeping in mind, that you would require in future, depending on your requirements. There have been issues when service providers are added to the network without specifying the appropriate maximum number of service providers.
It is important to size the generic IP pool correctly for the long term needs of the IWAN site. VPN requirements dictate that subnets must be defined and allocated internally (up front) before any sites are provisioned. Therefore, once the site and service provider sizing is set, it is frozen for the life of the controller. Please plan accordingly for long term IWAN site requirements. For instance, it is best if you specify the service provider, keeping in mind, that you would require in future, depending on your requirements. There have been issues when service providers are added to the network without specifying the appropriate maximum number of service providers.
Optionally, site specific LAN (VLAN) requirements may be defined and prioritized over the generic global IP pools wherever specific IP addresses are required.
Site-Specific Profile
Site-specific profile is required only for preprovising LAN IP addresses on each site, else site-specific profile is optional. Preprovisioning allows you to define a site using the site name and device combination before devices are added to the unclaimed list. This is accomplished by matching the device serial number with the site name. VLAN definition for each site allows you to specific IP address pool ranges, else generic IP pools provides the required LAN IP addresses.
Branch Site-Specific Profile
You can preprovision specifications for the branch sites. A single or dual router site can be defined using device serial numbers and site name along with VLANs for the device. Thus, branch sites are available before the devices display in the site provisioning workflow under unclaimed devices. Defining the site and VLAN enables you to easily configure the devices when the devices are provisioned in the site provisioning workflow. When the devices are claimed and provisioned, the site provisioning workflow does not conflict with the existing site configuration and site name.
You can remove or edit any of the global IP address pools at any point until you click Save & Continue. However, you cannot modify the IP address pools after you have configured the IP address pools. For dual router branch, you must enter the Site Specific IP address pool for one device.You must specify the serial numbers for each device.

Working on the IP Address Pool Tab

Note![]() The generic IP pool is used for overlay and loopback addresses. The generic IP pool is divided according to the number of remote sites and service providers as specified in the “IP Address Pools” tab. Please plan by understanding your future requirements by specifying the maximum number of service providers and remote sites they you plan to deploy. The IP address pool settings cannot be changed once specified.
The generic IP pool is used for overlay and loopback addresses. The generic IP pool is divided according to the number of remote sites and service providers as specified in the “IP Address Pools” tab. Please plan by understanding your future requirements by specifying the maximum number of service providers and remote sites they you plan to deploy. The IP address pool settings cannot be changed once specified.
The IP Address Pools tab allows you to define the IP pool. Use Check IP Range button for suggestion on the minimum prefix needed for generic IP pool and LAN Interface IP pools. For better scalability, you can also export or import IP addresses via.csv file into the application. Upon import, existing targeted network sites are updated with the new VLAN information. If some sites need to utilize specific IP addresses on the VLANs, the IP addresses can either be specified using the options in the IP Address Pools tab or import IP addresses via a.csv file.
Step 1![]() Select the IP Address Pools tab.
Select the IP Address Pools tab.

Step 2![]() To help size the global generic IP pools for your network, enter the long term maximum remote sites count and the number of unique service provider paths that you will require and click Check IP Range.
To help size the global generic IP pools for your network, enter the long term maximum remote sites count and the number of unique service provider paths that you will require and click Check IP Range.

The IP prefix identified is the minimum IP pool suggested to support the expected network scale. Optionally, by entering the expected average number of hosts behind each VLAN per site, a prefix for the global LAN IP pools is also suggested. Additionally, this dialog also provides suggestion for the LAN side IP requirements.
Step 4![]() Click Add Address Pool to enter an IP address along with the suggested or greater prefix.
Click Add Address Pool to enter an IP address along with the suggested or greater prefix.
The first range always defaults to the generic IP pool.
|
|
|
Slider bar shows the percentage of the addresses in the pool that has been used by the IWAN application. |

Step 5![]() Click Site Address Pool to enter an IP address and prefix based on the suggested sizing for a global LAN IP pool.
Click Site Address Pool to enter an IP address and prefix based on the suggested sizing for a global LAN IP pool.

Step 6![]() Repeat this step as required to add additional LAN IP pools.
Repeat this step as required to add additional LAN IP pools.
The following restrictions apply when you enter a VLAN Type of your choice:
- The VLAN type value should not be more than 200 characters in length.
- The VLAN type should not include ? character.
- The allowed number of site-specific address pools is 20 entries per site.

Note![]() If you do not enter the VLAN details, the configuration information is pushed on the physical interface, which is autopopulated when configuring the LAN during branch provisioning. In such cases, the site is assumed to have no VLANs.
If you do not enter the VLAN details, the configuration information is pushed on the physical interface, which is autopopulated when configuring the LAN during branch provisioning. In such cases, the site is assumed to have no VLANs.

Step 7![]() Optionally, click Import CSV or Export CSV to import or export profile based content.Use this step if you want quick processing for large number of site definitions.
Optionally, click Import CSV or Export CSV to import or export profile based content.Use this step if you want quick processing for large number of site definitions.
The global IP pool, site and VLAN definitions can be imported or updated with Import CSV option. The global IP pool, site and VLAN definitions that were previously imported via file or defined via the IP Pool Address tab can be exported using Export CSV option. The export workflow provides a template for subsequent import requirements. The content is presented in.csv format and the default exported file name is Controller_Profile_DD-MM-YYYY.csv. These workflows support preprovisioning, scalable site definitions and specific VLAN & IP pool needs.
Step 8![]() Optionally, click Export Allocated Addresses to get a view of the actual usage of IP addresses in the controller on a per site or function basis.
Optionally, click Export Allocated Addresses to get a view of the actual usage of IP addresses in the controller on a per site or function basis.
This option provides insight for visibility, DHCP or debugging needs. The content is presented in.csv format and default exported file name is Controller_IP_Allocation_DD-MM-YYYY.csv.
Step 9![]() Click Save and Continue to accept the changes and proceed to the next tab.
Click Save and Continue to accept the changes and proceed to the next tab.
Service Providers
Select the “Service Providers” tab to the type of links and the number of service providers. You can specify up to four links and four service providers. Of the four links, one link can be metered and public. You specify the gateway, interface details for the link in the IWAN Aggregation Site tab. After the hub and branches are configured, each link can be associated with a path preference when defining the application policies. For more information, see “Define Application Policy” section.

For MPLS facing WAN interface, a set of predefined Service Provider (SP) profiles are available. Select the profile that most closely matches the SP Service Level Agreement (SLA) for the branch sites. Egress QoS queuing will be applied on the WAN egress to fulfill the SP SLA.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Service provider profile or QoS model. |
|
After you select a profile, the profile details appear in the right hand side of the window.
In this example, for the 8 Class Model, 20% of the bandwidth is assigned to the Voice class, with the remaining bandwidth allocated as shown for the remaining classes.

The following fields are shown for each class of data within a profile.
Click Show Advanced —shows the DSCP values for each class, and which of the classes is a priority class.
To add a new service profile, based on an existing service provider profile, click on the icon next to a class name. The Add Service Profile dialog box appears.
For the new service profile enter a value for Profile Name and click Save.
Click Save and Continue to proceed to the next tab.
Select the “IWAN Aggregation Site” tab. See IWAN Aggregation Site.
IWAN Aggregation Site
Select the “IWAN Aggregation Site” tab to configure the hub routers with their respective WAN clouds. A default hub aggregation side with two datacenters, routers and service providers is provided. You can add datacenters, routers, and service providers as required for your network. You can create a link by clicking on a router and dragging to a cloud or vice versa. You can also delete the datacenters, routers, service providers, and links if they are not required by hovering on the network, router or link and clicking “X.”
You can add up to two datacenters and add or delete a device or a link after the hub is provisioned. You can only modify the datacenter settings and devices before you click Apply Changes for the new datacenter that was added.
Coexistence of IWAN Sites and Non-IWAN Sites
This feature allows communication between non-IWAN sites with the newly enabled IWAN POP (Hub) and spoke sites for staged migration of network. The advantages of this feature are as follows:
Prerequisites for Enabling Support of Non IWAN Sites side-by-side with IWAN solution
The following configurations must be completed before starting the Cisco IWAN App on APIC-EM workflows:
–![]() A loopback interface must be enabled on the border router. It is recommended that you specify a loopback IP address in the same subnet as the WAN interface.
A loopback interface must be enabled on the border router. It is recommended that you specify a loopback IP address in the same subnet as the WAN interface.
–![]() A static route must be added with the existing MPLS-CE as the default gateway (before provisioning the hub with Cisco IWAN App workflows).
A static route must be added with the existing MPLS-CE as the default gateway (before provisioning the hub with Cisco IWAN App workflows).
–![]() The loopback IP on the IWAN MPLS border router must be advertised via BGP (or another routing protocol used for peering with MPLS provider) on the MPLS-CE router. The loopback IP must be reachable from all remote sites.
The loopback IP on the IWAN MPLS border router must be advertised via BGP (or another routing protocol used for peering with MPLS provider) on the MPLS-CE router. The loopback IP must be reachable from all remote sites.

Effective with Cisco IWAN Release 1.1.0, you can have two hubs, two clouds and add more devices to the cloud, thereby enabling a multilink network. In other words, the multilink network can have two datacenters and each datacenter can have up to four devices with four links.
Heterogeneous WAN Sites
Effective with Cisco IWAN Release 2.0.0, you can perform the following for a provisioned site:
- Add WAN clouds and service providers in any order
- Add up to two MPLS or Internet links. The new links will not affect the existing device priority nor change the path preference.
- Connect hub devices to different service providers. Each device will be connected to only one service provider. Some branches can have a different set of paths than other branches.

Note![]() The above changes cannot be performed when provisioning the site.
The above changes cannot be performed when provisioning the site.
The following figure provides an example of heterogeneous topology with a primary hub, transit hub and different type of links (MPLS and Internet) to connect to the branch routers between the primary and transit hubs. In this topology, the transit hub is not connected to the primary hub.
Figure 4-1 Transit Hub Connected to MPLS Link365591
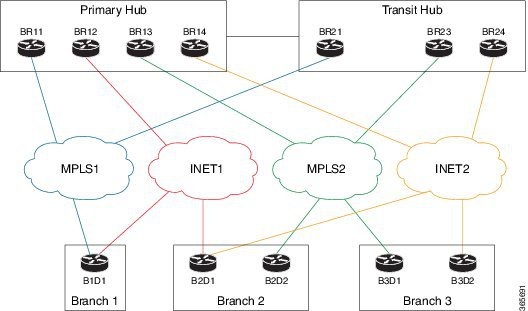
The following figure provides an example of heterogeneous topology with a primary hub, transit hub and different type of links (MPLS and Internet) to connect to the branch routers between the primary and transit hubs. In this topology, the transit hub is not connected to the primary hub.
Figure 4-2 Transit Hub Connected to Internet Link

Perform the following steps in the IWAN Aggregation Site :
Step 1![]() Select the IWAN Aggregation site tab.
Select the IWAN Aggregation site tab.
Step 2![]() Review the default topology. If you would like to enhance the topology by adding additional datacenters and links.
Review the default topology. If you would like to enhance the topology by adding additional datacenters and links.
Step 3![]() Click Add POP to add an additional datacenter. A transit hub is added.
Click Add POP to add an additional datacenter. A transit hub is added.

Note![]() You can specify two datacenters (hub sites) only during provisioning. You can add or delete datacenters after hub provisioning. Therefore, if you choose one datacenter when configuring the hub, you can add another datacenter later. Similarly, if you added two datacenters when configuring the hub, you can delete the datacenter.
You can specify two datacenters (hub sites) only during provisioning. You can add or delete datacenters after hub provisioning. Therefore, if you choose one datacenter when configuring the hub, you can add another datacenter later. Similarly, if you added two datacenters when configuring the hub, you can delete the datacenter.
Step 4![]() Optionally, you can rename the datacenter to name of your choice by selecting on the default datacenter name (TRANSIT-HUB-1).
Optionally, you can rename the datacenter to name of your choice by selecting on the default datacenter name (TRANSIT-HUB-1).
Step 5![]() Click Add Border Router to add border routers. You can also choose to add the border router to the hubs displayed on the page.
Click Add Border Router to add border routers. You can also choose to add the border router to the hubs displayed on the page.

Note![]() The Multilink feature allows you to add up to four border routers and connect the border routers via four links to the different service providers. You can also delete devices either from this page when provisioning the hub via the “IWAN Aggregation Site” tab or when provisioning the branch via the “Select Topology” tab.
The Multilink feature allows you to add up to four border routers and connect the border routers via four links to the different service providers. You can also delete devices either from this page when provisioning the hub via the “IWAN Aggregation Site” tab or when provisioning the branch via the “Select Topology” tab.
Step 6![]() Optionally, you can toggle Yes or No to assign the hub as an External MC.
Optionally, you can toggle Yes or No to assign the hub as an External MC.
Step 7![]() Click “+” on the hub router. The Configure Router dialog box appears.
Click “+” on the hub router. The Configure Router dialog box appears.
If you selected Yes for External MC, the following dialog appears.

If you selected No for External MC, the following dialog appears.

|
|
|
|---|---|
Specify the management IP Address for the hub router. |
|
Step 8![]() Click Validate. The Configure Router dialog appears.
Click Validate. The Configure Router dialog appears.

Note![]() If the hub is not present in the inventory, proceed further, else proceed to step 12.
If the hub is not present in the inventory, proceed further, else proceed to step 12.

|
|
|
|---|---|
The check box checked in step 2 above, if this hub router is the master controller. |
|
The above credentials need to be entered only one time. The values are populated for the remaining hub devices in the system.
If you choose to populate values for the SSH Telnet, you must configure the following commands on the device:
crypto key generate rsa modulus modulus-size. The modulus range is from 360 to 4096.
You must retrieve the generated RSA key pair by using the show crypto key mypubkey rsa command to run the ip ssh rsa keypair-name keypair-name command with the retrieved key pair name. This forces SSH to use the generated RSA keypair for SSH.
The device is verified in the background if the device is suitable for provisioning, and if there are errors or warnings, the Validation Status dialog appears displaying the validation errors or warnings. When the device is validated and ready for configuration, an orange icon with dotted lines appears.

This step is called Brownfield Validation, which indicates validation issues and the Validation Status dialog appears.
Step 10![]() Do one of the following:
Do one of the following:

You must fix them via command line interface navigating to the router before proceeding further and follow from steps 5 to 7 and select Revalidate. For explanation about messages displayed in the Validation Status dialog, see Appendix A, “Brownfield Validation Messages Description.”
Step 11![]() The hub router is added to the inventory and the Configure Router dialog appears.
The hub router is added to the inventory and the Configure Router dialog appears.
Step 12![]() Choose the LAN IP-Interface.
Choose the LAN IP-Interface.

Step 13![]() Configure the other hub routers in a similar method.
Configure the other hub routers in a similar method.
Step 14![]() Click on the link to configure and specify the link in the Configure Link dialog box.
Click on the link to configure and specify the link in the Configure Link dialog box.
The following and the subsequent dialog appear depending on the WAN type that you specified while configuring the type in the Service Provider tab for a public and private link respectively.



Note![]() Effective with Cisco IWAN Release 1.1, you can specify static IP addresses for DHCP links.
Effective with Cisco IWAN Release 1.1, you can specify static IP addresses for DHCP links.
Perform this step for each link in the network.
Step 15![]() Select Enable Non IWAN Sites to enable communication between IWAN and non-IWAN sites to leverage the coexistence feature, as part of the MPLS configure link..
Select Enable Non IWAN Sites to enable communication between IWAN and non-IWAN sites to leverage the coexistence feature, as part of the MPLS configure link..
Step 16![]() Choose the loopback IP address in the Loopback IP-Interface drop down list.
Choose the loopback IP address in the Loopback IP-Interface drop down list.
Select the preprovisioned loopback interface from the dropdown list. This enables Cisco IWAN App to form a route of existing sites with new IWAN sites

Note![]() The loopback interface must already be configured on the MPLS router. The loopback interface is required to support co-existence between IWAN and non-IWAN sites and the loopback interface must to be configured before adding the device to APIC-EM. It is recommended that you specify a loopback IP address in the same subnet as the WAN interface.
The loopback interface must already be configured on the MPLS router. The loopback interface is required to support co-existence between IWAN and non-IWAN sites and the loopback interface must to be configured before adding the device to APIC-EM. It is recommended that you specify a loopback IP address in the same subnet as the WAN interface.
Step 18![]() Click on the cloud, in this case, MPLS or Internet (Inet), to configure the WAN clouds via the Configure Provider dialog box.
Click on the cloud, in this case, MPLS or Internet (Inet), to configure the WAN clouds via the Configure Provider dialog box.

Where to go Next
Configure the LAN settings for the data center. See Configure LAN Settings for the Data Center.
Configure LAN Settings for the Data Center
Perform this step to populate WAN subnets in LAN routing.
Step 1![]() To configure LAN settings for a data center, click “+” next to “Configure LAN Settings, Datacenter”. The Configure LAN dialog appears.
To configure LAN settings for a data center, click “+” next to “Configure LAN Settings, Datacenter”. The Configure LAN dialog appears.

The values for the fields (mentioned in th table below) Routing Protocol, AS Number, and Datacenter Prefix are collected from the devices and autopopulated for ease of configuration. The common (matching) AS numbers between the devices are displayed for each routing protocols. You can change the AS numbers on device, but it is not recommended that you do so. If your LAN routing protocol is BGP, and there are no matching AS numbers, the AS number field is grayed out and you must manually modify the LAN side routing in the device. This release does not support BGP with different AS numbers.
If you select BGP as your routing protocol, you must select Advanced Setting to specify the IP addresses. This is not required if your routing protocol is EIGRP or OSPF.
After specifying the DC LAN and WAN settings, click Save & Continue or select the “Certified IOS Releases” tab.
Configure Master Controller
To configure management controller settings, click “+” next to “Configure External Master Controller”. This is required if your topology uses external master controller.

Note![]() For a dedicated master controller, the device must be greenfield validated. No conflicting configuration with IWAN or dynamic routing protocols are supported for LAN and WAN.
For a dedicated master controller, the device must be greenfield validated. No conflicting configuration with IWAN or dynamic routing protocols are supported for LAN and WAN.
In the Router Management IP textbox, enter the management IP address of the hub router and click Validate.
Enter values in the following fields and click Save.
|
|
|
|---|---|
 Feedback
Feedback