Release Notes for the Catalyst 4900M Series Switch and the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch, Cisco IOS 15.1(2)SGx
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Supported Hardware on Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F, and Catalyst 4900M Series Switches
Features Not Supported on the Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, and Catalyst 4948E-F Series Switches
New Hardware Features in Release 15.1(2)SG
New Software Features in Release 15.1(2)SG
Minimum and Recommended ROMMON Release
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG8
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG7
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG7
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG6
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG6
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG5
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG5
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG4
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG4
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG3
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG3
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG2
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG2
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG1
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG1
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E and Catalyst 4948E-F Series Switches, Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SGx
Current Release
IOS 15.1(2)SG8—Nov 11, 2016
Prior release
15.1(2)SG7, 15.1(2)SG6, 15.1(2)SG5, IOS 15.1(2)SG4, IOS 15.1(2)SG3, 15.1(2)SG2, 15.1(2)SG1, 15.1(2)SG
These release notes describe the features, modifications, and caveats for Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG on the Catalyst 4900M switch, the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch, and the Catalyst 4948E-F Ethernet Switch.
Cisco IOS Software Release 15.1(2)SG delivers new software and hardware innovations in campus access and aggregation deployments that span across many technologies including Security, Video, High Availability, Network Virtualization, IP Multicast and Lower TCO as following:
–![]() Lightweight DHCPv6 Relay Agent (LDRA)
Lightweight DHCPv6 Relay Agent (LDRA)
–![]() IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Multicast Suppression
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Multicast Suppression
–![]() IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) Guard
IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) Guard
–![]() Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Client Support
Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Client Support
–![]() Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Server Support
Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Server Support
–![]() SSH Keyboard Interactive Authentication
SSH Keyboard Interactive Authentication
–![]() SSHv2 Enhancements for RSA Keys
SSHv2 Enhancements for RSA Keys
Lower Total Cost of Ownership and Ease of Use
Routing and Multicast Enhancements
- BFD C bit support - RFC5882
- BGP Consistency Checker
- IPv6 BSR Scoped Zone support
- OSPFv3 Address Families
- OSPFv3 Time To Live Security
- Policy Based Routing: Recursive Next Hop
- FTP IPv6 Support
- IPSLA 4.0 - IPv6 phase 2
- IPSLA Multicast Support
- NTPv4 Orphan Mode support, Range for trusted key configuration
- TFTP IPv6 Support
- WSMA and XMLPI enhancement
Cisco Catalyst 4900M Series is a premium extension to the widely deployed Catalyst 4948 Series top of rack Ethernet switches for data center server racks. Optimized for ultimate deployment flexibility, the Catalyst 4900M Series can be deployed for 10/100/1000 server access with 1:1 uplink to downlink oversubscription, mix of 10/100/1000 and 10 Gigabit Ethernet servers or all 10 Gigabit Ethernet servers in the same rack. The Catalyst 4900M is a 320Gbps, 250Mpps, 2RU fixed configuration switch with
8 fixed wire speed X2 ports on the base unit and 2 optional half card slots for deployment flexibility and investment protection. Low latency, scalable buffer memory and high availability with 1+1 hot swappable AC or DC power supplies and field replaceable fans optimize the Catalyst 4900M for any size of data center.
With Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)XO, Cisco introduced the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch, which is the first Cisco Catalyst E-Series data center switch built from the start to deliver class-leading, full-featured server-access switching. The switch offers forty-eight 10/100/1000-Gbps RJ45 downlink ports and four 1/10 Gigabit Ethernet uplink ports and is designed to simplify data center architecture and operations by offering service provider-grade hardware and software in a one rack unit (1RU) form factor optimized for full-featured top-of-rack (ToR) data center deployments.
The Cisco Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch builds on the advanced technology of the Cisco Catalyst 4948 Switches, the most deployed ToR switch in the industry, with more than 10 million ports deployed worldwide. The Cisco Catalyst E-Series doubles the uplink bandwidth and offers true front-to-back airflow with no side or top venting. Stringent airflow management reduces data center operating costs by providing strict hot-aisle and cold-aisle isolation. Exceptional reliability and serviceability are delivered with optional internal AC and DC 1+1 hot-swappable power supplies and a hot-swappable fan tray with redundant fans.
With Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(54)WO, Cisco extended the widely deployed Cisco Catalyst® 4948E Ethernet Switch to offer back-to-front airflow with the Cisco Catalyst 4948E-F Switch.
For more information on the Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E and Catalyst4948E-F Ethernet Switches, visit:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6021/index.html .

Note![]() Although their Release Notes are unique, the platforms Catalyst 4900M/Catalyst 4948E/Catalyst 4948E-F and Catalyst 4500 leverage the same Software Configuration Guide, Command Reference Guide, and System Message Guide.
Although their Release Notes are unique, the platforms Catalyst 4900M/Catalyst 4948E/Catalyst 4948E-F and Catalyst 4500 leverage the same Software Configuration Guide, Command Reference Guide, and System Message Guide.
Cisco IOS Software Packaging
The Enterprise Services image supports Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and Catalyst 4900M Ethernet Switch Series software features based on Cisco IOS Software 15.1(2)SG, including enhanced routing. BGP capability is included in the Enterprises Services package.
The IP Base image supports Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) for Routed Access, Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) "limited" Stub Routing, Nonstop Forwarding/Stateful Switchover (NSF/SSO), and RIPv1/v2. The IP Base image does not support enhanced routing features such as BGP, Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), AppleTalk, Virtual Routing Forwarding (VRF-lite), GLBP, and policy-based routing (PBR).
The LAN Base image complements the existing IP Base and Enterprise Services images. It is focused on customer access and Layer 2 requirements and therefore many of the IP Base features are not required. The IP upgrade image is available if at a later date you require some of those features. The Cisco Catalyst 4900M Switch Series only supports the IP Base and Enterprise Services images.
Starting with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SG, on Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E and Catalyst 4948E-F, support for NEAT feature has been extended from IP Base to LAN Base and support for HSRP v2 IPV6 has been extended from Enterprise Services to IP Base.
Starting with Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG, support for IP SLAs and NSF has been extended from Enterprise Services to IP Base.

Note![]() The default image for WS-4900M, WS-C4948E, and WS-C4948E-F is IP Base.
The default image for WS-4900M, WS-C4948E, and WS-C4948E-F is IP Base.
Cisco IOS Release Strategy
Customers with Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and Catalyst 4900M series switches who need the latest hardware support and software features should migrate to Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG.
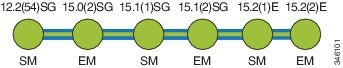
The Catalyst 4900M Series Switch has three maintenance trains: 12.2(53)SGx, 15.0(2)SGx and 15.1(2)SGx. The Catalyst 4948E/E-F switches have two maintenance trains: 15.0(2)SGx and 15.1(2)SGx.
Figure 1 displays the three active trains, 12.2(53)SG, 15.0(2)SG and 15.1(2)SG.

Note![]() Support for the Catalyst 4900M platform was introduced in Cisco IOS 12.2(40)XO. Support for the Catalyst 4948E platform was introduced in Cisco IOS 12.2(54)XO. Support for the Catalyst 4948E-F platform was introduced in Cisco IOS 12.2(54)SG1.
Support for the Catalyst 4900M platform was introduced in Cisco IOS 12.2(40)XO. Support for the Catalyst 4948E platform was introduced in Cisco IOS 12.2(54)XO. Support for the Catalyst 4948E-F platform was introduced in Cisco IOS 12.2(54)SG1.
Figure 1 Software Release Strategy for the Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F Series Switches
Support
Support for Cisco IOS Software Release 15.1(2)SG follows the standard Cisco Systems® support policy, available at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_end-of-life_policy.html
System Requirements
This section describes the system requirements on the Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F, and Catalyst 4900M Series Switches:
- Supported Hardware on Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F, and Catalyst 4900M Series Switches
- Feature Support by Image Type
- MIB Support
- Features Not Supported on the Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, and Catalyst 4948E-F Series Switches
- Orderable Product Numbers
Supported Hardware on Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F,
and Catalyst 4900M Series Switches
For details on Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, and Catalyst 4948E-F switch transceiver module compatibility, see the url:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps5455/products_device_support_tables_list.html
The following table lists the hardware supported on the Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, and Catalyst 4948E-F Series Switches.
8-Port Wire-Speed 10 Gigabit Ethernet (RJ-45) Note This linecard is not supported on the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. |
|
The following table lists the hardware supported on the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch.
The following table lists the hardware supported on the Catalyst 4948E-F Ethernet Switch.
Feature Support by Image Type

Note![]() The default image for the Catalyst 4900M Series Switch is Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG4. The default image for the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch and the Catalyst 4948E-F Ethernet Switch is 12.2(54)SG1.
The default image for the Catalyst 4900M Series Switch is Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG4. The default image for the Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch and the Catalyst 4948E-F Ethernet Switch is 12.2(54)SG1.
Table 4 lists the Cisco IOS software features for the Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and Catalyst 4900M series switches. For the full list of supported features, check the Feature Navigator application:
http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/CFN/
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) Hardware Offload Support |
|||
Crashdump Enhancement1 |
|||
IEEE 802.1ag D8.1 standard Compliant CFM, Y.1731 multicast LBM / AIS / RDI / LCK, IP SLA for Ethernet |
|||
IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) Standard Compliance |
|||
IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation (LACP) Port-Channel Standalone Disable |
|||
IPv6 First Hop Security (FHS): Lightweight DHCPv6 Relay Agent |
|||
IPv6 Multicast: Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Protocol, Versions 1 and 2 |
|||
Yes2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
IPv6 Switching: CEFv6 Switched Automatic IPv4-compatible Tunnels (in software) |
|||
IPv6 Switching: CEFv6 Switched Configured IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnels (in software) |
|||
IPv6 Tunneling: Automatic IPv4-compatible Tunnels (in software) |
|||
IPv6 Tunneling: Manually Configured IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnels (in software) |
|||
Medianet 2.0: Integrated Video Traffic Simulator (hardware-assisted IP SLA); IPSLA responder only |
|||
Medianet 2.0: Media Monitoring (Performance Monitoring and Mediatrace) |
|||
NEAT Enhancement: Re-Enabling BPDU Guard Based on User Configuration |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
Yes 2 |
|||
RADIUS Attribute 44 (Accounting Session ID) in Access Requests |
|||
Source Specific Multicast (SSM) - IGMPv3,IGMP v3lite, and URD |
|||
Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)3 |
|||
VLAN Mapping (VLAN Translation)4 |
|||
MIB Support
For information on MIB support, please refer to this URL:
http://ftp.cisco.com/pub/mibs/supportlists/cat4000/cat4000-supportlist.html
Features Not Supported on the Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, and Catalyst 4948E-F Series Switches
These features are not supported in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG on Catalyst 4900M, Catalyst 4948E, and Catalyst 4948E-L Series Switches:
–![]() Standard Xerox Network System (XNS) access list
Standard Xerox Network System (XNS) access list
–![]() Protocol type-code access list
Protocol type-code access list
- ADSL and Dial access for IPv6
- AppleTalk EIGRP
- Auto RP
- AutoQoS - VoIP
- Bridge groups
- CEF Accounting
- CER for E-911 Support
- CFM CoS
- Cisco-Port-QoS-MIB
- Cisco IOS software IPX ACLs:
–![]() <1200-1299> IPX summary address access list
<1200-1299> IPX summary address access list
- Cisco IOS software-based transparent bridging (also called “fallback bridging”)
- Connectionless (CLNS) routing; including IS-IS routing for CLNS. IS-IS is supported for IP routing only.
- DLSw (data-link switching)
- Global QoS (enable QoS)
- HTTP Software Upgrade
- IGRP (use EIGRP instead)
- ISSU
- Kerberos support for access control
- LLDP HA
- Lock and key
- MAC Address Notification
- MAC notification MIB support
- NAC L2 IP - Inaccessible authentication bypass
- NAT-PT for IPv6
- NSF with SSO
- Packet Based Storm Control
- Reflexive ACLs
- MPLS and routing IP over an MPLS network
- RPR
- UniDirectional Link Routing (UDLR)
New and Changed Information
These sections describe the new and changed information for the Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches running Cisco IOS software:
New Hardware Features in Release 15.1(2)SG
Release 15.1(2)SG provides the following new hardware on the Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches:
New Software Features in Release 15.1(2)SG
Release 15.1(2)SG provides the following new software on the Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches:
–![]() Lightweight DHCPv6 Relay Agent (LDRA)
Lightweight DHCPv6 Relay Agent (LDRA)
–![]() IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Multicast Suppression
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Multicast Suppression
–![]() IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) Guard
IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) Guard
–![]() Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Client Support
Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Client Support
–![]() Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Server Support
Secure Shell SSH Version 2 Server Support
–![]() SSH Keyboard Interactive Authentication
SSH Keyboard Interactive Authentication
–![]() SSHv2 Enhancements for RSA Keys
SSHv2 Enhancements for RSA Keys
Lower Total Cost of Ownership and Ease of Use
Minimum and Recommended ROMMON Release
Table 6 lists the minimum and recommended ROMMON releases for the Catalyst 4900M Series Switch, Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch, and Catalyst 4948E-F Ethernet Switch.

Note![]() ROMMON Release 12.2(44r)SG5 is the minimum required to run Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SG and is recommended for other releases.
ROMMON Release 12.2(44r)SG5 is the minimum required to run Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SG and is recommended for other releases.
Limitations and Restrictions
Following limitations and restrictions apply to the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches:
- Starting with Release IOS XE 3.3.0SG and IOS 15.1(1)SG, the seven RP restriction was removed
- The WS-X4920-GB-RJ45 card performs at wire speed until it operates at 99.6% utilization. Beyond this rate, the card will lose some packets.
- Compact Flash is not supported on a Cisco Catalyst 4900M switch running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(40)XO. Attempting to use Compact Flash may corrupt your data.
- IP classful routing is not supported; do not use the no ip classless command; it will have no effect, as only classless routing is supported. The command ip classless is not supported as classless routing is enabled by default.
- A Layer 2 LACP channel cannot be configured with the spanning tree PortFast feature.
- Netbooting using a boot loader image is not supported. See the “Related Documentation” section for details on alternatives.
- An unsupported default CLI for mobile IP is displayed in the HSRP configuration. Although this CLI will not harm your system, you might want to remove it to avoid confusion.
Workaround: Display the configuration with the show standby command, then remove the CLI. Here is sample output of the show standby GigabitEthernet1/1 command:
- For HSRP “preempt delay” to function consistently, you must use the standby delay minimum command. Be sure to set the delay to more than 1 hello interval, thereby ensuring that a hello is received before HSRP leaves the initiate state.
Use the standby delay reload option if the router is rebooting after reloading the image.
- You can run only.1q-in-.1q packet pass-through with the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches.
- For PVST, on the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches VLANs, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)SG supports a maximum of 3000 spanning tree port instances. If you want to use more than this number of instances, you should use MST rather than PVST.
- Because the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches support the FAT file system, the following restrictions apply:
–![]() The verify and squeeze commands are not supported.
The verify and squeeze commands are not supported.
–![]() The rename command is supported in FAT file system.
The rename command is supported in FAT file system.
For the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches, the rename command has been added for bootflash and slot0. For all other supervisor engines, the rename command is supported for nvram devices only.
–![]() the fsck command is supported for slot0 device. It is not supported in the file systems on supervisor engines other than 6-E.
the fsck command is supported for slot0 device. It is not supported in the file systems on supervisor engines other than 6-E.
–![]() In the FAT file system, the IOS format bootflash: command erases user files only. It does not erase system configuration.
In the FAT file system, the IOS format bootflash: command erases user files only. It does not erase system configuration.
–![]() The FAT file system supports a maximum of 63 characters for file/directory name. The maximum for path length is 127 characters.
The FAT file system supports a maximum of 63 characters for file/directory name. The maximum for path length is 127 characters.
–![]() The FAT file system does not support the following characters in file/directory names:{}#%^ and space characters.
The FAT file system does not support the following characters in file/directory names:{}#%^ and space characters.
–![]() The FAT file system honors the Microsoft Windows file attribute of "read-only" and "read-write", but it does not support the Windows file "hidden" attribute.
The FAT file system honors the Microsoft Windows file attribute of "read-only" and "read-write", but it does not support the Windows file "hidden" attribute.
–![]() Supervisor Engine 6-E uses the FAT file system for compact flash (slot0). If a compact flash is not formatted in FAT file system (such as compact flash on a supervisor engine other than 6-E), the switch does not recognize it.
Supervisor Engine 6-E uses the FAT file system for compact flash (slot0). If a compact flash is not formatted in FAT file system (such as compact flash on a supervisor engine other than 6-E), the switch does not recognize it.
- If an original packet is dropped due to transmit queue shaping and/or sharing configurations, a SPAN packet copy can still be transmitted on the SPAN port.
- All software releases support a maximum of 32,768 IGMP snooping group entries.
- Use the no ip unreachables command on all interfaces with ACLs configured for performance reasons.
- The threshold for the Dynamic Arp Inspection err-disable function is set to 15 ARP packets per second per interface. You should adjust this threshold depending on the network configuration. The CPU should not receive DHCP packets at a sustained rate greater than 1000 pps.
- If you first configure an IP address or IPv6 address on a Layer 3 port, then change the Layer 3 port to a Layer 2 port with the switchport command, and finally change it back to a Layer 3 port, the original IP/IPv6 address will be lost.
- If the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches request information from the Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) and the message exchange times out because the server does not respond, a message similar to this appears:
If this message appears, check that there is network connectivity between the switch and the ACS. You should also check that the switch has been properly configured as an AAA client on the ACS.
–![]() As IPSG learns the static hosts on each interface, the switch CPU may hit 100 per cent if there are a large number of hosts to learn. The CPU usage will drop once the hosts are learned.
As IPSG learns the static hosts on each interface, the switch CPU may hit 100 per cent if there are a large number of hosts to learn. The CPU usage will drop once the hosts are learned.
–![]() IPSG violations for static hosts are printed as they occur. If multiple violations occur simultaneously on different interfaces, the CLI displays the last violation. For example, if IPSG is configured for 10 ports and violations exist on ports 3,6 and 9, the violation messages are printed only for port 9.
IPSG violations for static hosts are printed as they occur. If multiple violations occur simultaneously on different interfaces, the CLI displays the last violation. For example, if IPSG is configured for 10 ports and violations exist on ports 3,6 and 9, the violation messages are printed only for port 9.
–![]() Inactive host bindings will appear in the device tracking table when either a VLAN is associated with another port or a port is removed from a VLAN. So, as hosts are moved across subnets, the hosts are displayed in the device tracking table as INACTIVE.
Inactive host bindings will appear in the device tracking table when either a VLAN is associated with another port or a port is removed from a VLAN. So, as hosts are moved across subnets, the hosts are displayed in the device tracking table as INACTIVE.
–![]() Autostate SVI does not work on EtherChannel.
Autostate SVI does not work on EtherChannel.
In such a scenario, the ipv6 MTU value programmed in hardware will be different from the ipv6 interface MTU value. This will happen if there is no room in the hw MTU table to store additional values.
You must free up some space in the table by unconfiguring some unused MTU values and subsequently disable/re-enable ipv6 on the interface or reapply the MTU configuration.
- To stop IPSG with Static Hosts on an interface, use the following commands in interface configuration submode:
To enable IPSG with Static Hosts on a port, issue the following commands:


Note![]() The issue above also applies to IPSG with Static Hosts on a PVLAN Host port.
The issue above also applies to IPSG with Static Hosts on a PVLAN Host port.
- Class-map match statements using match ip prec | dscp match only IPv4 packets whereas matches performed with match prec | dscp match both IPv4 and IPv6 packets.
- IPv6 QoS hardware switching is disabled if the policy-map contains IPv6 ACL and match cos in the same class-map with the ipv6 access-list has any mask range between /81 and /127. It results in forwarding packets to software which efficiently disable the QoS.
- Management port does not support non-VRF aware features.
- A Span destination of fa1 is not supported.
- The "keepalive" CLI is not supported in interface mode on the switch, although it will appear in the running configuration. This behavior has no impact on functionality.
- TDR is only supported on interfaces Gi1/1 through Gi1/48, at 1000BaseT under open or shorted cable conditions. TDR length resolution is +/- 10 m. If the cable is less than 10 m or if the cable is properly terminated, the TDR result displays "0" m. If the interface speed is not 1000BaseT, an "unsupported" result status displays. TDR results will be unreliable for cables extended with the use of jack panels or patch panels.
- Upstream ports on the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches support flow control auto negotiation in 1G mode only, and flow control is forced in 10G mode. If the interface is configured to auto-negotiate the flow control, and the interface is operating in 10G mode, the system forces flow control to ON and does not auto-negotiate.
- The following guidelines apply to Fast UDLD:
–![]() Fast UDLD is disabled by default.
Fast UDLD is disabled by default.
–![]() Configure fast UDLD only on point-to-point links between network devices that support fast UDLD.
Configure fast UDLD only on point-to-point links between network devices that support fast UDLD.
–![]() You can configure fast UDLD in either normal or aggressive mode.
You can configure fast UDLD in either normal or aggressive mode.
–![]() Do not enter the link debounce command on fast UDLD ports.
Do not enter the link debounce command on fast UDLD ports.
–![]() Configure fast UDLD on at least two links between each connected network device. This reduces the likelihood of fast UDLD incorrectly error disabling a link due to false positives.
Configure fast UDLD on at least two links between each connected network device. This reduces the likelihood of fast UDLD incorrectly error disabling a link due to false positives.
–![]() Fast UDLD does not report a unidirectional link if the same error occurs simultaneously on more than one link to the same neighbor device.
Fast UDLD does not report a unidirectional link if the same error occurs simultaneously on more than one link to the same neighbor device.
–![]() The Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches support fast UDLD on a maximum of 32 ports.
The Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches support fast UDLD on a maximum of 32 ports.
The outputs of certain commands, such as show ip route and show access-lists, contain non-deterministic text. While the output is easily understood, the output text does not contain strings that are consistently output. A general purpose specification file entry is unable to parse all possible output.
While a general purpose specification file entry may not be possible, a specification file entry might be created that returns the desired text by searching for text that is guaranteed to be in the output. If a string is guaranteed to be in the output, it can be used for parsing.
For example, the output of the show ip access-lists SecWiz_Gi3_17_out_ip command is this:
The first line is easily parsed because access list is guaranteed to be in the output:
The remaining lines all contain the term host. As a result, the specification file may report the desired values by specifying that string. For example, this line
will produce the following for the first and second rules
and the following for the third statement
Request the output of the show running-config command using NETCONF and parse that output for the desired strings. This is useful when the desired lines contain nothing in common. For example, the rules in this access list do not contain a common string and the order (three permits, then a deny, then another permit), prevent the spec file entry from using permit as a search string, as in the following example:
The XML output of show running-config command includes the following, which can then be parsed programmatically, as desired:
- Although the Catalyst 4900M series switch still supports legacy 802.1X commands used in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(46)SG and earlier releases (that is, they are accepted on the CLI), they do not display in the CLI help menu.
- Current IOS software cannot support filenames exceeding 64 characters.
- Although you can configure subsecond PIM query intervals on Catalyst 4500 platforms, such an action represents a compromise between convergence (reaction time) and a number of other factors (number of mroutes, base line of CPU utilization, CPU speed, processing overhead per 1 m-route, etc.). You must account for those factors when configuring subsecond PIM timers. We recommend that you set the PIM query interval to a minimum of 2 seconds. By adjusting the available parameters, you can achieve flawless operation; that is, a top number of multicast routes per given convergence time on a specific setup.
- With Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG3 (and 12.2(54)SG), we changed the default behavior such that your single supervisor, RPR, or fixed configuration switch does not reload automatically. To configure automatic reload, you must enter the diagnostic fpga soft-error recover aggressive command. (CSCth16953)
- The ROMMON version number column in the output of show module command is truncated.
Workaround: Use the show version command. CSCtr30294
Workaround: Select an alternate destination or source port. CSCty05405
- If a class-map is configured with exceed-action drop, re-configuring the same class-map with exceed-action transmit causes class-map configurations to conflict for the same class-map.
Workaround: If you plan to change a class-map action, such as exceed-action, you meed to remove the class-map with the no class c1 command under policy-map submode. Then, apply the new class-map with the updated changes. CSCsk70826)
- When you enter the show policy-map vlan vlan command, unconditional marking actions that are configured on the VLAN are not shown.
Workaround: None. However, if you enter the show policy-map name, the unconditional marking actions are displayed. CSCsi94144
Workarounds: Do one of the following:
–![]() After a reload, copy the startup-config to the running-config.
After a reload, copy the startup-config to the running-config.
–![]() Use a loopback interface as the target of the ip unnumbered command
Use a loopback interface as the target of the ip unnumbered command
–![]() Change the CLI configuration such that during bootup, the router port is created first.
Change the CLI configuration such that during bootup, the router port is created first.
- After posture validation succeeds, the following benign traceback messages may appear after you unconfigure the global RADIUS and IP device tracking commands:
This applies to classic or E-series Catalyst 4500 supervisor engines running
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(50)SG
- On the Cisco Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F and the Catalyst 4900M series switches, the host's MAC address is not synchronized to the standby supervisor engine after you unconfigure 802.1X on the port and reconnect the host to a IP phone (with CDP port status TLV support) that is connected to the switch.
If the switch were to run a supervisor switchover while in this state, the host's MAC address would not be present in the new active supervisor engine’s MAC address table, causing possible connectivity interruption on the host.
Workaround: Enter the shutdown command, followed by the no shutdown command on the interface. This triggers relearning and synchronizing of the host's MAC to the standby supervisor engine. CSCsw91661
- When multiple streams of CRC errors are encountered on a WS-C4900M configured with OAM Configuration of monitoring the errored frame seconds, OAM does not always report the value of errored frame seconds correctly.
To observe this issue, the following CLIs are configured with window size as the period for monitoring the errors and a low threshold equal to the number of CRC errored seconds seen/expected.
Workaround: Configure a lower value of low threshold such that the frame errors are seen divided into the expected number of frame errored seconds. CSCsy37181
- If time is not specified in the link debounce command, the default value depends on the supervisor engine. The default is 10 mS for the Catalyst 4948E, Catalyst 4948E-F, Catalyst 4900M, Supervisor Engine 6-E, and Supervisor Engine 6L-E. The default is 100 mS for all other supervisor engines.
–![]() Fast UDLD peer switch performs SSO.
Fast UDLD peer switch performs SSO.
–![]() Fast UDLD peer switch is reloaded.
Fast UDLD peer switch is reloaded.
–![]() One or more interfaces on a fast UDLD peer switch are shut down (or the port mode changes from switchport to routed, and vice versa).
One or more interfaces on a fast UDLD peer switch are shut down (or the port mode changes from switchport to routed, and vice versa).

Note![]() To reduce the likelihood of this event, connect at least two physical interfaces between fast UDLD peer switches. You must configure the interfaces with the same neighbor fast hello interval.
To reduce the likelihood of this event, connect at least two physical interfaces between fast UDLD peer switches. You must configure the interfaces with the same neighbor fast hello interval.
–![]() Reset the error disabled links with the udld reset command.
Reset the error disabled links with the udld reset command.
–![]() Configure error disable recovery with the commands errdisable recovery cause udld and
Configure error disable recovery with the commands errdisable recovery cause udld and
errdisable recovery interval value (between 30 and 86400 sec).
–![]() Manually clear errdisable on the local interface with a shutdown then a no shutdown.
Manually clear errdisable on the local interface with a shutdown then a no shutdown.
- On a peer interface on a switch, if errdisabled mode flap detection is set to a very small number (such as 2 flaps in 10 sec), a 10GE link flap may cause the peer interface to enter the errdisabled state.
Workarounds: The Cisco switch default link-flap detection value is 5 flaps in 10 seconds. Use the default value or larger numbers. CSCtg07677
- When you have enabled EPM logging and the client is authenticated via MAB or Webauth, the value of AUTHTYPE is DOT1X in EPM syslog messages irrespective of the authentication method.
Similarly, the show epm sessions command always displays the authentication method as DOT1X.
Workaround: To view the authentication method used for a client, enter the
show authentication sessions command. CSCsx42157
- With CFM enabled globally as well as on an ingress interface, CFM packets received on the interface are not policed with hardware control plane policing.
- When either the RADIUS-server test feature is enabled or RADIUS-server dead-criteria is configured, and either RADIUS-server deadtime is set to 0 or not configured, the RADIUS-server status is not properly relayed to AAA.
Workaround: Configure both dead-criteria and deadtime.
- If a large number of VLAN mappings are configured, a member port might fail to join a port channel and no warning is issued.
Workaround: Reduce the number of VLAN mappings. CSCtn56208
- If an interface whose IP address is being used as the Router ID is deleted or shuts down and you configure a service group with a multicast group-address, packet redirection to CE stops and packets are forwarded directly to the destination.
Workaround: Unconfigure and reconfigure the service group. CSCtn88087
- When a sampling monitor is configured on a routed port or on a VLAN (an SVI with just one port as a member) and bidir multicast is enabled, a packet sample may be exported even though the original multicast packet was not forwarded by the switch.
This issue only impacts Catalyst 4948E and Catalyst 4948E-F Ethernet Switches.
- Global WCCP service configuration fails to enable (WCCP global config is accepted but nvgen fails) on a newly deployed switch if the switch is not enabled for SVI or a Layer 3 interface.
Workaround: Enable a Layer 3 interface in the running config. CSCsc88636.
Workaround: None. The ip pim register-rate-limit command does not function. CSCub32679
- For packets with the same ingress and egress Layer 3 interface, ingress QoS marking policy does not work.
Workaround: Turn off ICMP redirect through the ip redirect command. CSCua71929
- While configuring an IPv6 access-list, if you specify hardware statistics as the first statement in v6 access-list mode (i.e. before issuing any other v6 ACE statement), it will not take effect. Similarly, your hardware statistics configuration will be missing from the output of the show running command.
You will not experience this behavior with IPv4 access lists.
Workaround: During IPv6 access-list configuration, configure at least one IPv6 ACE before the "hardware statistics" statement. CSCuc53234
- When an IPv6 FHS policy is applied on a VLAN and an EtherChannel port is part of that VLAN, packets received by EtherChannel (from neighbors) are not bridged across the local switch.
Workaround: Apply FHS policies on a non EtherChannel port rather than a VLAN. CSCua53148
Caveats
Caveats describe unexpected behavior in Cisco IOS releases. Caveats listed as open in a prior release are carried forward to the next release as either open or resolved.
For the latest information on PSIRTS, refer to the Security Advisories on CCO at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_advisory09186a0080b4a315.shtml
Cisco Bug Search Tool
The Bug Search Tool (BST) is the online successor to Bug Toolkit and is designed to improve the effectiveness in network risk management and device troubleshooting. The BST allows partners and customers to search for software bugs based on product, release, and keyword, and aggregates key data such as bug details, product, and version. The tool has a provision to filter bugs based on credentials to provide external and internal bug views for the search input. You can access the tool at: https://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch/.
To view the details of a caveat listed in this document:
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG8
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG7
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG6
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 15.1(2)SG6
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG5
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG5
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG4
This section lists the open caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG4:
- Cisco IOS -XE for Catalyst 3000 series, 4000 series, AIR-CT5760, and Cisco RF Gateway 10 (RFGW-10) includes a version of Bash that is affected by the vulnerabilities identified by the Common Vulnerability and Exposures (CVE) IDs:
Cisco has analyzed this vulnerability and concluded that while the previously listed products may run a vulnerable version of Bash, there are no exploitation vectors present - therefore, those products are not impacted.
Additional details about these vulnerabilities can be found at http://cve.mitre.org/cve/cve.html
- When more than one Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) is available on the downstream switch, and Mediatrace is invoked to provide flow statistics, the dynamic policy does not show statistics for a flow.
Mediatrace cannot find the correct inbound interface and applies the dynamic policy on a different interface from the one used for media flow.
- Configuring an interface as unidirectional with the unidirectional send-only | receive-only command still allows an interface to send (configured as Send-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) or receive (configured as Receive-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) packets in a bidirectional mode.
- When you add a "bfd" suffix to the snmp server host x.x.x.x configuration command, the BFD traps, ciscoBfdSessUp and ciscoBfdSessDown, are not generated.
Workaround: Do not specify a "bfd" suffix with the snmp-server host x.x.x.x configuration command. CSCtx51561
- If burst is not explicitly configured for a single rate policer, the show policy-map command displays an incorrect burst value.
Workaround: Enter the show policy-map interface command. CSCsi71036
Workarounds: Disable IGMP snooping on all the relevant VLANs before disabling it globally.
- In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)SG, if an Etherchannel is a member of a flexlink pair, then static MAC addresses configured on the EtherChannel are not moved to the alternate port when the EtherChannel fails (flexlink failure)
- When a CFM Inward Facing MEP(IFM) is configured on a VLAN that is not allocated on a switch port that is DOWN, the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command displays the
IFM CC Status as Inactive. Then, you allocate the VLAN, the CC-status remains Inactive.
You only see this symptom if you did not allocate a VLAN before you configure the IFM, then at a later time allocate the same VLAN.
Workaround: Unconfigure, then reconfigure the IFM on the port.
- VTP databases do not propagate through promiscuous trunk ports. If only promiscuous trunks are configured, users will not see the VLAN updates on the other switches in the VTP domain.
Workaround: For VTP database propagation, configure ISL/dot1q trunk port. CSCsu43445
- When you configure switchport block multicast on a switch running
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1 and later or 12.2(50)SG6 and later, Layer 2 multicast is not blocked.
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1, 12.2(50)SG6, the switchport block multicast command would block IP Multicast, Layer 2 multicast, and broadcast traffic (CSCta61825).
- WCCP service is not reacquired when a service group with a multicast group-address is unconfigured, and then reconfigured.
Workaround: Configure ip multicast-routing globally and establish ip pim sparse-dense-mode on the CE-facing interface. CSCtl97692
- When you enable both Cisco TrustSec and RADIUS accounting, a disparity occurs between the RADIUS client (Cisco switch) and the RADIUS/CTS server in how the authenticator field in the header is computed for DOT1X/RADIUS accounting messages.
A Cisco IOS AAA client uses the PAC secret to compute the authenticator; Cisco Secure ACS 5.2 uses the shared secret. This behavior causes a mismatch that results in a rejection of the accounting message, and the client marks the server as unresponsive.
- The Mediatrace Initiator may report the status "Abort due to route changed" when a MAC move happens on a switch configured as the Mediatrace Responder that is also connected to a video traffic generator.
- A Catalyst 4507R chassis might experience a watchdog NMI crash. Crashdump is not saved when the supervisor [engine] module reboots.
- In a scaled setup, if a QoS policy (with policer action) is attached to numerous targets and if you attempt to modify the policer rates, a switch crashes.
Workaround: Remove the policy from the targets to which it is attached, modify the policy, and re-attach. CSCum58148
This caveat applies to IOS Release 3.04.02.SG, 3.04.03.SG, and 3.04.04SG.
- Given an interface configured for LACP and OAM, when the connection between ASR9K(IOS XR) and a Catalyst 4500X(IOS XE) flaps, the link will not restore due to the following deadlock:
LACP PDU requires OAM to start on the ASR9K side; OAM PDU requires LACP to start on the Catalyst 4500X side. With the above scenario, after a flap the link gets stuck in (Suspended) LACP state on the Catalyst 4500X and in Non-connected state on the ASR9K.
To avoid this behavior, you must manually reconfigure the particular sequence.
–![]() Change the configuration sequence on the 4500X side, such that the LACP packet goes first, followed by OAM PDU:
Change the configuration sequence on the 4500X side, such that the LACP packet goes first, followed by OAM PDU:
–![]() Disable EFD on the ASR9K side.
Disable EFD on the ASR9K side.
–![]() Toggle OAM on ASR9K side. CSCun11927
Toggle OAM on ASR9K side. CSCun11927
- If active traffic exists on switch ports and you configure mac address-table static xxxx.xxxx.xxxx vlan X drop, the switch crashes.
- When the NI port of a laptop without AC power (i.e., operating only on battery mode) is connected to the PoE module (WS-X4748-RJ45V+E), the NIC link does not come up (i.e., remains in disconnected status).
Neither issuing shut then no shut nor disabling then re-enabling the NIC port resolves the problem.
–![]() Configure power inline never on the PoE port.
Configure power inline never on the PoE port.
- With following topology, odd size packets are dropped if traffic egresses on uplink ports of a Catalyst 4948-E switch operating at 1 Gig line rate:
IXIA(01/02) ------ (Gi1/2)C4948E(Ten1/49) ------ (05/02)IXIA
It's easier to observe this output drop with smaller random size packets.
- After resetting the line cards (WS-X4748-UPOE+E and WS-X4748-RJ45-E) and issuing the no shut command, port inconsistent error messages display.
Functionality is not impacted.
- When you apply a QoS Service policy simultaneously (under port-vlan config mode) on numerous VLANs with a service policy from Layer 2 to Layer 3, CPU Hog and Trace back display.
Workaround: Reapply the configurations after converting the port. CSCuo24626
- If Flexlink is configured on a standalone neighboring Catalyst 4500 switch that is connected to VSS, on reloading the switch, Traceback is seen and the switch hangs
Workaround: Remove Flexlink from the neighboring Catalyst 4500 switch. CSCun90931
The exact triggers are unknown.
Workaround: Reapply the configuration when the switch reboots. CSCum71764
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG4
This section lists the resolved caveats in Cisco Release 15.1(2)SG4:
- Before large PACLs are fully loaded in hardware, you might observe a false completion messages like the following:
This issue does not impact functionality.
You must wait for the ACLs to be programmed before performing other TCAM related changes. CSCtd57063
- When two distinct Layer 3 CE-facing interfaces exist, each connected to a CE to split WCCP between the two CEs, and you move a particular WCCP service (like 60 (ftp-native)) from one Layer 3 interface to the other, the target interface fails to completely transfer the service to the new CE from the old CE.
Workaround: Shutdown the CE-facing interface. Once all the mask-value entries point to the target CE, unshut the CE-facing interface. CSCtl09941
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG3
This section lists the open caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG3:
- If burst is not explicitly configured for a single rate policer, the show policy-map command displays an incorrect burst value.
Workaround: Enter the show policy-map interface command. CSCsi71036
Workarounds: Disable IGMP snooping on all the relevant VLANs before disabling it globally.
Workaround: Unconfigure any generic QOS policies from the system. The QoS policies with the match any attribute cause IPv6 entries to become active. If the switch is a pure Layer 2 device, remove the generic protocol family attributes and narrow it to the protocol family.
- In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)SG, if an etherchannel is a member of a flexlink pair, then static MAC addresses configured on the EtherChannel are not moved to the alternate port when the EtherChannel fails (flexlink failure)
- When a CFM Inward Facing MEP(IFM) is configured on a VLAN that is not allocated on a switch port that is DOWN, the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command displays the
IFM CC Status as Inactive. Then, you allocate the VLAN, the CC-status remains Inactive.
You only see this symptom if you did not allocate a VLAN before you configure the IFM, then at a later time allocate the same VLAN.
Workaround: Unconfigure, then reconfigure the IFM on the port.
- VTP databases do not propagate through promiscuous trunk ports. If only promiscuous trunks are configured, users will not see the VLAN updates on the other switches in the VTP domain.
Workaround: For VTP database propagation, configure ISL/dot1q trunk port. CSCsu43445
- If you simultaneously apply a service-policy to a port in the output direction and a service-policy to a vlan-range under that port in the output direction, the class-map hit counters in the output of the
show policy-map interface command are wrong.
The queue transmit counters as well as the policing statistics (if any) are correct. CSCsz20149
- When you configure switchport block multicast on a switch running
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1 and later or 12.2(50)SG6 and later, Layer 2 multicast is not blocked.
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1, 12.2(50)SG6, the switchport block multicast command would block IP Multicast, Layer 2 multicast, and broadcast traffic (CSCta61825).
- Before large PACLs are fully loaded in hardware, you might observe a false completion messages like the following:
This issue does not impact functionality.
You must wait for the ACLs to be programmed before performing other TCAM related changes. CSCtd57063
- With a NEAT configuration on an ASW (Catalyst 4500 series switch) connected to an SSW (Catalyst 3750 series switch) serving as a root bridge and with redundant links between ASW and SSW, the following occur:
–![]() The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
Workaround: Configure the ASW or any other switch upstream as the root-bridge for all the VLANs. CSCtg71030
- When two distinct Layer 3 CE-facing interfaces exist, each connected to a CE to split WCCP between the two CEs, and you move a particular WCCP service (like 60 (ftp-native)) from one Layer 3 interface to the other, the target interface fails to completely transfer the service to the new CE from the old CE.
Workaround: Shutdown the CE-facing interface. Once all the mask-value entries point to the target CE, unshut the CE-facing interface. CSCtl09941
- WCCP service is not reacquired when a service group with a multicast group-address is unconfigured, and then reconfigured.
Workaround: Configure ip multicast-routing globally and establish ip pim sparse-dense-mode on the CE-facing interface. CSCtl97692
- If you reboot a switch, the configured value of the interface MTU size for the elements of the port channel interface does not work for IPv6 traffic.
Workaround: After the switch reloads, enter shut and no shut on the port-channel interface.
- When you enable both Cisco TrustSec and RADIUS accounting, a disparity occurs between the RADIUS client (Cisco switch) and the RADIUS/CTS server in how the authenticator field in the header is computed for DOT1X/RADIUS accounting messages.
A Cisco IOS AAA client uses the PAC secret to compute the authenticator; Cisco Secure ACS 5.2 uses the shared secret. This behavior causes a mismatch that results in a rejection of the accounting message, and the client marks the server as unresponsive.
- When more than one Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) is available on the downstream switch, and Mediatrace is invoked to provide flow statistics, the dynamic policy does not show statistics for a flow.
Mediatrace cannot find the correct inbound interface and applies the dynamic policy on a different interface from the one used for media flow.
- When you add a "bfd" suffix to the snmp server host x.x.x.x configuration command, the BFD traps, ciscoBfdSessUp and ciscoBfdSessDown, are not generated.
Workaround: Do not specify a "bfd" suffix with the snmp-server host x.x.x.x configuration command. CSCtx51561
- During either a system- or user-initiated reload operation, the following message is observed when the system shuts down:
This message is not observed during a system bootup.
Workaround: None required. This message is information only. CSCtz15738
- The Mediatrace Initiator may report the status "Abort due to route changed" when a MAC move happens on a switch configured as the Mediatrace Responder that is also connected to a video traffic generator.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG3
This section lists the resolved caveats in Cisco Release 15.1(2)SG3:
- On systems performing multicast routing, a brief increase in CPU consumption occurs every few minutes. In large-scale environments, this CPU increase is more noticeable.
- A port configured for webauth is not programmed with the default or fallback ACL when sessions enter the INIT state.
- When a device authenticates with dot1x after authenticating with MAB, any policies applied by MAB remain in place.
–![]() Ensure that the dot1x supplicant always authenticates before MAB.
Ensure that the dot1x supplicant always authenticates before MAB.
–![]() Create MAB policies for dot1x hosts that do not supply a URL redirect. CSCui79988
Create MAB policies for dot1x hosts that do not supply a URL redirect. CSCui79988
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG2
This section lists the open caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG2:
- If burst is not explicitly configured for a single rate policer, the show policy-map command displays an incorrect burst value.
Workaround: Enter the show policy-map interface command. CSCsi71036
Workarounds: Disable IGMP snooping on all the relevant VLANs before disabling it globally.
Workaround: Unconfigure any generic QOS policies from the system. The QoS policies with the match any attribute cause IPv6 entries to become active. If the switch is a pure Layer 2 device, remove the generic protocol family attributes and narrow it to the protocol family.
- In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)SG, if an etherchannel is a member of a flexlink pair, then static MAC addresses configured on the EtherChannel are not moved to the alternate port when the EtherChannel fails (flexlink failure)
- When a CFM Inward Facing MEP(IFM) is configured on a VLAN that is not allocated on a switch port that is DOWN, the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command displays the
IFM CC Status as Inactive. Then, you allocate the VLAN, the CC-status remains Inactive.
You only see this symptom if you did not allocate a VLAN before you configure the IFM, then at a later time allocate the same VLAN.
Workaround: Unconfigure, then reconfigure the IFM on the port.
- VTP databases do not propagate through promiscuous trunk ports. If only promiscuous trunks are configured, users will not see the VLAN updates on the other switches in the VTP domain.
Workaround: For VTP database propagation, configure ISL/dot1q trunk port. CSCsu43445
- If you simultaneously apply a service-policy to a port in the output direction and a service-policy to a vlan-range under that port in the output direction, the class-map hit counters in the output of the
show policy-map interface command are wrong.
The queue transmit counters as well as the policing statistics (if any) are correct. CSCsz20149
- When you configure switchport block multicast on a switch running
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1 and later or 12.2(50)SG6 and later, Layer 2 multicast is not blocked.
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1, 12.2(50)SG6, the switchport block multicast command would block IP Multicast, Layer 2 multicast, and broadcast traffic (CSCta61825).
- Before large PACLs are fully loaded in hardware, you might observe a false completion messages like the following:
This issue does not impact functionality.
You must wait for the ACLs to be programmed before performing other TCAM related changes. CSCtd57063
- With a NEAT configuration on an ASW (Catalyst 4500 series switch) connected to an SSW (Catalyst 3750 series switch) serving as a root bridge and with redundant links between ASW and SSW, the following occur:
–![]() The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
Workaround: Configure the ASW or any other switch upstream as the root-bridge for all the VLANs. CSCtg71030
- When two distinct Layer 3 CE-facing interfaces exist, each connected to a CE to split WCCP between the two CEs, and you move a particular WCCP service (like 60 (ftp-native)) from one Layer 3 interface to the other, the target interface fails to completely transfer the service to the new CE from the old CE.
Workaround: Shutdown the CE-facing interface. Once all the mask-value entries point to the target CE, unshut the CE-facing interface. CSCtl09941
- WCCP service is not reacquired when a service group with a multicast group-address is unconfigured, and then reconfigured.
Workaround: Configure ip multicast-routing globally and establish ip pim sparse-dense-mode on the CE-facing interface. CSCtl97692
- If you reboot a switch, the configured value of the interface MTU size for the elements of the port channel interface does not work for IPv6 traffic.
Workaround: After the switch reloads, enter shut and no shut on the port-channel interface.
- When you enable both Cisco TrustSec and RADIUS accounting, a disparity occurs between the RADIUS client (Cisco switch) and the RADIUS/CTS server in how the authenticator field in the header is computed for DOT1X/RADIUS accounting messages.
A Cisco IOS AAA client uses the PAC secret to compute the authenticator; Cisco Secure ACS 5.2 uses the shared secret. This behavior causes a mismatch that results in a rejection of the accounting message, and the client marks the server as unresponsive.
- When more than one Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) is available on the downstream switch, and Mediatrace is invoked to provide flow statistics, the dynamic policy does not show statistics for a flow.
Mediatrace cannot find the correct inbound interface and applies the dynamic policy on a different interface from the one used for media flow.
- When you add a "bfd" suffix to the snmp server host x.x.x.x configuration command, the BFD traps, ciscoBfdSessUp and ciscoBfdSessDown, are not generated.
Workaround: Do not specify a "bfd" suffix with the snmp-server host x.x.x.x configuration command. CSCtx51561
- During either a system- or user-initiated reload operation, the following message is observed when the system shuts down:
This message is not observed during a system bootup.
Workaround: None required. This message is information only. CSCtz15738
- The Mediatrace Initiator may report the status "Abort due to route changed" when a MAC move happens on a switch configured as the Mediatrace Responder that is also connected to a video traffic generator.
- On systems performing multicast routing, a brief increase in CPU consumption occurs every few minutes. In large-scale environments, this CPU increase is more noticeable.
- Configuring an interface as unidirectional with the unidirectional send-only | receive-only command still allows an interface to send (configured as Send-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) or receive (configured as Receive-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) packets in a bidirectional mode.
- A port configured for webauth is not programmed with the default or fallback ACL when sessions enter the INIT state.
- When a device authenticates with dot1x after authenticating with MAB, any policies applied by MAB remain in place.
–![]() Ensure that the dot1x supplicant always authenticates before MAB.
Ensure that the dot1x supplicant always authenticates before MAB.
–![]() Create MAB policies for dot1x hosts that do not supply a URL redirect. CSCui79988
Create MAB policies for dot1x hosts that do not supply a URL redirect. CSCui79988
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG2
This section lists the resolved caveats in Cisco Release 15.1(2)SG2:
- A GLC-GE-100FX pluggable may not operate when used in WS-X4624-SFP-E, WS-X4640-CSFP-E or WS-X4612-SFP-E modules.
- The switch may reload unexpectedly or become inaccessible when the integrated web server is used, either through direct web access to the switch, or indirectly through the webauth feature.
Workaround: Enter either the no ip http server or the no ip http secure-server command. This disables the http/s server. CSCui14525
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG1
This section lists the open caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG1:
- If burst is not explicitly configured for a single rate policer, the show policy-map command displays an incorrect burst value.
Workaround: Enter the show policy-map interface command. CSCsi71036
Workarounds: Disable IGMP snooping on all the relevant VLANs before disabling it globally.
Workaround: Unconfigure any generic QOS policies from the system. The QoS policies with the match any attribute cause IPv6 entries to become active. If the switch is a pure Layer 2 device, remove the generic protocol family attributes and narrow it to the protocol family.
- In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)SG, if an etherchannel is a member of a flexlink pair, then static MAC addresses configured on the EtherChannel are not moved to the alternate port when the EtherChannel fails (flexlink failure)
- When a CFM Inward Facing MEP(IFM) is configured on a VLAN that is not allocated on a switch port that is DOWN, the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command displays the
IFM CC Status as Inactive. Then, you allocate the VLAN, the CC-status remains Inactive.
You only see this symptom if you did not allocate a VLAN before you configure the IFM, then at a later time allocate the same VLAN.
Workaround: Unconfigure, then reconfigure the IFM on the port.
- VTP databases do not propagate through promiscuous trunk ports. If only promiscuous trunks are configured, users will not see the VLAN updates on the other switches in the VTP domain.
Workaround: For VTP database propagation, configure ISL/dot1q trunk port. CSCsu43445
- If you simultaneously apply a service-policy to a port in the output direction and a service-policy to a vlan-range under that port in the output direction, the class-map hit counters in the output of the
show policy-map interface command are wrong.
The queue transmit counters as well as the policing statistics (if any) are correct. CSCsz20149
- When you configure switchport block multicast on a switch running
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1 and later or 12.2(50)SG6 and later, Layer 2 multicast is not blocked.
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1, 12.2(50)SG6, the switchport block multicast command would block IP Multicast, Layer 2 multicast, and broadcast traffic (CSCta61825).
- Before large PACLs are fully loaded in hardware, you might observe a false completion messages like the following:
This issue does not impact functionality.
You must wait for the ACLs to be programmed before performing other TCAM related changes. CSCtd57063
- With a NEAT configuration on an ASW (Catalyst 4500 series switch) connected to an SSW (Catalyst 3750 series switch) serving as a root bridge and with redundant links between ASW and SSW, the following occur:
–![]() The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
Workaround: Configure the ASW or any other switch upstream as the root-bridge for all the VLANs. CSCtg71030
- When two distinct Layer 3 CE-facing interfaces exist, each connected to a CE to split WCCP between the two CEs, and you move a particular WCCP service (like 60 (ftp-native)) from one Layer 3 interface to the other, the target interface fails to completely transfer the service to the new CE from the old CE.
Workaround: Shutdown the CE-facing interface. Once all the mask-value entries point to the target CE, unshut the CE-facing interface. CSCtl09941
- WCCP service is not reacquired when a service group with a multicast group-address is unconfigured, and then reconfigured.
Workaround: Configure ip multicast-routing globally and establish ip pim sparse-dense-mode on the CE-facing interface. CSCtl97692
- If you reboot a switch, the configured value of the interface MTU size for the elements of the port channel interface does not work for IPv6 traffic.
Workaround: After the switch reloads, enter shut and no shut on the port-channel interface.
- When you enable both Cisco TrustSec and RADIUS accounting, a disparity occurs between the RADIUS client (Cisco switch) and the RADIUS/CTS server in how the authenticator field in the header is computed for DOT1X/RADIUS accounting messages.
A Cisco IOS AAA client uses the PAC secret to compute the authenticator; Cisco Secure ACS 5.2 uses the shared secret. This behavior causes a mismatch that results in a rejection of the accounting message, and the client marks the server as unresponsive.
- When more than one Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) is available on the downstream switch, and Mediatrace is invoked to provide flow statistics, the dynamic policy does not show statistics for a flow.
Mediatrace cannot find the correct inbound interface and applies the dynamic policy on a different interface from the one used for media flow.
- When you add a "bfd" suffix to the snmp server host x.x.x.x configuration command, the BFD traps, ciscoBfdSessUp and ciscoBfdSessDown, are not generated.
Workaround: Do not specify a "bfd" suffix with the snmp-server host x.x.x.x configuration command. CSCtx51561
- During either a system- or user-initiated reload operation, the following message is observed when the system shuts down:
This message is not observed during a system bootup.
Workaround: None required. This message is information only. CSCtz15738
- The Mediatrace Initiator may report the status "Abort due to route changed" when a MAC move happens on a switch configured as the Mediatrace Responder that is also connected to a video traffic generator.
- On systems performing multicast routing, a brief increase in CPU consumption occurs every few minutes. In large-scale environments, this CPU increase is more noticeable.
- Configuring an interface as unidirectional with the unidirectional send-only | receive-only command still allows an interface to send (configured as Send-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) or receive (configured as Receive-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) packets in a bidirectional mode.
- The switch may reload unexpectedly or become inaccessible when the integrated web server is used, either through direct web access to the switch, or indirectly through the webauth feature.
Workaround: Enter either the no ip http server or the no ip http secure-server command. This disables the http/s server. CSCui14525
- A GLC-GE-100FX pluggable may not operate when used in WS-X4624-SFP-E, WS-X4640-CSFP-E or WS-X4612-SFP-E modules.
- A port configured for webauth is not programmed with the default or fallback ACL when sessions enter the INIT state.
- When a device authenticates with dot1x after authenticating with MAB, any policies applied by MAB remain in place.
–![]() Ensure that the dot1x supplicant always authenticates before MAB.
Ensure that the dot1x supplicant always authenticates before MAB.
–![]() Create MAB policies for dot1x hosts that do not supply a URL redirect. CSCui79988
Create MAB policies for dot1x hosts that do not supply a URL redirect. CSCui79988
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG1
This section lists the resolved caveats in Cisco Release 15.1(2)SG1:
- With IGMP snooping enabled, multicast traffic received through a tunnel interface is not forwarded through the Outgoing Interface List.
Workaround: Disable IGMP snooping. CSCuc65538
- When MLD snooping is enabled, control-plane policing on IPv6 ND packets stops working. This does not impact other control packets.
- When a port connected to a CDP, DHCP, or LLDP speaker goes down, a small memory leak occurs (typically less than 300 bytes).
Workaround: Disable these protocols on interfaces that might flap frequently. CSCub85948
- If REP is configured on a dot1q trunk and the native VLAN is administratively set to something other then the default, REP packets are not sent on the native VLAN
Workaround: Retain the trunk native VLAN as 1. CSCud05521
- When a session is neither authenticated nor granted fallback authorization (e.g. by entering guest-vlan or auth-fail-vlan) in multi-auth mode, unauthenticated sessions remain indefinitely and are not cleared by the system.
Workaround: Clear sessions manually with the clear authentication sessions command. CSCtg15739
- When a switch receives a change of auth(CoA) for a port, policies already applied to that port are not cleared.
Workaround: Send any policy with the CoA from the RADIUS server. CSCue62019
- If URL redirect installed as part of authorization and either of the following occurs, memory will be leaked:
–![]() a fast stream of traffic matches the URL redirect ACL as IPDT clears an address,
a fast stream of traffic matches the URL redirect ACL as IPDT clears an address,
–![]() a traffic stream matches the URL redirect ACL and no URL redirect policy is installed for that IP address,
a traffic stream matches the URL redirect ACL and no URL redirect policy is installed for that IP address,
If this occurs repeatedly, IPDT and other control packet processing ultimately ceases.
Workaround: If this behavior completely fills the CPU buffer, the switch must be reloaded. However, the frequency of encountering a stuck queue can be reduced to nearly zero by modifying the URL redirect ACL to permit only 80/443 traffic. CSCug56646
- If a dACL name is too long (about 24 characters, depending on the interface where it is applied), the ACL will be incorrectly shared over multiple ports.
Open Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG
This section lists the open caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG:
- If burst is not explicitly configured for a single rate policer, the show policy-map command displays an incorrect burst value.
Workaround: Enter the show policy-map interface command. CSCsi71036
Workarounds: Disable IGMP snooping on all the relevant VLANs before disabling it globally.
Workaround: Unconfigure any generic QOS policies from the system. The QoS policies with the match any attribute cause IPv6 entries to become active. If the switch is a pure Layer 2 device, remove the generic protocol family attributes and narrow it to the protocol family.
- In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(54)SG, if an etherchannel is a member of a flexlink pair, then static MAC addresses configured on the EtherChannel are not moved to the alternate port when the EtherChannel fails (flexlink failure)
- When a CFM Inward Facing MEP(IFM) is configured on a VLAN that is not allocated on a switch port that is DOWN, the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command displays the
IFM CC Status as Inactive. Then, you allocate the VLAN, the CC-status remains Inactive.
You only see this symptom if you did not allocate a VLAN before you configure the IFM, then at a later time allocate the same VLAN.
Workaround: Unconfigure, then reconfigure the IFM on the port.
- VTP databases do not propagate through promiscuous trunk ports. If only promiscuous trunks are configured, users will not see the VLAN updates on the other switches in the VTP domain.
Workaround: For VTP database propagation, configure ISL/dot1q trunk port. CSCsu43445
- If you simultaneously apply a service-policy to a port in the output direction and a service-policy to a vlan-range under that port in the output direction, the class-map hit counters in the output of the
show policy-map interface command are wrong.
The queue transmit counters as well as the policing statistics (if any) are correct. CSCsz20149
- When you configure switchport block multicast on a switch running
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1 and later or 12.2(50)SG6 and later, Layer 2 multicast is not blocked.
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(53)SG1, 12.2(50)SG6, the switchport block multicast command would block IP Multicast, Layer 2 multicast, and broadcast traffic (CSCta61825).
- Before large PACLs are fully loaded in hardware, you might observe a false completion messages like the following:
This issue does not impact functionality.
You must wait for the ACLs to be programmed before performing other TCAM related changes. CSCtd57063
- With a NEAT configuration on an ASW (Catalyst 4500 series switch) connected to an SSW (Catalyst 3750 series switch) serving as a root bridge and with redundant links between ASW and SSW, the following occur:
–![]() The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
The SVI (network) is unreachable. If an SVI exists on the ASW, because of the STP flap in the setup as well as the CISP operations, the SVI MAC configuration on the ASW is incorrect.
Workaround: Configure the ASW or any other switch upstream as the root-bridge for all the VLANs. CSCtg71030
- When two distinct Layer 3 CE-facing interfaces exist, each connected to a CE to split WCCP between the two CEs, and you move a particular WCCP service (like 60 (ftp-native)) from one Layer 3 interface to the other, the target interface fails to completely transfer the service to the new CE from the old CE.
Workaround: Shutdown the CE-facing interface. Once all the mask-value entries point to the target CE, unshut the CE-facing interface. CSCtl09941
- WCCP service is not reacquired when a service group with a multicast group-address is unconfigured, and then reconfigured.
Workaround: Configure ip multicast-routing globally and establish ip pim sparse-dense-mode on the CE-facing interface. CSCtl97692
- If you reboot a switch, the configured value of the interface MTU size for the elements of the port channel interface does not work for IPv6 traffic.
Workaround: After the switch reloads, enter shut and no shut on the port-channel interface.
- When you enable both Cisco TrustSec and RADIUS accounting, a disparity occurs between the RADIUS client (Cisco switch) and the RADIUS/CTS server in how the authenticator field in the header is computed for DOT1X/RADIUS accounting messages.
A Cisco IOS AAA client uses the PAC secret to compute the authenticator; Cisco Secure ACS 5.2 uses the shared secret. This behavior causes a mismatch that results in a rejection of the accounting message, and the client marks the server as unresponsive.
- When more than one Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) is available on the downstream switch, and Mediatrace is invoked to provide flow statistics, the dynamic policy does not show statistics for a flow.
Mediatrace cannot find the correct inbound interface and applies the dynamic policy on a different interface from the one used for media flow.
- When you add a "bfd" suffix to the snmp server host x.x.x.x configuration command, the BFD traps, ciscoBfdSessUp and ciscoBfdSessDown, are not generated.
Workaround: Do not specify a "bfd" suffix with the snmp-server host x.x.x.x configuration command. CSCtx51561
- During either a system- or user-initiated reload operation, the following message is observed when the system shuts down:
This message is not observed during a system bootup.
Workaround: None required. This message is information only. CSCtz15738
- The Mediatrace Initiator may report the status "Abort due to route changed" when a MAC move happens on a switch configured as the Mediatrace Responder that is also connected to a video traffic generator.
- With IGMP snooping enabled, multicast traffic received through a tunnel interface is not forwarded through the Outgoing Interface List.
Workaround: Disable IGMP snooping. CSCuc65538
- On systems performing multicast routing, a brief increase in CPU consumption occurs every few minutes. In large-scale environments, this CPU increase is more noticeable.
- When MLD snooping is enabled, control-plane policing on IPv6 ND packets stops working. This does not impact other control packets.
- When a port connected to a CDP, DHCP, or LLDP speaker goes down, a small memory leak occurs (typically less than 300 bytes).
Workaround: Disable these protocols on interfaces that might flap frequently. CSCub85948
- If REP is configured on a dot1q trunk and the native VLAN is administratively set to something other then the default, REP packets are not sent on the native VLAN
Workaround: Retain the trunk native VLAN as 1. CSCud05521
- When a session is neither authenticated nor granted fallback authorization (e.g. by entering guest-vlan or auth-fail-vlan) in multi-auth mode, unauthenticated sessions remain indefinitely and are not cleared by the system.
Workaround: Clear sessions manually with the clear authentication sessions command. CSCtg15739
- redirect-url and redirect-acl are not cleared after a successful CoA, causing the final step of Central Web Authentication to fail.
Workaround: Return a dACL in the authorization profile with successful guest authentication.
- If URL redirect installed as part of authorization and either of the following occurs, memory will be leaked:
–![]() a fast stream of traffic matches the URL redirect ACL as IPDT clears an address,
a fast stream of traffic matches the URL redirect ACL as IPDT clears an address,
–![]() a traffic stream matches the URL redirect ACL and no URL redirect policy is installed for that IP address,
a traffic stream matches the URL redirect ACL and no URL redirect policy is installed for that IP address,
If this occurs repeatedly, IPDT and other control packet processing ultimately ceases.
Workaround: If this behavior completely fills the CPU buffer, the switch must be reloaded. However, the frequency of encountering a stuck queue can be reduced to nearly zero by modifying the URL redirect ACL to permit only 80/443 traffic. CSCug56646
- If a dACL name is too long (about 24 characters, depending on the interface where it is applied), the ACL will be incorrectly shared over multiple ports.
Workaround: Shorten the dACL name. CSCug78653
- A switch running Supervisor Engine 6-E with IOS Release 15.1(2)SG may crash during CPU packet switching. The crash file would have the following vector:
- Configuring an interface as unidirectional with the unidirectional send-only | receive-only command still allows an interface to send (configured as Send-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) or receive (configured as Receive-only Unidirection Ethernet mode) packets in a bidirectional mode.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG
This section lists the resolved caveats in Cisco Release 15.1(2)SG:
- Dynamic ACLs do not function correctly if they include advanced operators, including dscp/ipp/tos, log/log-input, fragments and/or tcp flag operators.
Workaround: Remove these operators from any dynamic ACLs. CSCts05302
- A peer policy is not updated after reauthentication if the policy is changed on the AS beforehand. After reauthentication, the original peer policy is retained.
Workaround: Enter shut and no shut on the port. CSCts29515
- The Cisco IOS Software implementation of the virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) aware network address translation (NAT) feature contains a vulnerability when translating IP packets that could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition.
Cisco has released free software updates that address this vulnerability. Workarounds that mitigate this vulnerability are not available.
This advisory is available at the following link:
http://tools.cisco.com/security/center/content/CiscoSecurityAdvisory/cisco-sa-20130327-nat
Note: The March 27, 2013, Cisco IOS Software Security Advisory bundled publication includes seven Cisco Security Advisories. All advisories address vulnerabilities in Cisco IOS Software. Each Cisco IOS Software Security Advisory lists the Cisco IOS Software releases that correct the vulnerability or vulnerabilities detailed in the advisory as well as the Cisco IOS Software releases that correct all Cisco IOS Software vulnerabilities in the March 2013 bundled publication.
Individual publication links are in “Cisco Event Response: Semiannual Cisco IOS Software Security Advisory Bundled Publication” at the following link:
http://www.cisco.com/web/about/security/intelligence/Cisco_ERP_mar13.html
Related Documentation
Although their Release Notes are unique, the 4 platforms (Catalyst 4500, Catalyst 4900, Catalyst ME 4900, and Catalyst 4900M) use the same Software Configuration Guide, Command Reference Guide, and System Message Guide. Refer to the following home pages for additional information:
http://www.cisco.com//en/US/products/ps6021/index.html
Hardware Documents
Installation guides and notes including specifications and relevant safety information are available at the following URLs:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4500/hardware/installation/guide/78-14409-08/4500inst.html
- For information about individual switching modules and supervisors, refer to the Catalyst 4500 Series Module Installation Guide at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4500/hardware/configuration/notes/OL_25315.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4500/hardware/regulatory/compliance/78_13233.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps4324/prod_installation_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6021/prod_installation_guides_list.html
Software Documentation
Software release notes, configuration guides, command references, and system message guides are available at the following URLs:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6021/prod_release_notes_list.html
Software documents for the Catalyst 4500 Classic, Catalyst 4500 E-Series, Catalyst 4900 Series, and Catalyst 4500-X Series switches are available at the following URLs:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps4324/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps4324/prod_command_reference_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps4324/products_system_message_guides_list.html
Cisco IOS Documentation
Platform- independent Cisco IOS documentation may also apply to the Catalyst 4500 and 4900 switches. These documents are available at the following URLs:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6350/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6350/prod_command_reference_list.html
You can also use the Command Lookup Tool at:
http://tools.cisco.com/Support/CLILookup/cltSearchAction.do
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6350/products_system_message_guides_list.html
You can also use the Error Message Decoder tool at:
http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/index.cgi
Notices
The following notices pertain to this software license.
OpenSSL/Open SSL Project
This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit ( http://www.openssl.org/).
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com).
This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
License Issues
The OpenSSL toolkit stays under a dual license, i.e. both the conditions of the OpenSSL License and the original SSLeay license apply to the toolkit. See below for the actual license texts. Actually both licenses are BSD-style Open Source licenses. In case of any license issues related to OpenSSL please contact openssl-core@openssl.org.
Copyright © 1998-2007 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1.![]() Redistributions of source code must retain the copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
Redistributions of source code must retain the copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2.![]() Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions, and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions, and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3.![]() All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the following acknowledgment: “This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit ( http://www.openssl.org/)”.
All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the following acknowledgment: “This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit ( http://www.openssl.org/)”.
4.![]() The names “OpenSSL Toolkit” and “OpenSSL Project” must not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without prior written permission. For written permission, please contact openssl-core@openssl.org.
The names “OpenSSL Toolkit” and “OpenSSL Project” must not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without prior written permission. For written permission, please contact openssl-core@openssl.org.
5.![]() Products derived from this software may not be called “OpenSSL” nor may “OpenSSL” appear in their names without prior written permission of the OpenSSL Project.
Products derived from this software may not be called “OpenSSL” nor may “OpenSSL” appear in their names without prior written permission of the OpenSSL Project.
6.![]() Redistributions of any form whatsoever must retain the following acknowledgment:
Redistributions of any form whatsoever must retain the following acknowledgment:
“This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit ( http://www.openssl.org/)”.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE OpenSSL PROJECT “AS IS”' AND ANY EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE OpenSSL PROJECT OR ITS CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
Copyright © 1995-1998 Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). All rights reserved.
This package is an SSL implementation written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com).
The implementation was written so as to conform with Netscapes SSL.
This library is free for commercial and non-commercial use as long as the following conditions are adhered to. The following conditions apply to all code found in this distribution, be it the RC4, RSA, lhash, DES, etc., code; not just the SSL code. The SSL documentation included with this distribution is covered by the same copyright terms except that the holder is Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
Copyright remains Eric Young’s, and as such any Copyright notices in the code are not to be removed. If this package is used in a product, Eric Young should be given attribution as the author of the parts of the library used. This can be in the form of a textual message at program startup or in documentation (online or textual) provided with the package.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1.![]() Redistributions of source code must retain the copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
Redistributions of source code must retain the copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2.![]() Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3.![]() All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the following acknowledgement:
All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the following acknowledgement:
“This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com)”.
The word ‘cryptographic’ can be left out if the routines from the library being used are not cryptography-related.
4.![]() If you include any Windows specific code (or a derivative thereof) from the apps directory (application code) you must include an acknowledgement: “This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com)”.
If you include any Windows specific code (or a derivative thereof) from the apps directory (application code) you must include an acknowledgement: “This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com)”.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY ERIC YOUNG “AS IS” AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
The license and distribution terms for any publicly available version or derivative of this code cannot be changed. i.e. this code cannot simply be copied and put under another distribution license [including the GNU Public License].
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the “Related Documentation” section.
CCVP, the Cisco logo, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn is a service mark of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PIX, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SMARTnet, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback