About the Cisco DNA Service for Bonjour Solution
The Apple Bonjour protocol is a zero-configuration solution that simplifies rich services and enables intuitive experience between connected devices, services, and applications. Using Bonjour, you can discover and use IT-managed, peer-to-peer, audio and video, or Internet of Things (IoT) services with minimal intervention and technical knowledge. Bonjour is originally designed for single Layer 2 small to mid-size networks, such as home or branch networks. The Cisco DNA Service for Bonjour solution eliminates the single Layer 2 domain constraint and expands the matrix to enterprise-grade traditional wired and wireless networks, including overlay networks such as Cisco Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) and industry-standard BGP EVPN with VXLAN. The Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series LAN switches, Cisco Nexus 9300 Series Switches, and Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller follow the industry standard, RFC 6762-based multicast DNS (mDNS) specification to support interoperability with various compatible wired and wireless consumer products in enterprise networks.
The Cisco Wide Area Bonjour application on Cisco DNA Center enables mDNS service routing to advertise and discover services across enterprise-grade wired and wireless networks. The new-distributed architecture is designed to eliminate mDNS flood boundaries and transition to unicast-based service routing, providing policy enforcement points and enabling the management of Bonjour services.
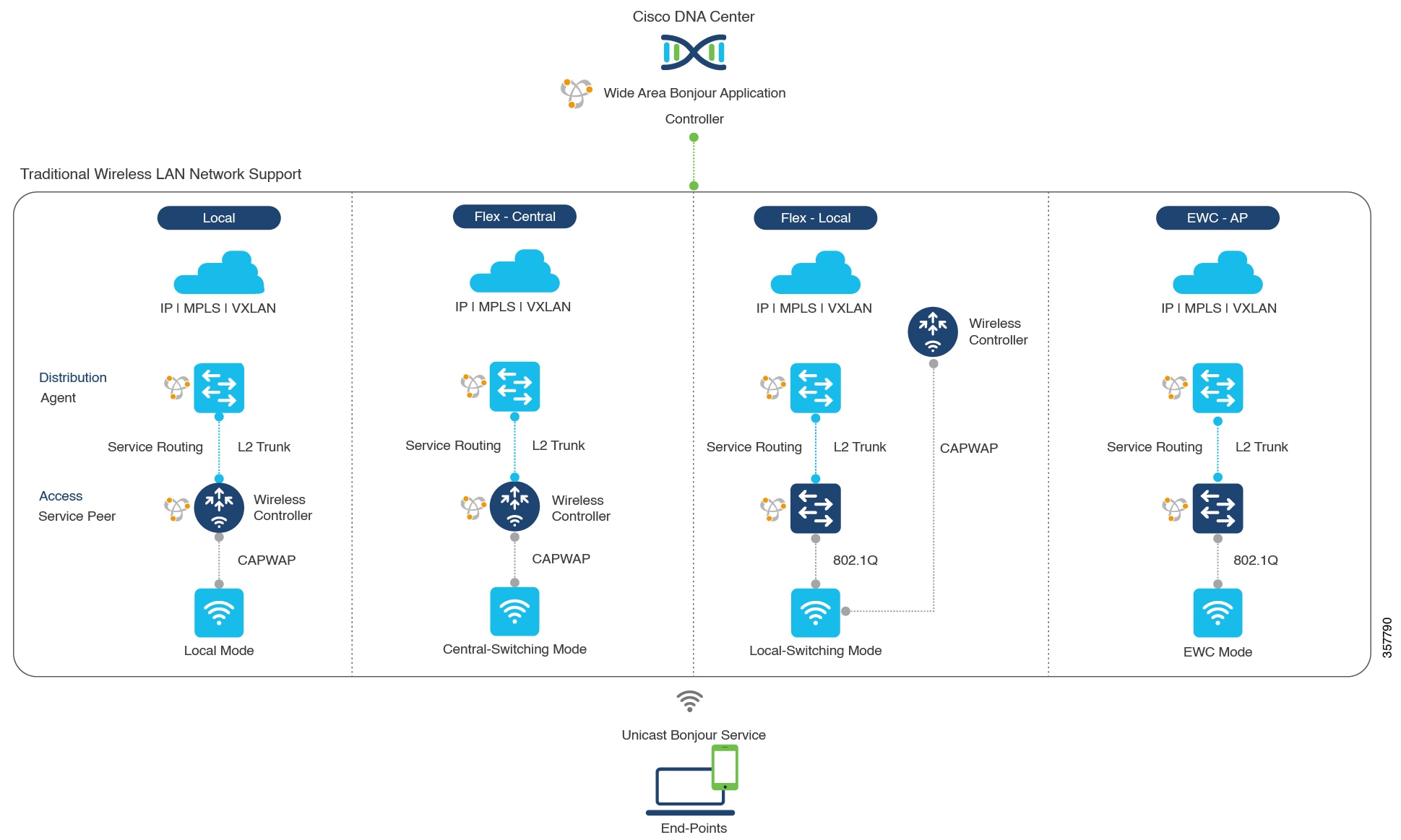
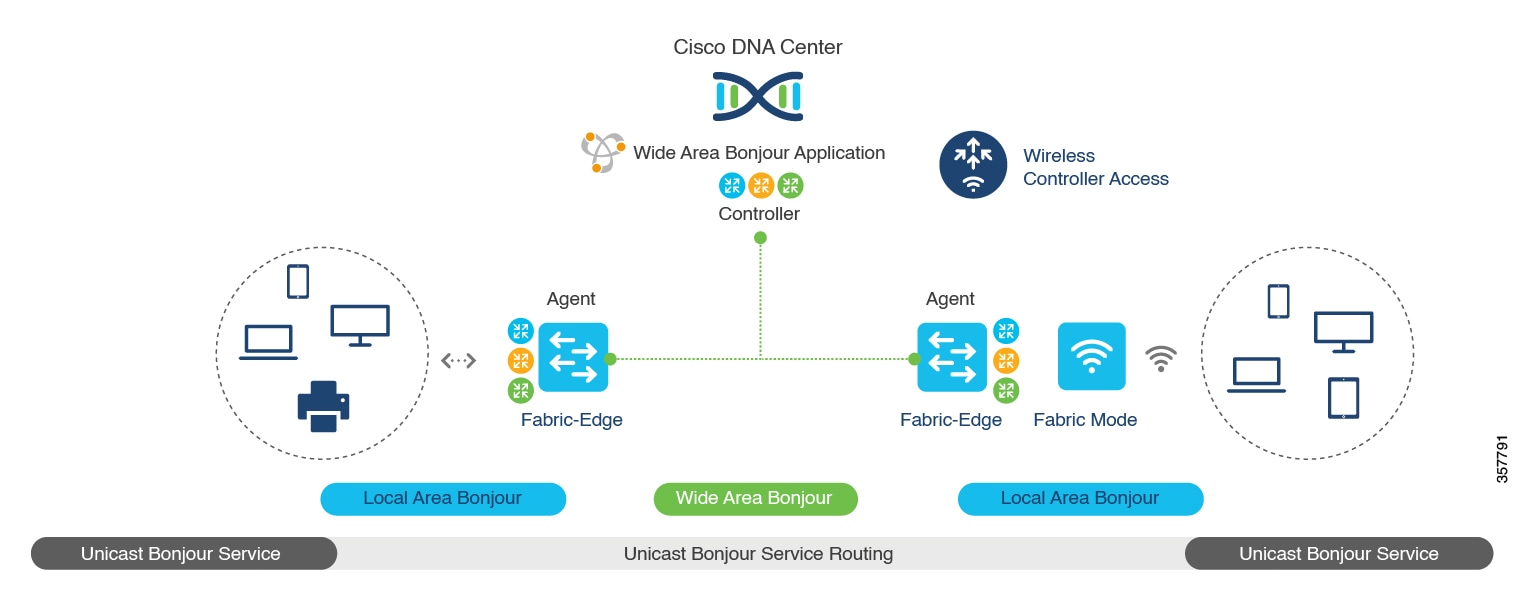
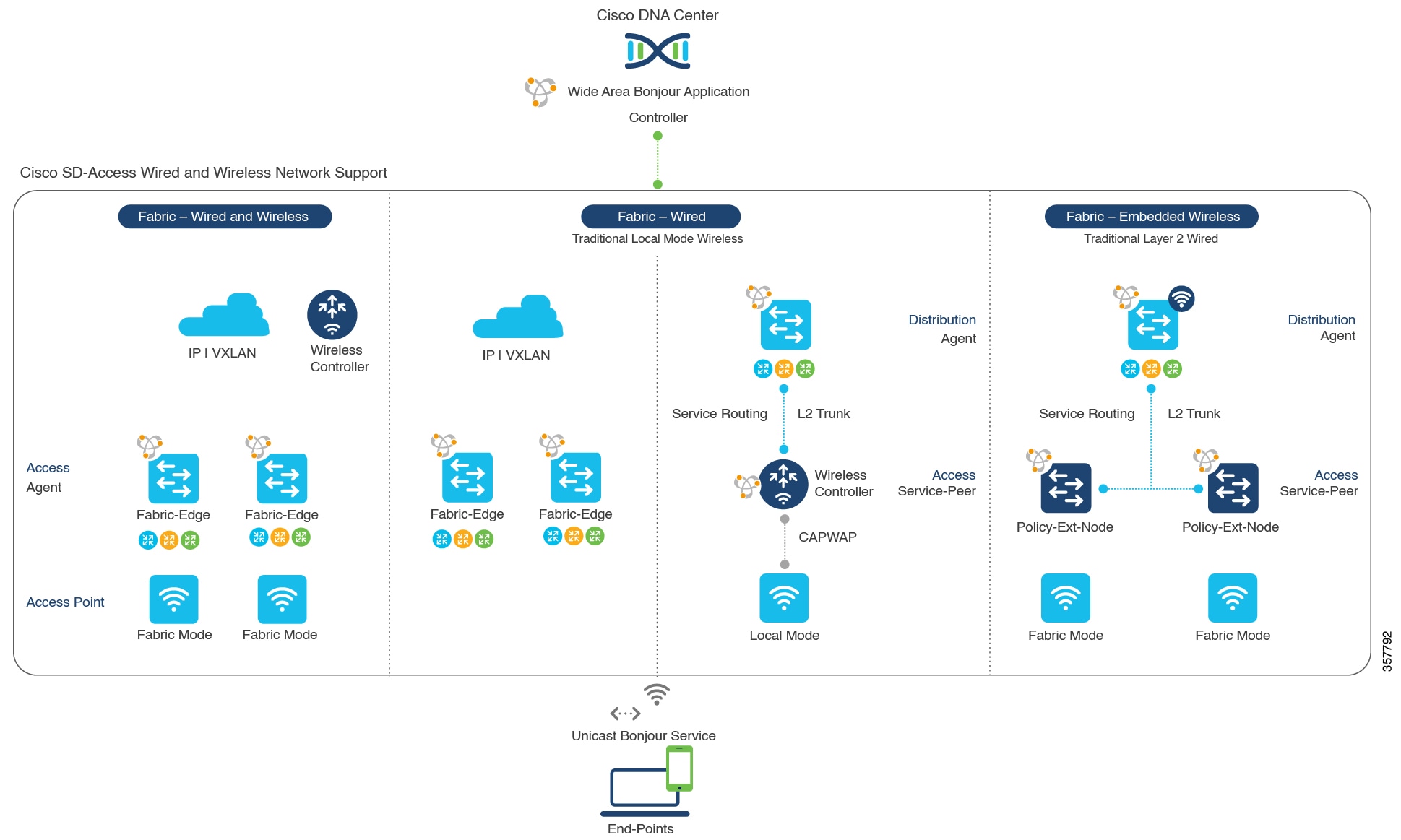
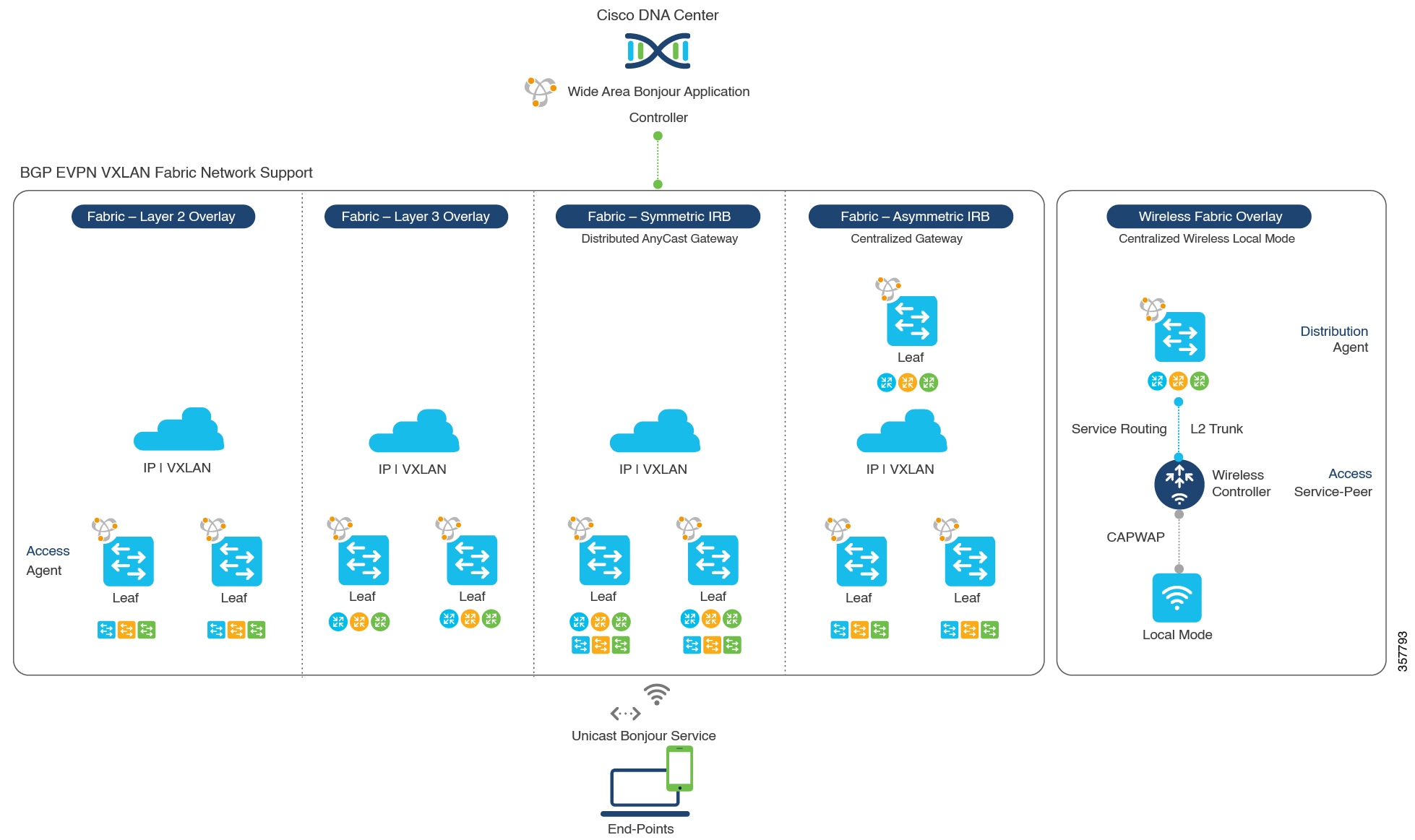
The following figure illustrates how the Cisco Wide Area Bonjour application operates across two integrated service-routing domains.

-
Local Area Service Discovery Gateway Domain - Unicast Mode: The new enhanced Layer 2 unicast policy-based deployment model. The new mDNS service discovery and distribution using the Layer 2 unicast address enables flood-free LAN and wireless networks. Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series Switches and Cisco Catalyst 9800 Series Wireless Controller in Layer 2 mode introduce a new service-peer role, replacing the classic flood-n-learn, for new unicast-based service routing support in the network. The service-peer switch and wireless controller also replace mDNS flood-n-learn with unicast-based communication with any RFC 6762 mDNS-compatible wired and wireless endpoints.
-
Wide-Area Service Discovery Gateway Domain: The Wide Area Bonjour domain is a controller-based solution. The Bonjour gateway role and responsibilities of Cisco Catalyst and Cisco Nexus 9300 Series Switches are extended from a single SDG switch to an SDG agent, enabling Wide Area Bonjour service routing beyond a single IP gateway. The network-wide distributed SDG agent devices establish a lightweight, stateful, and reliable communication channel with a centralized Cisco DNA Center controller running the Cisco Wide Area Bonjour application. The SDG agents route locally discovered services based on the export policy.

Note
The classic Layer 2 multicast flood-n-learn continues to be supported on wired and wireless networks with certain restrictions to support enhanced security and location-based policy enforcement. The Cisco Catalyst and Cisco Nexus 9300 Series Switches at Layer 3 boundary function as an SDG to discover and distribute services between local wired or wireless VLANs based on applied policies.



 Feedback
Feedback