Base Station Client Utility
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Information You Need For Configuration
Load New Firmware into Base Station
Base Station Client Utility
This chapter provides a general introduction to the Cisco Aironet Base Station Client Utility (BSCU) and describes the installation, screens, and options.
Here's what you'll find in this chapter:
•
Client Pull-Down Menu Options
Overview
The Cisco Aironet Base Station Client Utility (BSCU) simplifies the configuration and setup of the base station and the associated Cisco Aironet IEEE 802.11 DSSS client radio card (hereafter refered to as the client radio card) in the wireless PC. With the utility, you can configure and upgrade firmware on the client radio card, configure and upgrade firmware in the base station, perform diagnostic tests on the wireless network, and view current status and statistics of the client card.

CautionInstalling the BSCU configures the client radio card for Home Networking. To use the radio card in an enterprise system, you must reconfigure the card for the enterprise network using the Cisco Aironet Client Utility (ACU). The ACU is located on the Cisco Aironet 340 Series Base Station CD.
Requirements
The BSCU requires an installed Cisco Aironet client radio card in a PC running one of the following operating systems:
•
Microsoft Windows 95

Note
To support BSCU in Windows 95 and 95A requires the installation of IE4 or greater for needed networking files.
•
Microsoft Windows 98
•
Microsoft Windows NT
•
Microsoft Windows 2000
•
Microsoft Windows Me
Information You Need For Configuration
The base station is configured from a wireless PC with a client radio card. For wireless devices to establish initial communications with the base station, certain parameters must be set on the wireless devices and the base station. For proper operation, parameters in the base station must match the ISP settings.
Before configuring the base station, gather the following information (your network administrator or ISP should be able to provide any missing information):
•
Choose the operating mode of the base station from the following options:
•
Cable or DSL modem mode for connections to an ISP through a cable or DSL modem.
•
Dial-up mode connects the base station to a telephone line and uses the internal modem to communicate with an ISP.
•
PPP-over-Ethernet mode connects the base station to an ISP by using a Point-to-Point Protocol over a cable or DSL modem.
•
Access Point mode supports a standalone wireless network or connects to an internal LAN for wireless access. This configuration allows wireless terminals to access local LAN resources such as printers and servers.
•
For radio parameters, the following information is needed:
•
SSID—Service Set Identifier (SSID) is a special unique name assigned to a wireless radio network for identification purposes. To communicate, all wireless PCs and the base station must use the same SSID. Typically, this can be any name (1 to 32 ACSII characters); for example: Fido, Rover, 123, Air Plane, Apollo 10, Base Station 1, Charlie Brown, Alice, and so on.
•
WEP Encryption Key—A special sequence of characters used to restrict access to the wireless network. If you are using encryption, all wireless PCs and the base station must use the same encryption key. This is the same as the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Key parameter of an enterprise wireless device. Typically, this can be any value (1 to 13 ASCII characters or 1 to 26 hexadecimal characters); for example: 1234567890123, 5ABC234590123, 101Hubble2011, a@5gh%jk&V2+$, 31A454F1234BC89DE45CDE1237, and so on.

Note
In some ISP systems, the Login username might have a longer format similar to username@ISPname.net, or username@netname.ISPname.net.
•
For dial-up modem operation, gather the following information:
•
Login username—The name of the ISP account.
•
Login password—The password associated with the ISP account.
•
Phone number—The dial-in telephone number for the ISP.
•
Tone or pulse dial—A telephone line setting used by the modem.
•
Domain name—The domain name of the ISP network; for example: ISPname.net or netname.ISPname.net.
•
For Cable or DSL modem operation, gather the following information:
•
Base station name—The name assigned to the base station.
•
Auto DHCP—Indicates whether an external DHCP server is used.
•
Base station IP address—The ISP assigned external address.
•
Subnet Mask—The ISP assigned subnet mask.
•
Default Gateway—The ISP assigned gateway.
•
DNS Server 1—The ISP assigned primary server.
•
DNS Server 2—The ISP assigned secondary server.
•
Domain name—The domain name of the ISP network; for example: ISPname.net or netname.ISPname.net.
•
For PPP-over-Ethernet operation, gather the following information:
•
Login username—The name of the ISP account.
•
Login password—The password associated with the ISP account.
•
Service name—The name of the ISP service.
•
Domain name—The domain name of the ISP network; for example: ISPname.net or netname.ISPname.net.
•
For Access Point operation, gather fhe following information:
•
Base station name—The name assigned to the base station.
•
Auto DHCP—Indicates whether an external DHCP server is used.
•
Base station IP address—The base station assigned IP address.
•
Subnet Mask—The base station network subnet mask.
•
Default Gateway—The network gateway.
•
DNS Server 1—The network primary server.
•
DNS Server 2—The network secondary server.
Configuring the Wireless PC
You can use the BSCU from a wireless PC to set and change the base station's configuration parameters. However, the wireless PC must be properly configured to communicate with the base station. To revise the wireless PC network parameters, refer to "Wireless PC Network Settings," and the Help guides provided by your operating system.
Step 1
In the PC's TCP/IP Protocol properties set your radio card to automatically obtain an IP address from a DHCP server. This is the easiest and recommended method; however, you can manually set the following IP address information:
•
Set the IP address to 192.168.200.xxx. Where xxx is a value from 102 to a maximum value of 254.
•
Set the subnet mask to 255.255.255.000.
•
Set the default gateway to 192.168.200.1.
BSCU Installation and Setup
The BSCU is installed from the Cisco Aironet 340 Series Base Station CD shipped with the unit. The setup program installs the BSCU and the Base Station Connection Status utility (see Chapter 4).

Note
If the Base Station Connection Status utility was previously installed, right-click the telephone icon in the system tray and select exit prior to installing the BSCU.
Follow these steps to install the BSCU:
Step 1
Put the Cisco Aironet 340 Series Base Station CD in the CD-ROM drive of the wireless PC used to configure the base station.
Step 2
Use Microsoft Windows Explorer to view the contents of the CD. Double-click the BSCU folder, and double-click the setup.exe file. Follow the steps provided by the installation wizard.

Note
You can specify a specific destination and program folder or use the default folders indicated by the BSCU.
Step 3
Select Talk To A Base Station To Access The Internet, when requested by the installation wizard.

Note
The option Talk Directly To Other Computers is not used with the base station.
After the utility is installed, double-click the BSCU icon located on the computer desktop to activate the utility. The BSCU main screen is shown in .
Figure 2-1

BSCU Main Screen
The main screen provides a status line and the time on the bottom of the screen. The status line indicates whether the client radio card is associated or not. When it is associated, the status line indicates the base station name and the IP address where it is associated. If the client radio card is unable to obtain the IP address from the base station, the base station MAC address is displayed.
The main screen contains four pull-down menu options:
•
Client—used to change the client radio parameters (see page 7). From this selection, you can configure a client radio card to match base station settings, examine wireless network information, test the wireless network, or load new firmware into a client radio card.
•
Base Station—used to set-up the base station and client radio card (page 25). From this selection, you can initially configure or change base station settings, select operating modes (connection types) or load new base station and modem firmware.
•
Options—used for optional features (see page 42). From this selection, you can load client radio card configuration information to a floppy disk for use in setting up additional wireless PCs or change the BSCU Status Bar clock to display seconds.
•
Help—provides help on the BSCU screen parameters (see page 45).
When initially setting up or changing base station parameters, use the Base Station tab. From this tab, you can configure the base station parameters and the BSCU will automatically configure the client radio card to match your settings.
After you set up or change the base station parameters, use the Client tab in all the other wireless PCs to configure their client radio cards to match your new base station settings.
Client Pull-Down Menu Options
The Client pull-down menu (see ) specifies several options that are associated with the client radio card in the PC. Table 2-1 describes the pull-down menu options.
Figure 2-2 Client Pull-Down Menu Screen

Table 2-1 Client Pull-Down Menu Options
Load New Client Firmware
Loads new firmware into the client radio card. (see page 8)
Edit Client Properties
Sets client radio card parameters. (see page 8)
Statistics
Shows the current receive and transmit statistics of the client radio card. (see page 13)
Status
Shows the current setting and status of the client radio card, including firmware version number, data rate, output power, frequency, association status, and more. (see page 16)
TCP/IP Linktest
Uses the Windows TCP/IP protocol to perform a link test on the wireless network and provides an overall link quality rating. (see page 18)
RF Connection Test
Supports active and passive modes. In passive mode, the current status is read from the client radio card every second. In active mode, the current status is obtained using data packets sent to and received from a specified destination device. (see page 20)
Load New Client Firmware
This option loads new firmware into the client radio card located in the wireless PC running BSCU. When you select this option, an Open dialog box appears that helps you locate or specify the desired new firmware image file (similar to filename.img).
After you specify the firmware image file, the client radio card's firmware is updated and a completion status is displayed.

CautionIf power fails during the loading of new firmware, your client radio card might be inoperable. If you are unable to reload new firmware, contact technical support for assistance.
Edit Client Properties
This option helps you verify or change the parameter settings for the client radio card in the wireless PC. The Wireless Client Network Parameters screen (see ) appears when the Edit Client Properties option is selected. Table 2-2 describes the screen parameters and indicates how to change the values. Table 2-3 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2-3 Wireless Client Network Parameters Screen

The Computer Name shown on the screen is the name used by your Microsoft operating system to identify your computer on the wired network. This name is also used to identify your wireless PC on the wireless network. This name must be unique for each wireless PCs.

CautionInadvertently changing the Computer Name setting can cause other network programs on the PC to be inoperable and your PC login password to be unrecognized. Use caution when changing this setting.

Note
The SSID and WEP Encryption Key settings in the client radio card for all wireless PCs must exactly match the base station settings.

Note
For security reasons the WEP Encryption Key value is not constantly displayed. The key value is displayed while being entered and will display until you accept the changes on the Wireless Client Network Parameters screen, by clicking the OK button (see Figure 2-3).
Table 2-2 Wireless Client Network Parameters
Computer Name
The name assigned to the wireless PC and used to identify the PC on the wireless and wired networks. All computer names on a network must be unique.
To change this value, enter a new name in the entry box.
Range: 1 to 16 ASCII characters
Default: Operating system's Network paremeter setting
SSID
Identifies the base station's radio network and must be used by all wireless devices communicating with the base station.
To change this value, enter a new name in the entry box.
Range: 1 to 32 ASCII characters
Default: tsunami
WEP Encryption Key Entry Method
Selects the encryption key entry method.
Range: Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F) or ASCII Text
Default: Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F)
WEP Encryption Key
Used with 128-bit encryption to provide security. The encryption key used must be set up exactly the same on all wireless devices and the base station. On enterprise wireless devices the encryption key corresponds to the WEP key.
To change the key, enter a new encryption key in the entry box.

Note
The WEP Encryption Key parameter is only available on client radio cards that support 128-bit WEP.

Note
The WEP Encryption Key is only displayed during entry. After the key is entered, the field is blank.
(For extra information see WEP Key Conversion.)
Range: ASCII entry—1 to 13 ASCII characters
Hex entry—1 to 26 characters using 0 to 9 and A to F.
Default: 30313233343536373839303132—Hex entry

Note
The ASCII characters you can use are the printable characters displayed on the PC keyboard.
Data Rate
Specifies the data rate used to communicate with the base station. For the home wireless network this option cannot be changed.
Default: Auto
Enable Encryption (WEP)
Enables or disables the use of 128-bit encryption. A check mark in the selection box indicates WEP Encryption is enabled, and a blank box indicates WEP Encryption is disabled.
To change this option, click in the selection box.

Note
This parameter is available only on client radio cards that support 128-bit WEP.
Range: Enabled or Disabled
Default: 128-bit Encryption Enabled
Network Type
The Base Station (Infrastructure) option indicates the radio card communicates with a base station. The No Base Station (AdHoc) option indicates the radio card uses Ad-Hoc mode to communicate with another wireless device (for additional information refer to the Cisco Aironet Client Utility (ACU) documentation for your client card). To change this option, click the desired selection.
Range: No Base Station (AdHoc) or
Base Station (Infrastructure)
Default: Base Station (Infrastructure)
The base station's default parameters are shown below:
•
SSID—tsunami
•
Encryption key entry method—Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F)
•
WEP Encryption Key—30313233343536373839303132 (Hex entry)
•
Network Type—Base Station (Infrastructure)
•
Data Rate—Auto
•
Encryption—Enabled

Note
The following base station radio settings are not shown in the BSCU screens and you cannot change them in the utility.
•
Authentication Type—Open
•
Encryption—128-bit Encryption
•
Association—Mixed Cells allowed

Note
The base station default parameters are set to 128-bit encryption and mixed-cell operation. For client radio cards that do not support 128-bit encryption and mixed-cell operation, the BSCU does not provide the WEP Encryption Key and Enable Encryption (WEP) options.

Note
After the base station is configured with non-default values, mixed-cell operation is no longer active.
WEP Key Conversion
The BSCU supports two entry methods for the WEP Encryption Key parameter:
•
ASCII—1 to 13 ASCII characters
When using the ASCII option, the BSCU converts each ASCII character into its corresponding 8-bit hexadecimal code value. For example: the entry 1 2 3 4 A B C ! @ # [ is converted into 31 32 33 34 41 42 43 21 40 23 5B 00 00 (spaces added for clarity). In this example, two null characters were inserted to complete the entry.

Note
For entries less than 13 characters, the BSCU inserts ASCII null characters to complete the 13 characters. Each ASCII null character converts into the 00 hexadecimal character.

Note
The entry is case sensitive; for example, the "a "character is different from the "A" character.
•
Hexadecimal—1 to 26 characters, using 0 to 9 and A to F
When using the Hexadecimal option, the BSCU converts two entered characters into one 8-bit hexadecimal code. For example: the entry 1 2 3 8 9 0 5 6 A B C D E F 7 is converted into 12 38 90 56 AB CD EF 70 00 00 00 00 00 (spaces added for clarity). In this example, 11 null characters are inserted to complete the entry.

Note
For entries less than 26 characters, the BSCU inserts ASCII null characters to complete the 26 characters. Two ASCII null characters convert into the 00 hexadecimal character.

Note
The entry is not case sensitive; that is, you can use upper or lower case alpha characters (A to F or a to f).
Statistics
The Statistics option provides the current receive and transmit statistics from the client radio card once per second. The 340 Series Statistics screen is shown in :
Figure 2-4 340 Series Statistics Screen

The 340 Series Statistics screen is divided into Receive Statistics and Transmit Statistics. The Receive Statistics area provides information regarding received data packets and beacons (see Table 2-4). The Transmit Statistics area provides information on transmitted data packets and beacons (see Table 2-5). The buttons on the bottom of the 340 Series Statistics screen are defined in Table 2-6.
Status
The 340 Series Status screen (see ) shows the current settings and status of the client radio card, including firmware version number, data rate, output power, frequency, association status, etc. The status information from the radio card is updated once per second. Table 2-7 describes the 340 Series Status screen parameters. Table 2-8 describes the buttons on the bottom of the 340 Series Status screen.
Figure 2-5 340 Series Status Screen

Table 2-8 Buttons on the Status Screen
OK
Exits the screen.
Help
Provides information on the screen and its parameters.
TCP/IP Linktest
This option uses the TCP/IP protocol to perform a link test on the wireless or wired network and provides an overall link quality rating based on the transmitted and received data packets. illustrates the TCP/IP Linktest screen, and Table 2-9 describes the parameters on the screen.

Note
The TCP/IP protocol must be installed and operational on the wireless PC being used in this test.
You can use this test to evaluate the performance of the RF link on which the wireless PC is located. The statistics are constantly updated until the test is stopped. The test can be started and stopped as often as desired. Both current and cumulative totals are presented.
Figure 2-6 TCP/IP Linktest Screen

RF Connection Test
The RF Connection Test reads the current status from the client radio card once per second to quickly scan wireless signal strength. This test can be set up for single or continuous operation.
The test has two modes of operation: passive (default) and active. The passive mode does not initiate any RF network traffic but only monitors the RF traffic to provide signal strength, signal quality, and link-speed indications. shows the RF Connection Test screen and illustrates the passive mode parameters being monitored.
The active mode actively sends and receives packets to or from the associated base station and indicates percent complete and percent successful. Active mode is initiated when you change the default test configuration using the Setup button. illustrates the RF Connection Test screen with the active mode test results shown.
If the wireless PC is portable, you can use the active mode to determine the wireless network coverage area by performing the test in various locations.
Table 2-11 describes the parameters on the RF Connection Test screens. Table 2-12 describes the buttons on the bottom of the RF Connection Test screens. shows the RF Connection Test Setup screen. Table 2-13 describes the parameters and indicates how to change them. Table 2-14 describes the buttons on the bottom of the RF Connection Test Setup screen.
Figure 2-7 RF Connection Test Screen - Passive Mode

This screen illustrates the default screen of the RF connection test. The results from passive mode operation of the RF connection test indicate the receive side the wireless network is active and operational, but not that the wireless PC can successfully transmit to the base station.
The passive mode operation of the RF connection test does not cause additional loading on the wireless network because it does not transmit messages. This test can be used to provide a quick view of the condition of the wireless network from the wireless PC's location. Typically, when the overall link quality is excellent or good the wireless PC should be able to communicate successfully on the wireless network from the current location.
Figure 2-8 RF Connection Test Screen - Active Mode

The active mode test is a better indication of the condition of the RF link because messages flow in both directions—to the base station and from the base station.
Table 2-12 Buttons on the RF Connection Test Screen
Setup
Allows the user to change test default parameters (see and Table 2-13).
Start
Initiates a test. When the test is started, the button becomes the Stop button.
Stop
Stops a test that is running. When the test is stopped, the button changes into the Start button.
OK
Terminates the test, resets statistics to zero, and exits the screen.
Cancel
Exits the screen without starting the test.
Help
Provides information on the screen and its parameters
You can use the RF Connection Test Setup screen to change the default settings and enter active mode. In active mode, the test can evaluate the wireless network from the wireless PC's location by transmitting messages and receiving responses.
You can use the Setup screen to specify a base station by entering its MAC address. The test can also be set to operate continuously or to be directed to a wireless device of another manufacturer.
Figure 2-9 RF Connection Test Setup Screen

Base Station Pull-Down Menu
The Base Station pull-down menu allows you to initially configure or change the base station and client radio card settings (see ). Table 2-15 defines the selectable options in the pull-down menu.
Figure 2-10 Base Station Pull-Down Menu

Table 2-15 Base Station Pull-Down Menu Options
Set Up Base Station
You can use this option to set-up the configuration parameters in the base station and the client radio card (see "Set Up Base Station" section).
Load New Firmware Into Base Station
You can use this option to load new firmware into the base station (see "Preferences" section).
Load New Modem Firmware
You can use this option to load new firmware into the base station's optional modem (see "Load New Modem Firmware" section).
Set Up Base Station
The Set Up Base Station option allows you to set up and configure the base station and the client radio card in the wireless PC. When you select this option, the Set Up Base Station With My Settings Screen appears; on it you can view the current base station configuration settings. You can change the settings by clicking Edit Base Station Settings, or you can accept the current settings by clicking OK.
When you click OK to accept the base station settings, the BSCU configures the base station to the settings, then automatically configures the client radio in the wireless PC to the same base station settings.
The configuration parameters displayed on the Set Up Base Station With My Settings Screen depend upon the selected base station mode (connection type). The screen parameter descriptions are provided in the sections on connection properties.
illustrates the base station default parameter settings, and Table 2-16 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2-11 Set Up Base Station With My Settings Screen

Table 2-16 Buttons on the Setup Base Station With My Settings Screen
Edit Base Station Settings
Allows you to configure the base station radio and operating mode (connection type) parameters (see Base Station Wireless Network Parameters).
OK
Saves parameters and exits the screen.
Cancel
Exits the screen without changing parameters.
Base Station Wireless Network Parameters
When you click the Edit Base Station Settings button, the Base Station Wireless Network Parameters Screen () displays allowing you to accept or change the SSID, the WEP key entry method, the WEP Encryption Key, and the encryption setting for the base station and client card. When you are satisfied with the parameter settings on the screen, click Next. This saves the base station wireless network configuration parameters and displays the Base Station Properties Screen.
Table 2-17 describes the parameters on the Base Station Wireless Network Parameters Screen, and Table 2-18 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2-12 Base Station Wireless Network Parameters Screen


Note
The SSID and WEP Encryption Key settings in the client radio card for all wireless PCs must exactly match the settings in the base station. After you change these parameters in the base station, use the BSCU in all the other wireless PCs to reconfigure their client cards to match the new settings.

Note
For security reasons the WEP Encryption Key value is not constantly displayed. The key value is displayed while you are entering it and continues to display until you accept the base station configuration changes by clicking OK on the Set Up Base Station With My Settings screen (see Figure 2-11).
Table 2-17 Base Station Wireless Network Parameters
SSID
Identifies the base station's radio network and must be used by all wireless devices communicating with the base station.
To change this value, enter a new name in the entry box.
Range: 1 to 32 ASCII characters
Default: tsunami
WEP Encryption Key Entry Method
Selects the encryption key entry method. To changes this value, click Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F), or ASCII Text.
Range: Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F) or ASCII Text
Default: Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F)
WEP Encryption Key
Provides security with 128-bit encryption. The encryption key must be set up exactly the same on all wireless devices and the base station. On enterprise wireless devices the encryption key corresponds to the WEP key.
This entry is only available on client radio cards that support 128-bit WEP.

Note
This entry is only available on client radio cards that support 128-bit WEP.
(For additional information see "WEP Key Conversion" section.)
Range: ASCII entry—1 to 13 ASCII characters
Hex entry—1 to 26 characters using 0 to 9 and A to F
Default: 30313233343536373839303132—Hex entry

Note
The ASCII characters you can use are the printable characters displayed on the PC keyboard
Enable Encryption (WEP)
Enables or disables the use of 128-bit encryption. A check mark in the selection box indicates WEP Encryption is enabled, and a blank box indicates WEP Encryption is disabled.
To change this option, click in the selection box.

Note
This entry is available only on client radio cards that support 128-bit WEP.
Range: Enabled or Disabled
Default: 128-bit Encryption Enabled
Table 2-18 Buttons on the Base Station Wireless Network Parameters Screen
More Info
Provides information on the screen and its parameters.
Defaults
Sets the base station default values for the parameters (see Base Station Default Parameters).
Next
Saves any changes, and exits the screen (see Base Station Properties).
Cancel
Exits the screen without saving any changes, and returns to the Set Up Base Station With My Settings screen.
Base Station Default Parameters
The base station default parameters are shown below:
•
SSID—tsunami
•
Encryption key entry method—Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F)
•
WEP Encryption Key—30313233343536373839303132 (Hex entry)
•
Network Type—Base Station (Infrastructure)
•
Data Rate—Auto
•
Encryption—Enabled

Note
The following base station radio settings are not shown in the BSCU screens and you cannot change them in the utility.
•
Authentication Type—Open
•
Encryption—128-bit Encryption
•
Association—Mixed Cells allowed

Note
The base station default parameters are set to 128-bit encryption and mixed-cell operation. For client radio cards that do not support 128-bit encryption and mixed-cell operaton, the BSCU does not provide the WEP Encryption Key and Enable Encryption (WEP) options.

Note
Once the base station is configured with non-default values, mixed-cell operation is no longer active.
WEP Key Conversion
The BSCU supports two entry methods for the WEP Encryption Key parameter:
•
ASCII—1 to 13 ASCII characters
When using ASCII option, the BSCU converts each ASCII character into its corresponding 8-bit hexadecimal code value. For example: the entry 1 2 3 4 A B C ! @ # [ is converted into 31 32 33 34 41 42 43 21 40 23 5B 00 00 (spaces added for clarity). In this example, two null characters were inserted to complete the entry.

Note
For entries less than 13 characters, the BSCU inserts ASCII null characters to complete the 13 characters. Each ASCII null character converts into the 00 hexadecimal character.

Note
The entry is case sensitive; for example, the "a " character is different from the "A" character.
•
Hexadecimal—1 to 26 characters, using 0 to 9 and A to F.
When using the Hexadecimal option, the BSCU converts two entered characters into one 8-bit hexadecimal code. For example: the entry 0 1 2 3 8 9 0 5 A B C D E F 7 is converted into 01 23 89 05 AB CD EF 70 00 00 00 00 00 (spaces added for clarity). In this example, 11 null characters were inserted to complete the entry.

Note
For entries less than 26 characters, the BSCU inserts ASCII null characters to complete the 26 characters. Two ASCII null characters convert into the 00 hexadecimal character.

Note
The entry is not case sensitive; that is, you can use upper or lower case alpha characters (A to F or a to f).
Base Station Properties
The Base Station Properties Screen allows you to select the following connection type options:
•
Use Built In 56K Modem for Internet Connection (see "Dial-Up Modem Properties" section)
•
Use Cable or DSL Modem for Internet Connection (see "Cable/DSL Modem Properties" section)
•
Use PPP over Ethernet for Internet Connection (see "PPP-Over-Ethernet Properties" section)
•
Use as Access Point for Wireless Clients Only (see "Access Point Properties" section)
Figure 2-13 illustrates the Base Station Properties Screen containing the default connection type (operating mode). Table 2-19 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2-13 Base Station Properties Screen
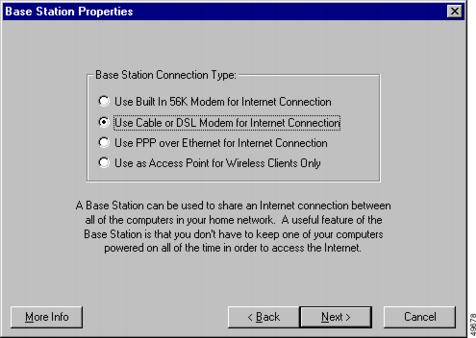
Table 2-19 Buttons on the Base Station Properties Screen
More Info
Provides additional information on the screen parameters.
Back
Returns to the Base Station Wireless Network Properties screen.
Next
Saves parameters and goes to the next screen (see the following connection type descriptions).
Cancel
Exits the screen without changing parameters, and returns to the Set Up Base Station With My Settings Screen.
Dial-Up Modem Properties
You can use the dial-up modem option to enter information required to access the dial-up facility for your ISP. shows the Dialup Modem Properties Screen. Table 2-20 describes the dial-up modem properties and how to change the parameters. Table 2-21 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.

CautionWhen the base station is configured for dial-up operation, do not connect it to a wired LAN being supported by another DHCP server. This might produce conflicting IP address assignments on the wired LAN because the base station DHCP server function supports both wireless and wired devices in dial-up mode.

Note
The base station does not support the proprietary AOL dial-up protocol.

Note
If your wireless PC's Internet browser and e-mail programs initiate auto-dial, you must reconfigure the programs to use a LAN connection rather than a dial-up connection to prevent them from attempting to dial the ISP.
Figure 2-14 Dialup Modem Properties Screen

Cable/DSL Modem Properties
With the cable or DSL modem option you can configure a high-speed connection for the base station. You can change the parameters used to access your ISP account, but the parameter values must be obtained from your ISP.
shows the Cable/DSL Modem Properties Screen, and Table 2-22 describes the screen parameters. Follow the instructions in the table to set or change any parameter. When you are satisfied with the parameter settings, click Next.
Table 2-23 describes the manual entry prameters and Table 2-24 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2-15 Cable/DSL Modem Properties Screen

Table 2-22 Cable/DSL Modem Parameters
Base Station Name
Specifies the name used to identify the base station. To change this value, enter a new name in the entry box.

Note
A blank entry box (no visible value) will result in the base station name being replaced with a null entry (no assigned name).

Note
A new name is activated when the base station power is cycled by removing and reconnecting the power cable.
Range: 1 to 16 ASCII characters
Default: BSM340_xxxxxx, or BSE340_xxxxxx
(The xxxxxx denotes the last six digits of the base station MAC address—a unique hardware-based number used to identify the base station on Ethernet links.)
(The BSM denotes the modem option, and the BSE denotes an Ethernet only option.)
Obtain IP Address Automatically
When this entry is set to On, the base station automatically obtains IP address information from a DHCP server. When this entry is set to Off, you must manually enter the network values provided by your ISP (refer to Table 2-23 for manual entry information needed).
To change this field, click On or Off.
Range: On or Off
Default: On
PPP-Over-Ethernet Properties
The PPP-over-Ethernet mode is used when your ISP uses the Point-to-Point Protocol through a cable or DSL modem. You can change the parameters used to access your ISP account, but you must obtain the parameter values from your ISP. Figure 2-16 contains the PPP Over Ethernet Properties screen. Follow the instructions in Table 2-25 to set or change any parameters. Table 2-26 describes the buttons on the bottom of the PPP Over Ethernet Properties screen.

Note
In some ISP systems, using a login username is the only way to identify that PPP-over-Ethernet is being used in your cable or DSL modem configuration.
Figure 2-16 PPP Over Ethernet Properties Screen

Access Point Properties
In Access Point mode the base station can connect to an internal wired LAN. In this mode the wireless devices can access the wired LAN for network resources. The Access Point Properties screen is shown in Figure 2-17 and the parameters are listed in Table 2-27; follow the instructions in the table to set or change any parameter. Table 2-28 describes the manual entry prameters and Table 2-29 describes the buttons on the bottom of the Access Point Properties screen.
shows the manual network address fields. The extra network address fields occur when the Obtain IP Address Automatically parameter is set to No. When this parameter is set to Yes, the base station automatically obtains the network address information from an external DHCP server on the wired network.
In Access Point mode the base station does not provide a DHCP server function or a NAT function for the wireless or wired devices. If the wired network contains a DHCP server, the wireless PCs can be set to automatically obtain network information through DHCP when using the radio card. The base station functions as a typical Access Point and pass DHCP packets to or from the DHCP server.

Note
To obtain the base station IP address when using an external DHCP server, you can use the IP Setup Utility (IPSU) found on the Cisco Aironet 340 Series Base Station CD (see Installing the IPSU).
Figure 2-17 Access Point Properties Screen
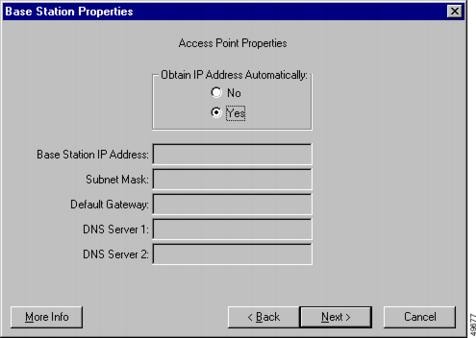
Table 2-27 Access Point Properties Parameters
Obtain IP Address Automatically
When this parameter is set to On, the base station obtains IP address information from an external DHCP server. When this parameter is set to Off, you must manually enter the network information shown in Table 2-28.
To change this parameter, click On or Off.
Range: On or Off
Default: On
See Table 2-28 for manual entry information.
Load New Firmware into Base Station
With the Load New Firmware Into Base Station option you can upgrade the firmware in the base station. A standard Open dialog box appears, allowing you to locate the appropriate base station firmware image file. The image file has a name similar to filename.450. Select the file and then click the Open button. The firmware update progress is indicated by a progress bar showing the percentage complete. When the upgrade is finished, the progress bar indicates 100%.]

Note
During the firmware upgrade, do not turn the base station power off. Failure to fully complete the upgrade may result in a non-operatable unit.
You can exit the process without loading new firmware by selecting the Cancel button.
Load New Modem Firmware
With the Load New Modem Firmware option you can upgrade the firmware in the base station modem. A standard Open dialog box appears in which you can locate the appropriate base station modem firmware file. The firmware file has a name similar to filename.MDM. Select the file and then click the Open button. The firmware update progress is indicated by a progress bar showing the percentage complete. When the upgrade is finished, the progress bar indicates 100%

Note
During the firmware upgrade, do not turn the base station power off. Failure to fully complete the upgrade may result in a non-operatable unit.
You can exit the process without loading new firmware by clicking the Cancel button.
Options Pull-Down Menu
The Options pull-down menu (see ) allows you to create a floppy disk copy of the configuration information to use when configuring new wireless PCs. Also, it enables you to revise the Status Bar Clock setting to display seconds. Table 2-30 defines the selectable options in the pull-down menu.
Figure 2-18 Options Pull-Down Menu
Table 2-30 Options Pull-Down Menu Selections
Install Additional Computer
You can use this option to save the client radio card configuration parameters to a disk file to set up another wireless PC (see "Install Additional Computer" section).
Preferences
You can use this option to display seconds in the Status Bar Clock (see "Preferences" section).
Install Additional Computer
You can use the Install Additional Computer option to save the client radio card configuration parameters to set up additional wireless PCs with a client radio card. The configuration information is saved to a floppy disk for portability to a new wireless PC when you click Save to Floppy Drive on the bottom of the Install Additional Computer screen.
shows the Install Additional Computer screen and Table 2-31 describes the buttons on the bottom of the screen.
The following configuration information is saved:
•
PC's network name
•
SSID
•
WEP Encryption Key
•
Encryption enabled or disabled
Figure 2-19 Install Additional Computer Screen

Table 2-31 Buttons on the Install Additional Computer Screen
Save To Floppy Drive
You can use this button to save the client radio card configuration parameters to a floppy disk. The floppy disk can be used to configure a client radio card in another wireless PC (see "Edit Client Properties" section).
OK
Saves parameters and exits the screen.
Cancel
Exits the screen without changing parameters.
Preferences
With the Preferences option you can display seconds in the Status Bar Clock that appears on the bottom of the Cisco Aironet Base Station Client Utility's main screen (see Figure 2-1). illustrates the Preferences Option screen. To configure the Status Bar Clock to display seconds, click Display Seconds on Clock.
Figure 2-20 Preferences Option Screen

Getting Help
To access information about BSCU, press F1 or select Contents from the Help pull-down menu (see Figure 2-21). An overview of BSCU is displayed.
From the Overview of the Cisco Aironet Base Station Client Utility screen, you can access additional information.
•
To access information on specific menu options, click Contents; double-click Base Station Client Utility Commands, the desired menu (such as Options Menu), and the desired topic (such as Preferences).
•
To access information on specific parameters, click Contents; then double-click the following selections when they appear: Configurable Parameters, Series 340/350 Wireless LAN Adapter, Wireless Network Parameters, and the desired parameter (such as Computer Name).
•
To access information on specific diagnostic topics, click Contents; double-click Run Time Diagnostic Information, a diagnostic category (such as Running a TCP/IP Linktest), and the desired topic (such as TCP/IP Linktest).
•
To search for a specific topic, click Index, select an index entry, and click Display.
•
To search for a specific word or phrase, click Contents or Index, click the Find tab, and follow the instructions in the Find Setup Wizard window.
Figure 2-21

Help Pull-Down Menu Screen
Exiting BSCU
To exit BSCU, select Exit from the Client pull-down menu (see Figure 2-22).
Figure 2-22 Exit Option

 Feedback
Feedback