Release Notes for Cisco 5700 Series Wireless LAN Controller, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.XE
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco IOS XE 3.6 Software for Cisco 5700 WLC
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.10E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.9E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.8E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.6E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5aE
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5E
–B Domain Compliant Cisco APs in this Release
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.4E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.3E
Configuring OPENAUTH and WEBAUTH in Parallel
WEBAUTH Command Output Examples
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.2E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.1E
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.0E
Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch Models
Cisco Catalyst 3650 Switch Models
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Models
Access Points and Cisco Mobility Services Engine
Wireless Web UI Software Requirements
Upgrading the Controller Software
Interoperability with Other Client Devices
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.10E
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.9E
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.8E
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.10E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.9E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.8E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.6E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5Ea
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5E
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.4E
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.3E
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.2E
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.1E
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.0E
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco IOS XE 3.6 Software for Cisco 5700 WLC
This Release Note document provides an overview of the features in the Cisco IOS XE 3.6 software on the Cisco 5700 Series Wireless LAN Controller (WLC).
Introduction
The Cisco 5700 Series Wireless LAN Controller (Cisco 5700 Series WLC) is designed for 802.11ac performance with maximum services, scalability, and high resiliency for mission-critical wireless networks. With an enhanced software programmable ASIC, the Cisco WLC delivers wire-speed performance with services such as Advanced QoS, Flexible NetFlow Version 9, and downloadable access control lists (ACLs) enabled in a wireless network. The controller works with other controllers and access points (APs) to provide network managers with a robust wireless LAN solution. The Cisco 5700 WLC provides:
- Network traffic visibility through Flexible NetFlow Version 9
- RF visibility and protection
- Support for features such as CleanAir, ClientLink 2.0, and VideoStream
The Cisco IOS XE software represents the continuing evolution of the Cisco IOS operating system. The Cisco IOS XE architecture and well-defined set of APIs extend the Cisco IOS software to improve portability across platforms and extensibility outside the Cisco IOS environment. The Cisco IOS XE software retains the same look and feel of the Cisco IOS software, while providing enhanced future-proofing and improved functionality.
For more information about the Cisco IOS XE software, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/iosswrel/ps9442/ps11192/ps11194/QA_C67-622903.html
Revision History
|
– |
|
|
– |
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.10E
There are no new features in this release. See Caveats section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.9E
There are no new features in this release. See Caveats section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.8E
There are no new features in this release. See Caveats section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
There are no new features in this release. See Caveats section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.6E
There are no new features in this release. See Caveats section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5aE
There are no new features in this release. See Caveats section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5E
Support for –B Domain
The FCC (USA) rule making on 5 GHz released on April 1, 2014 (FCC 14-30 Report and Order) goes into effect for products that are sold or shipped on or after June 2, 2016. Cisco APs and Cisco WLCs will comply with the new rules by supporting the new regulatory domain (–B) for the US and will create new AP SKUs that are certified under the new rules. Examples of new rules include new 5-GHz band channels permitted for outdoor use, and transmission (Tx) power level increased to 1W for indoor, outdoor, and point-to-point transmissions.

Note![]() Cisco APs and Cisco WLCs that are in the –A domain category can continue to operate and even coexist with –B domain devices without any issues.
Cisco APs and Cisco WLCs that are in the –A domain category can continue to operate and even coexist with –B domain devices without any issues.
We recommend that you upgrade Cisco APs and Cisco WLCs to the appropriate software release that supports –B domain.
–B Domain Compliant Cisco APs in this Release
- AP700i/w
- 1040
- 1140
- 1260
- 1530
- AP1570 (V02)
- AP1600i/e
- AP1700i
- AP2600i/e
- AP2700i/e
- AP3500i/e
- AP3600i/e
- AP3700p
For other updates in this release, see Caveats.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.4E
- The TACACS+ login procedure using custom method list is simplified wherein configuring a default method list is no longer required when the same server group is used.
No new features or other enhancements are included in this release.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.3E
- Multiple VLAN support for Wired Guest Access with both Anchor and Foreign as Cisco 5760 WLC—Wired guest anchor can now support multiple VLANs and multiple guest LANs. Separate VLANs can be assigned for each security profile like openauth, webauth and web consent. For more information about the Wired Guest Anchor feature, see “Multiple VLAN Support for Wired Guest Access with Cisco 5760 WLC as Both Anchor and Foreign Controller” section.
- Long URL—The webauth parameter map supports external URLs with a maximum length of 256 characters. While configuring a login URL for web authentication, ensure that complete length of the redirected URL does not exceed 550 characters. Use the following commands to configure external webauth parameter map with long URL:
- Credentials support in HTTP GET Request—You can customize the HTML pages to send credentials through an HTTP GET Request.

Note![]() We recommend password encryption while using an HTTP GET Request.
We recommend password encryption while using an HTTP GET Request.
- Appending AP radio MAC or Service Set Identifier (SSID) or client MAC—External URLs sent to a client can be appended with an AP radio MAC address, or SSID, or client MAC address, or any of these combinations, so that a web authentication redirect URL sent to the wireless client is parsed by an external server based on the appended attribute configured in the parameter map. For example, an external server can use this attribute information present in the redirect URL to send the login page based on the AP location, or SSID, or the client MAC address. The following are the commands to configure this feature:
- Multiprivilege level support to log in to web UI through TACACS+—In releases prior to Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.3, users were restricted to privilege level 15. In this release, users with privilege level 1can log in, access, and monitor Cisco WLC through TACACS+ or local authentication. Users with privilege level 0 are denied access. However, we recommend that you do not configure TACACS privilege levels for some commands on Cisco WLC, as it returns privilege level 15 for all users, which can interfere with WEB user interface configuration.
- Cisco Aironet 1570 Series Access Point—This release supports the Cisco Aironet 1570 Series Access Point, in local mode.
- WebAuth sleeping client—This allows successfully authenticated devices to stay logged in for a configured period without reauthentication.
The sleeping-client timeout timeout-in-minutes command is added under the webauth parameter map.
– There is one-to-one mapping between the device MAC and username and password. After an entry is added to the sleeping-client cache, the device or the user gets policies for the user stored in the cache. Therefore, any other user using the device also gets the same policies as the user stored in the sleeping-client cache. The user can force normal authentication by logging out. To do that, the user must explicitly enter the following URL:
– Mobility is not supported. If the client roams from one controller to another, the client undergoes normal authentication on the foreign controller.
You have to configure extended ACL on the box and add the deny rule to allow the external server ip address. An example is given below:
This release introduces a new CLI in global parameter-map to configure the BYPASS_ACL. So, to configure the extended BYPASS_ACL under global parameter-map, use the following commands:
After the configuration, content of the BYPASS-ACL would be merged with intercept-acl or redirect acl. So, the traffic destined for the ip addresses which are configured in BYPASS_ACL would be allowed enabling the user to access multiple external servers during the authentication.
Permit 443 is not advised and to avoid the users from making mistakes while defining CWA ACL, a built-in ACL is provided, which needs some modification for bypassing traffic to CWA server. (the Controller or Switch creates a default URL Redirect- ACL with mandatory ACEs [permit http traffic, deny dns and dhcp] excluding “permit tcp any any eq 443”.) Using this ACL, the user needs to configure only “deny” rule for ISE Server/Any external Server to access it.
Default ACL Name: CISCO-CWA-URL-REDIRECT-ACL
You can see the ACL using show ip access-list command. After modifying the ACL, its available from the show running-config command output.
1. Modify the Default ACL “CISCO-CWA-URL-REDIRECT-ACL” to add “deny ip any host <server-ip>” above 100. If there is a requirement to allow multiple servers, use multiple “deny” rules.
2. Configure the Default ACL Name in ISE as redirect-url for CWA authorization profile.
Multiple VLAN Support for Wired Guest Access with Cisco 5760 WLC as Both Anchor and Foreign Controller
Restrictions
- Wired guest VLAN on the access switch should not have any switch virtual interfaces (SVIs) present on any of the local switches. It should terminate directly on the foreign controller, so that the traffic is exported to the anchor.
- The anchor VLAN should not be allowed on the foreign controller’s uplink. Doing so may result in unexpected behavior.
- The foreign and anchor guest LANs should not be on the same VLAN.
- Wired guest configuration should only be performed during scheduled network downtime period.
Overview
In enterprise networks, there is typically a need for providing network access to a network’s guests on the campus. Guest access requirements include providing connectivity to the Internet or other selective enterprise resources to both wired and wireless guests in a consistent and manageable manner. The same wireless LAN controller can be used to provide access to both types of guests on the campus. For security reasons, a large number of enterprise network administrators segregate guest access to a demilitarized zone (DMZ) controller via tunneling. The guest access solution is also used as a fallback method for guest clients that fail dot1x and MAB authentication methods.
This document covers deployment of Wired Guest Access feature on Cisco 5760 WLC acting as Foreign Anchor and Cisco 5760 WLC acting as Guest Anchor in the DMZ. The feature works in a similar fashion on Cisco Catalyst 3650 switch acting as foreign controller.
A guest user connects to the designated wired port on an access layer switch for access. Optionally, it may be made to go through Web Consent or Web Authentication modes, depending upon the security requirements. After guest authentication succeeds, access is provided to the network resources and the guest controller manages the client traffic. Foreign controller is the primary switch where a client connects for network access; it also initiates tunnel requests. Guest anchor is the switch where a client gets anchored.
Before the guest access feature can be deployed, a mobility tunnel is established between the foreign anchor and guest anchor switches. The guest access feature works for both MC (Foreign Controller) to MC (Guest Anchor) and MA (Foreign Controller) to MC (Guest Anchor) models. The foreign anchor switch trunks wired guest traffic to the guest anchor controller. Multiple guest anchors can be configured for load balancing. The client is anchored to a DMZ anchor controller. It is also responsible for handling DHCP IP address assignment and authentication of a client. After the authentication is completed, the client is able to access the network.
Deployment Scenarios
The following sections describe common scenarios where the wired clients connect to access switches for network access. Two modes of access are explained with different examples. In both the methods, the wired guest access feature can act as a fallback method for authentication. This is typically a scenario where a guest user brings an end device that is unknown to the network. Since the end device is missing endpoint supplicant, it will fail the dot1x mode of authentication. Similarly, MAC authentication bypass (MAB) will also fail, as the MAC address of the end device is unknown to the authenticating server. It is worth noting that in such implementations, corporate end devices successfully get access to network as they would either have a dot1x supplicant or MAC addresses in the authenticating server for validation. This enables flexibility in deployment, because the administrator does not have to restrict and tie up ports specifically for guest access.
The figure below shows the topology used in this deployment scenario:
Figure 1-1 Wired Guest Access with Cisco 5760 WLC as Both Guest Anchor and Foreign Controller
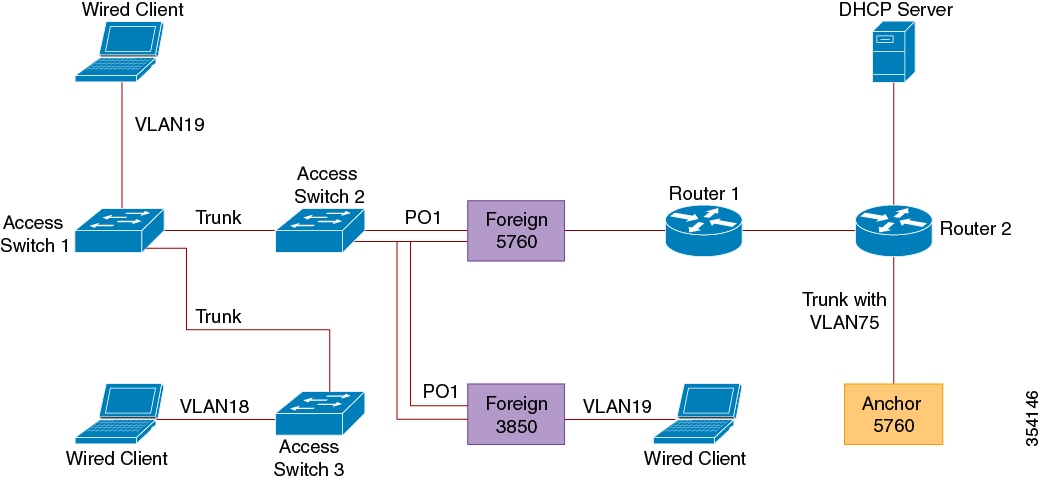
Open Authentication
Step 1![]() Enable IP Device Tracking (IPDT) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on client VLANs (VLAN75). The client VLAN should be created in the guest anchor:
Enable IP Device Tracking (IPDT) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on client VLANs (VLAN75). The client VLAN should be created in the guest anchor:
Step 2![]() Create VLAN 75 and a L3 VLAN interface:
Create VLAN 75 and a L3 VLAN interface:
Step 3![]() Create a guest LAN specifying the client VLAN, with Cisco 5760 WLC acting as the mobility-anchor. (For openmode, use the no security web-auth command.)
Create a guest LAN specifying the client VLAN, with Cisco 5760 WLC acting as the mobility-anchor. (For openmode, use the no security web-auth command.)
Foreign Configuration
Step 1![]() Enable DHCP and create a VLAN. The client VLAN need not be on the foreign controller.
Enable DHCP and create a VLAN. The client VLAN need not be on the foreign controller.
Step 2![]() The switch detects MAC address of the incoming client on the port channel configured with the access-session port-control auto command and applies the OPENAUTH subscriber policy. The OPENAUTH policy should be created first, as described below:
The switch detects MAC address of the incoming client on the port channel configured with the access-session port-control auto command and applies the OPENAUTH subscriber policy. The OPENAUTH policy should be created first, as described below:

Note![]() The policy can be applied on the port where the end device is connected while the 3850/3650 is acting as the Foreign.
The policy can be applied on the port where the end device is connected while the 3850/3650 is acting as the Foreign.
Step 3![]() Configure MAC learning on the foreign controller for the VLAN:
Configure MAC learning on the foreign controller for the VLAN:
Step 4![]() The OPENAUTH policy is referred to sequentially, which in this example points to a service template named SERV-TEMP3-OPENAUTH as defined below:
The OPENAUTH policy is referred to sequentially, which in this example points to a service template named SERV-TEMP3-OPENAUTH as defined below:
Step 5![]() The service template contains a reference to the tunnel type and name. The VLAN 75 client should exist only on the guest anchor because it is responsible for handling client traffic:
The service template contains a reference to the tunnel type and name. The VLAN 75 client should exist only on the guest anchor because it is responsible for handling client traffic:
Step 6![]() A tunnel request is initiated from the foreign controller to the guest anchor for the wired client and a ‘tunneladdsuccess’ message is displayed to indicate that the tunnel build up process is completed.
A tunnel request is initiated from the foreign controller to the guest anchor for the wired client and a ‘tunneladdsuccess’ message is displayed to indicate that the tunnel build up process is completed.
On the access switch 1, a wired client connects to the Ethernet port that is set to access mode by the network administrator. It is portGigabitEthernet 1/0/11 in this example.
Guest Anchor Configuration
Step 1![]() Enable IPDT and DHCP snooping on a client VLAN, in this example VLAN75 is created on the guest anchor.
Enable IPDT and DHCP snooping on a client VLAN, in this example VLAN75 is created on the guest anchor.
Step 2![]() Create VLAN 75 and the L3 VLAN interface:
Create VLAN 75 and the L3 VLAN interface:
Step 3![]() Configure the RADIUS server and the parameter map.
Configure the RADIUS server and the parameter map.
Step 4![]() Create a guest LAN specifying the client VLAN, with Cisco 5760 WLC acting as the mobility anchor:
Create a guest LAN specifying the client VLAN, with Cisco 5760 WLC acting as the mobility anchor:
Foreign Configuration
Step 1![]() Enable DHCP and create a VLAN. The client VLAN does not have to be set up on the foreign controller.
Enable DHCP and create a VLAN. The client VLAN does not have to be set up on the foreign controller.
Step 2![]() The switch detects MAC address of the incoming client on the port channel configured with access-session port-control auto command and applies the WEBAUTH subscriber policy. The WEBAUTH policy should be created first, as described below:
The switch detects MAC address of the incoming client on the port channel configured with access-session port-control auto command and applies the WEBAUTH subscriber policy. The WEBAUTH policy should be created first, as described below:
Step 3![]() MAC learning should be configured on the foreign controller for the VLAN:
MAC learning should be configured on the foreign controller for the VLAN:
Step 4![]() The WEBAUTH policy is referred to sequentially, which in this example points to a service template named SERV-TEMP3-WEBAUTH, as defined below:
The WEBAUTH policy is referred to sequentially, which in this example points to a service template named SERV-TEMP3-WEBAUTH, as defined below:
Step 5![]() The service template contains a reference to the tunnel type and name. The client VLAN75 should exist only on the guest anchor as it is responsible for handling client traffic:
The service template contains a reference to the tunnel type and name. The client VLAN75 should exist only on the guest anchor as it is responsible for handling client traffic:
Step 6![]() A tunnel request is initiated from the foreign controller to the guest anchor for the wired client. A ‘tunneladdsuccess’ message is displayed to indicate that the tunnel build-up process is completed.
A tunnel request is initiated from the foreign controller to the guest anchor for the wired client. A ‘tunneladdsuccess’ message is displayed to indicate that the tunnel build-up process is completed.
On access switch 1, a wired client connects to the Ethernet port that is set to access mode by the network administrator. It is portGigabitEthernet 1/0/11 in this example.
Configuring OPENAUTH and WEBAUTH in Parallel
If you have two guest LANs and wants to assign them to different clients, base them on the VLANs on which the clients are learned.
Guest Anchor Configuration
Step 1![]() Enable IPDT and DHCP snooping on a client VLAN, in this case VLAN75. The client VLAN should be created on the guest anchor.
Enable IPDT and DHCP snooping on a client VLAN, in this case VLAN75. The client VLAN should be created on the guest anchor.
Step 2![]() Create VLAN 75 and the L3 VLAN interface:
Create VLAN 75 and the L3 VLAN interface:
Step 3![]() Create a guest LAN specifying the client VLAN, with Cisco 5760 WLC acting as the mobility anchor. (For openmode, use the no security web-auth command.)
Create a guest LAN specifying the client VLAN, with Cisco 5760 WLC acting as the mobility anchor. (For openmode, use the no security web-auth command.)
Foreign Configuration
Step 1![]() Enable DHCP and create a VLAN. Note that the client VLAN need not have to be setup on the foreign controller.
Enable DHCP and create a VLAN. Note that the client VLAN need not have to be setup on the foreign controller.
Step 2![]() The switch detects MAC address of the incoming client on the port channel configured with access-session port-control auto command and applies the DOUBLEAUTH subscriber policy. The vlan18, vlan19 class maps are explained in “Step4
The switch detects MAC address of the incoming client on the port channel configured with access-session port-control auto command and applies the DOUBLEAUTH subscriber policy. The vlan18, vlan19 class maps are explained in “Step4![]() ”. Everything else is WEBAUTH. Using the second “always” class-map with “match-first” event, create the DOUBLEAUTH policy, as described below:
”. Everything else is WEBAUTH. Using the second “always” class-map with “match-first” event, create the DOUBLEAUTH policy, as described below:
Step 3![]() Configure MAC learning on the foreign controller for VLAN 18 and VLAN 19.
Configure MAC learning on the foreign controller for VLAN 18 and VLAN 19.
Step 4![]() The ‘VLAN 18 and VLAN 19 class maps contain the VLAN match criteria based on which the guest LAN, under which the client falls in is differentiated.
The ‘VLAN 18 and VLAN 19 class maps contain the VLAN match criteria based on which the guest LAN, under which the client falls in is differentiated.
Step 5![]() The OPENAUTH policy is referred to sequentially, which in this example points to a service template named SERV-TEMP3-OPENAUTH, as defined below:
The OPENAUTH policy is referred to sequentially, which in this example points to a service template named SERV-TEMP3-OPENAUTH, as defined below:
Step 6![]() The service template contains a reference to the tunnel type and name. The VLAN 75 client should exist only on the guest anchor because it is responsible for handling client traffic:
The service template contains a reference to the tunnel type and name. The VLAN 75 client should exist only on the guest anchor because it is responsible for handling client traffic:
Step 7![]() A tunnel request is initiated from the foreign controller to the guest anchor for the wired client. A ‘tunneladdsuccess’ message is displayed to indicate that the tunnel build-up process is complete.
A tunnel request is initiated from the foreign controller to the guest anchor for the wired client. A ‘tunneladdsuccess’ message is displayed to indicate that the tunnel build-up process is complete.
On the access swicth, there are multiple wired clients connecting to either VLAN 18 or VLAN 19, which can be then be assigned guest LANs accordingly.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.2E
No features were added or enhanced for this release. For more information about updates in this release, see the “Caveats” section.
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.1E
- Support for Cisco Aironet 1700 Series Access Points
- VLAN tagging support for Cisco Aironet 700W Series Access Points
- MAC Authentication per WLAN
- Support for Cisco Prime Infrastructure 2.1.2
What’s New in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.0E
Use this URL to access the Cisco IOS XE Release 3E Documentation Roadmap: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/ios-nx-os-software/ios-xe-3e/tsd-products-support-series-home.html |
Provides quick and easy access to all relevant documentation for specific platforms. Look for Quick Links to Platform Documentation on the respective platform documentation pages. |
Provides platform and software documentation for these technologies: |
|
(LAN-Lite, LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Switch-based agent support for zero-touch automated device installation solution called NG-PNP. |
|
(LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Ensures that the Network Device Admission Control-authenticated 802.1X links between Cisco TrustSec devices are in open state even when the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server is not reachable. |
|
(LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Enhances the functionality of Cisco TrustSec with Security Group Tag Exchange Protocol (SXP) V4 by adding support for SXP bindings that can be propagated in both directions between a speaker and a listener over a single connection. |
|
(LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Controls and manages Cisco TrustSec access control on a network device based on an attribute-based access control list. When a security group access control list (SGACL) is enabled globally, the SGACL is enabled on all interfaces in the network by default. Use the Enablement of Security Group ACL at the Interface Level feature to disable the SGACL on a Layer 3 interface. |
|
(LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) By default, enables a standard CLI view, including all commands. |
|
Displays the authentication results on the main HTML page, and not in a po-up window. |
|
Ensures that one or more custom HTML pages can be downloaded and configured from a single tar file bundle. The images and custom pages containing the images are also a part of the same downloadable tar file bundle. |
|
Supports image file names without prefixes and removes the requirement of users having to specify the wireless management interface IP to indicate the source of image in the HTML code. |
|
Enables multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) to operate across Layer 3 boundaries. |
|
(IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services.) Allows the device sensor to extract the HTTP packet Type-Length-Value (TLV) to derive useful information about the end-device type. |
|
Allows you to create a banner page and set an inactivity timeout for HTTP or HTTP Secure (HTTPS) connections. The banner page allows you to log in to the server when the session is invalid or expired. |
|
(LAN-Lite, LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Allows you to select the type, length, value (TLV) fields that are sent on a particular interface to filter information sent through Cisco Discovery Protocol packets. |
|
(LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Enables networks to redirect guest users to the URL they had originally requested. This feature is enabled by default and requires no configuration. |
|
(LAN-Lite, LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services/ IP Enterprise Services) Determines the level of network access provided to an endpoint based on the type of the endpoint device. This feature also permits hardbinding between the end device and the interface. Autoconfig falls under the umbrella of Smart Operations solution. |
|
(LAN-Lite, LAN-Base, IP-Lite, IP-Base, IP Services and IP Enterprise Services) Provides a mechanism to configure multiple commands at the same time and associate them with a target, such as an interface. An interface template is a container of configurations or policies that can be applied to specific ports. |
|
Provides unique customization capabilities and event- driven automation within Cisco products. |
|
Supports CleanAir Express on the Cisco 1600 Series Access Points. For more information about CleanAir Express, see http://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/solutions/collateral/enterprise-networks/cleanair-technology/aag_c22-594304.pdf |
|
Support the following APs in this release: Note The Cisco Aironet 1530 Series APs are supported only in local mode; the APs in mesh mode are not supported. |
|
Access control lists (ACLs), when configured using a fully qualified domain name (FQDN), enables ACLs to be applied based on the destination domain name. The destination domain name is then resolved to an IP address, which is provided to the client as part of DNS response. Guest users can log in using web authentication with parameter map that consists of FQDN ACL name. You can apply an access list to a specific domain. The RADIUS server then sends the AAA attribute fqdn-acl-name to the controller. The operating system checks for the pass-through domain list and its mapping, and permits the FQDN. The FQDN ACL allows clients to access only configured domains without authentication. The FQDN ACL is supported only for IPv4 wireless sessions. |
|
Local policies can profile devices based on HTTP and DHCP to identify the end devices on the network. Users can configure device-based policies and enforce the policies per user or per device policy on the network. Local policies allow profiling of mobile devices and basic onboarding of the profiled devices to a specific VLAN. They also assign ACL and QoS or configure session timeouts. |
|
You can validate rogue clients by utilizing the resources available in the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE). Using Cisco MSE, you can dynamically list the clients joining to the controller. The list of clients joined to the controller is stored in the Cisco MSE as a centralized location, where the controller communicates with Cisco MSE and validates the client before reporting if a rogue client is a valid one or not. Cisco MSE maintains the MAC addresses of clients joined to the controller. The communication between the controller and Cisco MSE is an on-demand service as the controller requests this service from Cisco MSE. |
|
Marking and policing actions for ingress SSID and client policies are applied at an access point. The SSID and client ingress policies that you configure in the controller are pushed to the AP. The AP performs policing and marking actions for each packet. However, the controller selects the QoS policies. Marking and policing of egress SSID and client policies are applied at the controller. QoS statistics are collated for client and SSID targets in the ingress direction. Statistics are supported only for ingress policies with a maximum of five classes on wireless targets. For very large policies, statistics for ingress policies are not visible at the controller. The frequency of the statistics depends on the number of clients associated with the AP. |
|
Application Visibility and Control (AVC) classifies applications using deep-packet inspection techniques with the Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR2) engine, and provides application-level visibility and control (QoS) in wireless networks. After the applications are recognized, the AVC feature enables you to either drop, mark, or police data traffic. AVC is configured by defining a class map in a QoS client policy to match a protocol. AVC QoS actions are applied with AVC filters in both upstream and downstream directions. The QoS actions supported for upstream flow are drop, mark, and police, and those supported for downstream flow are mark and police. AVC QoS is applicable only when the application is classified correctly and matched with the class map filter in the policy map. |
|
Supports new hardware for DWDM SFP+ and 10 G ZR SFP+ modules. For a list of all the supported SFP+ modules, see: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/interfaces_modules/transceiver_modules/compatibility/matrix/OL_6974.html |
|
Supports NetFlow Data Export Format Version 10 (IPFIX). For more information, see the Cisco Flexible NetFlow Configuration Guide. |
|
You do not have to create a separate WLAN for 802.11r support. You can specify the non-802.11r clients to associate with an SSID that is enabled with 802.11r. |
Supported Hardware
Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch Models
Network Modules
Table 3 lists the three optional uplink network modules with 1-Gigabit and 10-Gigabit slots. You should only operate the switch with either a network module or a blank module installed.
Four 1-Gigabit small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module slots. Any combination of standard SFP modules are supported. SFP+ modules are not supported. |
|
Cisco Catalyst 3650 Switch Models
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP (small form-factor pluggable) uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 PoE+1 downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, four 1-Gigabit SFP uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
||
Stackable 24 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, two 1-Gigabit SFP and two 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Full PoE downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 1025-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 PoE+ downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 640-W power supply |
||
Stackable 48 10/100/1000 Ethernet downlink ports, four 10-Gigabit SFP+ uplink ports, 250-W power supply |
Optics Modules
Catalyst switches support a wide range of optics. Because the list of supported optics is updated on a regular basis, see the tables at this URL for the latest (SFP) compatibility information:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps5455/products_device_support_tables_list.html
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Models
Access Points and Cisco Mobility Services Engine
Table 6 lists the supported products of the Cisco 5700 Series WLC.
Table 7 lists the specific supported Cisco access points.
Compatibility Matrix
Table 8 lists the software compatibility matrix.
For more information on the compatibility of wireless software components across releases, see the Cisco Wireless Solutions Software Compatibility Matrix.
Software Version
Table 9 shows the mapping of the Cisco IOS XE version number and the Cisco IOS version number.
Upgrading the Controller Software
To upgrade the Cisco IOS XE software, and to install the packages from a new software bundle file, use the software install privileged EXEC command. You can install the software bundle from the local storage media or it can be installed over the network using TFTP or FTP.
The software install command expands the package files from the specified source bundle file and copies them to the local flash: storage device. When the source bundle is specified as a tftp: or ftp: URL, the bundle file is first downloaded into the switch's memory (RAM); the bundle file is not copied to local storage media.
After the package files are expanded and copied to flash, the running provisioning file (flash:packages.conf) is updated to reflect the newly installed packages, and the controller displays a reload prompt:
Important Upgrade Note
- After you upgrade to Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.xE, the web authentication success page behavior is different from the behavior seen in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3.X SE. After a successful authentication on the WebAuth login page, the original requested URL opens in a pop-up window and not on the parent page. Therefore, we recommend that you upgrade the web authentication bundle so that the bundle is in the format that is used by the AireOS Wireless LAN Controllers.
To download a sample Web Authentication bundle, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Browse to http://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.html.
Browse to http://software.cisco.com/download/navigator.html.
Step 2![]() Choose Products > Wireless > Wireless LAN Controller > Standalone Controller > Cisco 5700 Series Wireless LAN Controllers > Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller.
Choose Products > Wireless > Wireless LAN Controller > Standalone Controller > Cisco 5700 Series Wireless LAN Controllers > Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller.
Step 3![]() Click Wireless Lan Controller Web Authentication Bundle.
Click Wireless Lan Controller Web Authentication Bundle.
Step 4![]() Choose Release 3.6.x and click Download.
Choose Release 3.6.x and click Download.
Step 5![]() After the download, follow the instructions provided in the Read Me file that is attached in the bundle.
After the download, follow the instructions provided in the Read Me file that is attached in the bundle.

Note![]() In a high-availability scenario, if you download the web authentication bundle to the active controller, the bundle cannot be synchronized with the standby controller. Therefore, we recommend that you also manually download the web authentication bundle to the standby controller.
In a high-availability scenario, if you download the web authentication bundle to the active controller, the bundle cannot be synchronized with the standby controller. Therefore, we recommend that you also manually download the web authentication bundle to the standby controller.
Features
The Cisco 5700 Series WLC is the first Cisco IOS-based controller built with smart ASIC for next generation unified wireless architectures. The Cisco 5700 Series WLC can be deployed both as a Mobility Controller in Converged Access solutions and as a Centralized Controller.
For more information about the features, see the product data sheet at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/wireless/5700-series-wireless-lan-controllers/datasheet-listing.html
Interoperability with Other Client Devices
This section describes the interoperability of this version of the controller software release with other client devices.
Table 11 lists the client types on which the tests were conducted. The clients included laptops, handheld devices, phones, and printers.
Important Notes
- With Cisco Prime Infrastructure 2.1.1, the refresh configuration and inventory collection tasks from the controller might take anywhere from 20 minutes to 40 minutes. For more information, see CSCum62747 on the Bug Search Tool.
- Although visible in the CLI, the following commands are not supported:
–![]() authorize-lsc-ap (CSCui93659)
authorize-lsc-ap (CSCui93659)
–![]() Mesh, FlexConnect, and OfficeExtend access point deployment
Mesh, FlexConnect, and OfficeExtend access point deployment
Limitations and Restrictions
- We recommend that you configure the access-session interface-template sticky timer timer-value command at the global or interface configuration mode, and not within the template.
- The web UI access for the controller should be enabled only by using the IP address of the controller. For example, http://<ip>. We recommend that you do not use https://<ip>/wireless address, as it might result in Privilege Level 1 access. To mitigate this problem, you either refresh the browser or use https://<ip> address.
- The web UI home page may not load when the ip http access class command is enabled. When you encounter this issue, we recommend that you perform the following tasks:
1. Run the show iosd liin command.
2. Get the internet-address and configure the same IP as permit in the access list.
- For web UI access using the TACACS server, the custom method-list for authentication and authorization pointing to the TACACS server group does not work. Use the default authorization method list pointing to the same TACACS server group for the web UI to work.
- We recommend that you run the exception dump device second flash command after the install process. This helps to store the crash files in a secondary flash during a crash when there is no available space in the main memory area to store the crash information.
- Flex links are not supported. We recommend that you use spanning tree protocol (STP) as the alternative.
- Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec:
–![]() Cisco TrustSec can be configured only on physical interfaces, not on logical interfaces.
Cisco TrustSec can be configured only on physical interfaces, not on logical interfaces.
–![]() Cisco TrustSec for IPv6 is not supported.
Cisco TrustSec for IPv6 is not supported.
–![]() Dynamic binding of IP-SGT is not supported for hosts on Layer 3 physical routed interfaces because the IP Device Tracking feature for Layer 3 physical interfaces is not supported.
Dynamic binding of IP-SGT is not supported for hosts on Layer 3 physical routed interfaces because the IP Device Tracking feature for Layer 3 physical interfaces is not supported.
–![]() Cisco TrustSec cannot be configured on a pure bridging domain with the IPSG feature enabled. You must either enable IP routing or disable the IPSG feature in the bridging domain.
Cisco TrustSec cannot be configured on a pure bridging domain with the IPSG feature enabled. You must either enable IP routing or disable the IPSG feature in the bridging domain.
–![]() Cisco TrustSec on the controller supports up to 255 security group destination tags for enforcing security group ACLs.
Cisco TrustSec on the controller supports up to 255 security group destination tags for enforcing security group ACLs.
Caveats
- Cisco Bug Search Tool
- Open Caveats
- Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.10E
- Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.9E
- Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.8E
- Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
- Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.6E
- Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5Ea
- Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5E
- Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.4E
- Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.2E
- Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.1E
- Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.0E
Cisco Bug Search Tool
Caveats describe unexpected behavior in a product. The Open Caveats section lists open caveats that apply to the current release and may apply to previous releases. A caveat that is open for a prior release and is still unresolved applies to all future releases until it is resolved.
To view the details of the software bugs pertaining to your product, perform the following task:
Click the Caveat ID/Bug ID number in the table.
The corresponding Bug Search Tool page is displayed with details of the Caveat ID/Bug ID.
The Bug Search Tool (BST), which is the online successor to the Bug Toolkit, is designed to improve the effectiveness in network risk management and device troubleshooting. The BST allows partners and customers to search for software bugs based on product, release, and keyword, and aggregates key data, such as bug details, product, and version. The tool has a provision to filter bugs based on credentials to provide external and internal bug views for the search input.
To view the details of a caveat whose ID you do not have, perform the following procedure:
1.![]() Access the BST using your Cisco user ID and password:
Access the BST using your Cisco user ID and password:
https://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch/
2.![]() In the Bug Search window that is displayed, enter the necessary information in the corresponding fields.
In the Bug Search window that is displayed, enter the necessary information in the corresponding fields.
For more information about how to use the Cisco Bug Search Tool effectively, including how to set email alerts for bugs and to save bugs and searches, see the Bug Search Tool Help & FAQ page.
Open Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.10E
There are no resolved caveats in Cisco IOS XE release 3.6.10E.
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.9E
There are no resolved caveats in Cisco IOS XE release 3.6.9E.
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.8E
There are no resolved caveats in Cisco IOS XE release 3.6.8E.
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.7E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.6E
Resolved Caveats for Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5Ea
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.5E
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.4E
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.3E
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.2E
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.1E
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
Resolved Caveats in Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6.0E
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
Troubleshooting
For the most up-to-date, detailed troubleshooting information, see the Cisco TAC website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/support/index.html
Choose Product Support > Wireless. Then choose your product and click Troubleshoot and Alerts to find information for the problem that you are experiencing.
Related Documentation
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/ios-nx-os-software/ios-xe-3e/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps12598/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
http://www.cisco.com/go/designzone
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/index.cgi
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which lists all new and revised Cisco Technical documentation, as an RSS feed and deliver content directly to your desktop using a read application. The RSS feeds are a free service.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1721R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback