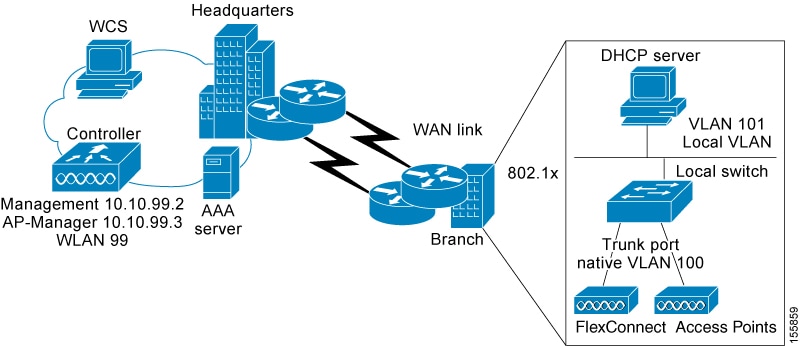
FlexConnect Overview
FlexConnect is a wireless solution for branch office and remote office deployments. It enables customers to configure and control access points (AP) in a branch or remote office from the corporate office through a wide area network (WAN) link without deploying a controller in each office. The FlexConnect access points can switch client data traffic locally and perform client authentication locally when their connection to the controller is lost. When they are connected to the controller, they can also send traffic back to the controller. In the connected mode, the FlexConnect access point can also perform local authentication.
A FlexConnect AP can, on a per-WLAN basis, either tunnel client data in CAPWAP to the controller (called Central Switching), or have client data egress at the AP’s LAN port (called Local Switching). With Locally Switched WLANs, the AP can tag client traffic in separate VLANs, to segregate the traffic from its management interface.
For a Locally Switched WLAN, the client authentication can either be handled by the controller (Central Authentication) or by the AP (Local Authentication).
If a FlexConnect AP should lose its CAPWAP connection to its controller, it goes into Standalone mode. In Standalone mode, any Centrally Switched WLANs are down, but Locally Switched WLANs remain operational. If the Locally Switched WLAN is configured for Central Authentication, the associated clients remain connected when the AP goes into Standalone mode, but will be unable to form new associations. A Locally Switched WLAN that uses Local Authentication remains operational whether the AP is in Standalone or Connected mode.
The controller software has a more robust fault tolerance methodology to FlexConnect access points. In previous releases, whenever a FlexConnect access point disassociates from a controller, it moves to the standalone mode. The clients that are centrally switched are disassociated. However, the FlexConnect access point continues to serve locally switched clients. When the FlexConnect access point rejoins the controller (or a standby controller), all clients are disconnected and are authenticated again. This functionality has been enhanced and the connection between the clients and the FlexConnect access points are maintained intact and the clients experience seamless connectivity. When both the access point and the controller have the same configuration, the connection between the clients and APs is maintained.
After the client connection has been established, the controller does not restore the original attributes of the client. The client username, current rate and supported rates, and listen interval values are reset to the default values only after the session timer expires.
There is no deployment restriction on the number of FlexConnect access points per location. Multiple FlexConnect groups can be defined in a single location.
The controller can send multicast packets in the form of unicast or multicast packets to the access point. In FlexConnect mode, the access point can receive multicast packets only in unicast form.
 Note |
Although NAT and PAT are supported for FlexConnect access points, they are not supported on the corresponding controller. Cisco does not support configurations in which the controller is behind a NAT/PAT boundary. |
VPN and PPTP are supported for locally switched traffic if these security types are accessible locally at the access point.
FlexConnect access points support multiple SSIDs.
Workgroup bridges and Universal Workgroup bridges are supported on FlexConnect access points for locally switched clients.
FlexConnect supports IPv6 clients by bridging the traffic to local VLAN, similar to IPv4 operation. FlexConnect supports Client Mobility for a group of up to 100 access points.
When AP is changed from local mode to FlexConnect mode, the AP does not reboot. However, when the AP is changed from FlexConnect mode to local mode, the AP reboots and displays the following error message:
FlexConnect Authentication Process
When an access point boots up, it looks for a controller. If it finds one, it joins the controller, downloads the latest software image and configuration from the controller, and initializes the radio. It saves the downloaded configuration in nonvolatile memory for use in standalone mode.
 Note |
Once the access point is rebooted after downloading the latest controller software, it must be converted to the FlexConnect mode. |
 Note |
802.1X is not supported on the AUX port for Cisco 2700 series APs. |
A FlexConnect access point can learn the controller IP address in one of these ways:
-
If the access point has been assigned an IP address from a DHCP server, it can discover a controller through the regular CAPWAP or LWAPP discovery process.

Note
OTAP is not supported.
-
If the access point has been assigned a static IP address, it can discover a controller through any of the discovery process methods except DHCP option 43. If the access point cannot discover a controller through Layer 3 broadcast, we recommend DNS resolution. With DNS, any access point with a static IP address that knows of a DNS server can find at least one controller.
-
If you want the access point to discover a controller from a remote network where CAPWAP or LWAPP discovery mechanisms are not available, you can use priming. This method enables you to specify (through the access point CLI) the controller to which the access point is to connect.

Note
For more information about how access points find controllers, see the controller deployment guide at: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/technology/controller/deployment/guide/dep.html.
When a FlexConnect access point can reach the controller (referred to as the connected mode), the controller assists in client authentication. When a FlexConnect access point cannot access the controller, the access point enters the standalone mode and authenticates clients by itself.
 Note |
The LEDs on the access point change as the device enters different FlexConnect modes. See the hardware installation guide for your access point for information on LED patterns. |
When a client associates to a FlexConnect access point, the access point sends all authentication messages to the controller and either switches the client data packets locally (locally switched) or sends them to the controller (centrally switched), depending on the WLAN configuration. With respect to client authentication (open, shared, EAP, web authentication, and NAC) and data packets, the WLAN can be in any one of the following states depending on the configuration and state of controller connectivity:
-
central authentication, central switching—In this state, the controller handles client authentication, and all client data is tunneled back to the controller. This state is valid only in connected mode.
-
local authentication, local switching—In this state, the FlexConnect access point handles client authentication and switches client data packets locally. This state is valid in standalone mode and connected mode.
In connected mode, the access point provides minimal information about the locally authenticated client to the controller. The following information is not available to the controller:
-
Policy type
-
Access VLAN
-
VLAN name
-
Supported rates
-
Encryption cipher
Local authentication is useful where you cannot maintain a remote office setup of a minimum bandwidth of 128 kbps with the round-trip latency no greater than 100 ms and the maximum transmission unit (MTU) no smaller than 576 bytes. In local authentication, the authentication capabilities are present in the access point itself. Local authentication reduces the latency requirements of the branch office.
-
Notes about local authentication are as follows:
-
Guest authentication cannot be done on a FlexConnect local authentication-enabled WLAN.
-
Local RADIUS on the controller is not supported.
-
Once the client has been authenticated, roaming is only supported after the controller and the other FlexConnect access points in the group are updated with the client information.
-
-
-
authentication down, switch down—In this state, the WLAN disassociates existing clients and stops sending beacon and probe requests. This state is valid in both standalone mode and connected mode.
-
authentication down, local switching—In this state, the WLAN rejects any new clients trying to authenticate, but it continues sending beacon and probe responses to keep existing clients alive. This state is valid only in standalone mode.
When a FlexConnect access point enters standalone mode, WLANs that are configured for open, shared, WPA-PSK, or WPA2-PSK authentication enter the “local authentication, local switching” state and continue new client authentications. his configuration is also correct for WLANs that are configured for 802.1X, WPA-802.1X, WPA2-802.1X, or Cisco Centralized Key Management, but these authentication types require that an external RADIUS server be configured. You can also configure a local RADIUS server on a FlexConnect access point to support 802.1X in a standalone mode or with local authentication.
Other WLANs enter either the “authentication down, switching down” state (if the WLAN was configured for central switching) or the “authentication down, local switching” state (if the WLAN was configured for local switching).
When FlexConnect access points are connected to the controller (rather than in standalone mode), the controller uses its primary RADIUS servers and accesses them in the order specified on the RADIUS Authentication Servers page or in the config radius auth add CLI command (unless the server order is overridden for a particular WLAN). However, to support 802.1X EAP authentication, FlexConnect access points in standalone mode need to have their own backup RADIUS server to authenticate clients.
 Note |
A controller does not use a backup RADIUS server. The controller uses the backup RADIUS server in local authentication mode. |
You can configure a backup RADIUS server for individual FlexConnect access points in standalone mode by using the controller CLI or for groups of FlexConnect access points in standalone mode by using either the GUI or CLI. A backup server configured for an individual access point overrides the backup RADIUS server configuration for a FlexConnect.
When web-authentication is used on FlexConnect access points at a remote site, the clients get the IP address from the remote local subnet. To resolve the initial URL request, the DNS is accessible through the subnet's default gateway. In order for the controller to intercept and redirect the DNS query return packets, these packets must reach the controller at the data center through a CAPWAP connection. During the web-authentication process, the FlexConnect access points allows only DNS and DHCP messages; the access points forward the DNS reply messages to the controller before web-authentication for the client is complete. After web-authentication for the client is complete, all the traffic is switched locally.
When a FlexConnect access point enters into a standalone mode, the following occurs:
-
The access point checks whether it is able to reach the default gateway via ARP. If so, it will continue to try and reach the controller.
If the access point fails to establish the ARP, the following occurs:
-
The access point attempts to discover for five times and if it still cannot find the controller, it tries to renew the DHCP on the ethernet interface to get a new DHCP IP.
-
The access point will retry for five times, and if that fails, the access point will renew the IP address of the interface again, this will happen for three attempts.
-
If the three attempts fail, the access point will fall back to the static IP and will reboot (only if the access point is configured with a static IP).
-
Reboot is done to remove the possibility of any unknown error the access point configuration.
Once the access point reestablishes a connection with the controller, it disassociates all clients, applies new configuration information from the controller, and allows client connectivity again.
 Feedback
Feedback