- Preface
- Chapter 1 - Overview
- Chapter 2 - Adding and Deleting Location Servers
- Chapter 3 - Synchronizing Cisco WCS and Location Servers
- Chapter 4 - Editing Location Server Properties
- Chapter 5 - Managing Location Server Users and Groups
- Chapter 6 - Configuring Event Notifications
- Chapter 7 - Monitoring Location Servers and Site
- Chapter 8 - Performing Maintenance Operations
- Index
Overview
Cisco 2700 series location appliances operate within the Cisco Wireless LAN Solution infrastructure. Location appliances compute, collect, and store historical location data using Cisco wireless LAN controllers and access points to track the physical location of wireless devices. Up to 2,500 laptop clients, palmtop clients, VoIP telephone clients, active Radio Frequency Identifier (RFID) asset tags, rogue access points and clients can be tracked.
The collected location data can be viewed in GUI format in the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), the centralized WLAN management platform. However, before you can use the WCS, you must perform an initial configuration using a CLI console session as described in the Quick Start Guide: Cisco 2700 Series Location Appliance.
The following sections describe the main topics covered in this guide:
•![]() "Display of Location Data" section
"Display of Location Data" section
•![]() "Maintenance Operations" section
"Maintenance Operations" section
•![]() "WCS and Location Server Synchronization" section
"WCS and Location Server Synchronization" section
•![]() "Monitoring Capability" section
"Monitoring Capability" section
•![]() "Configuration and Administration" section
"Configuration and Administration" section
•![]() "Compatibility Matrix" section
"Compatibility Matrix" section
Display of Location Data
After it is configured, each location server communicates directly with the Cisco wireless LAN controllers to which it was assigned to collect operator-defined location data. You can then use the associated Cisco WCS server to communicate with each location server to transfer and display selected data.
You can configure location appliances to collect data for Cisco Wireless LAN Solution clients, rogue access points, rogue clients, mobile stations, and RFID asset tags at separate intervals which you define.
Event Notification
Location servers provide the functionality for sending event notifications to registered listeners over the following transport mechanisms:
•![]() Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
•![]() Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) mail
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) mail
•![]() Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
•![]() SysLog
SysLog

Note ![]() WCS can act as a listener receiving event notifications over SNMP.
WCS can act as a listener receiving event notifications over SNMP.
Without event notification, Cisco WCS and third-party applications will need to periodically request location information from location servers. (Figure 1-1).
Figure 1-1 Pull Communication Model
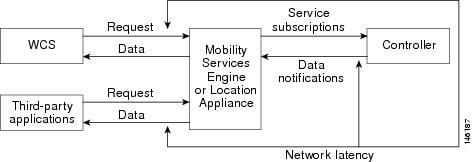
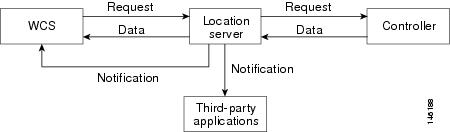
The pull communication model, however, is not suitable for applications that require more real-time updates to location information. For these applications, you can configure location servers to send event notifications (push) when certain conditions are met by the registered listeners (Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-2 Push Communication Model
Maintenance Operations
You can use Cisco WCS to back up the location server to a predefined FTP folder on any Cisco WCS server at defined intervals. You can also restore the location server data from that Cisco WCS Server. Other location server maintenance operations that you can perform include downloading new application code to all associated location server from any Cisco WCS server, defragmenting the Cisco WCS database, restarting location servers, and clearing location server configurations.
WCS and Location Server Synchronization
To maintain accurate location information, you can use Cisco WCS to configure location servers so that they are synchronized with network design, event group, and controller elements. Cisco WCS provides you with two ways to synchronize these elements and locations servers: manual and automatic (auto-sync).
Monitoring Capability
You can use Cisco WCS to monitor alarms and events generated by location servers. You can also download log files and view location server status information.
Configuration and Administration
You use Cisco WCS to perform different configuration and administrative tasks, including adding and removing location servers, configuring location server properties, managing users and groups and importing and exporting asset location information.
Compatibility Matrix
Table 1-1 describes compatibility between WCS and location server versions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
WCS 3.0 |
Supported |
Supported1 |
Not supported |
Not supported |
WCS 3.1 |
Supported2 |
Supported |
Supported from WCS 3.1.35.0 onward3 |
Supported from WCS 3.1.35.0 onward3 |
WCS 3.2 |
Supported3, 4, 5 |
Supported |
Supported6 |
|
WCS 4.0 |
Supported2, 3, 4, 5, 7 |
Supported3, 4, 5, 7 |
Supported7 |
Supported |
1 Certain antenna attributes are ignored by WCS. 2 Certain antenna attributes are ignored by the location server. 3 Asynchronous notification features are ignored by the location server. 4 Backup and restore operations for the location server may time out. 5 Searching for elements by a specific MAC address or asset name will not work until the location server SW is upgraded. 6 Battery level and location notification update features are ignored by WCS. Location smoothing parameters and contributing access point (AP) debug options are ignored by WCS. 7 Battery level and location notification update features are ignored by the location server. Location smoothing parameters and contributing access point (AP) debug options are ignored by the location server. |
.
 Feedback
Feedback