Editing Location Server Properties
This chapter describes how to configure location server properties.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• "Editing General Properties" section
"Editing General Properties" section
• "Editing Polling Parameters" section
"Editing Polling Parameters" section
• "Editing History Parameters" section
"Editing History Parameters" section
• "Editing Advanced Parameters" section
"Editing Advanced Parameters" section
• "Editing Location Parameters" section
"Editing Location Parameters" section
• "Editing LOCP Parameters" section
"Editing LOCP Parameters" section
Editing General Properties
You can use Cisco WCS to edit the general properties of location servers registered in the WCS database. You can edit the following general properties: contact name, user name, password and HTTPS.
To edit the general properties of a location server, follow these steps:
Step 1  In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers to display the All Location Servers window.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers to display the All Location Servers window.
Step 2  Click the name of the location server you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server you want to edit.
Step 3  Modify the parameters as appropriate. A description of each of the features and possible values is summarized in Table 4-1.
Modify the parameters as appropriate. A description of each of the features and possible values is summarized in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 General Properties
|
|
|
Contact Name |
Enter a contact name for the location server. |
User Name |
Enter the login user name for the Cisco WCS server that manages the location server. |
Password |
Enter the login password for the Cisco WCS server that manages the location server. |
Port |
8001 |
HTTPS |
Check the HTTPS enable check box to enable HTTPS. Note  When you have a non-default port or HTTPS turned on, you must pass the correct information along with the command. For example, getserverinfo must include -port <<port>> -protocol <<HTTP/HTTPS>>. Similarly, for stopping the server, stoplocserver - port <<port>> -protocol <HTTP/HTTPS>>. When you have a non-default port or HTTPS turned on, you must pass the correct information along with the command. For example, getserverinfo must include -port <<port>> -protocol <<HTTP/HTTPS>>. Similarly, for stopping the server, stoplocserver - port <<port>> -protocol <HTTP/HTTPS>>. |
Step 4  Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Editing Polling Parameters
You can use Cisco WCS to modify the time periods (polling intervals) for polling client stations, rogue access points, asset tags, and statistics of clients and asset tags. Additionally, you can turn off tracking and reporting of ad hoc rogue clients.
The polling interval is the period of time between polling cycles. For example, if a polling cycle requires 30 seconds to complete, and the polling interval is 300 seconds, polling cycles start every 330 seconds, as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 Polling Interval
When configuring polling intervals, use shorter intervals to increase the granularity of data collection. To decrease the granularity of data collection, use longer intervals.
Note  The polling intervals are independent of the number of times that WCS users request a data refresh from the location server.
The polling intervals are independent of the number of times that WCS users request a data refresh from the location server.
To configure polling parameters for a location appliance, follow these steps:
Step 1  In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. The All Servers window appears.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. The All Servers window appears.
Step 2  Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. The General Properties window appears.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. The General Properties window appears.
Step 3  From the Administration menu, choose Polling Parameters to display the administrative configuration options.
From the Administration menu, choose Polling Parameters to display the administrative configuration options.
Step 4  Modify the polling parameters as appropriate. Table 4-2 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the polling parameters as appropriate. Table 4-2 lists each parameter and its description.
Table 4-2 Polling Parameters:
|
|
|
Retry Count |
Enter the number of times to retry a polling cycle. Default value is 3. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Timeout |
Enter the number of seconds before a polling cycle times out. Default value is 5. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Client Stations |
Check the Enable check box to enable client station polling and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 300. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Asset Tags |
Check the Enable check box to enable asset tag polling and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 600. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999.
Note  Before the location server can collect asset tag data from controllers, you must enable the detection of active RFID tags using the CLI command config rfid status enable on the controllers. Before the location server can collect asset tag data from controllers, you must enable the detection of active RFID tags using the CLI command config rfid status enable on the controllers.
|
Statistics |
Check the Enable check box to enable statistics polling for the location server, and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 900. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Rogue Clients and Access Points |
Check the Enable check box to enable rogue access point polling and enter the polling interval in seconds. Default value is 600. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Exclude Ad-Hoc Rogues |
Check the check box to turn off the tracking and reporting of ad hoc rogues in the network. As a result, ad hoc rogues are not displayed on WCS maps or its events and alarms reported. |
Step 5  Click Save to store the new settings in the location server database.
Click Save to store the new settings in the location server database.
Editing History Parameters
You can use Cisco WCS to specify how often to collect client station, rogue access point, and asset tag histories from the controllers associated with a location server.
You can also program the location server to periodically prune (remove) duplicate data from its historical files to reduce the amount of data stored on its hard drive.
To configure location server history settings, follow these steps:
Step 1  In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
Step 2  Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Step 3  Click Administration (left-hand side) to display the administrative configuration options.
Click Administration (left-hand side) to display the administrative configuration options.
Step 4  Click History Parameters.
Click History Parameters.
Step 5  Modify the following history parameters as appropriate. Table 4-3 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the following history parameters as appropriate. Table 4-3 lists each parameter and its description.
Table 4-3 History Parameters:
|
|
|
Archive for |
Enter the number of days for the location server to retain a history of each enabled category. Default value is 30. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Prune data starting at |
Enter the number of hours and minutes at which the location server starts data pruning (between 0 and 23 hours, and between 1 and 59 minutes). Also enter the interval in minutes after which data pruning starts again (between 0, which means never, and 99900000). Default start time is 23 hours and 50 minutes, and the default interval is 1440 minutes. |
Client Stations |
Check the Enable check box to turn historical data collection on, and enter the number of minutes between data collection events. Default value is 120. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Asset Tags |
Check the Enable check box to turn historical data collection on, and enter the number of minutes between data collection events. Default value is 180. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999.
Note  Before the location server can collect asset tag data from controllers, you must enable the detection of RFID tags using the CLI command config rfid status enable. Before the location server can collect asset tag data from controllers, you must enable the detection of RFID tags using the CLI command config rfid status enable.
|
Rogue Clients and Access Points |
Check the Enable check box to turn historical data collection on (disabled by default), and enter the number of minutes between data collection events. Default value is 360. Allowed values are from 1 to 99999. |
Step 6  Click Save to store your selections in the location server database.
Click Save to store your selections in the location server database.
Editing Advanced Parameters
You can use Cisco WCS to modify troubleshooting parameters for a location appliance.
To edit location server advanced parameters, follow these steps:
Step 1  In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
Step 2  Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Step 3  Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Step 4  Click Advanced Parameters (left-hand side) and scroll to the bottom of that window to see the options that can be modified.
Click Advanced Parameters (left-hand side) and scroll to the bottom of that window to see the options that can be modified.
Step 5  Modify the advanced parameters as necessary. Table 4-4 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the advanced parameters as necessary. Table 4-4 lists each parameter and its description.
Table 4-4 Advanced Parameters
|
|
|
Advanced Debug |
Check the check box to enable advanced debugging. Uncheck the check box to disable advanced debugging.
Caution
 Enable advanced debugging only under the guidance of TAC personnel because advanced debugging slows the location server down. Enable advanced debugging only under the guidance of TAC personnel because advanced debugging slows the location server down.
|
Number of Days to Keep Events |
Enter the number of days to keep logs. Change this value as required for monitoring and troubleshooting. |
Session Timeout |
Enter the number of minutes before a session times out. Change this value as required for monitoring and troubleshooting. |
Absent Data cleanup interval |
Interval in minutes for data cleanup. |
Step 6  Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Editing Location Parameters
You can use Cisco WCS to specify whether the location server retains its calculation times and how soon the location server deletes its collected Receiver Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) measurement times. You can also apply varying smoothing rates to manage location movement of an element.
To configure location parameters, follow these steps:
Step 1  In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
Step 2  Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Step 3  Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Step 4  Click Location Parameters.
Click Location Parameters.
Step 5  Modify the location parameters as appropriate. Table 4-5 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the location parameters as appropriate. Table 4-5 lists each parameter and its description.
Table 4-5 Location Parameters:
|
|
|
Calculation time |
Check the corresponding check box to enable the calculation of the time required to compute location.
Caution
 Enable only under Cisco TAC personnel guidance because enabling this parameter slows down overall location calculations. Enable only under Cisco TAC personnel guidance because enabling this parameter slows down overall location calculations.
|
OW Location |
Check the corresponding check box to enable Outer Wall (OW) calculation as part of location calculation. Note  The OW Location parameter is ignored by the location server. The OW Location parameter is ignored by the location server. |
Relative discard RSSI time |
Enter the number of minutes since the most recent RSSI sample after which RSSI measurement should be considered stale and discarded. For example, if you set this parameter to 3 minutes and the location server receives two samples at 10 and 12 minutes, it keeps both samples. An additional sample received at 15 minutes is discarded. Default value is 3. Allowed values range from 0 to 99999. A value of less than 3 is not recommended. |
Absolute discard RSSI time |
Enter the number of minutes after which RSSI measurement should be considered stale and discarded, regardless of the most recent sample. Default value is 60. Allowed values range from 0 to 99999. A value of less than 60 is not recommended. |
RSSI Cutoff |
Enter the RSSI cutoff value, in decibels (dBs) with respect to one (1) mW (dBm), above which the location server will always use the access point measurement. Default value is -75. Note  When 3 or more measurements are available above the RSSI cutoff value, the location server will discard any weaker values and use the 3 (or more) strongest measurements for calculation; however, when only weak measurements below the RSSI cutoff value are available, those values are used for calculation. When 3 or more measurements are available above the RSSI cutoff value, the location server will discard any weaker values and use the 3 (or more) strongest measurements for calculation; however, when only weak measurements below the RSSI cutoff value are available, those values are used for calculation.
Caution
 Modify only under Cisco TAC personnel guidance. Modifying this value can reduce the accuracy of location calculation. Modify only under Cisco TAC personnel guidance. Modifying this value can reduce the accuracy of location calculation.
|
Smooth Location Positions |
Smoothing compares an elements prior location to its most recent reported location by applying a weighted average calculation to determine its current location. The specific weighted average calculation employed is tied to the given smoothing option selected. Default value is More Smoothing. Options: • None: Elements assumed to be in location indicated by most recent polling None: Elements assumed to be in location indicated by most recent polling • Less: Prior location weighted at 25% and New location weighted at 75% Less: Prior location weighted at 25% and New location weighted at 75% • Average: Prior location weighted at 50% and New location weighted at 50% Average: Prior location weighted at 50% and New location weighted at 50% • More: Prior location weighted at 75% and New location weighted at 25% More: Prior location weighted at 75% and New location weighted at 25% • Maximum: Prior location weighted at 90% and New location weighted at 10% Maximum: Prior location weighted at 90% and New location weighted at 10% |
Step 6  Click Save to store your selections in the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to store your selections in the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Editing LOCP Parameters
LOCP is the location protocol that manages communication between the location server and the controller. Transport of telemetry, emergency and chokepoint information between the location server and the controller is managed by this protocol.
Note •
• The LOCP parameter is only seen on location servers installed with release 3.0 and higher software. Additionally, telemetry, emergency and chokepoint information is only seen on controllers and WCS installed with release 4.1 and higher software and on location servers running release 3.0 and higher software.
The LOCP parameter is only seen on location servers installed with release 3.0 and higher software. Additionally, telemetry, emergency and chokepoint information is only seen on controllers and WCS installed with release 4.1 and higher software and on location servers running release 3.0 and higher software.
• The TCP port (16113) that the controller and location server communicate over MUST be open (not blocked) on any firewall that exists between the controller and location server for LOCP to function.
The TCP port (16113) that the controller and location server communicate over MUST be open (not blocked) on any firewall that exists between the controller and location server for LOCP to function.
To configure LOCP parameters, follow these steps:
Step 1  In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
Step 2  Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Step 3  Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Step 4  Click LOCP Parameters.
Click LOCP Parameters.
Step 5  Modify the LOCP parameters as appropriate. Table 4-6 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the LOCP parameters as appropriate. Table 4-6 lists each parameter and its description.
Note  No change in the default parameter values is recommended unless network is experiencing slow response or excessive latency.
No change in the default parameter values is recommended unless network is experiencing slow response or excessive latency.
Table 4-6 LOCP Parameters
|
|
|
Echo Interval |
Defines how frequently an echo request is sent from a location server to a controller. The default value is 15 seconds. Allowed values range from 1 to 120 seconds. Note  If a network is experiencing slow response, you can increase the values of the echo interval, neighbor dead interval and the response timeout values to limit the number of failed echo acknowledgements. If a network is experiencing slow response, you can increase the values of the echo interval, neighbor dead interval and the response timeout values to limit the number of failed echo acknowledgements. |
Neighbor Dead Interval |
The number of seconds that the location server waits for a successful echo response from the controller before declaring the neighbor dead. This timer begins when the echo request is sent. The default values is 30 seconds. Allowed values range from 1 to 240 seconds. Note  This value must be at least two times the echo interval value. This value must be at least two times the echo interval value. |
Response Timeout |
Indicates how long the location server waits before considering the pending request as timed out. The default value is 1 second. Minimum value is one (1). There is no maximum value. |
Retransmit Interval |
Interval of time that the location server waits between notification of a response time out and initiation of a request retransmission. The default setting is 3 seconds. Allowed values range from 1 to 120 seconds. |
Maximum Retransmits |
Defines the maximum number of retransmits that are done in the absence of a response to any request. The default setting is 5. Allowed minimum value is zero (0). There is no maximum value. |
Step 6  Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
![]() "Editing General Properties" section
"Editing General Properties" section ![]() "Editing Polling Parameters" section
"Editing Polling Parameters" section ![]() "Editing History Parameters" section
"Editing History Parameters" section ![]() "Editing Advanced Parameters" section
"Editing Advanced Parameters" section ![]() "Editing Location Parameters" section
"Editing Location Parameters" section ![]() "Editing LOCP Parameters" section
"Editing LOCP Parameters" section ![]() In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers to display the All Location Servers window.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers to display the All Location Servers window. ![]() Click the name of the location server you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server you want to edit. ![]() Modify the parameters as appropriate. A description of each of the features and possible values is summarized in Table 4-1.
Modify the parameters as appropriate. A description of each of the features and possible values is summarized in Table 4-1. ![]() Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases. 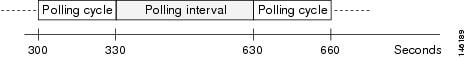

![]() The polling intervals are independent of the number of times that WCS users request a data refresh from the location server.
The polling intervals are independent of the number of times that WCS users request a data refresh from the location server. ![]() In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. The All Servers window appears.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. The All Servers window appears. ![]() Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. The General Properties window appears.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. The General Properties window appears. ![]() From the Administration menu, choose Polling Parameters to display the administrative configuration options.
From the Administration menu, choose Polling Parameters to display the administrative configuration options. ![]() Modify the polling parameters as appropriate. Table 4-2 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the polling parameters as appropriate. Table 4-2 lists each parameter and its description. ![]() Click Save to store the new settings in the location server database.
Click Save to store the new settings in the location server database. ![]() In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. ![]() Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. ![]() Click Administration (left-hand side) to display the administrative configuration options.
Click Administration (left-hand side) to display the administrative configuration options. ![]() Click History Parameters.
Click History Parameters. ![]() Modify the following history parameters as appropriate. Table 4-3 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the following history parameters as appropriate. Table 4-3 lists each parameter and its description. ![]() Click Save to store your selections in the location server database.
Click Save to store your selections in the location server database. ![]() In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. ![]() Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. ![]() Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options. ![]() Click Advanced Parameters (left-hand side) and scroll to the bottom of that window to see the options that can be modified.
Click Advanced Parameters (left-hand side) and scroll to the bottom of that window to see the options that can be modified. ![]() Modify the advanced parameters as necessary. Table 4-4 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the advanced parameters as necessary. Table 4-4 lists each parameter and its description. ![]() Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases. ![]() In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. ![]() Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. ![]() Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options. ![]() Click Location Parameters.
Click Location Parameters. ![]() Modify the location parameters as appropriate. Table 4-5 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the location parameters as appropriate. Table 4-5 lists each parameter and its description. ![]() Click Save to store your selections in the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to store your selections in the Cisco WCS and location server databases. 
![]() •
•![]() The LOCP parameter is only seen on location servers installed with release 3.0 and higher software. Additionally, telemetry, emergency and chokepoint information is only seen on controllers and WCS installed with release 4.1 and higher software and on location servers running release 3.0 and higher software.
The LOCP parameter is only seen on location servers installed with release 3.0 and higher software. Additionally, telemetry, emergency and chokepoint information is only seen on controllers and WCS installed with release 4.1 and higher software and on location servers running release 3.0 and higher software. ![]() The TCP port (16113) that the controller and location server communicate over MUST be open (not blocked) on any firewall that exists between the controller and location server for LOCP to function.
The TCP port (16113) that the controller and location server communicate over MUST be open (not blocked) on any firewall that exists between the controller and location server for LOCP to function. ![]() In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers.
In Cisco WCS, choose Location > Location Servers. ![]() Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit.
Click the name of the location server whose properties you want to edit. ![]() Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options.
Click Advanced (left-hand side) to expand the advanced menu options. ![]() Click LOCP Parameters.
Click LOCP Parameters. ![]() Modify the LOCP parameters as appropriate. Table 4-6 lists each parameter and its description.
Modify the LOCP parameters as appropriate. Table 4-6 lists each parameter and its description. 
![]() No change in the default parameter values is recommended unless network is experiencing slow response or excessive latency.
No change in the default parameter values is recommended unless network is experiencing slow response or excessive latency. ![]() Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases.
Click Save to update the Cisco WCS and location server databases. 
 Feedback
Feedback