Overview
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cisco Context Aware Mobility Solution Overview
Cisco 3300 Series Mobility Services Engines
Viewing Contextual Information
Configuration and Administration
Adding and Deleting Mobility Services Engine
Editing Mobility Services Engine Properties
Mobility Services Engine Synchronization
Context Aware Planning and Verification
Overview
This chapter describes the role of the Cisco 3300 Series Mobility Services Engine, a component of the Cisco Context Aware Mobility (CAM) Solution, within the overall Cisco Unified Wireless Network (CUWN).
Additionally, Context Aware Software (CAS), which is installed on the mobility services engine (MSE) and is a component of the Context Aware Mobility Solution, is addressed.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•
"Cisco Context Aware Mobility Solution Overview" section
•
"Viewing Contextual Information" section
•
"Configuration and Administration" section
•
"Mobility Services Engine Synchronization" section
•
"Context Aware Planning and Verification" section
•
"Monitoring Capability" section
•
"Maintenance Operations" section
•
"System Compatibility" section
Cisco Context Aware Mobility Solution Overview
The foundation of the Cisco Context Aware Mobility Solution is the controller-based architecture of the CUWN. The CUWN includes the following primary components: access points, wireless LAN controllers, the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS) management application and the Cisco 3300 Series Mobility Services Engine.
Cisco 3300 Series Mobility Services Engines
The Cisco 3300 Series Mobility Services Engine (MSE) operates with CAS which is a component of the Cisco Context Aware Mobility Solution. (Figure 1-1).
Figure 1-1 Context Aware Mobility Solution

CAS
CAS allows a mobility services engine to simultaneously track thousands of mobile assets and clients by retrieving contextual information such as location, temperature, and availability from Cisco access points.
CAS relies on two engines for processing the contextual information it receives. The Context Aware Engine for Clients processes data received from Wi-Fi clients and the Context Aware Engine for Tags processes data received from Wi-Fi tags; both of these engines can be deployed together or separately depending on the business need.

Note
•
You must purchase licenses from Cisco to retrieve contextual information on tags and clients from access points.
•
Licenses for tags and clients are offered independently. (The clients' license also includes tracking of rogue clients and rogue access points).
•
Licenses for tags and clients are offered in various quantities, ranging from 3,000 to 18,000 units.
•
For details on tag and client licenses, refer to the Cisco 3350 Mobility Services Engine Release Note at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Viewing Contextual Information
The collected contextual information can be viewed in GUI format in the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), the centralized WLAN management platform.

Note
However, before you can use Cisco WCS, initial configuration for the mobility services engine is required using a command-line (CLI) console session. Details are described in the Cisco 3350 Mobility Services Engine Getting Started Guide at the following link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/tsd_products_support_series_home.html.
After its installation and initial configuration is complete, the mobility services engine can communicate with multiple Cisco wireless LAN controllers to collect operator-defined contextual information. You can then use the associated Cisco WCS to communicate with each mobility services engine to transfer and display selected data.
You can configure the mobility services engine to collect data for clients, rogue access points, rogue clients, mobile stations, and active RFID asset tags.
Event Notification
A mobility services engine sends event notifications to registered listeners over the following transport mechanisms:
•
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
•
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) mail
•
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
•
SysLog

Note
Cisco WCS can act as a listener receiving event notifications over SNMP. Without event notification, Cisco WCS and third-party applications will need to periodically request location information from location-based services. (Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-2 Pull Communication Model
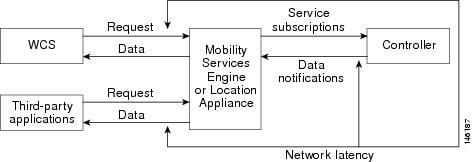
The pull communication model, however, is not suitable for applications that require more real-time updates to location information. For these applications, you can configure the mobility services engine to send event notifications (push) when certain conditions are met by the registered listeners.
Configuration and Administration
You can use Cisco WCS to perform different configuration and administrative tasks, including adding and removing a mobility services engine, configuring mobility services engine properties and managing users and groups as summarized below.
Adding and Deleting Mobility Services Engine
You can use Cisco WCS to add and delete mobility services engine within the network. Refer to Chapter 2, "Adding and Deleting Systems" for configuration details.
Editing Mobility Services Engine Properties
You can use Cisco WCS to configure the following parameters on the mobility services engine. Refer to Chapter 4, "Configuring Mobility Services Engine Properties" for configuration details.
•
General Properties: Enables you to assign a contact name, username, password, and HTTP for the mobility services engine.
•
History Parameters: Enables you to specify how often the mobility services engine collects historical data on client station, rogue access point, and asset tags from controllers to manage the amount of data stored on the mobility services engine hard drive.
•
Advanced Parameters: Enables you to set the number of days events are kept, set session time out values, set an absent data interval cleanup interval, and enable or disable Advanced Debug.
•
NMSP Parameters: Enables you to modify Network Mobility Services Protocol (NMSP) parameters such as echo and neighbor dead intervals as well as response and retransmit periods. NMSP is the protocol that manages communication between the mobility services engine and the controller. Transport of telemetry, emergency, and chokepoint information between the mobility services engine and the controller is managed by this protocol.
Editing CAS Properties
You can use Cisco WCS to configure the following parameters for CAS. Refer to the "Context Aware Planning and Verification" section in Chapter 7 for configuration details.
Location of an element (clients, tags, rogue clients and rogue access points) is one of the components that is retrieved from access points by the Context Aware Software (CAS) installed on a mobility services engine. CAS retrieves location as well as additional contextual information such as temperature and asset availability about a client or tagged asset from access points.

Note
Context Aware Software incorporates and expands the function of Cisco location-based services software.
•
Tracking Parameters: Enables you to define the mobile assets (such as client stations, active asset tags; and rogue clients and access points) that you want to actively track, set limits on how many of a specific mobile asset you want to track, and disable tracking and reporting of ad hoc rogue clients and access points.
•
Filtering Parameters: Enables you to define filters to exclude probing clients as well as tags and non-probing clients based on their MAC addresses.
–
Probing clients are clients that are associated to another controller but whose probing activity causes them to be seen by another controller and counted as a client by the probed controller as well as its primary controller.
•
Location Parameters: Enables you to specify whether the mobility services engine retains its calculation times and how soon the mobility services engine deletes its collected RSSI measurement times. It also enables you to apply varying smoothing rates to manage location movement of an element.
Managing Users and Groups
You can use Cisco WCS to add, delete, and edit user session and user group parameters as well as add and delete host access records. Refer to the "Managing Users and Groups" section in Chapter 5 for configuration details.
Mobility Services Engine Synchronization
Cisco WCS pushes network designs (logical maps of elements), controllers and event definitions to the mobility services engine to maintain accurate location information between the mobility services engine and controller. Cisco WCS provides you with two ways to synchronize: manual and automatic (auto-sync). Refer to the "Synchronizing Mobility Services Engines"section in Chapter 3 for specifics.
Context Aware Planning and Verification
To plan and optimize access point deployment, you can use Cisco WCS to calibrate linear or data points. Additionally, you can analyze the location accuracy of non-rogue and rogue clients and asset tags on an area or floor map using the accuracy tool, and you can use chokepoints to enhance location accuracy for tags. Refer to the "Context Aware Planning and Verification" section in Chapter 7 for specifics.
Monitoring Capability
You can use Cisco WCS to monitor alarms, events, and logs generated by mobility services engine. You can also monitor the status of mobility services engines, clients, and tagged assets. Additionally, you can generate a utilization report for the mobility services engine to determine CPU and memory utilization as well as counts for clients, tags and rogue access points and clients. Refer to the "Monitoring the System" section in Chapter 8 for specifics.
Maintenance Operations
You can use Cisco WCS to import and export asset location and other contextual information, recover a password, back up mobility services engine data to a predefined FTP folder on Cisco WCS at defined intervals, and restore the mobility services engine data from that Cisco WCS. Other mobility services engine maintenance operations that you can perform include: downloading new software images to all associated mobility services engines from any Cisco WCS station, defragmenting the mobility services engine database, restarting a mobility services engine, shutting down a mobility services engine and clearing mobility services engine configurations. Refer to the "Performing Maintenance Operations" section in Chapter 9 for specifics.
System Compatibility

Note
Refer to the Cisco 3350 Mobility Services Engine Release Note for the latest system (controller, WCS, mobility services engine) compatibility information, feature support, and operational notes for your current release at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/tsd_products_support_series_home.htm
 Feedback
Feedback