Release Notes for Cisco Mobility Services Engine, Release 8.0.110.0
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco Mobility Services Engine, Release 8.0.110.0
Cisco Mobility Services Engine and Services
Cisco MSE Compatibility Matrix
Upgrading From Cisco MSE 8.x to CMX 10.x
Upgrading from Cisco CMX 10.x to CMX 8.x
Upgrading the MSE to 8.0.110.0 from 7.x Release
Upgrading the MSE to 8.0.110.0 from 7.x Release Without Data Migration
Restoring an Old Database to 8.0.110.0
Updated Software Version Shown in the Prime Infrastructure After Polling
MSE License Product Numbers and SKUs
Ordering Support for Physical and Virtual Appliance
Base Location Services Licenses
CMX Licenses (Previously known as Advanced Location Services)
Base Location Services to CMX Upgrade License
wIPS Enhanced Local Mode License
wIPS Monitor Mode/Monitor Module License
Cisco MSE Virtual Appliance Product Specifications
Operational Notes for Mobility Services Engine
Resolution to NMSP/SHA2 keyhash Mismatch Issue
How and When to Use the db.tar installer
Reboot MSE After Fresh Installation or Upgrade
Automatic Installation Script for Initial Setup
Mandatory Default Root Password Change
Configuring the Prime Infrastructure Communication Username and Password Using MSE setup.sh
Configuration Changes for Greater Location Accuracy
Wireless Security Module with 3600 AP
AeroScout Engine Module Changes
Ports to be Opened for High Availability Between MSEs
Synchronizing Floor Maps in Location Service
Operational Notes for Context Aware Service
Synchronization Required When Upgrading to Release 8.0.110.0 or Importing CAD Floor Images
Floor Change or Minimum Distance Required for Location Transitions to Post to the History Log
Non-Cisco Compatible Extensions Tags Not Supported
Cisco Compatible Extensions Version 1 Tags Required at a Minimum
Monitoring Information Varies for Clients and Tags
Location History Time stamps Match Browser Location
Tablets and Smartphone with Limited Probe Requests Might Affect Location
Repeat Use of FloorID returns +1 After Every Hour
Operational Notes for CMX Analytics
Peer’s Certificate Invalid Signature Error with Firefox Browser
Operational Notes for Facebook Wi-Fi
Operational Notes for CMX Connect and Engage
Operational Notes for Mobile SDK
Enabling Root Access Control (RAC) in HA Mode
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco Mobility Services Engine, Release 8.0.110.0
First Published: December, 2014
Last Updated: February, 2015
These release notes describe what is new in this release, instructions to upgrade to this release, open and resolved caveats for this release, and related information for release 8.0.110.0 of the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) and its services.
- Location Service
- Wireless Intrusion Protection System (wIPS)
- Mobile Concierge Service
- CMX Analytics Service
- CMX Connect & Engage

Note![]() Before installing this software, see the “Upgrading the MSE” section for details on compatibility with the Cisco Wireless LAN controllers (WLC) and the Cisco Prime Infrastructure.
Before installing this software, see the “Upgrading the MSE” section for details on compatibility with the Cisco Wireless LAN controllers (WLC) and the Cisco Prime Infrastructure.

Note![]() Licenses are re quired to run all services. For ordering information, see the “Base Location license” section.
Licenses are re quired to run all services. For ordering information, see the “Base Location license” section.

Note![]() Cisco MSE 3310 and 3350 are not supported beyond Release 7.3.
Cisco MSE 3310 and 3350 are not supported beyond Release 7.3.
Contents
These release notes contain the following sections:
- Introduction
- Upgrading the MSE
- Licensing Information for MSE
- MSE License Product Numbers and SKUs
- What’s New in This Release
- Important Notes
- Operational Notes for Mobility Services Engine
- Caveats
- If You Need More Information
- Troubleshooting
- Related Documentation
- Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Introduction
This section introduces the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) and the various services that it supports.
Cisco Mobility Services Engine and Services
The Cisco Mobility Services Engine supports various services within the overall Cisco Unified Wireless Network (CUWN).
The Cisco Mobility Services Engine currently supports the following services:
- Location Service—Also known as Context Aware Service (CAS). This is the core service of the Mobility Services Engine (MSE) that turns on Wi-Fi client tracking and location API functionality. Allows MSE to simultaneously track thousands of mobile assets and clients by retrieving contextual information such as presence, location, telemetry data, and historical information.
- Wireless Intrusion Protection Service—Provides wireless-specific network threat detection and mitigation against malicious attacks, security vulnerabilities, and sources of performance disruption within the CUWN infrastructure. wIPS visualizes, analyzes, and identifies wireless threats, and centrally manages mitigation and resolution of security and performance issues using Cisco monitor mode and Enhanced Local Mode (ELM) Access Points. Proactive threat prevention is also supported to create a hardened wireless network core that is impenetrable by most wireless attacks.
- Mobile Concierge—Mobile Concierge enables the Cisco Mobility Services Advertisement Protocol (MSAP). This protocol enables direct communication between the MSE and mobile devices, allowing content to be pushed directly to the mobile device pre-association. This functionality is dependent on the mobile device supporting 802.11u and MSAP.
- CMX Analytics Service—The CMX Analytics service analyzes wireless device location information in a particular network. The CMX Analytics service uses the data provided by the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) to calculate the location of Wi-Fi devices in the Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). In addition, the FastLocate feature sends information about the RSSI strength of data packets to the Cisco WLC that can be used for location calculations.
When a wireless device is enabled in a network, it transmits probe request packets to identify the wireless network in its neighborhood. Even after connecting to the access point in the WLAN, the client devices continue to transmit probe request packets to identify other access points for better quality of service. The access points gather these request and the associated RSSI from the various wireless devices and forwards them to the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). The controller then forwards this information to the MSE.
The basic data that is collected from various APs, when analyzed, produces information and knowledge about the movement and behavior patterns of people who are using Wi-Fi devices in the building. For example, the building can be an airport, shopping mall, city center, and so on. The CMX Analytics service helps the airport authorities or the building owners to understand the movement of passengers or customer within their building. This helps them improve the signage, make changes to the under utilized areas, and so on.
- CMX Connect and Engage Service—Formerly known as Browser Engage Service. The CMX Connect and Engage service provides Connect, a guest Wi-Fi onboarding solution, as well as zone and message configuration for the CMX Software Development Kit (SDK).

Note![]() From Release 7.5 onwards, Cisco Location engine is used to track clients and tags. If AeroScout engine is detected when you are upgrading from Release 7.2 and later Releases to Release 7.5, then a warning message is displayed about removing the AeroScout license and engine. If you accept, the installer will remove all partner engine sub services. If you do not accept the removal of partner engine, then the installer will exit.
From Release 7.5 onwards, Cisco Location engine is used to track clients and tags. If AeroScout engine is detected when you are upgrading from Release 7.2 and later Releases to Release 7.5, then a warning message is displayed about removing the AeroScout license and engine. If you accept, the installer will remove all partner engine sub services. If you do not accept the removal of partner engine, then the installer will exit.

Note![]() Starting from Release 7.4, the evaluation licenses for 100 clients, 100 tags, and 10 wIPS monitor mode access points come standard on each Mobility Services Engine installed for 120 days, which earlier from Release 6.0 till Release 7.3 was installed for 60 days.
Starting from Release 7.4, the evaluation licenses for 100 clients, 100 tags, and 10 wIPS monitor mode access points come standard on each Mobility Services Engine installed for 120 days, which earlier from Release 6.0 till Release 7.3 was installed for 60 days.

Note![]() From Release 7.4 onwards, licensing is based on AP count and not based on tracked device count.
From Release 7.4 onwards, licensing is based on AP count and not based on tracked device count.
Software Compatibility Matrix
Table 1 lists the Cisco MSE compatibility matrix.
Table 2 lists the Cisco MSE compatibility matrix for legacy software versions.
Cisco MSE Compatibility Matrix
Table 1 lists the Cisco MSE compatibility matrix.

Note![]() AeroScout CLE is no longer bundled with MSE starting from Release 7.5 Release. However, AeroScout CLE is compatible with MSE Release 7.5 and above using the API interface.
AeroScout CLE is no longer bundled with MSE starting from Release 7.5 Release. However, AeroScout CLE is compatible with MSE Release 7.5 and above using the API interface.

Note![]() Cisco MSE 3310 and 3350 are not supported beyond Release 7.3.
Cisco MSE 3310 and 3350 are not supported beyond Release 7.3.

Note![]() This compatibility matrix lists only the compatibility information of Cisco MSE with other Cisco wireless products. This matrix does not reflect compatibility information between Cisco WLC and Cisco Prime Infrastructure or Cisco NCS. For compatibility information about Cisco Prime Infrastructure with Cisco WLC and other wireless products, see the Cisco Prime Infrastructure Release Notes.
This compatibility matrix lists only the compatibility information of Cisco MSE with other Cisco wireless products. This matrix does not reflect compatibility information between Cisco WLC and Cisco Prime Infrastructure or Cisco NCS. For compatibility information about Cisco Prime Infrastructure with Cisco WLC and other wireless products, see the Cisco Prime Infrastructure Release Notes.
Upgrading the MSE
For instructions on automatically downloading the software using the Prime Infrastructure or for manually downloading the software using a local or remote connection, see the “Updating Mobility Services Engine Software” section in Chapter 2 of the Cisco Mobility Services Engine Getting Started Guide.
You can find these documents at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/prod_installation_guides_list.html
This section contains the following topics:
- Upgrade Scenarios
- Compressed Software Image
- Updated Software Version Shown in the Prime Infrastructure After Polling
- Licensing Information for MSE
- Base Location license
Upgrade Scenarios
The following scenarios are available to upgrade MSE to 8.0.110.0 from 7.x releases:

Note![]() Do not run uninstall on the 7.4, 7.5, or 7.6 Release, instead stop the MSE and directly run the installer.
Do not run uninstall on the 7.4, 7.5, or 7.6 Release, instead stop the MSE and directly run the installer.

Note![]() Cisco MSE no longer supports management from HTTP. As a workaround, use HTTPS or allow HTTP in the Cisco MSE firewall with “iptables - L”.
Cisco MSE no longer supports management from HTTP. As a workaround, use HTTPS or allow HTTP in the Cisco MSE firewall with “iptables - L”.
- You can downgrade a device installed with CMX 10.x to MSE 8.x. Refer to the Software Recovery of MSE Using a USB or Flash Drive in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 guide given below. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/mse/8-0/MSE-CMX/8_0_MSE_CAS/8_0_MSE_CAS_chapter_010010.html
- Upgrading the MSE to 8.0.110.0 from 7.x Release Without Data Migration
- Restoring an Old Database to 8.0.110.0
Upgrading From Cisco MSE 8.x to CMX 10.x
You can upgrade a device installed with MSE 8.x to CMX 10.x. Refer to the Software Recovery of MSE Using CIMC in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 guide given below.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/mse/8-0/MSE-CMX/8_0_MSE_CAS/8_0_MSE_CAS_chapter_010010.html
You can downgrade a device installed with CMX 10.x to MSE 8.x. Refer to the Software Recovery of MSE Using a USB or Flash Drive in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 guide given below. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/mse/8-0/MSE-CMX/8_0_MSE_CAS/8_0_MSE_CAS_chapter_010010.html
Upgrading the MSE to 8.0.110.0 from 7.x Release
To upgrade from 7.x release to 8.0.110.0, follow these steps:

Note![]() You must untar the MSE software image before placing it in the /opt/installers directory (CSCuo09569).
You must untar the MSE software image before placing it in the /opt/installers directory (CSCuo09569).
Step 1![]() Download the 8.0.110.0 software image from Cisco.com. The file to be downloaded is: CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz.
Download the 8.0.110.0 software image from Cisco.com. The file to be downloaded is: CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz.

Warning![]() If you are downloading the above file on a Windows system, remember that some browsers modify the downloaded filename. If the downloaded filename is not correct, you must update it to the correct filename before using Prime Infrastructure to transfer the file, or directly copying the file to MSE. The correct filename is CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz
If you are downloading the above file on a Windows system, remember that some browsers modify the downloaded filename. If the downloaded filename is not correct, you must update it to the correct filename before using Prime Infrastructure to transfer the file, or directly copying the file to MSE. The correct filename is CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz
Step 2![]() Back up the MSE using Prime Infrastructure (highly recommended).
Back up the MSE using Prime Infrastructure (highly recommended).
Step 3![]() To download software to a Mobility Services Engine, choose Services > Mobility Services Engine from the Prime Infrastructure UI.
To download software to a Mobility Services Engine, choose Services > Mobility Services Engine from the Prime Infrastructure UI.
Step 4![]() Click the name of the mobility services engine to which you want to download software.
Click the name of the mobility services engine to which you want to download software.
Step 5![]() Choose System > Maintenance > Download Software from the left sidebar menu.
Choose System > Maintenance > Download Software from the left sidebar menu.
Step 6![]() To download software, do one of the following:
To download software, do one of the following:
- To download software listed in the Prime Infrastructure directory, select the Select from uploaded images to transfer into the Server radio button. Choose a binary image from the drop-down list.
Prime Infrastructure downloads the binary image to the FTP server directory you specified during the Prime Infrastructure installation.
- To use download software available locally or over the network, select the Browse a new software image to transfer into the Server radio button, and click Choose File. Locate the file, and click Open.
Step 7![]() Click Download to send the software to the /opt/installers directory on the Mobility Services Engine.
Click Download to send the software to the /opt/installers directory on the Mobility Services Engine.
Step 8![]() When using Prime Infrastructure to transfer the image to MSE, the file will be decompressed, and the “.gz” will be removed from the filename. Verify that the MSE image file (CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar) is in the Mobility Services Engines /opt/installers directory.
When using Prime Infrastructure to transfer the image to MSE, the file will be decompressed, and the “.gz” will be removed from the filename. Verify that the MSE image file (CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar) is in the Mobility Services Engines /opt/installers directory.

Note![]() When copying the image file directly to the MSE, without using Prime Infrastructure, the filename on MSE will remain unchanged and it will be CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz.
When copying the image file directly to the MSE, without using Prime Infrastructure, the filename on MSE will remain unchanged and it will be CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz.
Step 9![]() Go to /opt/installers and create a directory to extract the installer files using the command:
Go to /opt/installers and create a directory to extract the installer files using the command:
mkdir 8.0.110.0
Step 10![]() Move to the new directory using the command: cd 8.0.110.0
Move to the new directory using the command: cd 8.0.110.0
Step 11![]() To unpack the installation files, run the following command:
To unpack the installation files, run the following command:
tar xvf./CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin.tar
This unpack yields the following three files. These three files must be in the same directory when running the installer. The installation process uses the MSE_PUB.pem and signhash.bin to validate the integrity of the MSE image.

Note![]() If the MSE image file was transfered directly to the MSE and not downloaded using PI, then the following command should be used to decompress and unpack the installer files:
If the MSE image file was transfered directly to the MSE and not downloaded using PI, then the following command should be used to decompress and unpack the installer files:
tar zxvf../CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0.bin.tar.gz
Step 12![]() Make sure that the CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin file has execute permissions for the root user. If not, enter the following command:
Make sure that the CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin file has execute permissions for the root user. If not, enter the following command:
chmod +x CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin
Step 13![]() Manually stop the MSE service using the following command:
Manually stop the MSE service using the following command:
/etc/init.d/msed stop or service msed stop
Step 14![]() To install the new Mobility Services Engine image, enter the following command:
To install the new Mobility Services Engine image, enter the following command:
/opt/installers/8.0.110.0/CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-64bit.bin

Note![]() The installation process takes a minimum of 30 minutes. The actual installation time depends on the amount of data present in your system. After the installation, you need to reboot the system before starting the MSE.
The installation process takes a minimum of 30 minutes. The actual installation time depends on the amount of data present in your system. After the installation, you need to reboot the system before starting the MSE.
Step 15![]() Start the new Mobility Services Engine software by entering the following command. If you attempt to start the MSE, it just returns an error saying that MSE needs to be rebooted.
Start the new Mobility Services Engine software by entering the following command. If you attempt to start the MSE, it just returns an error saying that MSE needs to be rebooted.
Step 16![]() The system must be rebooted after upgrading the MSE. After exiting the installer, enter the command reboot at the prompt to reboot the MSE.
The system must be rebooted after upgrading the MSE. After exiting the installer, enter the command reboot at the prompt to reboot the MSE.
Upgrading the MSE to 8.0.110.0 from 7.x Release Without Data Migration
To upgrade from 7.x release to 8.0.11.0 without data migration, follow these steps.

Note![]() Use the db installer CISCO-MSE-K9-8-0-110-0-64.bit-db.tar to upgrade to 8.0.110.0 without migrating any data from the previous release.
Use the db installer CISCO-MSE-K9-8-0-110-0-64.bit-db.tar to upgrade to 8.0.110.0 without migrating any data from the previous release.
Step 1![]() Back up the existing database using the Prime Infrastructure. (We recommended this).
Back up the existing database using the Prime Infrastructure. (We recommended this).
All data existing on the system will be lost and a fresh blank database will be created.
Step 2![]() To download software to a mobility services engine, choose Services > Mobility Services Engine from the Prime Infrastructure user interface.
To download software to a mobility services engine, choose Services > Mobility Services Engine from the Prime Infrastructure user interface.
Step 3![]() Click the name of the mobility services engine to which you want to download software.
Click the name of the mobility services engine to which you want to download software.
Step 4![]() Choose System > Maintenance > Download Software from the left sidebar menu.
Choose System > Maintenance > Download Software from the left sidebar menu.
Step 5![]() To download software, do one of the following:
To download software, do one of the following:
- To download software listed in the Prime Infrastructure directory, select the Select from uploaded images to transfer into the Server radio button. Choose a binary image from the drop-down list. Prime Infrastructure downloads the binary image to the FTP server directory you specified during the Prime Infrastructure installation.
- To use download software available locally or over the network, select the Browse a new software image to transfer into the Server radio button, and click Choose File. Locate the file, and click Open.
Step 6![]() Click Download to send the software to the /opt/installers directory on the mobility services engine.
Click Download to send the software to the /opt/installers directory on the mobility services engine.
Step 7![]() Choose System > Maintenance > Download Software from the left sidebar menu.
Choose System > Maintenance > Download Software from the left sidebar menu.
Step 8![]() Select the file and click Download.
Select the file and click Download.
Step 9![]() Browse to your local directory where you have downloaded the file and send the software to the /opt/installers directory on the mobility services engine.
Browse to your local directory where you have downloaded the file and send the software to the /opt/installers directory on the mobility services engine.
Step 10![]() Untar the file: tar -xvf CISCO-MSE-K9-8-0-110-0-64.bit-db.tar. This gives you the following:
Untar the file: tar -xvf CISCO-MSE-K9-8-0-110-0-64.bit-db.tar. This gives you the following:
–![]() database_installer_part1of4.zip
database_installer_part1of4.zip
–![]() database_installer_part20f4.zip
database_installer_part20f4.zip
–![]() database_installer_part3of4.zip
database_installer_part3of4.zip
–![]() database_installer_part4of4.zip
database_installer_part4of4.zip
Step 11![]() To decompress (unzip) the file, execute: tar -xvf CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz.
To decompress (unzip) the file, execute: tar -xvf CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-0-64bit.bin.tar.gz.
Step 12![]() Enter the following command:
Enter the following command:
Step 13![]() Stop the MSE service using the following command:
Stop the MSE service using the following command:
Step 14![]() Uninstall the existing MSE software. Invoke the uninstall script from the /opt/mse/uninstall folder. Choose deletion of database when prompted.
Uninstall the existing MSE software. Invoke the uninstall script from the /opt/mse/uninstall folder. Choose deletion of database when prompted.
Step 15![]() Invoke the MSE installer CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-0-64bit.bin.
Invoke the MSE installer CISCO-MSE-L-K9-8-0-110-0-0-64bit.bin.
Restoring an Old Database to 8.0.110.0
To restore an old database, follow these steps:

Note![]() The regular Restore option on the Prime Infrastructure cannot be used to restore a backup from an older MSE releases such as 6.0, 7.0.105.0, or 7.0.110.0 onto 8.0.110.0.
The regular Restore option on the Prime Infrastructure cannot be used to restore a backup from an older MSE releases such as 6.0, 7.0.105.0, or 7.0.110.0 onto 8.0.110.0.
Step 1![]() Stop the MSE service: /etc/init.d/msed stop
Stop the MSE service: /etc/init.d/msed stop
Step 2![]() Uninstall the software and select to delete the database.
Uninstall the software and select to delete the database.
Step 3![]() To restore the backup data, you must first install the appropriate version of MSE software. Use the table below to determine the correct version of MSE to install.
To restore the backup data, you must first install the appropriate version of MSE software. Use the table below to determine the correct version of MSE to install.
Step 4![]() Once you have installed the software, restore the desired database backup onto this new MSE using the regular procedure from Prime Infrastructure.
Once you have installed the software, restore the desired database backup onto this new MSE using the regular procedure from Prime Infrastructure.
Step 5![]() To migrate data to 7.x.x.x, follow the steps in the “You can downgrade a device installed with CMX 10.x to MSE 8.x. Refer to the Software Recovery of MSE Using a USB or Flash Drive in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 guide given below. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/mse/8-0/MSE-CMX/8_0_MSE_CAS/8_0_MSE_CAS_chapter_010010.html” section.
To migrate data to 7.x.x.x, follow the steps in the “You can downgrade a device installed with CMX 10.x to MSE 8.x. Refer to the Software Recovery of MSE Using a USB or Flash Drive in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 guide given below. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/mse/8-0/MSE-CMX/8_0_MSE_CAS/8_0_MSE_CAS_chapter_010010.html” section.
Compressed Software Image
If you download the Mobility Services Engine image *.gz file using the Prime Infrastructure, the Mobility Services Engine automatically decompresses (unzips) it, and you can proceed with the installation as before.
If you manually download the compressed *.gz file using FTP, you must decompress the files before running the installer. These files are compressed under the LINUX operating system and must be decompressed using the tar zxvf command. For more information, see the Manually Downloading Software section in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0.
To make the bin file executable, use the chmod +x filename.bin command.
The MSE virtual appliance is distributed as:
- Open Virtualization Format (OVF) for VMware
- Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) for Microsoft Hyper-V
- Open Virtualization Format (OVF) for Citrix XenServer
For more information on deploying the MSE virtual appliance, see the Cisco MSE Virtual Appliance Configuration Guide, Release 8.0.
Updated Software Version Shown in the Prime Infrastructure After Polling
After a software update, the new Mobility Services Engine software version does not immediately appear in Mobility Services Engine queries on the Prime Infrastructure. Up to 5 minutes is required for the new version to appear. Prime Infrastructure, by default, queries the Mobility Services Engine for status every 5 minutes.
Licensing Information for MSE
The Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) provides a wide variety of location-based services. To enable these services, the following are required:
–![]() Physical Appliance—An activation license is not required.
Physical Appliance—An activation license is not required.
–![]() Virtual Appliance—Virtual Appliance instance requires a MSE Virtual Appliance Activation license (L-MSE-7.0-K9). It is not sufficient to simply have a service/feature license on an MSE Virtual Appliance.
Virtual Appliance—Virtual Appliance instance requires a MSE Virtual Appliance Activation license (L-MSE-7.0-K9). It is not sufficient to simply have a service/feature license on an MSE Virtual Appliance.
There are three types of MSE licenses available:
Client and wIPS licenses are installed from the Prime Infrastructure UI (Administration > License Center). See, Chapter 2: “Adding and Deleting Mobility Services Engines and Licenses” in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0, Cisco Wireless Intrusion Prevention System, Release 8.0, and Cisco Location Analytics Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 respectively.
For complete details on ordering and downloading licenses, see the Cisco Mobility Services Engine Licensing and Ordering Guide at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/wireless/ps9733/ps9742/data_sheet_c07-473865.html
Base Location license
The Base Location Services License is equivalent to the Location Services license in software release 7.4, which itself replaced the Context Aware Services (CAS) license in the software versions prior to release 7.4. This license is used for device endpoint tracking, enabling basic calculation of the x,y coordinates of a tracked device. The license count is based on the number of APs supported since release 7.4.
The part number format of this license is L-LS-100AP. Here 'LS' refers to Location Services and '100AP' refers to 100 AP count.
CMX License
The CMX license, called Advanced Location license in release 7.4, supports new features, such as:
The CMX license includes the Base Location license features used for device tracking and the new additional features of CMX.
The part number format of this license is L-AD-LS-100AP. Here 'AD-LS' refers to Advanced Location services license and '100AP' gives the AP count supported.
wIPS License
There are 3 deployment options:
- Enhanced Local mode: Number of wIPS licenses required equals the number of access points in local mode (data serving) deployed in the network.
- Monitor mode: Number of wIPS licenses required equals the number of access points configured in the full-time monitor mode.
- Monitor module: Number of wIPS licenses required equals the number of wireless security and spectrum intelligence modules deployed in the network.

Note![]() AP with a third module needs a monitor mode wips license even if AP is running in local mode.
AP with a third module needs a monitor mode wips license even if AP is running in local mode.
- Provides advanced spectrum capability and the ability to detect presence and track rogue device, interferers, Wi-Fi clients and RFID tags. Cisco Base Location also enables third-party solutions that use the MSE API.
Licensing is based on the number of access points in the environment. The licenses are additive.

Note![]() Connected Mobile Experiences licenses will be End of Life with standard 6 months of End of Sales and until then both Connected Mobile Experiences and LS licenses will co-exist.
Connected Mobile Experiences licenses will be End of Life with standard 6 months of End of Sales and until then both Connected Mobile Experiences and LS licenses will co-exist.
MSE License Product Numbers and SKUs
Ordering Support for Physical and Virtual Appliance
The MSE Virtual appliance activation license is required for every instance of an MSE Virtual Appliance. No separate license is required for high availability. To enable high availability, you need to deploy a primary Cisco MSE appliance with Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences and wIPS licenses, and a secondary Cisco MSE appliance without any Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences or wIPS license
Table 8 lists the ordering support for physical and virtual appliance.
CMX Licenses (Previously known as Advanced Location Services)
The CMX licenses include the Base Location Service licenses. There is no need to purchase a separate Base Location Service license when purchasing a CMX license.
Cisco MSE Virtual Appliance Product Specifications
What’s New in This Release
This section provides a brief description of what is new in Release 8.0.110.0. For more information about instruction on how to configure these features, see the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Cisco Wireless Intrusion Prevention System Configuration Guide, Cisco CMX Analytics Service Configuration Guide, Cisco CMX Connect and Engage Configuration Guide, and Cisco MSE Virtual Appliance Configuration Guide at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
HA Certificate Install Script
A new script is added to install signed certificates for HA connection between primary and secondary in 8.0.110.0 Release. See Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 for more information.
iOS 8 Dynamic MAC Filtering
Apple devices running iOS8 (or higher) under certain conditions have the ability to probe the network utilizing randomized MAC addresses. As a result, a single device may be counted several times by the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences (CMX) solution. The MSE 8.0.110.0 has the ability to filter out the randomized MAC addresses and track or count only those devices with valid MAC address for use with the Cisco CMX services.
To enable the iOS 8 randomized MAC filtering, follow these steps:
1.![]() Launch the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) user interface by typing https://mseip/mseui/ in the Web Browser.
Launch the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) user interface by typing https://mseip/mseui/ in the Web Browser.
2.![]() Click Configuration icon on the top right of the home page.
Click Configuration icon on the top right of the home page.
3.![]() Choose Context Aware Service > Filtering to display the configuration options.
Choose Context Aware Service > Filtering to display the configuration options.
4.![]() Under the MAC Filtering Params group box, enable the following filtering parameters:
Under the MAC Filtering Params group box, enable the following filtering parameters:
1. Enable Location MAC Filtering
2. Filter Locally Administered MAC Addresses
Figure 1 Editing MAC Filtering Params

From Cisco MSE CLI, you need to stop and then start all Cisco MSE services using these commands:
Important Notes
This section describes the operational notes and navigation changes for Connected Mobile Experiences, wIPS, and the Mobility Services Engine for Release 6.0.103.0 and later releases.
Features and operational notes are summarized separately for the Mobility Services Engine, Connected Mobile Experiences, and wIPS.
Operational Notes for Mobility Services Engine
This section lists the operational notes for the Mobility Services Engine and contains the following topics:
- Resolution to NMSP/SHA2 keyhash Mismatch Issue
- DNS Server
- How and When to Use the db.tar installer
- Reboot MSE After Fresh Installation or Upgrade
- Automatic Installation Script for Initial Setup
- Controller and Associated Mobility Services Engine Must be Mapped to the Same NTP and Prime Infrastructure Server
- Mandatory Default Root Password Change
- Configuring the Prime Infrastructure Communication Username and Password Using MSE setup.sh
- Configuration Changes for Greater Location Accuracy
- Wireless Security Module with 3600 AP
- AeroScout Engine Module Changes
- Ports to be Opened for High Availability Between MSEs
- Synchronizing Floor Maps in Location Service
- MSE Location REST APIs
Resolution to NMSP/SHA2 keyhash Mismatch Issue
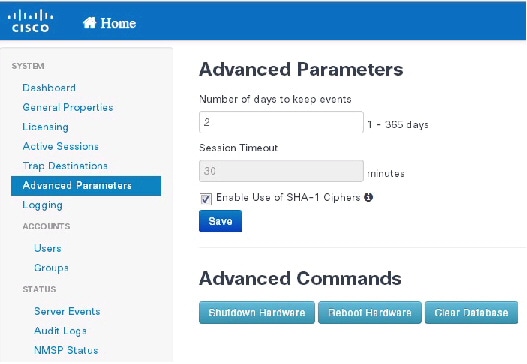
MSE 8.0 by default supports SHA-2 keyhash algorithm for peer authentication with Cisco WLC 8.0 during the SSL handshake. Prime Infrastructure 1.4.2 and 2.1 supports only SHA-1 AP (or MSE) Authorization template when synchronizing Cisco WLC with the MSE. This causes keyhash mismatch issue because the PI and MSE uses different keyhash algorithm on Cisco WLC 8.0. An option is added to the Advanced Parameters page in the MSE user interface (UI) to allow the user to force MSE 8.0 to use SHA-1 keyhash algorithm.
Follow these instructions to configure SHA-1 Cipher:
1.![]() Launch the MSE admin UI by typing https://mseip/mseui/app in the web browser.
Launch the MSE admin UI by typing https://mseip/mseui/app in the web browser.
3.![]() Choose System > Advanced Parameters from the left sidebar menu.
Choose System > Advanced Parameters from the left sidebar menu.
4.![]() Select the Enable Use of SHA-1 Ciphers check box (see Figure 2).
Select the Enable Use of SHA-1 Ciphers check box (see Figure 2).
6.![]() Un-synchronize Cisco WLC from MSE, and then re-synchronize WLC with MSE from PI.
Un-synchronize Cisco WLC from MSE, and then re-synchronize WLC with MSE from PI.
7.![]() The NMSP status should go into active state.
The NMSP status should go into active state.

Note![]() If the FIPS mode (also known as Root Access Control) is enabled on the MSE, then this option will not be available to the users as FIPS mode requires all operations in SHS-2.
If the FIPS mode (also known as Root Access Control) is enabled on the MSE, then this option will not be available to the users as FIPS mode requires all operations in SHS-2.
How and When to Use the db.tar installer

Note![]() You can use the db.tar installer file when you want to install the MSE newly along with the fresh DB installation. The recommended method is to follow the usual Upgrade process unless you want a fresh installation.
You can use the db.tar installer file when you want to install the MSE newly along with the fresh DB installation. The recommended method is to follow the usual Upgrade process unless you want a fresh installation.
Reboot MSE After Fresh Installation or Upgrade
After a new installation or upgrade of the MSE software, you must reboot the MSE using the “reboot” command.
Automatic Installation Script for Initial Setup
An automatic setup wizard is available to help you initially set up the Mobility Services Engine.
An example of the complete automatic setup script is provided in the Cisco Mobility Services Engine Getting Started Guide.
You can find these documents at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/prod_installation_guides_list.html
Controller and Associated Mobility Services Engine Must be Mapped to the Same NTP and Prime Infrastructure Server
Communication between the Mobility Services Engine, the Prime Infrastructure, and the controller are in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Configuring the Network Time Protocol (NTP) on each system provides devices with the UTC time. An NTP server is required to automatically synchronize time between the controller, Prime Infrastructure, and the Mobility Services Engine.
The Mobility Services Engine and its associated controllers must be mapped to the same NTP server and the same Prime Infrastructure server.
Local time zones can be configured on a Mobility Services Engine to assist network operations center personnel in locating events within logs.

Note![]() You can configure NTP server settings while running the automatic installation script. See the Cisco Mobility Services Engine Getting Started Guide Started Guide for details on the automatic installation script at the following URL:
You can configure NTP server settings while running the automatic installation script. See the Cisco Mobility Services Engine Getting Started Guide Started Guide for details on the automatic installation script at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/prod_installation_guides_list.html
Mandatory Default Root Password Change
You must change the default root password of the Mobility Services Engine while running the automatic installation script to ensure optimum network security.
You can also change the password using the Linux passwd command.

Note![]() For the initial login, even if you choose Skip (S), you will be prompted to enter the password. This is because it is mandatory to change the root password at the initial login.
For the initial login, even if you choose Skip (S), you will be prompted to enter the password. This is because it is mandatory to change the root password at the initial login.
Configuring the Prime Infrastructure Communication Username and Password Using MSE setup.sh
You can configure the Prime Infrastructure Communication username and password using the MSE setup.sh script file.
Scenarios which you might encounter while configuring the Prime Infrastructure username and password are as follows:
- If you configure a new Prime Infrastructure username and password, the password provided is applicable for the new Prime Infrastructure username created.
- If you only configure the Prime Infrastructure username without configuring the Prime Infrastructure password, then the default password admin is applied to the configured username.
- If you only configure the Prime Infrastructure password without configuring the Prime Infrastructure username, then the password for the admin user is changed.
- If you configure an existing username for the Prime Infrastructure username and also configure the password, then the password for that existing user is changed.

Note![]() These users are API users, and they do not have corresponding OS users on the MSE appliance.
These users are API users, and they do not have corresponding OS users on the MSE appliance.
Configuration Changes for Greater Location Accuracy
In some RF environments, where location accuracy is around 60 to 70% or where incorrect client or tag floor location map placements occur, you might need to modify the moment RSSI thresholds in the Context Aware Service > Advanced > Location Parameters page on the Prime Infrastructure.
The following RSSI parameters might require modification:
- locp-individual-rssi-change-threshold
- locp-aggregated-rssi-change-threshold
- locp-many-new-rssi-threshold-in-percent
- locp-many-missing-rssi-threshold-in-percent

Wireless Security Module with 3600 AP
If you are attempting to deploy Wireless Security Module (WSM) with 3600 APs, then APs should be placed in monitor mode with submode wIPS and advanced wIPS engine enabled on the Prime Infrastructure.
AeroScout Engine Module Changes
Starting Release 7.5, the AeroScout engine module is removed from both the Connected Mobile Experiences setup and location code. During installation, if you are upgrading from Release 7.2 and later to Release 7.5, then you will be prompted to remove the AeroScout engine. If you agree to remove, the it removes the AeroScout engine and by default, the Cisco Tag Engine is started as part of Connected Mobile Experiences. If you do not agree to remove the AeroScout engine, then installation will exit.
Ports to be Opened for High Availability Between MSEs
The following is the list of ports to be opened for High Availability between MSEs:
Synchronizing Floor Maps in Location Service
While synchronizing floor maps in location service, we recommend that you synchronize floor maps in batches of 1000 access points at a time.
MSE Location REST APIs
The MSE Location REST APIs always show the last known state of clients. When it shows the last known state as Probing, it does not mean that the client is probing currently. This is the same with other fields such as x, y, floorid. Networkstatus is the only field that shows whether the client is active or inactive, and all other fields show the last known values.
Operational Notes for Context Aware Service
This section lists the operational notes for a Mobility Services Engine and contains the following topics:
- Synchronization Required When Upgrading to Release 8.0.110.0 or Importing CAD Floor Images
- Floor Change or Minimum Distance Required for Location Transitions to Post to the History Log
- Non-Cisco Compatible Extensions Tags Not Supported
- Cisco Compatible Extensions Version 1 Tags Required at a Minimum
- Calibration Models and Data
- Advanced Location Parameters
- Location History Time stamps Match Browser Location
- Tablets and Smartphone with Limited Probe Requests Might Affect Location
Synchronization Required When Upgrading to Release 8.0.110.0 or Importing CAD Floor Images
When upgrading to Release 8.0.110.0 from Release 7.x, you must synchronize after the software upgrade and also when CAD-generated floor images are imported into the Prime Infrastructure.
Floor Change or Minimum Distance Required for Location Transitions to Post to the History Log
When history logging is enabled for any or all elements (client stations, asset tags, rogue clients, and access points), a location transition for an element is posted only if it changes floors or the new location of the element is at least 30 feet (10 meters) from its original location.

Note The other conditions for history logging are as follows:
- Clients: Association, authentication, re-association, re-authentication, or disassociation.
- Tags: Tag Emergency button.
- Interferers: Interferer severity change, cluster center change, or merge.
See Services > Mobility Services > Device Name > Context Aware Service > Administration > History Parameters.
Logs can be viewed at Services > Mobility Services > Device Name > Systems > Log.
Non-Cisco Compatible Extensions Tags Not Supported
The Mobility Services Engine does not support non-Cisco CX Wi-Fi tags. Additionally, these non-compliant tags are not used in location calculations or shown on the Prime Infrastructure maps.
Cisco Compatible Extensions Version 1 Tags Required at a Minimum
Only Cisco CX Version 1 (or later) tags are used in location calculations and mapped in the Prime Infrastructure.
Monitoring Information Varies for Clients and Tags
In the Monitor > Clients page (when Location Debug is enabled), you can view information on the last heard access point and its corresponding Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) reading.
Calibration Models and Data
Calibration models always applies to Wireless clients, Interferers, Rogue APs, and Rogue Clients.
See Chapter 7, “Context-Aware Planning and Verification” in the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0 for more details on client calibration.
Advanced Location Parameters
Settings for advanced location parameters related to RSSI, chokepoint usage, location smoothing, and assignment of outside walls on floors, are not applicable to tags.
See the “Editing Advanced Location Parameters” section in Chapter 7 of the Cisco Connected Mobile Experiences Configuration Guide, Release 8.0.
See Services > Mobility Services > Device Name > Context Aware Service > Advanced > Location Parameters.
Location History Time stamps Match Browser Location
The Prime Infrastructure time stamp is based on the browser location and not on the Mobility Services Engine settings. Changing the time zone on the Prime Infrastructure or on the Mobility Services Engine does not change the time stamp for the location history.
Tablets and Smartphone with Limited Probe Requests Might Affect Location
Many tablets, smartphones, and other Wi-Fi devices with power save mode do not continuously send out probe requests after an initial association to the CUWN. Therefore, calculating the location accuracy of such devices using RSSI readings is not always optimal.
Repeat Use of FloorID returns +1 After Every Hour
In the relevant CAS API, the use of the parameter FLOORID is not guaranteed to return the same value on consecutive calls. It may get changed by such activities as resynchronizing the MSE. Instead, the parameter FLOORAESUID should be used. The API call getStationHistoryListByArgs now can use both parameters in MSE Release 8.0.
wIPS Profile
wIPS profile cannot be pushed to Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) Version 7.5 or prior using the Prime Infrastructure 1.4.x or 2.x with MSE 7.6 Release.
Operational Notes for CMX Analytics
This section lists the operational notes for CMX Analytics service and contains the following topics:
Peer’s Certificate Invalid Signature Error with Firefox Browser
While using the newer version of Firefox browser to connect to the MSE user interface or CMX Analytics user interface, an error message appears saying “Peer’s certificate has an invalid signature”. For more information on how to fix this, see the https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/questions/776144.
To fix this, follow these steps:
- Open the Firefox browser.
- Enter about:config in the address/URL.
- Enter browser.xul in the Filter box.
- Check if browser.xul.error_pages.expert_bad_cert property exists with a value of false.
- Right-click on browser.xul.error_pages.expert_bad_cert and select Toggle. The value will change to true.
- Exit from Firefox.
- Restart the browser and try the CMX Analytics user interface. You are now asked to add the exception.
WebGL Compatibility
The CMX Analytics in Release 8.0 provides ability to view the analytic results in both 2D (Open Street Maps) and 3D (WebGL) environments. This provides improved understanding of results on multiple floor paths or when dwell times are calculated throughout a multi-storey building. The 3D environment presents the same information as the 2D environment.
WebGL is an advanced feature that provides graphic capabilities. All browsers do not support WebGL on a particular hardware. Verify your browser compatibility in the Get WebGL website. If your browser supports WebGL, then you must see a spinning cube.
If your browser does not support WebGL, you must do the following:
- Update your latest drivers for video card.
- For Google Chrome, follow the instructions given for WebGL and 3D Graphics in the Google Chrome support website.
- For Firefox, follow these steps to enable WebGL:
–![]() Download the latest build of Firefox browser and launch Firefox on your computer.
Download the latest build of Firefox browser and launch Firefox on your computer.
–![]() In the browser address line, enter about:config
In the browser address line, enter about:config
–![]() In the Search text box, enter webgl to filter the settings
In the Search text box, enter webgl to filter the settings
–![]() Double click webgl.enabled_for_all_sites
Double click webgl.enabled_for_all_sites
–![]() Set the webgl.enabled_for_all_sites=true
Set the webgl.enabled_for_all_sites=true
–![]() Choose Safari > Preferences.
Choose Safari > Preferences.
–![]() Select the Show Develop menu in menu bar check box.
Select the Show Develop menu in menu bar check box.
–![]() Choose Enable WebGL from the Develop menu.
Choose Enable WebGL from the Develop menu.

Note![]() If your system does not support 3D, then the analytic results are displayed only in 2D Open Street Maps view.
If your system does not support 3D, then the analytic results are displayed only in 2D Open Street Maps view.
Jboss Issue
Sometimes CMX Analytics service does not start up because of a stray Jboss process that runs as a root user. If Analytics engine does not start and if you notice a stray Jboss process with root permissions running, then you must to do the following:
Operational Notes for Facebook Wi-Fi
When you try to pair a location with the Facebook page, it may fail with no notification in Connect and Engage user interface. One of the reasons could be due to Facebook site outage. You can check Facebook API health at the following URL: http://developers.facebook.com/status/
Operational Notes for CMX Connect and Engage
While upgrading the Prime Infrastructure server, the map IDs and the information also gets updated. This results in the new identifiers for maps. The new identifiers are not automatically synchronized with the CMX Connect and Engage. This causes the location updates to use the new identifiers but the CMX Connect and Engage will not be aware of the new identifiers and cause the location updates to get ignored. To resolve this issue, you must update maps in the CMX Connect and Engage user interface. To update maps, login to CMX Connect and Engage user interface and choose Maps from left sidebar menu and click Update Maps from PI.
Operational Notes for Mobile SDK
Two different venues with the same MSEs receiving location updates result in the device location bouncing from one venue to another venue. The Mobile Application Server (MAS) receives updates and changes the location to the most recent update received. The client location then changes from the most recent location update which can be from either venue.
Enabling Root Access Control (RAC) in HA Mode
To enable Root Access Control (RAC) in HA mode, you need to enable RAC on both primary and secondary MSEs. The RAC configuration is not synchronized across the primary and secondary servers and hence you need to enable it on both servers. This will enable the RAC configurations to work on the active server properly in case of a failover or failback.
Caveats
Cisco Bug Search Tool
The Bug Search Tool (BST), which is the online successor to Bug Toolkit, is designed to improve the effectiveness in network risk management and device troubleshooting. The BST allows partners and customers to search for software bugs based on product, release, and keyword, and aggregates key data such as bug details, product, and version. The tool has a provision to filter bugs based on credentials to provide external and internal bug views for the search input.
To view the details of a caveat listed in this document:
1.![]() Access the BST (use your Cisco user ID and password) at https://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch/.
Access the BST (use your Cisco user ID and password) at https://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch/.
Resolved Caveats
Use the BST to view the details of a caveat listed in this section. For more information about the BST, see the “Cisco Bug Search Tool” section.
If You Need More Information
If you need information about a specific caveat that does not appear in these release notes, you can use the Cisco Bug Toolkit to find caveats of any severity. Click this URL to browse to the Bug Toolkit:
http://tools.cisco.com/Support/BugToolKit/
(If you request a defect that cannot be displayed, the defect number might not exist, the defect might not yet have a customer-visible description, or the defect might be marked Cisco Confidential.)
Troubleshooting
For the most up-to-date, detailed troubleshooting information, see the Cisco TAC website at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/index.html
Click Troubleshooting, choose your product, and then click the Troubleshoot and Alerts heading on the product page to find information on the problem you are experiencing and other service advisories.
Related Documentation
The following documents are related to the Mobility Services Engine:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9817/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
http://www-author.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/mobility-services-engine/products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html
http://www-author.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/wireless/mobility-services-engine/products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9742/prod_installation_guides_list.html
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the “Related Documentation” section. Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback