Hyper-V 2016 および Citrix XenDesktop を使用した Cisco HyperFlex M5 オールフラッシュ ハイパーコンバージド システム
Hyper-V 2016 および Citrix XenDesktop を使用した Cisco HyperFlex M5 オールフラッシュ ハイパーコンバージド システム
Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 を使用した仮想デスクトップ インフラストラクチャとしての Cisco HyperFlex の設計と導入
最終更新日:2018 年 8 月 21 日

Cisco Validated Design プログラムについて
Cisco Validated Design (CVD) プログラムは、お客様による信頼性の高い、確実かつ速やかな展開を容易にするために、デザイン、テスト、および文書化されたシステムおよびソリューションで構成されています。詳細に
ついては、以下を参照してください。
http://www.cisco.com/go/designzone
このマニュアルに記載されているデザイン、仕様、表現、情報、および推奨事項(総称して「デザイン」)は、
本マニュアル作成時点における、障害も含めた「現状のまま」として提供されます。シスコ及びそのサプライヤ
は、商品性の保証、特定目的への準拠の保証、及び権利を侵害しないことに関する保証、あるいは取引過程、
使用、取引慣行によって発生する保証をはじめとする、一切の保証責任を負わないものとします。いかなる場合においても、シスコ及びそのサプライヤは、このデザインを使用すること、または使用できないことによって発生する利益の損失やデータの損傷をはじめとする、間接的、派生的、偶発的、あるいは特殊な損害について、あらゆる可能性がシスコまたはそのサプライヤに知らされていたとしても、それらに対する責任を一切負わないものとします。
デザインは予告なしに変更されることがあります。このマニュアルに記載されているデザインの使用は、すべてユーザ側の責任になります。これらのデザインは、シスコ、シスコのサプライヤ、またはシスコのパートナーからの技術的な助言や他の専門的な助言に相当するものではありません。ユーザは、デザインを実装する前に技術
アドバイザに相談してください。シスコによるテストの対象外となった要因によって、結果が異なることがあります。
CCDE、CCENT、Cisco Eos、Cisco Lumin、Cisco Nexus、Cisco StadiumVision、Cisco TelePresence、Cisco WebEx、Cisco ロゴ、DCE、Welcome to the Human Network は商標です。Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn、および Cisco Store はサービス マークです。Access Registrar、Aironet、AsyncOS、Bringing the Meeting To You、Catalyst、CCDA、CCDP、CCIE、CCIP、CCNA、CCNP、CCSP、CCVP、Cisco、Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert ロゴ、Cisco IOS、Cisco Press、Cisco Systems、Cisco Systems Capital、Cisco Systems ロゴ、Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS)、Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers、Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers、Cisco UCS S-Series Storage Servers、Cisco UCS Manager、Cisco UCS Management Software、Cisco Unified Fabric、Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure、Cisco Nexus 9000 Series、Cisco Nexus 7000 Series。Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager、Cisco NX-OS Software、Cisco MDS Series、Cisco Unity、Collaboration Without Limitation、EtherFast、EtherSwitch、Event Center、Fast Step、Follow Me Browsing、FormShare、GigaDrive、HomeLink、Internet Quotient、IOS、iPhone、iQuick Study、LightStream、Linksys、MediaTone、MeetingPlace、MeetingPlace Chime Sound、MGX、Networkers、Networking Academy、Network Registrar、PCNow、PIX、PowerPanels、ProConnect、ScriptShare、SenderBase、SMARTnet、Spectrum Expert、StackWise、The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient、TransPath、WebEx、および WebEx ロゴは Cisco Systems, Inc. またはその関連会社の米国および一部の国における登録商標です。
本書または Web サイトにおけるその他の商標は、第三者の知的財産です。パートナーという言葉が使用されて
いても、シスコとその他の会社とのパートナーシップを示すものではありません (0809R)。
© 2018 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
目次
Cisco Unified Computing System
Cisco Unified Computing System のコンポーネント
Cisco VIC1340 コンバージド ネットワーク アダプタ
Cisco UCS 2304XP ファブリック エクステンダ
Cisco HyperFlex コンバージド データ プラットフォーム ソフトウェア
Cisco HyperFlex Connect HTML5 対応の管理 Web ページ
Citrix XenApp™ と XenDesktop™ 7.16
マシンの更新または再起動のスケジュールの前に、複数の通知を送信
ハイパーバイザのテンプレートからの VM のプロビジョニング用 API のサポート
Cisco Unified Computing System の Citrix XenDesktop のアーキテクチャと設計、および Cisco HyperFlex のストレージ設計の基本
プロジェクト計画とソリューション サイジングに関する確認事項の例
Deployment Hardware and Software
Cisco Unified Computing System Configuration
Deploy and Configure HyperFlex Data Platform
Deploying HX Data Platform Installer on Hyper-V Infrastructure
Deploy the HX Data Platform Installer OVA with a Static IP Address
Cisco UCS Manager Configuration using HX Data Platform Installer
Microsoft Windows OS and Hyper-V Installation
Configure vMedia and Boot Policies through Cisco UCS Manager
Deploying HX Data Platform Installer and Cluster Configuration
Post HyperFlex Cluster Installation for Hyper-V 2016
Build the Virtual Machines and Environment for Workload Testing
Software Infrastructure Configuration
Install and Configure XenDesktop Delivery Controller, Citrix Licensing, and StoreFront
Configure the XenDesktop Site Administrators
Configure Additional XenDesktop Controller
Add the Second Delivery Controller to the XenDesktop Site
Install and Configure StoreFront
Additional StoreFront Configuration
Install XenDesktop Virtual Desktop Agents
Persistent Static Provisioned with MCS
Citrix XenDesktop Policies and Profile Management
Configure Citrix XenDesktop Policies
Configuring User Profile Management
Testing Methodology and Success Criteria
Recommended Maximum Workload and Configuration Guidelines
Four Node Cisco HXAF220c-M5S Rack Server and HyperFlex All-Flash Cluster
Appendix A – Cisco Nexus 93108YC Switch Configuration
日本語は部分翻訳のみ、全文は英語版を参照下さい。
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/unified_computing/ucs/UCS_CVDs/hx301a_vdi_hyperv_xd716.html
エグゼクティブ サマリー
市場の変化に即応するためには、瞬時に対応できる開発プロセスを支えるシステムが欠かせません。Cisco HypFerlex™ システムでは、ハイパーコンバージェンスの持てる力を最大限に引き出し、IT をワークロード
ニーズに適応させることができます。ソフトウェア デファインド インフラストラクチャ アプローチを採用したこのシステムでは、Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ ノードによるソフトウェア デファインド コンピューティング、強力な Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform を利用したソフトウェア デファインド ストレージ、そして Cisco® Application Centric Infrastructure (Cisco ACI™) と統合できる Cisco UCS ファブリックによるソフトウェア
デファインド ネットワークが 1 つのシステムに統合されています。
この一元化された技術により、サーバ、ストレージ、ネットワークが統合された適応性の高いクラスタとして実現します。この中では、リソースの迅速な導入、適合、拡大・縮小、管理が可能で、アプリケーションとビジネスを効率化できます。
このドキュメントは、4 ノード(Cisco HyperFlex HXAF220C-M5SX サーバ 4 台)の Cisco HyperFlex
システムで、最大 450 ユーザの混合ワークロードを扱う場合のアーキテクチャ リファレンスと設計ガイドです。Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 仮想デスクトップで、Office 2016 マシンの作成サービスが動作する Microsoft Windows 10 を実行する場合の導入ガイダンスとパフォーマンス データを提供します。このソリューションでは、あらかじめ統合され、ベスト プラクティスに則ったデータセンター アーキテクチャが採用されており、Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS)、Cisco Nexus® 9000 ファミリ スイッチ、Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform
ソフトウェア バージョン 3.0.1a での構築が対象となっています。
ソリューションのコアとなる部分は、Cisco HyperFlex HXAF220C-M5SX ハイパーコンバージド ノード上で 100 % 仮想化しており、オンボード M.2 SATA SSD ドライブを介して起動される Microsoft Hyper-V 2016
ハイパーバイザおよび Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform ストレージ コントローラ VM を実行します。仮想
デスクトップは XenDesktop 7.16 で構成されており、従来の永続/非永続仮想デスクトップ (Windows 7/8/10)、ホスト アプリケーションおよびリモート デスクトップ サービス (RDS) (Microsoft Server 2008 R2)、Windows Server 2012 R2 または Windows Server 2016 ベースのデスクトップが含まれています。これまでにない拡張性とシンプルな管理が実現されており、4 ノードの Cisco HyperFlex クラスタで、Citrix XenDesktop Provisioning Services または Machine Creation Services による Windows 10 デスクトップ (450)、完全クローン
デスクトップ (450)、XenApp サーバ ベース型デスクトップ (600) をプロビジョニングできます。
本ドキュメントを利用することで、このソリューションを導入するお客様に対して、推奨されるベスト
プラクティスとサイジングに関するガイドラインも提供します。
このソリューションでは、450 の仮想デスクトップ マシンを 5 分以内で起動させ、ユーザが就業開始するような、HyperFlex 上の仮想ワークスペースを利用開始するケースでも、大きな遅延が発生しないようにします。
これまでの HyperFlex に関する Cisco Validated Design (CVD) での分析の結果、Cisco UCS B200 M5、Cisco UCS C220 M5、Cisco UCS C240 M5 を使用した HyperFlex ハイパーコンバージド ハイブリッド構成ノード 8 台のクラスタ サイズの制限を上回るリニア スケーラビリティが確認されています。Cisco HXAF220 M5 または Cisco HXAF240 M5 ノードで HX Data Platform 3.0.1 を実行する新しい HyperFlex オール フラッシュ
システムでは、N+1 のサーバ耐障害性を備えた上で、クラスタあたりのナレッジ ワーカー ユーザ数を最大 1,000 に拡張できます。
このソリューションでは、ハードウェア アクセラレーション グラフィックのワークロードもサポートしています。Cisco HyperFlex HXAF240c M5 ノード、および Cisco UCS C240 M5 コンピューティング サーバでは、
それぞれ最大 2 枚の NVIDIA M10 カードまたは P40 カードをサポートできます。Cisco UCS B200 M5 サーバでは、高密度、高パフォーマンスのグラフィック ワークロード用に、最大 2 枚の NVIDIA P6 カードをサポートします。この機能と Citrix XenDesktop との統合方法の詳細については、NVIDIA GPU およびソフトウェアを使用した第 5 世代サーバに関する『Cisco Graphics White Paper』[英語] を参照してください。
本ソリューションにより、仮想デスクトップを使用するエンド ユーザに対して非常に優れた操作性が提供されます。Login VSI 4.1.25 を使用して Knowledge Worker ワークロードをベンチマーク モードで評価したところ、テストしたすべての提供方法で、エンドユーザの反応時間を示す平均指数が 1 秒を下回りました。これは業界でも最も高い性能にあることを示しています。
はじめに
データセンター設計の分野における最近の傾向としては、ハイパーコンバージド インフラストラクチャを小規模ながら初めて、細かく拡張できることが求められつつあります。事前検証済みの IT プラットフォームに合わせて仮想化をもちいることで、あらゆる規模のお客様がこの新しい技術を使用した「ジャストインタイムのインフラ
提供」を模索しています。Cisco HyperFlex ハイパー コンバージド ソリューションでは、導入時間を短縮できるため、俊敏性の向上とコストの削減が可能です。最高品質のストレージ、サーバ、ネットワーク コンポーネントを使用して、デスクトップ仮想化のワークロード処理基盤として動作し、迅速かつ着実な導入とスケール アウトを可能とする効率的なアーキテクチャ設計が実現します。
対象読者
対象読者としては、セールス エンジニア、フィールド コンサルタント、プロフェッショナル サービス、IT
マネージャ、パートナー エンジニアリング、およびインフラストラクチャにより IT の効率向上と革新を
実現したいお客様が挙げられますが、それらに限定されるわけではありません。
このドキュメントの使用目的
このドキュメントは、Cisco HyperFlex オールフラッシュ システムの Cisco Validated Design (CVD) として、段階的な設計、構成、実装について説明します。この Cisco HyperFlex オールフラッシュ システムでは、Cisco UCS 6300 シリーズ ファブリック インターコネクトおよび Cisco Nexus 9300 シリーズ スイッチを使用した Citrix XenDesktop/XenApp のワークロードが 4 つ別個に実行されます。
最新情報
Cisco HyperFlex オールフラッシュ システムの Cisco Validated Design で、第 5 世代 UCS をベースにした HyperFlex システムに搭載可能なインテル Xeon スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサーをベースとした仮想
デスクトップ インフラストラクチャの検証結果をご案内するのは、今回が初めてとなります。次の内容が
含まれます。
· Cisco Nexus 9000 と Cisco HyperFlex を使用する場合の Cisco UCS 3.2(3)および Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform 3.0.1a サポートの検証。
· Microsoft Hyper-V 2016
Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Persistent デスクトップと Citrix Machine Creation Services
Cisco HX Data Platform を正常にインストールするには、特定のソフトウェアおよびハードウェアの
バージョン、ネットワーク設定が必要です。すべての要件については、Cisco HyperFlex Systems Getting Started Guide [英語] を参照してください。
ハードウェアとソフトウェアのすべての依存関係の一覧については、Cisco UCS Manager の Web ページを参照してください。Hardware and Software Interoperability for Cisco HyperFlex HX-Series [英語]
データセンターの市場分野は、業界標準のシステム上で動作する仮想化の進んだプライベート、パブリック、
ハイブリッド クラウド コンピューティング モデルに移行しつつあります。こうした環境では、管理が容易で
拡張性に優れ、繰り返し使用可能な統一的な設計ポイントが必要になります。
このような要因から、事前設計されたコンピューティング、ネットワーキング、ストレージの構成要素に対する
ニーズが生じ、初期設計のコスト削減、管理のシンプル化、水平スケーラビリティ、高い使用率の実現への最適化が求められています。
使用例として以下が挙げられます。
· 大企業のデータセンター(障害発生時の対象範囲は小さい)
· サービス プロバイダーのデータセンター(障害発生時の対象範囲は小さい)
· 一般企業・期間の汎用的データセンター
· 地方オフィス/分散環境
· 小中規模における独立、個別展開
この Cisco Validated Design では、Microsoft Server 2016 をベースとした Citrix XenDesktop Microsoft Windows 10 仮想デスクトップと Citrix XenApp サーバ デスクトップ セッション両方の統合基盤として機能
するハードウェアとソフトウェアの定義・設定情報を含んでいます。単一システムとして、Cisco HyperFlex
ハードウェアおよびデータ プラットフォーム ソフトウェア、Cisco Nexus® スイッチ、Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS®)、Citrix XenDesktop、Microsoft Hyper-V を対象とした複合ワークロード ソリューションが含まれます。設置面積は、業界で標準的な 42U ラックシステムの 8 ラック ユニット分に相当し、
ネットワーキング コンポーネント、コンピューティング コンポーネント、ストレージ コンポーネントなどに適した設計となっています。Cisco Nexus スイッチおよび Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクトには充分なポート密度があり、ネットワーク コンポーネントに複数の HyperFlex クラスタを搭載し、単一の Cisco UCS ドメインとすることが可能です。
Cisco Validated Design アーキテクチャの主な利点は、お客様の要件に合わせて環境をカスタマイズできることです。要件や要求の変化に合わせて簡単に拡張でき、スケール アップ(Cisco Validated Design ユニットに
リソースを追加)とスケール アウト(Cisco Validated Design ユニット自体を追加)の両方が可能です。
このドキュメントで詳しく説明するリファレンス アーキテクチャでは、ハイパーコンバージド デスクトップ
仮想化ソリューションの特長として復元力、費用面でのメリット、導入の容易さが強調されています。単一の
インターフェイスで複数のプロトコルを利用することができ、まさに一度接続すれば事足りるアーキテクチャ
であることから、顧客の選択と投資保護が実現します。
シスコと Microsoft 社のテクノロジーを結集することにより、効率性と堅牢性が高く、手頃なデスクトップ
仮想化ソリューションが生まれました。このソリューションは、仮想デスクトップとホステッド共有デスクトップが混在する導入をサポートし、さまざまな使用例に対応できます。ソリューションの主要コンポーネントには、
次のようなものがあります。
· 同じサイズで、より強力に。Cisco HX シリーズ ノードは、768 GB の 2666 Mhz メモリを備えた
デュアル 18 コア 2.3 GHz Intel Xeon (Gold 6140) スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサーと Citrix XenDesktop を搭載しており、同一ハードウェアの過去にリリースされた世代の製品に比べ、より多くの
仮想デスクトップをサポートします。さらに、この調査で使用された Intel Xeon Gold 6140 18 コア
スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサーを利用したケースでは、サーバごとの容量の増加とコストのバランスが実現されました。
· デザインに組み込まれたハイ アベイラビリティによる耐障害性。仮想デスクトップおよび
インフラストラクチャ ワークロード用に、複数の Cisco HX シリーズ ノード、Cisco UCS ラック サーバ、Cisco UCS ブレード サーバをベースとして、さまざまな設計が行われており、テストされたあらゆる
ペイロードに対して、N+1 のサーバ耐障害性が考慮されています。
· 厳しいブート シナリオで限界に対するストレス テストを実施。450 ユーザのホステッド仮想
デスクトップと 600 ユーザのホステッド共有デスクトップが混在する環境をブートし、5 分以内に XenDesktop Studio への登録が完了しました。コールド スタートが非常に高速で安定したデスクトップ仮想化システムをお客様に提供できます。
· シミュレーションされたログイン ストームで限界に対するストレス テストを実施。450 人のユーザ全員がログインして、プロセッサが過負荷になったり、メモリまたはストレージ リソースを使い果たしたり
することなく、ワークロードは 48 分の間、定常状態で実行されました。非常に要求の厳しいログイン
および起動ストームを簡単に処理できるデスクトップ仮想化システムをお客様に提供できます。
· データセンター向けの非常にコンパクトなコンピューティング。Cisco Nexus スイッチと Cisco
ファブリック インターコネクトを含んだ初期段階のシステム構成は、8 ラック ユニットで 450 ユーザを
サポートできるようになっています。1 つまたは複数のノードを追加することで、Citrix XenDesktop の
ユーザを、クラスタスケール上の上限(現在はハイパーコンバージド ノード 16、コンピューティング専用ノード 16)に達するまで Cisco HyperFlex クラスタに段階的に追加できます。
· 100 % の仮想化:この CVD のデザインでは、Microsoft Hyper-V 2016 での 100 % の仮想化が検証済み
です。仮想デスクトップ、ユーザ データ、プロファイル、サポートするすべてのインフラストラクチャ
コンポーネント(Active Directory、SQL サーバ、Citrix XenDesktop コンポーネント、XenDesktop VDI
デスクトップ、XENAPP サーバを含む)が仮想マシンとしてホストされました。これにより、システム全体が Cisco HyperFlex ハイパーコンバージド インフラストラクチャとステートレスな Cisco UCS HX
シリーズ サーバで実行されることになり、お客様にメンテナンス性と容量追加における高い柔軟性を
提供します(ソリューションのキャパシティを最大に高め、最適な経済性を追求するため、VM の
インフラストラクチャは HX クラスタの外側の Cisco UCS C220 M4 ラック サーバ 2 台でホストされています)。
· シスコのデータセンターの管理:シスコは、シンプルな拡張性、一貫性の保証、容易なメンテナンスを
実現する新しい Cisco UCS Manager 3.2(2) ソフトウェアによって、業界におけるリーダーシップを維持しています。また、Cisco UCS Manager、Cisco UCS Central、Cisco UCS Director の継続的な開発に取り組んでおり、ローカル側、Cisco UCS ドメイン間、全世界における顧客環境の一貫性を確実なものとしています。Cisco UCS ソフトウェア スイートを提供することで、導入/運用管理をさらにシンプルにし、顧客組織におけるコンピューティング、ストレージ、ネットワーキングの各分野の専門家が、制御できる範囲を引き続き広げられるようにします。
· Cisco 40G ファブリック:40G ユニファイド ファブリックには、6300 シリーズ ファブリック
インターコネクトに関する追加検証が加えられ、より厳しいワークロード テストを実施しながら、
優れたユーザ応答時間が維持されました。
· Cisco HyperFlex Connect (HX Connect):HyperFlex v2.5 では、HTML 5 をベースとした新しい Web UI が導入され、Cisco HyperFlex の主要管理ツールとして利用可能となっています。これはクラスタ上で
一元化された制御ポイントとして機能します。管理者はボリュームの作成、データ プラットフォームの状態を監視、リソース使用率を管理できます。またこのデータを使用して、クラスタをいつ拡張する必要があるかを予測することもできます。
· Cisco HyperFlex ストレージのパフォーマンス:Cisco HyperFlex では、業界トップクラスの
ハイパーコンバージド ストレージ性能が実現されており、相当に負荷の高い I/O バースト(ログイン ストームなど)でも効率的に処理できます。低遅延で書き込みスループットが高く、シンプルで柔軟なビジネス継続性を実現し、デスクトップ単位のストレージ コストの削減を支援します。
· Cisco HyperFlex の俊敏性:Cisco HyperFlex システムにより、ユーザがインフラストラクチャに対してシームレスにストレージを追加、アップグレード、削除でき、仮想デスクトップの要件を満たせるように
なります。
· パフォーマンスと拡張性の最適化。ホステッド共有デスクトップ セッションの場合、仮想マシンに割り
当てられた vCPU の数が、サーバ上で使用可能なハイパースレッド(論理)コアの数を超えない場合に最高のパフォーマンスが得られました。つまり、最高のパフォーマンスは、仮想化 RDS システムを実行して
いる仮想マシンに対して、限度を超えた CPU リソースをコミットしない場合に得られます。
シスコ デスクトップ仮想化ソリューション:データセンター
進化する職場環境
今日の IT 部門は、急速に進化する職場環境に直面しています。海外の請負業者、分散したコールセンターの運営、ナレッジワーカーとタスク ワーカー、パートナー、コンサルタント、世界各地から時間を問わず接続してくる
パートナー、コンサルタント、幹部など、ユーザの多様化と地理的分散はますます進んでいます。
こうしたユーザのモバイル化も進み、従来のようにオフィスだけでなく、社内の会議室やホーム オフィス、
移動中やホテル、さらにはコーヒー ショップなどで仕事する従業員が増えています。また、従業員は、
増え続ける多様なクライアント コンピューティング デバイスやモバイル デバイスから、自分の好みのデバイス
を選べることも望んでいます。こうした傾向から IT 部門にますます求められるのは、企業データの保護と、
ユーザ、エンドポイント デバイス、デスクトップ アクセスの複合的なシナリオによるデータの漏洩や損失の防止です(図 1)。
これらの課題は、古くなった PC や制限のあるローカル ストレージに対応するためのデスクトップ更新サイクルや、新しいオペレーティング システム(特に Microsoft Windows 10 や生産性ツール、Microsoft Office 2016)への移行によって複雑化しています。
図 1 シスコ データセンター パートナー コラボレーション

デスクトップ仮想化を推進する主な要素として、制御の向上と管理コストの削減によるデータ セキュリティの
向上、キャパシティの拡大・縮小、TCO の削減が挙げられます。
シスコ デスクトップ仮想化における重点項目
シスコは、優れたデスクトップ仮想化データセンター インフラストラクチャを提供するため、シンプル化、
セキュリティ、拡張性という 3 つの主要要素を重視しています。プラットフォームのモジュール化され、連係するソフトウェアが、シンプルで、セキュアで、スケーラブルなデスクトップ仮想化プラットフォームを実現します。
シンプル化
Cisco UCS と Cisco HyperFlex により、業界標準のコンピューティングに対して、先進的な新しいアプローチを提供し、デスクトップ仮想化におけるデータセンター インフラストラクチャの中核を担います。Cisco UCS の
数多くの機能および利点の代表的な例として、必要なサーバ数やサーバあたりで使用されるケーブル数が大幅に
削減されること、および Cisco UCS サービス プロファイルを通してサーバを迅速に導入または
再プロビジョニングできることが挙げられます。管理が必要なサーバやケーブル数が削減され、サーバおよび仮想デスクトップ プロビジョニングが合理化されることによって、操作が大幅にシンプル化されます。
Cisco UCS Manager サービス プロファイルとシスコ エコパートナー ソリューションのクローニングを利用すると、数千ものデスクトップを数分でプロビジョニングできます。このアプローチにより、エンド ユーザの生産性が高まり、ビジネスの俊敏性が向上するため、IT リソースを他のタスクに割り当てることができます。
Cisco UCS Manager は、データセンターで日常的に生じるサーバ、ネットワーク、ストレージ アクセス
インフラストラクチャの構成やプロビジョニングなどのエラーが発生しやすい操作を自動化します。さらに、1 RU あたりのメモリ・CPU 密度の高い Cisco UCS B シリーズ ブレード サーバ、C シリーズ、HX シリーズ ラック
サーバにより、高いデスクトップ密度が実現し、サーバ インフラストラクチャに求められる要件を軽減することができます。
シンプル化は、デスクトップ仮想化を実装する際の問題を減らす上でも役立ちます。シスコと Microsoft 社などをはじめとするテクノロジー パートナーが、HyperFlex などの事前定義済みハイパーコンバージド
アーキテクチャ インフラストラクチャ パッケージを含む検証済み統合アーキテクチャを開発しました。シスコ デスクトップ仮想化ソリューションは、Microsoft Hyper-V を使用してテストされています。
安全性
仮想デスクトップは本質的に従来の物理的なものよりもセキュアですが、セキュリティに関する新たな課題も伴います。ミッションクリティカルな Web サーバやアプリケーション サーバと、仮想デスクトップなどが共通
インフラストラクチャを使用している場合、セキュリティの脅威の上で高いリスクを負うようになりました。
仮想マシン間でのトラフィックが、セキュリティ面での重要な検討課題となっています。特に、Microsoft Live Migration のようにサーバ インフラストラクチャ内を仮想マシンが移動する場合など、動的な環境において、IT マネージャがリスクに対処する必要が生じています。
つまり、拡大されたコンピューティング インフラストラクチャにおける仮想マシンのモビリティの動的かつ流動的な性質を考慮すると、デスクトップ仮想化により、ポリシーやセキュリティを仮想マシン レベルで認識する
必要性が大きく高まります。新しい仮想デスクトップを容易に増加させることが可能になったことが、仮想化対応のネットワークおよびセキュリティ インフラストラクチャの重要性を高めています。デスクトップ仮想化のためのシスコのデータセンター インフラストラクチャ(Cisco UCS および Cisco Nexus ファミリ ソリューション)では、デスクトップからハイパーバイザまで包括的に対応したセキュリティを通して、データセンター、
ネットワーク、およびデスクトップのセキュリティを強化します。セキュリティは、仮想デスクトップの
セグメンテーション、仮想マシン対応のポリシーや管理、および LAN や WAN のインフラ全体のネットワーク
セキュリティによって強化されます。
拡張性
デスクトップ仮想化ソリューションは拡大を続けています。したがって、そのような拡大に応じて、
ソリューションの規模の拡張や推定が可能でなければなりません。シスコ デスクトップ仮想化ソリューションは、デスクトップ密度(サーバごとのデスクトップ数)が高く、サーバを追加することでほぼリニアに性能が増加します。シスコのデータセンター インフラストラクチャが提供する柔軟なプラットフォームを利用すると、このような拡大にも対応でき、ビジネスの俊敏性が向上します。Cisco UCS Manager のサービス プロファイルにより、
オンデマンドでのデスクトップのプロビジョニングが可能となり、数千単位のデスクトップの展開が、数十単位
での展開と同じように容易になります。
Cisco HyperFlex サーバは、ほぼリニアに性能を向上させ、規模を拡大することができます。Cisco UCS には、特許取得済みの Cisco 拡張メモリ テクノロジーが実装されており、より少ないソケットで大きなメモリ面積を
実現しています(2 および 4 ソケットのサーバで最大 1.5 テラバイト (TB) の拡張性を実現)。構成要素として
ユニファイド ファブリック テクノロジーを使用しており、Cisco UCS サーバでの集約帯域幅は、サーバごとに
最大 80 Gbps にまで拡張できます。また、ノースバウンド Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクトでは、
ラインレートでの 2 テラビット/秒 (Tbps) での送信が可能です。これにより、デスクトップ仮想化の I/O と
メモリにおけるボトルネックの発生を防ぎます。Cisco UCS は高性能と低遅延を実現したユニファイド
ファブリックベース ネットワーキング アーキテクチャであり、高精細ビデオやコミュニケーション トラフィックなどの非常に通信量の多い仮想デスクトップ トラフィックをサポートします。さらに、Cisco HyperFlex は、シスコ
デスクトップ仮想化ソリューションの一部として、起動時やログイン ストーム時のデータの可用性と最適な
パフォーマンスを維持します。Citrix XenDesktop や Cisco HyperFlex ソリューションをベースとした最近の Cisco Validated Design では、拡張性とパフォーマンスが重視されており、450 以上のホステッド仮想デスクトップとホステッド共有デスクトップが 5 分以内に起動されます。
Cisco UCS および Cisco Nexus データセンター インフラストラクチャでは、デスクトップ仮想化、
データセンター アプリケーション、クラウド コンピューティングをサポートする、サーバ、ネットワーク、
およびストレージ リソースの透過的拡張機能を備えた、成長のための理想的なプラットフォームが提供されます。
節約と成功
簡素化された、安全性と拡張性の高いデスクトップ仮想化向けシスコ データセンター インフラストラクチャでは、他のアプローチと比べて時間とコストを節約できます。Cisco UCS により、サーバあたり仮想デスクトップ密度が業界トップレベルの水準で提供されます。そして、導入コスト (CapEx) と運用コスト (OpEx) の両方が
削減され、早期の投資回収および継続的なコスト削減(投資効果 (ROI) の向上と総所有コストの削減)が実現します。また、Cisco UCS アーキテクチャとシスコ ユニファイド ファブリックにより、サーバごとの必要な
ケーブル数やポート数が減ることで、より低コストのネットワーク インフラストラクチャを構築できます。
また、ストレージの階層化と重複排除テクノロジーによって、ストレージ コストを下げ、デスクトップ ストレージのニーズを最大 50 % にまで削減します。
デスクトップ仮想化対応の Cisco HyperFlex を利用することで、導入が簡素化され、生産性発揮までの時間が
短縮され、ビジネスの俊敏性が向上します。IT スタッフおよびエンド ユーザは迅速に生産性を向上させることができ、企業が、仮想デスクトップを必要に応じて時間や場所を問わず導入できるため、新規のビジネス チャンスに迅速に対応できます。シスコの高性能なシステムとネットワークは物理 PC デスクトップ環境に近いユーザ
エクスペリエンスを実現し、ユーザは時と場所を問わず生産性を発揮できます。
組織のデスクトップ仮想化の効果を測定するには、通常、直近および長期での効率性や有効性を確認します。
シスコ デスクトップ仮想化ソリューションは非常に効率性が高く、迅速な導入が可能な上、必要なデバイスやケーブルの数が少ないため、コストを削減できます。また、エンド ユーザの選択したデバイスに必要なサービスが提供され、同時に IT の運用、管理、データ セキュリティも向上するため、大変高い効果が見込めます。このような効果は、仮想化分野を主導するパートナーとシスコとの業界内でも最高のパートナーシップと設計のテストや検証を元に実現されており、ソリューション ライフサイクルを通じて顧客を支援します。また、デスクトップ仮想化向けプラットフォームとして、安全かつ柔軟で拡張可能なシスコのプラットフォームを使用することで、長期的な効果を担保します。
最終的には、デスクトップ仮想化製品のそれぞれのエンド ユーザが、優れたエクスペリエンスを享受できるかが評価の基準になります。Cisco HyperFlex ではクラス最高の性能が提供されており、1 秒を切るベースライン応答時間とフル ロード時の 1 秒足らずの平均指数応答時間が実現されています。
使用例
· 医療:デスクトップと端末間のモビリティ、コンプライアンス、コスト
· 官公庁:テレワーキング導入、ビジネス継続性、業務の連続性 (COOP) トレーニング センター
· 金融:リテール バンクの IT コスト削減、保険代理店、コンプライアンス、プライバシー
· 教育:幼稚園から高校までの生徒のアクセス、高等教育、リモート学習
· 地方自治体:機関間の IT およびサービスの統合、セキュリティ
· 小売:ブランチオフィス IT コストの削減およびリモート ベンダー
· 製造:タスク ワーカーおよびナレッジ ワーカーと海外請負業者
· Microsoft Windows 10 への移行
· グラフィック要件の厳しいアプリケーション
· セキュリティおよびコンプライアンスの取り組み
· リモート オフィスおよびブランチ オフィス、またはオフショア施設の開設
· 合併と買収などによるクライアント基盤の統合
図 2 では、Cisco Validated Design コンポーネント上に構築された Hyper-V 2016 における Citrix XenDesktop とネットワーク接続について示しています。この参照アーキテクチャは、ワイヤワンス (wire-once) 戦略を強化するものです。新たなストレージがアーキテクチャに追加され、ホストから Cisco UCS ファブリック
インターコネクトまでの配線をやり直す必要がありません。
図 2フルスケール、単一 UCS ドメイン、シスコのシングル ラック アーキテクチャ

物理トポロジ
Cisco HyperFlex System は、1 組の Cisco UCS 6200/6300 シリーズ ファブリック インターコネクトから
構成されており、クラスタあたり最大 16 の HXAF シリーズ ラック マウント サーバを備えています。さらに、クラスタごとに最大 16 のコンピューティング専用サーバを追加できます。Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード シャーシを追加することで、ハイブリッド クラスタ設計において追加のコンピューティング リソースに Cisco UCS B200 M5 ブレード サーバを使用できます。また、Cisco UCS C240 と C220 ラックサーバを、追加の
コンピューティング リソースに使用することもできます。1 組のファブリック インターコネクトに、最大 8 つの HX クラスタを個別に構築・共存させることが可能です。ファブリック インターコネクトは、すべての HX
シリーズ ラック マウント サーバとすべての Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード シャーシの両方に接続されます。
インストール時には、ファブリック インターコネクトから顧客のデータセンター ネットワークに、
ノースバウンド ネットワーク接続とも呼ばれるアップストリーム ネットワーク接続が行われます。
![]() この調査では、Cisco 6332-16UP ファブリック インターコネクトを Cisco Nexus 93108YCPX スイッチにアップリンクしました。
この調査では、Cisco 6332-16UP ファブリック インターコネクトを Cisco Nexus 93108YCPX スイッチにアップリンクしました。
図 3 および図 4 では、ハイパーコンバージド トポロジ、ハイブリッド ハイパーコンバージド トポロジ、
コンピューティング専用トポロジについて示しています。
図 3 Cisco HyperFlex の標準トポロジ

図 4Cisco HyperFlex ハイパーコンバージドおよびコンピューティング専用ノード トポロジ

ファブリック インターコネクト
ファブリック インターコネクト (FI) は、管理クラスタとして動作する 2 つのユニットのペアとして展開され、
A サイド ファブリックおよび B サイド ファブリックからなる 2 つの別個のネットワーク ファブリックを
構成します。そのため、設計上の要素表記として、FI A や FI B またはファブリック A、ファブリック B という
呼称がもちいられます。これらのファブリック インターコネクトは両方とも常にアクティブで、冗長構成や
高可用性構成のためのネットワーク ファブリック上でデータを通過させます。Cisco UCS Manager などの
管理サービスにおいても、2 つの FI がクラスタ形式で提供されます。つまり、一方の FI がプライマリでもう一方の FI がセカンダリとなり、クラスタ化されたローミング IP アドレスが付与されます。このプライマリ/
セカンダリの関係は管理クラスタに関してのみであり、データ伝送には影響を与えません。
ファブリック インターコネクトには以下のポートがあり、Cisco UCS ドメインの適切な管理のためには、それらのポートに接続する必要があります。
· Mgmt:GUI または CLI ツールを通じて、ファブリック インターコネクトや Cisco UCS ドメインを管理する際に使用するポート (10/100/1000 Mbps) です。また、ドメイン内の管理対象サーバへのリモート KVM、IPMI、SoL セッションにも使用されます。これは通常、管理ネットワークに接続されます。
· L1:Cisco UCS 管理クラスタを構成する際のクロス接続ポートです。これは、RJ45 プラグを備えた標準の CAT5/CAT6 イーサネット ケーブルを使用して、ファブリック インターコネクトのペアの L1 ポートに直接接続されます。スイッチやハブに接続する必要はありません。
· L2:Cisco UCS 管理クラスタを構成する際のクロス接続ポートです。これは、RJ45 プラグを備えた標準の CAT5/CAT6 イーサネット ケーブルを使用して、ファブリック インターコネクトのペアの L2 ポートに直接接続されます。スイッチやハブに接続する必要はありません。
· Console:ファブリック インターコネクトに直接コンソール アクセスを行うための RJ45 シリアル
ポートです。通常、RJ45 アダプタを備えたシリアル ケーブルを使用して、FI の初期設定プロセスを実施
する際に使用されます。また、ターミナル アグリゲータ、またはリモート コンソール サーバ デバイス
にも接続できます。
HX シリーズ ラック マウント サーバ
HX シリーズ コンバージド サーバは、Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクトに、直接接続モードで
接続されます。このオプションを使用すると、Cisco UCS Manager は、管理通信とデータ通信の両方にシングル ケーブルを使用して HX シリーズ ラックマウント サーバを管理できます。HXAF220C-M5SX と HXAF240C-M5SX サーバの両方で、Cisco VIC 1387 ネットワーク インターフェイス カード (NIC) を、デュアル 40 ギガビット
イーサネット (GbE) ポートを備えたモジュール型 LAN on Motherboard (MLOM) スロットに取り付けて構成
することができます。標準接続、および情報接続を行うには、VIC 1387 のポート 1 を FI A のポートにつなぎ、VIC 1387 のポート 2 を FI B のポートにつなぎます(図 5)。
![]() このケーブル配線に誤りがあると、エラー、検出の失敗、冗長接続の失敗につながる可能性があります。
このケーブル配線に誤りがあると、エラー、検出の失敗、冗長接続の失敗につながる可能性があります。
図 5 HX シリーズ サーバの接続

Cisco UCS B シリーズ ブレード サーバ
ハイブリッド HyperFlex クラスタには、コンピューティング容量の強化策として、Cisco UCS B200 M5
ブレード サーバも 1 ~ 8 台組み合わせることができます。他の Cisco UCS B シリーズ ブレード サーバと同様に、Cisco UCS B200 M5 は、Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード シャーシ内に取り付ける必要があります。ブレード
シャーシには、1 ~ 4 基の電源装置と 8 台のモジュール型冷却ファンを装着できるようになっています。シャーシの背面には、シスコ ファブリック エクステンダを取り付けるためのベイが 2 つあります。ファブリック
エクステンダ(一般的に IO モジュール、または IOM とも呼ばれます)は、シャーシをファブリック インターコネクトに接続します。内部的には、シャーシのバック プレーンにある各ブレード サーバに取り付けられた Cisco VIC 1340 カードに、ファブリック エクステンダが接続されます。標準的な方法で接続するには、左側の IOM または IOM 1 から 10 GbE リンク(1 ~ 4)か 40 GbE リンク(ネイティブ X 2)を FI A に接続し、右側の IOM または IOM 2 から同じ数の 10 GbE リンクを FI B に接続します(図 6)。ケーブルの設定が不正な場合は、エラー、検出の失敗、冗長接続の失敗につながる可能性があります。
図 6Cisco UCS 5108 シャーシの接続

論理ネットワークの設計
Cisco HyperFlex システムでは、通信パスが 4 つの定義ゾーンに分類されています(図 6)。
· 管理ゾーン:このゾーンは、物理ハードウェア、ハイパーバイザ ホスト、ストレージ プラットフォーム
コントローラ仮想マシン (SCVM) を管理する際に必要な接続で構成されます。これらのインターフェイスと IP アドレスは、LAN や WAN の全体で、HX システムを管理する担当者全員で利用できる必要があります。このゾーンでは、ドメイン ネーム システム (DNS)、Network Time Protocol (NTP) サービスへのアクセス権限があり、セキュア シェル (SSH) 通信が許可されている必要があります。このゾーンは、複数の物理
コンポーネントと仮想コンポーネントからできています。
- ファブリック インターコネクト管理ポート。
- Cisco UCS 外部管理インターフェイス。サーバやブレードによって使用され、FI 管理ポートを通じて応答します。
- Hyper-V ホスト管理インターフェイス。
- ストレージ コントローラ VM 管理インターフェイス。
- ローミング HX クラスタ管理インターフェイス。
· VM ゾーン:このゾーンは、HyperFlex ハイパーコンバージド システム内で実行されるゲスト VM へのサービス ネットワーク IO に必要な接続で構成されます。通常、このゾーンには、ネットワークのアップリンクを介して Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクトにトランクされる複数の VLAN が含まれており、802.1Q VLAN ID のタグが付けられます。これらのインターフェイスと IP アドレスは、LAN や WAN の全体を通じて、HX システムのゲスト VM と通信する必要があるスタッフやコンピュータ
エンドポイントのすべてで利用できるようになっている必要があります。
· ストレージ ゾーン:このゾーンは、Cisco HX Data Platform ソフトウェア、Hyper-V ホスト、および
ストレージ コントローラ VM が HX 分散データ ファイルシステムにサービス提供するために使用する接続で構成されます。適切に運用するためには、これらのインターフェイスと IP アドレスが相互に通信できる必要があります。通常の運用では、このトラフィックはすべて Cisco UCS ドメイン内で発生しますが、
ハードウェア障害が生じた場合には、Cisco UCS ドメインのネットワーク ノースバウンドを通過する必要があります。そのため、HX ストレージ トラフィックに使用される VLAN は、Cisco UCS ドメインからの
ネットワーク アップリンクを通過し、FI B から FI A に到達するか、その逆が可能である必要があります。このゾーンは、基本的にはジャンボ フレームでのトラフィックになるため、Cisco UCS のアップリンク
でジャンボ フレームを有効にする必要があります。このゾーンには、複数のコンポーネントがあります。
- HX クラスタ内の各 HYPER-V ホストのストレージ トラフィックに使用する vmnic
インターフェイス。
- ストレージ コントローラ VM ストレージ インターフェイス。
- ローミング HX クラスタ ストレージ インターフェイス。
· ライブ マイグレーション ゾーン:このゾーンは、ホストからホストへのゲスト VM のライブ
マイグレーションを有効にするために、Hyper-V ホストによって使用される接続から構成されます。通常の運用では、このトラフィックはすべて Cisco UCS ドメイン内で発生しますが、ハードウェア障害が生じた場合には、Cisco UCS ドメインのネットワーク ノースバウンドを通過する必要があります。そのため、HX ストレージ トラフィックに使用される VLAN は、Cisco UCS ドメインからのネットワーク アップリンクを通過し、FI B から FI A に到達するか、その逆が可能である必要があります。

参照ハードウェア構成は次のとおりです。
· Cisco Nexus 93108YCPX スイッチ X 2
· Cisco UCS 6332-16UP ファブリック インターコネクト X 2
· HyperFlex Data Platform バージョン 3.0.1a を実行する Cisco HX シリーズ ラック サーバ X 4
デスクトップ仮想化の場合、導入には Microsoft Hyper-V を実行する Citrix XenDesktop が含まれます。設計に
おいては、永続デスクトップ/非永続デスクトップ用に大規模な構成要素が意図され、4 ノード構成ごとに次の
密度で提供されます。
· MCS を使用した Citrix XenDesktop Windows 10 非永続仮想デスクトップ X 450
![]() 今回の調査においては、すべての Windows 10 仮想デスクトップが 4 GB のメモリでプロビジョニングされました。通常、永続デスクトップのユーザは、より多くのメモリを必要とします。4 GB 以上のメモリが必要な場合、Cisco HXAF220c-M5SX HX シリーズ ラック サーバ上のセカンド メモリ チャネルが利用される
今回の調査においては、すべての Windows 10 仮想デスクトップが 4 GB のメモリでプロビジョニングされました。通常、永続デスクトップのユーザは、より多くのメモリを必要とします。4 GB 以上のメモリが必要な場合、Cisco HXAF220c-M5SX HX シリーズ ラック サーバ上のセカンド メモリ チャネルが利用される
必要があります。
ここで提供されるデータにより、顧客環境に合わせて VDI デスクトップを実行できるようになります。たとえば、
既存のサーバにドライブを追加することで、I/O キャパシティやスループットを改善することができます。もしくは、新しい機能を導入するために、特別なハードウェアやソフトウェア機能を追加することができます。このドキュメントでは、図 2 で示したベース アーキテクチャ導入の詳細な手順について案内しますこれらの手順には、物理的な
ネットワークのケーブリングやコンピューティング デバイス、ストレージ デバイスの設定などがすべて含まれます。
設定のガイドライン
このドキュメントでは、Cisco HyperFlex の仮想デスクトップにおけるさまざまな種類のワークロードに対して、Cisco Validated Design (CVD) での冗長構成や高可用性設定を行う際の詳細について説明します。どの冗長
コンポーネントが各手順で設定されるかを示す設定のガイドラインが提示されます。たとえば、Cisco Nexus A
および Cisco Nexus B は、設定される Cisco Nexus スイッチのペア メンバーを識別します。同様に、Cisco UCS 6332 ファブリック インターコネクトも識別されます。さらに、このドキュメントでは、複数の Cisco UCS
および HyperFlex ホスト(VM-Host-Infra-01、VM-Host-Infra-02、VM-Host-VDI-01 などのように連番で識別されます)をプロビジョニングするための詳細な手順について説明します。最後に、環境に関連する情報を、所定の手順で指定する必要がある点についてふれます。<text> がコマンド構造の一部として表示されます。
この項では、この調査で概要を示すソリューションで使用されているインフラストラクチャ コンポーネントに
ついて説明します。
Cisco Unified Computing System
Cisco UCS Manager (UCSM) は、Cisco Unified Computing System™ (Cisco UCS) と Cisco HyperFlex の
すべてのソフトウェアとハードウェアのコンポーネントを、直感的な GUI、コマンドライン インターフェイス (CLI)、XML API によって統合管理できる機能を備えています。一元管理機能を備えた単一の管理ドメインがあり、複数のシャーシや数千台もの仮想マシンを制御できます。
Cisco UCS は、コンピューティング、ネットワーキング、およびストレージ アクセスを統合した次世代のデータセンター プラットフォームです。仮想環境向けに最適化されており、業界標準のオープン テクノロジーを利用して設計されたもので、総所有コスト (TCO) の削減とビジネスの俊敏性強化を目的としています。このシステムは、低遅延のロスレス 40 ギガビット イーサネット ユニファイド ネットワーク ファブリックと、エンタープライズクラスの x86 アーキテクチャ サーバを統合します。これはすべてのリソースが単一の管理ドメインに集約された、統合型の拡張性に優れたマルチシャーシ対応のプラットフォームです。
Cisco Unified Computing System のコンポーネント
Cisco UCS の主なコンポーネントは、次のとおりです。
· コンピューティング:インテル® Xeon® スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサーをベースとしたブレード サーバ、ラック サーバ、ハイパーコンバージド サーバをシステムに組み込んだ、まったく新しいクラスのコンピューティング システムをベースとする設計です。
· ネットワーク:このシステムは低遅延でロスレスの 40 Gbps ユニファイド ネットワーク ファブリック上で統合されています。このネットワーク基盤は、現状では LAN、SAN、高性能コンピューティング (HPC) ネットワークとして扱われている異なるネットワークを統合します。ユニファイド ファブリックにより、ネットワーク アダプタ、スイッチ、およびケーブルの数が減少し、電力と冷却の要件が緩和されるため、コスト削減につながります。
· 仮想化:仮想環境のスケーラビリティ、パフォーマンス、および運用制御を強化することで、仮想化の
可能性を最大限に活用します。シスコのセキュリティ、ポリシー適用、および診断機能は仮想化環境にまで拡張されており、変化するビジネス要件や IT 要件により適切に対応できます。
· ストレージ:Cisco HyperFlex ラック サーバにより、強力な HX データ プラットフォーム ソフトウェア
を使用した高性能で復元力の高いストレージを提供します。顧客は、耐障害性要件に応じて、少なくとも
3 つのノード(レプリケーション ファクタ 2/3)を展開できます。これらのノードは、HyperFlex
ストレージとコンピューティング クラスタを構成します。各ノードのオンボード ストレージはクラスタ レベルで集約され、すべてのノードで自動的に共有されます。
· 管理:Cisco UCS の特色は、あらゆるシステム コンポーネントを統合し、ソリューション全体を 1 つの大きなサーバ・ネットワーク・ストレージ リソースとして、Cisco UCS Manager ソフトウェアから管理できることです。すべてのシステムの構成プロセスや動作を管理できる直感的な GUI、CLI、堅牢な API を備えています。直近の開発結果として、Cisco Intersight というクラウド ベースの管理システムも用意されています。
Cisco UCS と Cisco HyperFlex は、次の機能を提供するように設計されています。
· TCO の削減と、ビジネスの俊敏性の向上。
· ジャストインタイムのプロビジョニングとモビリティのサポートによる、IT スタッフの生産性の向上。
· 単一の統合されたシステムにより、データセンターのテクノロジーを統合し、全体として管理、サービスを提供。
· 数百台の個別サーバと数千台の仮想マシンに対応する設計と要件に合わせて I/O 帯域幅を拡張できる拡張性。
· 業界のリーダー企業とのパートナー エコシステムによって支えられている業界標準を提供。
Cisco UCS Manager は、複数のブレード シャーシ、ブレード/ラック サーバ、および数千単位の仮想マシンに
わたる Cisco Unified Computing System のすべてのソフトウェア コンポーネントとハードウェア
コンポーネントを管理する、統合された組み込みソフトとしての管理機能を提供します。Cisco UCS Manager は、すべての機能にわたって管理情報にアクセスできる直感的な GUI、コマンドライン インターフェイス (CLI)、および XML API を介して Cisco UCS 全体を 1 つのエンティティとして管理します。
Cisco HyperFlex システムは、サーバおよびメモリ リソース、統合されたネットワーク接続、VM ストレージ用の高性能の分散ログ構造ファイル システム、仮想化サーバ用のハイパーバイザ ソフトウェア、これらが単一の Cisco UCS 管理ドメインに統合された、完結型の仮想サーバ プラットフォームです。
図 8Cisco HyperFlex システムの概要

バージョン 3.0.1 の拡張機能
新しいソフトウェア機能
このリリースでは、クラウド ネイティブのワークロードの中でもミッション クリティカルなもののサポートに
関して、大きな進展がありました。
· 複数のハイパーバイザ:VMware vSphere、Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 をサポートしています。
インストール要件と手順の詳細については、VMware 用 Cisco HyperFlex システム インストレーション
ガイド、および『Cisco HyperFlex Systems Installation Guide on Microsoft Hyper-V(Microsoft Hyper-V での Cisco HyperFlex System インストール ガイド)』を参照してください。
· ストレッチ クラスタ:単一の HyperFlex クラスタで 2 つのデータセンターをカバーすることで、高い
水準の可用性を可能とする機能です。詳細については、『Cisco HyperFlex Systems Stretched Cluster Guide(Cisco HyperFlex System ストレッチ クラスタ ガイド)』を参照してください。
· Kubernetes FlexVolume ドライバ:永続型ボリュームの Kubernetes ポッドへの自動プロビジョニングを有効にします。
· 復元力の向上:論理可用性ゾーン (LAZ) を有効にすることで、自動的にクラスタを分割し、ノードの
復元力を高め、ディスク障害に対処します。この機能は、HyperFlex クラスタに 8 つ以上のコンバージド ノードがある場合にのみ有効になります。クラスタが LAZ に対応している場合は、1 つのノードで同時に展開が行われます。詳細については、リリース 3.0(1a) の公開済みの問題を参照してください。
· ディザスタ リカバリ ワークフロー:Cisco HX Connect を使用したディザスタ リカバリ ワークフローの強化(計画/未計画の VM 移行)詳細については、『Cisco HyperFlex Systems Administration Guide, Release 3.0(Cisco HyperFlex System 管理ガイド)』を参照してください。
· REST API:HyperFlex REST API 開発者向けの追加ガイダンスとして、クイックスタート ガイドを Cisco DevNet に用意しています。詳細については、『Cisco HyperFlex Systems REST API Getting Started Guide(Cisco HyperFlex System REST API スタートアップ ガイド』を参照してください。
· リンク モード:vCenter の強化されたリンク モード機能を使用して、複数の環境用の HyperFlex
プラグインをサポートします。
新しいハードウェア機能
· HX 容量スケーリング オプションの拡張
- 大型フォーム ファクタ (LFF) HX M5 240 シャーシで、最大 12 台の 6 TB/8 TB ドライブをサポート
します。注:現在は、HX M5 240 ノードでのみサポートしています。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック シートを参照してください。
- 18.06TiB の最大クラスタ キャパシティを備えた 1.8 TB SFF HDD を、ハイブリッド M5 エッジ
ノードでのみサポートします。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック シートを参照してください。
- 強化されたノード拡張オプション:32 のコンピューティング ノードで、最大 32 のコンバージェンス(クラスタあたり)をサポートします。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック
シートを参照してください。
· Intel Optane SSD のサポートにより、ドライブ レベルでの高いパフォーマンスと耐久性をサポートします。HyperFlex で最新のフラッシュ メモリ技術である 3D Xpoint の要件を満たしています。新しい
キャッシング ドライブ オプションとして、Intel Optane NVMe SSD HX-NVMEXP-I375 を追加しました。
![]() M5 オール フラッシュ構成でのみサポートされます。詳細については、次を参照してください。Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック シート、『Cisco HX220c M5 HyperFlex Node Installation Guide(Cisco HX220c M5 HyperFlex ノード インストール ガイド)』、『Cisco HX240c M5 HyperFlex Node Installation Guide(Cisco HX240c M5 HyperFlex ノード インストール ガイド)』
M5 オール フラッシュ構成でのみサポートされます。詳細については、次を参照してください。Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック シート、『Cisco HX220c M5 HyperFlex Node Installation Guide(Cisco HX220c M5 HyperFlex ノード インストール ガイド)』、『Cisco HX240c M5 HyperFlex Node Installation Guide(Cisco HX240c M5 HyperFlex ノード インストール ガイド)』
· HX240c M5 ノードは、従来の NVIDIA カードに加えて、AMD マルチユーザ GPU (MxGPU)
ハードウェア ベースのグラフィック仮想化をサポートします。AMD FirePro S7150 シリーズ GPU が HX240c M5 ノードで使用できるようになりました。これらのグラフィック アクセラレータにより、安全性とパフォーマンスに優れた、コスト効率の高い VDI 環境が有効になります。詳細については、次を参照してください。Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック シート、『Cisco HX240c M5 HyperFlex Node Installation Guide(Cisco HX240c M5 HyperFlex Node インストール ガイド)』導入手順については、AMD GPU の導入を参照してください。
· HyperFlex Edge の構成を拡張:HyperFlex Edge の発注時の PID が新しくなり、より柔軟でシンプルな構成が可能になり、コストが削減できます。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ スペック シートを参照してください。
サポート対象バージョンおよびシステム要件
Cisco HX Data Platform を正常にインストールするには、特定のソフトウェアおよびハードウェアのバージョン、ネットワーク設定が必要です。
要件の一覧については、『Cisco HyperFlex Systems Installation Guide on Microsoft Hyper-V(Microsoft Hyper-V での Cisco HyperFlex System インストール ガイド)』を参照してください。
ハードウェアおよびソフトウェアの相互運用性
ハードウェアとソフトウェアの相互依存関係の一覧については、それぞれの Cisco UCS Manager リリース
バージョンの Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズにおけるハードウェアおよびソフトウェアの相互運用性 [英語] を参照してください。
Microsoft Hyper-V のソフトウェア要件
ソフトウェア要件には、互換性のあるバージョンの Cisco HyperFlex システム (HX) コンポーネントと Microsoft サーバ コンポーネントを使用していることの確認が含まれます。
HyperFlex ソフトウェアのバージョン
HX コンポーネント(Cisco HX データ プラットフォーム インストーラ、Cisco HX データ プラットフォーム、Cisco UCS ファームウェア)が別々のサーバにインストールされています。HX ストレージ クラスタで使用される各サーバの各コンポーネントと、その中で使用される各サーバの各コンポーネントに互換性があることを確認します。
· 事前に設定された HX サーバに同じバージョンの Cisco UCS サーバ ファームウェアがインストールされていることを確認します。Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクト (FI) のファームウェア バージョンが異なっている場合は、『Cisco HyperFlex System アップグレード ガイド』を参照して、ファームウェア バージョンの調整手順について確認してください。
· M5:新しくハイブリッドまたはオール フラッシュ(Cisco HyperFlex HX240c M5 または HX220c M5)導入する場合、Cisco UCS Manager 3.2(3b) 以降がインストールされていることを確認します。
· SED ベースの HyperFlex システムの場合、M4 SED システムであれば、A バンドル
(インフラストラクチャ)と C バンドル(ラック サーバ)が、Cisco UCS Manager バージョン 3.1(3h) 以上であることを確認します。M5 SED システムであれば、すべてのバンドルが Cisco UCS Manager
バージョン 3.2(3b) 以上であることを確認します。
Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクト
Cisco UCS 6300 シリーズ ファブリック インターコネクトは、Cisco UCS の中核であり、システムの
ネットワーク接続と管理の機能を提供します。Cisco UCS 6300 シリーズは、ライン レート、低遅延、ロスレスの 40 ギガビット イーサネット、FCoE、ファイバ チャネル機能を提供します。
ファブリック インターコネクトは、Cisco UCS B シリーズ ブレード サーバ、Cisco UCS C-シリーズおよび HX
シリーズ ラックサーバ、Cisco UCS 5100 シリーズ ブレード サーバ シャーシの管理および通信の基盤となります。ファブリック インターコネクトに接続されているすべてのサーバは、可用性の高い単一の管理ドメインの
一部として管理されます。さらに、Cisco UCS 6300 シリーズは、ユニファイド ファブリックをサポートしているため、ドメイン内のすべてのブレードが LAN と SAN の両方に接続できます。
ネットワーキングでは、Cisco UCS 6300 シリーズはカットスルー アーキテクチャを使用し、パケット サイズや対応サービスに依存せず、すべてのポートで低遅延のラインレート 40 ギガビット イーサネット、2.56
テラビット (Tb) のスイッチング容量、シャーシあたり 320 Gbps の帯域幅をサポートします。この製品シリーズでは、シスコの低遅延でロスレスの 40 ギガビット イーサネット ユニファイド ネットワーク ファブリック機能をサポートし、これによりイーサネット ネットワークの信頼性、効率性、拡張性が向上します。ファブリック インターコネクトでは、ロスレス イーサネット ファブリックに対する複数のトラフィック クラスがブレード サーバからインターコネクトにかけてサポートされます。ネットワーク インターフェイス カード (NIC)、ホスト バス
アダプタ (HBA)、ケーブル、スイッチを統合可能な FCoE が最適化されたサーバ設計によって、TCO を大幅に削減できます。
図 9Cisco UCS 6332 ファブリック インターコネクト

図 10 Cisco UCS 6332-16UP ファブリック インターコネクト

Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ ノード
ソフトウェア デファインド インフラをベースとする Cisco HyperFlex システムでは、Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS) サーバによるソフトウェア デファインドのコンピューティング、強力な Cisco HX Data Platform を利用したソフトウェア デファインド ストレージ、そして Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (Cisco ACI™) とも連携・統合可能な Cisco UCS ファブリックによるソフトウェア デファインド
ネットワーキングが一元化されています。こうしたテクノロジーにより接続とハードウェア管理を一元化することで、統合されたリソース プールをビジネス ニーズに合わせて提供できる、適応性の高い統合クラスタが実現します。
Cisco HyperFlex クラスタには(ディスク ストレージと共に)最低 3 つの HX シリーズ ノードが必要です。
データはこれらのうち最低 2 つのノードで複製され、3 番目のノードは単一ノードの障害時に運用を継続する上で必要になります。各ノードのディスク ストレージには 1 台の高性能 SSD ドライブが搭載されており、データ キャッシュと書き込み要求への迅速な応答 (ACK) を可能にしています。また、各ノードの最大データ容量には、プラットフォームの回転ディスクかエンタープライズ レベルの SSD の物理的な容量が備えられています。
Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5S ラック サーバ
HXAF220c M5 サーバは、インテル® Xeon® プロセッサー スケーラブル ファミリ、24 個の 2666MHz DIMM 用 DIMM スロット、最大 128 GB の個別 DIMM 容量、および最大 3.0 TB の総 DRAM 容量を搭載した 1U
フォーム ファクタで Cisco HyperFlex ポートフォリオの機能を拡張します。
この構成の Cisco HyperFlex オール フラッシュ ノードは設置面積が小さく、ストレージ キャパシティ用として、起動ドライブとして動作する M.2 SATA SSD ドライブを 1 台、240 GB のソリッド ステート ドライブ (SSD) データ ロギング ドライブを 1 台、400 GB の SSD ログ書き込みドライブを 1 台、3.8 テラバイト (TB) もしくは 960 GB の SATA SSD ドライブを最大 8 台含んでいます。1 つの HX クラスタには、最小で 3 個、最大で 16 個のノードを構成できます。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HXAF220c-M5S スペックシートを参照してくだ
さい。
図 11 Cisco UCS HXAF220c M5SX ラック サーバの正面図


図 12 Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5SX ラック サーバの背面図


Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5S は、データセンターおよびリモート サイト向での高いパフォーマンスと柔軟性を
提供し、最適化を可能とします。このエンタープライズクラスのサーバは、Web インフラストラクチャから分散型データベースの処理サービスに関して妥協することなく、市場で最高レベルの性能、汎用性、密度を実現します。Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5SX は、プログラム制御機能を備えた使いやすい Cisco UCS Manager ソフトウェアと、Cisco® Single Connect テクノロジーによる簡素化されたサーバ アクセスにより、ステートレスで実際の
処理サービスおよび仮想化での処理状況に合わせて迅速に実行することが可能です。インテル Xeon スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサー製品ファミリを基盤とし、64 GB の DIMM を使用した場合、最大 1.5 TB のメモリ、最大 10 台のディスク ドライブを搭載でき、最大 40 Gbps の I/O スループットを実現します。Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5S は、要求の厳しいアプリケーション処理の実行に必要とされる優れたパフォーマンス、柔軟性、I/O スループットを提供します。
Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5S では、次の内容が提供されます。
· 最大 2 つのマルチコア インテル Xeon スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサー。最大 56 プロセス コア
· 業界標準の DDR4 メモリ用 DIMM スロット 24 個、2666 MHz のメモリアクセス速度をサポート、合計で最大 1.5 TB のメモリ容量(64 GB DIMM 使用時)
· 10 台のホットプラグ対応 SAS および SATA HDD または SSD
· Cisco UCS VIC 1387、2 ポート、80 ギガビット イーサネットおよび FCoE:モジュラ型 (mLOM) 対応メザニン アダプタ
· Cisco FlexStorage ローカル ドライブ ストレージ サブシステム。柔軟なブートおよびローカル
ストレージ機能により、ハイパーバイザのインストールおよび起動が可能
· エンタープライズ クラスのパススルー RAID コントローラ
· Cisco FlexStorage モジュールの追加、変更、削除が容易
Cisco HyperFlex HXAF240c-M5SX ノード
この最適化されたキャパシティ構成には、最低限 3 つのノードが含まれています。クラスタ ストレージを補強
する SED SATA または SAS SSD ドライブが最大 23 台、240 GB SATA SSD ハウスキーピング ドライブが
1 台、400 GB SAS SSD キャッシング ドライブが 1 台、起動ドライブとして動作する M.2 SATA SSD
ドライブが 1 台構成可能です。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HXAF240c M5 ノード スペック シートを参照してください。
図 13 HXAF240c-M4SX ノード


HyperFlex HX220C-M4S ハイブリッド ノード
この設置面積の少ない構成には、最低限 3 つのノードが含まれており、クラスタ ストレージの容量を補強する 1.2 テラバイト (TB) SAS ドライブが 6 台、240 GB SSD ハウスキーピング ドライブが 1 台、480 GB SAS SSD キャッシング ドライブが 1 台、起動ドライブとして動作する 240 Gb SATA M.2 SSD 1 台構成可能です。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HX220c M5 ノード スペック シートを参照してください。
図 14 HX220C-M4S ノード


HyperFlex HX240C-M4SX ハイブリッド ノード
この最適化されたキャパシティ構成には、最低限 3 つのノードが含まれています。クラスタ ストレージを補強
する 1.2 TB SAS ドライブが最大 23 台、240 GB SSD ハウスキーピング ドライブが 1 台、1.6 TB SSD
キャッシング ドライブが 1 台、起動ドライブとして動作する 240 Gb SATA M.2 SSD が 1 台構成可能です。詳細については、Cisco HyperFlex HX240c M5 ノードのスペック シートを参照してください。
図 15 HX240C-M5SX ノード


Cisco VIC 1387 MLOM インターフェイス カード
Cisco UCS 仮想インターフェイス カード (VIC) 1387 は、Cisco UCS HX シリーズ ラック サーバに搭載可能なカードで、拡張された着脱可能小型フォームファクタ (QSFP+) の 40 Gbps イーサネットおよび Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) を 2 ポート搭載したモジュール型 LAN On Motherboard (mLOM) アダプタです (図 11)。mLOM スロットを使用すれば PCIe スロットを使用せずに Cisco VIC を構成できるため、I/O の拡張性が向上します。シスコの次世代統合型ネットワーク アダプタ (CNA) テクノロジーを取り入れることで、将来の機能リリースにおける投資を保護します。このカードにより、ポリシーベースでステートレス、かつ俊敏性に優れたサーバ インフラストラクチャが実現します。PCIe 標準準拠のインターフェイスを最大 256 個までホストに提供可能で、ネットワーク インターフェイス カード (NIC) またはホスト バス アダプタ (HBA) として動的に構成することができます。カードの特性は、ブート時にサーバに関連付けられたサービス プロファイルを使用して動的に設定されます。PCIe インターフェイスの番号、タイプ(NIC または HBA)、ID(MAC アドレスおよび World Wide Name (WWN))、フェールオーバー ポリシー、帯域幅、Quality of Service (QoS) ポリシーは、すべてサービス プロファイルから決定されます。
図 16 Cisco VIC 1387 mLOM カード

Cisco HyperFlex コンピューティング ノード
Cisco UCS B200 M5 ブレード
ワークロードに対して、コンピューティング リソースやメモリ リソースを追加する必要が生じたが、追加できるストレージ容量がない場合には、コンピューティング専用のハイブリッド クラスタ構成を使用することができます。この構成を使用する場合には、HyperFlex コンバージド ノードが最小で 3 台(最大で 16 台)と、追加の
コンピューティング容量として Cisco UCS B200-M5 ブレード サーバが 1 ~ 16 台必要になります。HX
シリーズ ノードは前述のように設定し、Cisco UCS B200 M5 サーバにはブート ドライブが搭載されています。Cisco UCS B200 M5 コンピューティング ノードを使用するは、Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード サーバ シャーシ、および Cisco UCS 2300/2200 シリーズ ファブリック エクステンダのペアも必要です。詳細については、Cisco UCS B200 M5 ブレード サーバ スペック シートを参照してください。

Cisco VIC1340 コンバージド ネットワーク アダプタ
Cisco UCS 仮想インターフェイス カード (VIC) 1340(図 18)は、Cisco UCS B シリーズ ブレード サーバの M4 世代に特化して設計された、2 ポート 40 Gbps イーサネットまたはデュアル 10 Gbps イーサネット X 4、Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) 対応のモジュール型 LAN on Motherboard (mLOM) です。オプションのポート エクスパンダと組み合わせて使用すると、40 Gbps イーサネットの 2 つのポートに対して Cisco UCS VIC 1340 の機能を有効にできます。
Cisco UCS VIC 1340 では、ポリシーベースでステートレス、かつ俊敏性の高いサーバ インフラストラクチャを構築できます。このインフラストラクチャは、ネットワーク インターフェイス カード (NIC) またはホスト バス アダプタ (HBA) として動的に設定可能な、最大 256 の PCIe 規格準拠インターフェイスをホストに提供します。さらに、Cisco UCS VIC 1340 は Cisco UCS ファブリック インターコネクト ポートを仮想マシンに拡張し、サーバ仮想化の展開および管理を簡素化する Cisco® Data Center Virtual Machine Fabric Extender (VM-FEX) をサポートします。

図 19 では、Cisco UCS B シリーズ B200 M4 ブレード サーバに搭載された Cisco UCS VIC 1340 仮想インターフェイス カードを示しています。
図 19 Cisco UCS B200 M5 に搭載された Cisco UCS VIC 1340

Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード シャーシ
Cisco UCS 5100 シリーズ ブレード サーバ シャーシは、Cisco Unified Computing System の重要な構成要素
であり、スケーラブルで柔軟なブレード サーバ シャーシを提供します。Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード サーバ
シャーシは、高さが 6 ラック ユニット (6 RU) で、業界標準の 19 インチ ラックシステムに搭載可能です。1 台
のシャーシに最大で 8 個のハーフ幅の Cisco UCS B シリーズ ブレード サーバを格納できます。また、
ハーフ幅とフル幅の両方のブレードのフォーム ファクタに対応できます。
ホットスワップ可能な 4 基の単相電源装置にシャーシの前面からアクセスできます。これらの電源装置の効率は 92 % で、非冗長、N + 1 冗長、およびグリッド冗長の各構成をサポートするように設定できます。シャーシの
背面には、8 基のホットスワップ可能なファン、4 つの電源コネクタ(各電源装置に 1 つ)、Cisco UCS
ファブリック エクステンダ用の 2 つの I/O ベイがあります。パッシブ ミッド プレーンでは、各ファブリック
エクステンダのサーバ スロットあたりで最大 40 Gbps の I/O 帯域幅が提供されます。このシャーシは、
40 ギガビット イーサネット標準もサポート可能です。
図 20 Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード シャーシ(前面と背面)

Cisco UCS 2304XP ファブリック エクステンダ
Cisco UCS 2304 ファブリック エクステンダは、ファブリック インターコネクトとブレード シャーシに格納
されている各ブレードサーバの間でユニファイド ファブリック接続するモジュールとして組み込みます。
40 ギガビット イーサネット接続を提供し、接続配線、診断、サーバ ネットワーク管理を簡素化します。本製品は第 3 世代の I/O モジュール (IOM) となり、第 2 世代の Cisco UCS 2200 シリーズ ファブリック エクステンダと
共通のモジュールサイズで、現在提供中の Cisco UCS 5108 ブレード サーバ シャーシと互換性を持ちます。
Cisco UCS 2304 によって、Cisco UCS 6300 シリーズ ファブリック インターコネクトと Cisco UCS 5100
シリーズ ブレード サーバ シャーシとの間で I/O ファブリック接続され、すべてのブレードサーバとシャーシが
ロスレスで、ユーザ定義可能な Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) ファブリックによって1 つに結ばれます。ファブリック エクステンダは分散型ラインカードと同様の製品であるため、スイッチング処理は行わず、
ファブリック インターコネクトの拡張部分として管理されます。このようなアプローチを取ることで、ブレード シャーシから各種スイッチが取り払われ、システム全体構造の複雑さが低減します。また、Cisco UCS の規模を拡大してシャーシの数を増やしても、必要なスイッチの数が増えることはないので、TCO が削減され、すべてのシャーシを可用性の高い 1 つの管理ドメインとして扱うことが可能になります。
Cisco UCS 2304 ではファブリック インターコネクトと併せてシャーシ環境(電源、ファン、ブレード)も管理できます。したがって、シャーシごとに管理のためのモジュールを構成する必要もありません。
Cisco UCS 2304 ファブリック エクステンダは Cisco UCS 5100 シリーズ ブレードシャーシの背面に取り付けられます。Cisco UCS 5100 シリーズ ブレードシャーシ 1 台あたり最大 22 台のファブリック エクステンダを搭載でき、接続帯域の拡大と冗長性を実現します(図 22)。
Cisco UCS 2304 ファブリック エクステンダには 40 ギガビット イーサネット、FCoE 対応の Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable (QSFP+) ポートが 4 個あり、これらのポートでブレード シャーシとファブリック
インターコネクトに接続します。それぞれの Cisco UCS 2304 では、40 ギガビット イーサネット ポートが 1 基あり、ミッド プレーンを経由してシャーシのハーフ幅スロットにそれぞれ接続されます。その結果、合計で 40G X 8 のコンピューティング用インターフェイスが提供されます。通常は冗長性を得るためファブリック
エクステンダをペアで構成し、その 2 台により、最大 320 Gbps の I/O をシャーシに提供することが可能です。
図 21 Cisco UCS 2304XP ファブリック エクステンダ

Cisco UCS C220 M5 ラック サーバ
Cisco UCS C220 M5 ラック サーバは、1 RU フォーム ファクタのエンタープライズクラスの
インフラストラクチャ サーバです。インテル Xeon スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサー製品ファミリと
次世代の DDR4 メモリが組み込まれており、12 Gbps の SAS スループットにより、非常に高いパフォーマンスと効率性を実現します。ワークロードに対して追加のコンピューティング リソースやメモリ リソースが必要になる一方でストレージ容量を追加できない場合にも、HX シリーズ コンバージド ノードの数に応じて、Cisco UCS C220 M5 ラック サーバをコンピューティング専用ハイブリッド HX クラスタの構築に使用することができます。この構成には、HX シリーズ コンバージド ノードが最小で 3 台(最大で 16 台)と、追加のコンピューティング容量として Cisco UCS C220-M4 ラック サーバが 1 ~ 16 台が含まれています。
図 22 Cisco UCS C220 M5 ラック サーバ

Cisco UCS C240 M5 ラック サーバ
Cisco UCS C240 M5 ラック サーバは、2 ソケット、2 ラック ユニット (2RU) フォーム ファクタの
エンタープライズクラスのサーバです。インテル Xeon スケーラブル ファミリー プロセッサー製品ファミリと次世代の DDR4 メモリが組み込まれており、12 Gbps の SAS スループットにより、非常に高いパフォーマンスと、多岐にわたるストレージと I/O の集中するインフラストラクチャ ワークロードに対する優れた拡張性を提供します。Cisco UCS C240 M5 ラック サーバは、HX シリーズ コンバージド ノードの数に応じて、コンピューティング リソースとメモリ リソースを追加することで、コンピューティング専用ハイブリッド HX クラスタの拡張に使用することができます。この構成には、HX シリーズ コンバージド ノードが最小で 3 台(最大で 16 台)と、
追加のコンピューティング容量として Cisco UCS C240-M4 ラック サーバが 1 ~ 16 台が含まれています。
図 23 Cisco UCS C240 M5 ラック サーバ

Cisco HyperFlex コンバージド データ プラットフォーム ソフトウェア
HX データ プラットフォームは専用の高性能な分散ファイルシステムで、多岐にわたるエンタープライズクラス データ管理サービスを提供します。データ プラットフォームの技術革新により、分散ストレージ技術が再定義され、従来のハイパーコンバージド インフラストラクチャを凌ぐ性能を発揮します。このデータ プラットフォームにはエンタープライズ共有ストレージ システムに期待されるすべての機能があるため、複雑なファイバ チャネル ストレージ ネットワークとデバイスの設定や管理をする必要がなくなります。このプラットフォームは操作を
簡素化し、データの可用性を保証します。エンタープライズクラスのストレージ機能には、次のものがあります。
· レプリケーションがクラスタ全体のデータを複製するため、単一または複数のコンポーネントに障害が発生した場合にも、データの可用性は影響を受けません(設定されたレプリケーション ファクタの設定により
ます)。
· 重複排除は常にオンになっているので、仮想クラスタ内のストレージ要件を削減できます。仮想クラスタ内では、クライアント仮想マシンにおける複数のオペレーティング システムのインスタンスが複製された
大量のデータ アクセスを提供します。
· 圧縮:データ ストレージ使用量を削減し、コストを削減します。ログ構造のファイル システムは、
さまざまなサイズのブロックを保存し、内部のフラグメンテーションを減らすよう設計されています。
· シン プロビジョニング:実際に利用する必要性が生じるまでストレージ スペースを消費しないため、
データ ボリュームの増加を抑制し、ストレージに「成長に合わせて投資」できます。
· 高速でスペース効率の高いクローン機能により、ストレージ ボリュームを迅速に複製可能です。そのため、仮想マシンをメタデータの操作だけで複製でき、実際のデータ コピーは書き込み操作に対してのみ実行されます。
· スナップショットはバックアップとリモートレプリケーション操作を促進し、常時「オン」状態となって
いるため、データ可用性のニーズに対応します。
Cisco HyperFlex Connect HTML5 対応の管理 Web ページ
Cisco HyperFlex の主要な管理ツールとして、新しい HTML 5 ベースの Web UI を使用できます。これは
クラスタ上で一元化された制御ポイントとして機能します。管理者はボリュームを作成し、データ
プラットフォームの状態をモニタリングし、リソースの使用率を管理できます。またこのデータを使用して、クラスタをいつ拡張する必要があるかを予測することもできます。HyperFlex Connect UI を使用するには、Web ブラウザから HyperFlex クラスタの IP アドレス http://<hx controller cluster ip> にアクセスします。
Cisco Intersight 管理 Web ページ
Cisco Intersight は、IT 運用管理 (ITOM) を単純化および自動化し、日常的な業務作業をより容易により効率的
にします。Cisco Intersight クラウド ベース プラットフォームを通じて、Cisco UCS および HyperFlex
システムの適応型管理という考え方をさらに拡張します。データセンターからエッジまでの IT インフラストラクチャの自動操作、簡素化と効率性を提供します。


図 24 HyperFlex Connect GUI

レプリケーション ファクタ
各ストレージ ブロックで重複する複製の数に関するポリシーは、クラスタのセットアップ時に選択され、
「レプリケーション ファクタ」 (RF) と呼ばれます。
· レプリケーション ファクタ RF3:ストレージ層に対して I/O 書き込みがあるたびに、書き込まれた
ブロックからさらに 2 つの複製が追加され、別の場所に保存されます。つまりブロックの複製が合計 3 つ作成されます。ブロックの各複製が同じディスク上、またはクラスタ上の同じノードに複数保存されない
ようにブロックが分散されます。この仕組みにより、2 つのノード全体で同時に障害が発生してもデータ
損失が発生せず、バックアップなどのリカバリ プロセスによる復元が可能になります。
· レプリケーション ファクタ RF2:ストレージ層に対して I/O 書き込みがあるたびに、書き込まれた
ブロックからさらに 1 つの複製が追加され、別の場所に保存されます。つまりブロックの複製が合計 2 つ作成されます。ブロックの各複製が同じディスク上、またはクラスタ上の同じノードに複数保存されない
ようにブロックが分散されます。この仕組みにより、1 つのノード全体で障害が発生してもデータ損失が
発生せず、バックアップなどのリカバリ プロセスによる復元が可能になります。
データ分散化
キャッシング レイヤを使用してパフォーマンスが最適化されるように、着信データがクラスタ内のすべての
ノードに分散されます。すべてのノードに均等に保存されているストライプ ユニットに対して、新しいデータをマッピングすることで、効果的なデータ分散化を実現します。データ レプリカの数は、設定したポリシーによって決まります。アプリケーションがデータを書き込むと、そのデータは関連する情報ブロックが含まれている
ストライプ ユニットに基づいて適切なノードに送信されます。このデータ分散化アプローチを、同時に複数のストリームを書き込める機能と組み合わせることで、ネットワークとストレージのホット スポットを回避できます。また、仮想マシンの場所にかかわらず同じ I/O パフォーマンスを実現でき、ワークロード配置の柔軟性も向上します。これは、データをローカルで使用するアプローチを取り、利用可能なネットワーキング リソースと I/O リソースを完全に使用せず、ホット スポットに対して脆弱な他のアーキテクチャとは逆のアプローチになります。
Hyper-V Cluster Optimization などのツールを使用して仮想マシンを新しい場所に移動する場合に、Cisco HyperFlex HX データ プラットフォームではデータを移動する必要がありません。このアプローチにより、
システム間での仮想マシンの移動に伴う影響やコストを大幅に削減できます。
データ操作
データ プラットフォームに分散型のログ構造ファイル システムを採用することで、ノードの構成に応じて
キャッシング容量やストレージ容量の処理方法が変化します。
オールフラッシュメモリ構成の場合、データ プラットフォームでは SSD にキャッシング レイヤが使用され、
書き込み時の処理速度を向上させます。そして、SSD でキャパシティ レイヤが構成され、読み込み要求が SSD で取得されたデータに対して、直接実行されます。読み込み処理の速度を向上させるために、専用の読み込み
キャッシュを用意する必要はありません。
新しいデータは、可用性要件に対応できるように複数のノードにわたってストライプされます(通常は 2 台または 3 台のノードです)。設定したポリシーに基づき、新しい書き込み操作は、クラスタ内の別のノードにある SSD ドライブに複製されます。その後で、永続的な書き込み操作として認識されます。このアプローチにより、SSD やノードで障害が発生した場合のデータ損失の可能性を低減できます。なお、データを長期間格納する場合には、
書き込み操作がオールフラッシュ メモリ構成にあるキャパシティ レイヤの SSD に移行されます。
ログ構造ファイル システムでは、2 つのうち 1 つの書き込みログ(RF=3 の場合は 3 つのうち 1 つ)に、
容量が満たされるまで順に書き込みが行われます。そして、最初のレイヤからキャパシティ レイヤにデータが
移行される際に、他の書き込みログに切り替えられます。既存のデータが(論理的に)上書きされる場合、ログ
構造のアプローチではシンプルに新しいブロックを付加し、メタデータを更新します。このレイアウトの利点は、シーク操作に大きく時間を費やすことがないように SSD を構成できることです。これにより、データへの書き込み操作と上書き操作がランダムに実行されることによるフラッシュ メディア上のトータルの書き込み処理数を削減し、SSD における書き込み操作の増幅レベルを低減させます。
各ノードのキャパシティ レイヤに移行されたデータは、重複排除されて圧縮されます。このプロセスは書き込み操作が認識された後に行われるため、これらの操作でパフォーマンスに悪影響が及ぶことはありません。小さな
重複排除ブロック サイズにより、重複排除率が向上します。さらに圧縮によりデータ スペースを削減します。
その後、データはキャパシティ レイヤに移動され、書き込みキャッシュ セグメントは解放されて再利用可能に
なります(図 25)。
図 25 Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform 書き込みオペレーション フロー
キャパシティ レイヤから頻繁に読み取られる直近のデータであるホット データ セットは、メモリにキャッシュ
されます。しかしながら、オールフラッシュ構成では、高性能の SSD にすでに永続型のデータ コピーがある
ことから、そのようなキャッシュにはパフォーマンス上の利点がなく、キャッシュの読み込みに SSD は使用されません。これらの構成では、SSD で読み込みキャッシュを使用するとボトルネックとなり、SSD 全体で集約された帯域幅を使用する際の妨げとなる可能性があります。
データ最適化
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform には、精密なインライン重複排除や可変ブロック インライン圧縮が搭載されており、キャッシュ(SSD、メモリ)レイヤおよびキャパシティ(SSD または HDD)レイヤのオブジェクトに
対して常に有効になっています。他社のソリューションでは、パフォーマンス維持のためにこれらの機能を無効にする必要があります。一方、シスコのデータ プラットフォームの重複排除と圧縮機能は、パフォーマンスを維持、強化し、物理ストレージのキャパシティ要件を大幅に削減できるように設計されています。
データ重複排除
データ重複排除は、クラスタ内のすべてのストレージ(メモリ、SSD ドライブを含む)で使用されます。この
プラットフォームは、特許出願中の Top-K Majority アルゴリズムを基盤とし、実証的研究の成果を活用しています。実証的研究では、小さなデータ ブロックに分割し、少数のデータ ブロックに基づけば、ほとんどのデータは大幅に重複排除できる可能性があることが示されています。頻繁に使用されるブロックのみに対して
フィンガープリントとインデックスを作成することにより、少量のメモリで高い重複排除率を実現でき、クラスタ ノード内の価値の高いリソースであるメモリ使用量を節約できます(図 26)。
図 26 Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform はパフォーマンスに影響を与えずにデータ ストレージを最適化
インライン圧縮
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform は、データ セットに対して高性能なインライン圧縮を使用し、ストレージ
容量を節約します。他の製品も圧縮機能を提供していますが、パフォーマンスに悪影響を及ぼす場合が少なくありません。一方、シスコのデータ プラットフォームは CPU オフロード指示を使用して、圧縮操作による
パフォーマンスへの影響を軽減します。さらに、ログ構造の分散オブジェクト レイヤは、以前に圧縮されたデータの変更(書き込み操作)に影響を及ぼしません。新規の変更は圧縮されて新しい場所に書き込まれ、既存の(古い)データは削除用にマークされます(そのデータをスナップショット内で保持する必要がある場合を除きます)。
書き込み操作の前に、変更対象のデータを読み取る必要はありません。一般的には読み取り、変更、書き込み
という手順が必要ですが、この機能はその手順に伴う悪影響を回避し、書き込みパフォーマンスを大幅に向上させます。
ログ構造の分散オブジェクト
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform では、ログ構造の分散オブジェクト ストア レイヤにより、データを
グループ化して圧縮します。データは、重複排除エンジンでフィルタされ、自己アドレス可能なオブジェクトになります。これらのオブジェクトは、ログ構造でディスクに順次書き込まれます。すべての新しい I/O(ランダム I/O を含む)は、キャッシング層(SSD、メモリ)および永続層(SSD または HDD)の両方に順次書き込まれます。オブジェクトはクラスタ内のすべてのノードにわたって分散されるため、ストレージ容量を均等に使用できます。
シーケンシャル レイアウトを使用することで、プラットフォームのフラッシュ メモリの耐久性を向上させることができます。読み取り、変更、書き込みという手順ではないため、圧縮、スナップショット、複製操作の
パフォーマンスには影響がほとんどないか、まったくありません。また、全体的なパフォーマンスに対しても同様です。
データ ブロックはオブジェクトに圧縮され、固定サイズのセグメント内に順次配置されます。次に、それらの
セグメントはログ構造で順次配置されます(図 27)。ログ構造セグメント内の圧縮された各オブジェクトは、キーを使用して一意にアドレス可能です。各キーはフィンガープリントされ、チェックサムと保存されており、高度なデータ整合性を実現します。また、オブジェクトが時系列で書き込まれるため、このプラットフォームはメディアやノードの障害から迅速に回復できます。障害が発生してデータが削除された場合、その時点より後にシステムが受信したデータのみを再度書き込めば回復できるからです。
図 27 Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform はパフォーマンスに影響を与えずにデータ ストレージを最適化
暗号化
セキュアな状態で暗号化されたストレージにより、データ プラットフォームのキャッシング レイヤと永続型
レイヤの両方を随時暗号化します。エンタープライズ キー管理ソフトウェアによる統合、またはパスフレーズで保護されたキーによる統合を通じて、保管中のデータを暗号化することで、HIPAA、PCI DSS、FISMA、SOX 規制に準拠できます。プラットフォーム自体が連邦情報処理標準 (FIPS) 140-1 に沿うように強化され、暗号化ドライブにキー管理の仕組みを備えることで FIPS 140-2 標準にも準拠します。
データ サービス
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform では、スペース効率の高いデータ サービスがスケーラブルに実装されています。これらのサービスには、シン プロビジョニング、スペース再利用、ポインタベースのスナップショット、
クローンが含まれ、パフォーマンスには影響が及びません。
シン プロビジョニング
このプラットフォームでは、予測に基づいてディスク容量を購入してインストールする必要がないため、長期間使用されないままになるリスクを避けられ、ストレージを効率的に使用できます。仮想データ コンテナは、任意の量の論理スペースをアプリケーションに示せます。一方、必要な物理記憶域の量は、書き込まれるデータによって決定されます。ビジネス要件に応じて、既存ノードのストレージを拡張したり、ストレージ集約型ノードを追加してクラスタを拡張したりできます。必要になる前の段階で容量確保のためにストレージを購入しておく必要性はなくなります。
スナップショット
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform はメタデータベースのゼロコピー スナップショットを使用して、
バックアップ操作やリモート複製を容易にします。これらの機能は、データを常時利用できる必要がある企業にとって極めて重要です。スペース効率の高いスナップショットにより、物理ストレージ容量の消費を心配せずに、データのオンライン バックアップを頻繁に実行できます。データはオフライン移動や、これらのスナップショットからの迅速な復元が可能です。
· 高速なスナップショットの更新:スナップショットに変更されたデータが含まれている場合、新しい場所に書き込まれ、メタデータが更新されます。読み取り、変更、書き込みという手順を実行する必要はありません。
· 高速なスナップショットの削除:スナップショットは迅速に削除できます。このプラットフォームでは、SSD 上の少量のメタデータを削除するだけで済みます。デルタディスク技術を使用するソリューションで必要となる、長時間の統合プロセスは不要です。
· 柔軟なスナップショット:Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform を使用すると、個別のファイル ベースで
スナップショットを作成できます。仮想環境内で、これらのファイルは仮想マシンのドライブにマッピングされます。柔軟に異なる仮想マシンに異なるスナップショット ポリシーを適用できます。
多くの基本的なバックアップ アプリケーションでは、データ セット全体、または前回のバックアップ以降に変更されたブロックが、ストレージあるいはオペレーティング システムが処理可能な速度で読み取られます。この
場合、HyperFlex が Cisco UCS 上に 10GbE で構築されていることから、複数のバックアップ スループットが
数ギガビット/秒単位となり、パフォーマンスに影響が生じる可能性があります。Windows Server Backup などの基本的なバックアップ アプリケーション、特に初回のバックアップで変更ブロック トラッキングなどが行われ
ない場合には、ピーク時以外の時間にスケジュールする必要があります。
Veeam Backup and Replication v9.5 などのフル機能のバックアップ アプリケーションでは、バックアップ
アプリケーションが利用できるスループットを制限して、遅延の影響を受けやすいアプリケーションを稼働時間中に保護する機能があります。v9.5 Update 2 のリリースによって、Veeam は HX のネイティブ スナップショットを統合した製品になりました。HX のネイティブ スナップショットでは、デルタ ディスク スナップショットに
よるパフォーマンスの低下が起こらず、スナップショットを削除する際の統合作用に影響を与えるサイズの
大きなディスク IO が発生しません。
SQL の管理者にとって特に重要となるのは、Veeam Explorer for SQL です。Microsoft VSS フレームワーク内
でのトランザクション レベルを回復させることができます。Veeam Explorer for SQL Server では SQL Server データベースの復元が可能で、バックアップ復元ポイントから、特定の時点までのログ再生から、特定の
トランザクションまでのログ再生から、という 3 つの方法があります。その際に、VM または SQL Server を
オフラインにする必要はありません。
高速でスペース効率の高いクローン
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform では、クローンは書き込み可能なスナップショットです。クローンを使用
すると、テストや開発環境用に、仮想デスクトップやアプリケーションなどの項目を迅速にプロビジョニングできます。これらの高速でスペース効率の高いクローンにより、ストレージ ボリュームを迅速に複製可能です。そのため、仮想マシンをメタデータの操作だけで複製でき、実際のデータ コピーは書き込み操作に対してのみ実行されます。このアプローチでは、何百個ものクローンの作成や削除を数分で行えます。フルコピー方式と比較すると、このアプローチは時間を大幅に節約し、IT の俊敏性や生産性を高められます。
クローンは作成時に重複排除されます。それぞれのクローンに差が生じ始めた場合は、共通するデータは共有され、固有のデータのみが新たな記憶域に保存されます。差が生じたクローン内にあるデータ重複は、重複排除エンジンが排除し、クローンのストレージ フットプリントをさらに削減します。
データ レプリケーションと可用性
Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform では、ログ構造の分散オブジェクト レイヤが新しいデータを複製し、データの可用性を高めます。設定したポリシーに基づき、書き込みキャッシュに書き込まれたデータは、異なるノードにある 1 台または 2 台の SSD ドライブに同時に複製されます。その後で、書き込み操作がアプリケーションに認識されます。このアプローチにより、新しい書き込みが迅速に認識されるとともに、SSD やノードの障害から
データを保護できます。SSD またはノードで障害が発生した場合、データの利用可能なコピーを使用して、別の SSD ドライブまたはノード上でレプリカが迅速に再作成されます。
ログ構造の分散オブジェクト レイヤは、書き込みキャッシュからキャパシティ レイヤに移動されたデータも複製します。この複製されたデータは、先ほどと同様に、SSD やノードの障害から保護されています。2 つの
レプリカ(合計 3 つのデータ コピー)があるため、クラスタは 2 台の SSD ドライブ、または 2 台のノードで、関連性のない障害が発生しても対応でき、データ損失のリスクがありません。関連性のない障害とは、複数の物理ノードで発生する障害のことです。同じノード上で発生した障害は、同じデータのコピーに影響することから、単一の障害として扱われます。たとえば、ノードのあるディスクで障害が起き、続いて同じノードの別のディスクで障害が発生した場合、これらの関連する障害は、そのシステムでは 1 件の障害とみなされます。この場合、クラスタは、別のノードで関連性のない障害が発生しても耐えられる場合があります。フォールトトレラントな構成および設定の一覧については、Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform のシステム管理者ガイドを参照してください。
Cisco HyperFlex HX コントローラ ソフトウェアで問題が発生した場合、そのノード内にあるアプリケーション
からのデータ要求は、クラスタ内の別のコントローラに自動で転送されます。この機能を使用すると、クラスタやデータの可用性に影響を与えずに、コントローラ ソフトウェアのアップグレードやメンテナンスをローリング
方式で実施できます。この自己修復機能は、Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform が実稼働アプリケーションに
最適な理由の 1 つです。
さらに、ネイティブ レプリケーションにより、ローカルまたはリモート クラスタに整合性のとれたクラスタ
データが転送されます。ネイティブ レプリケーションを使用することで、ローカルまたはリモート環境の
スナップショットを取得したり、特定の時点のコピーを格納したりすることができ、バックアップやディザスタ
リカバリにもちいることができます。
データ リバランシング
分散ファイル システムには、堅牢なデータ リバランシング機能が必要です。Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform では、メタデータ アクセスでオーバーヘッドが生じず、リバランシングが極めて効率的です。リバランシングは、中断を伴わないオンライン プロセスであり、キャッシング レイヤと永続レイヤの両方で実行されます。データを詳細に特定して移動することで、ストレージ容量の使用を改善します。このプラットフォームでは、ノードや
ドライブが追加または削除された場合や、それらで障害が発生した場合に、既存データが自動でリバランスされます。新しいノードがクラスタに追加されると、その容量とパフォーマンスを新しいデータと既存データで利用可能になります。リバランシング エンジンは、既存データを新しいノードに分配し、クラスタ内にあるすべてのノードの容量とパフォーマンスが均等に使用されるようにします。ノードで障害が発生した場合や、ノードがクラスタから削除された場合は、リバランシング エンジンがデータのコピーを再構築し、それらのノードからクラスタ内にある利用可能なノードに分配します。
オンライン アップグレード
Cisco HyperFlex HX シリーズ システムと HX データ プラットフォームではオンライン アップグレードがサ
ポートされており、業務を中断することなく、環境の更新や拡張を行えます。プロセッサ性能の追加、BIOS、
ドライバ、ハイパーバイザ、ファームウェアのダウンロードおよびインストール、Cisco UCS Manager の
アップデート、強化、バグ修正などの物理リソースの拡張を容易に行うことができます。
Cisco Nexus 93108YCPX スイッチ
Cisco Nexus 93180YC-EX スイッチは、48 個の 1/10/25 Gbps Small Form Pluggable Plus (SFP+) ポートと 6 個の 40/100 Gbps Quad SFP+ (QSFP+) アップリンク ポートを備えています。すべてのポートはライン
レートであり、1 ラックユニット (1RU) のフォーム ファクタで 3.6 Tbps のスループットを提供します。
柔軟なアーキテクチャ
· 従来型とリーフ/スパイン型の両方のアーキテクチャに対応した、トップオブラック、ファブリック
エクステンド アグリゲーション、ミドルオブロー ファイバベースのサーバ アクセス接続を含む
· Cisco ACI アーキテクチャのリーフ ノード サポートを含む
· Cisco Nexus 2000 ファブリック エクステンダのサポートにより、拡張性の向上と管理のシンプル化を実現
多機能
· パフォーマンス、復元力、拡張性、管理性、およびプログラマビリティを確保するように設計された Cisco NX-OS ソフトウェアの改良バージョン
· ACI 対応インフラストラクチャにより、ユーザが自動化されたポリシーベースでのシステム管理を活用可能
· ネットワーク サービスを提供する仮想拡張 LAN (VXLAN) ルーティング
· ライン レートでのデータ収集による充実したトラフィック フローのテレメトリ
· ポート単位およびキュー単位でリアルタイムにバッファ利用状態を把握し、トラフィックのマイクロ
バーストやアプリケーションのトラフィック パターンをモニタリング可能
リアルタイムの可視化とテレメトリ
· Cisco Tetration Analytics プラットフォームと組み込みのハードウェア センサーによる、豊富な
トラフィック フロー テレメトリとライン レートでのデータ収集
· Cisco Nexus Data Broker によるネットワーク トラフィックのモニタリングと分析
· ポート単位およびキュー単位でリアルタイムにバッファの利用状態を把握し、トラフィックのマイクロ
バーストやアプリケーションのトラフィック パターンをモニタリング
高可用性と効率に優れた設計
· 高性能な非ブロック アーキテクチャ
· ホットアイル/コールドアイル型の構成への容易な導入
· ホットスワップ可能な冗長構成の電源モジュールおよびファン トレイ
運用のシンプル化
· Pre-boot Execution Environment (PXE) と Power-On Auto Provisioning (POAP) のサポートにより、
ソフトウェアのアップグレードと設定ファイルのインストールをシンプル化
· Puppet、Chef、Ansible などの DevOps ツールとスイッチの設定と自動化
· インテリジェントな API により、HTTP/HTTPS インフラストラクチャ上で実行する
リモート プロシージャ コール(RPC、JSON または XML)を介したスイッチ管理が可能
· Python スクリプトにより、スイッチのコマンドライン インターフェイス (CLI) へのプログラム的な
アクセスを提供
· ホット/コールド パッチとオンライン診断を含む
投資保護
· シスコの 40 GB 双方向トランシーバを使用し、40 ギガビット イーサネット用に既存の 10 ギガビット イーサネット ケーブル設備の再利用が可能
· 10 Gb/25 Gb でのアクセス接続および 40 Gb/100 Gb でのアップリンクをサポートすることで、より速い速度でのデータセンターのインフラストラクチャの移行と切り替えを促進
· 1 RU フォーム ファクタで 1.44 Tbps の帯域幅
· 1/10 Gbps SFP+ 固定ポート X 48
· アップリンク接続用の 40 Gbps QSFP+ 固定ポート X 6(QSFP to SFP または SFP+ アダプタ (QSA) を介して 10 Gb ポートに変換可能)
· 1 ~ 2 マイクロ秒の遅延
· 前面から背面、背面から前面への切り替えが可能なエアーフロー設定
· 80 PLUS プラチナ規格に準拠した、ホットスワップ可能な冗長構成の 1+1 電源モジュール
· ホットスワップ可能な冗長構成の 2+1 ファン トレイ
図 28 Cisco Nexus 93108YC スイッチ

Microsoft Hyper-V 2016
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 は、Windows ハイパーバイザ、Windows Server ドライバ モデル、
仮想化コンポーネントのみを含んだスタンドアロンの製品です。シンプルで信頼性の高い仮想化ソリューションを提供し、サーバ使用率の向上とコストの削減を支援します。
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 の Windows ハイパーバイザ テクノロジーは、Windows Server 2016 の Hyper-V ロールと同じものです。したがって、Windows Server 2016 の Hyper-V ロールで利用できる
コンテンツの大半は、Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2016 にも当てはまります。
Microsoft System Center 2016
このドキュメントでは、Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM)、および Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) のインストール手順については説明しません。SCOM および SCVMM 2016 を
インストールするには、Microsoft のガイドラインに従ってください。
· SCOM:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/scom/deploy-overview [英語]
· SCVMM:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/system-center/vmm/install-console [英語]
Citrix XenApp™ と XenDesktop™ 7.16
企業の IT 部門には、コストの管理、制御の一元化、企業のセキュリティ ポリシーの適用を行いつつ、Microsoft Windows アプリケーションやデスクトップのプロビジョニングを行うという課題が課せられています。デバイスの種類や使用可能なネットワーク帯域幅にかかわらず、あらゆる場所でユーザに Windows アプリケーションを
導入し、モバイル ワーカーの生産性を向上させます。Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 を使用することで、IT 部門は
データ資産を保護し、設備投資や運用コスト削減しながら、アプリケーションやデスクトップのプロビジョニングを効果的に制御できます。
XenDesktop 7.16 リリースでは、次のような利点を提供しています。
· あらゆる使用例をカバーした包括的な仮想デスクトップを配信。XenDesktop 7.16 リリースには、
XenApp のすべての機能が含まれ、ユーザに対してアプリケーションのみを提供したり、デスクトップ全体を提供したりすることができます。管理者は、同じ管理コンソールから、XenApp の公開済み
アプリケーションやデスクトップを展開(低コストで IT 制御を最大化)できますし、パーソナライズされた VDI デスクトップ(イメージの管理をシンプル化)を展開することもできます。Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 では、共通のポリシーと統合されたツールが利用して、インフラストラクチャ リソースとユーザ アクセスの両方を管理することができます。
· BYO (Bring Your Own) デバイスのサポートと選択のシンプル化。XenDesktop 7.16 では、企業の
何千もの Microsoft Windows ベース アプリケーションやモバイル デバイスに対して、最適化された
パフォーマンスと、ネイティブ感覚の操作感をもたらします。HDX テクノロジーにより、グラフィック
集約型の設計やエンジニアリング アプリケーションに対しても、「高解像度」のユーザ
エクスペリエンスを生み出します。
· アプリケーションおよびデスクトップ管理のコストと複雑さを低減。XenDesktop 7.16 により、IT 部門
が俊敏性に優れ、コスト効率の高いクラウド サービスを活用でき、季節的な需要の変動や突発的な
キャパシティの変化に対応できるようになります。IT 部門は、プライベートまたはパブリック クラウドに XenDesktop アプリケーションやデスクトップのワークロードを導入できます。
· 一元化による機密情報の保護。XenDesktop では、情報資産がデータセンターに存在することから、
アプリケーションの一元化や知的財産の保護と、データの利用を同時に行うことができ、企業データの損失リスクを軽減します。
· Virtual Delivery Agent の改善。XenDesktop 7.16 では、主要な改善項目として、ユニバーサル プリント サーバとドライバの強化、Windows 10 での HDX 3D Pro グラフィック アクセラレーションのサポートが行われています。
· ユーザの高解像度エクスペリエンスの改善。XenDesktop 7.16 では、画期的なディスプレイ プロトコル
の開発において、引き続き先駆的な取り組みが行われており、Thinwire ディスプレイ リモート処理
プロトコルの強化や HDX 3D Pro 用の Framehawk のサポートが実施されています。
Citrix XenApp と XenDesktop は、統合型アーキテクチャ上に構築されたアプリケーションおよびデスクトップ仮想化ソリューションです。管理が容易で、あらゆる組織のユーザのニーズを満たすのに十分な柔軟性を備えています。XenApp と XenDesktop には、IT タスクを簡素化して自動化する、共通の管理ツール セットがあります。オンプレミス導入と同じアーキテクチャと管理ツールを使用して、パブリック クラウド、プライベート クラウド、およびハイブリッド クラウドの導入を管理できます。
Citrix XenApp の機能を以下に示します。
· サーバ ベースのホスト型アプリケーションとも呼ばれる XenApp 公開アプリ:これは、Microsoft Windows サーバから任意のタイプのデバイス(Windows PC、Mac、スマートフォン、タブレットなど)にホストされるアプリケーションです。一部の XenApp エディションには、モバイル デバイス上での Windows アプリケーションのユーザ エクスペリエンスをさらに最適化するテクノロジーが組み込まれています。たとえば、ネイティブ モバイル デバイスのディスプレイ、ナビゲーション、コントロールを自動的に Windows アプリケーションに変換し、モバイル ネットワーク上のパフォーマンスを向上させ、開発者があらゆるモバイル環境にカスタム Windows アプリケーションを最適化できるようになっています。
· サーバ ホスト型デスクトップとも呼ばれる XenApp 公開デスクトップ:これは、Windows サーバ
オペレーティング システムからホストされる、低コストのロックダウン型 Windows 仮想デスクトップです。このデスクトップは、コール センターの従業員など、標準の一連作業を行うユーザに最適です。
· 仮想マシン ホスト型アプリケーション:これは、サーバ環境でホストできないアプリケーションのために Windows デスクトップ オペレーティング システムを実行しているマシンからホストされる
アプリケーションです。
· Microsoft App-V で提供される Windows アプリケーション:このアプリケーションは、他の XenApp
導入に使用される管理ツールと同じものを使用します。
· Citrix XenDesktop:重要な機能強化が行われ、お客様は Windows アプリケーションおよびデスクトップをモバイル サービスとして容易に配信でき、同時に管理の複雑さと関連コストの問題にも対応できます。このリリースの機能強化は、次のとおりです。
· XenApp と XenDesktop での製品アーキテクチャの統一:FlexCast Management Architecture (FMA)。
このリリースでは、ホステッド共有アプリケーション (RDS) と包括的な仮想デスクトップ (VDI) の両方を
提供する単一の管理インターフェイス セットが用意されています。Citrix XenApp ファームと XenDesktop ファームが別々にプロビジョニングされていた以前のリリースとは異なり、XenDesktop 7.16 リリースでは、管理者は単一のインフラストラクチャを導入し、一貫性のあるツール セットを使用して、混在する
アプリケーションとデスクトップのワークロードを管理することができます。
· クラウドへの導入の拡張をサポート。このリリースでは、Microsoft Azure、Amazon Web Services (AWS)、もしくは任意のクラウド プラットフォームを利用したパブリック クラウドまたはプライベート クラウド
から、ハイブリッド クラウドのプロビジョニングを行うことができます。クラウド導入は、従来の
オンプレミス インフラストラクチャ上の導入と同じ管理コンソールを通して、設定、管理、監視されます。
Citrix XenDesktop の機能を以下に示します。
· VDI デスクトップ:これらの仮想デスクトップは、1 つの共有サーバ ベースの環境で動作するのではなく、それぞれが Microsoft Windows デスクトップ オペレーティング システムを実行します。また、ユーザが自由にパーソナライズできる各ユーザ用のデスクトップを提供できます。
· ホスト型物理デスクトップ:このソリューションは、データセンター内から、ブレード サーバのような
強力な物理マシンへのセキュアなアクセスを提供するのに最適です。
· リモート PC アクセス:このソリューションを使用すれば、ユーザは、セキュアな XenDesktop 接続を
介してどこからでも物理 Windows PC にログインすることができます。
· サーバ VDI:これは、マルチテナント クラウド環境にホスト型デスクトップを提供するために設計されたソリューションです。
· ユーザが仮想デスクトップを使用し続けるための機能:これらの機能により、ユーザはネットワークに接続していなくても作業を続けることができます。
この製品リリースには、次の新機能や拡張機能が含まれています。
![]() XenDesktop の一部のエディションには、XenApp で利用できる機能が含まれます。
XenDesktop の一部のエディションには、XenApp で利用できる機能が含まれます。
ゾーン
複数の地点が広範囲に分散して WAN で接続されている配置の場合、ネットワークの遅延と信頼性が問題となり
ます。ゾーンを設定することで、リモート ロケーションのユーザがローカルのリソースに接続でき、WAN に
おける大きなセグメントを通過させることなく通信が行えます。また、ゾーンを使用することで、単一の Citrix Studio コンソール、Citrix Director、サイト データベースから効率的にサイトを管理することができます。これにより、導入、スタッフ配置、ライセンシング、リモート ロケーションの別のデータベースに含まれる追加のサイトのメンテナンスにかかるコストを削減できます。
ゾーンは、あらゆる規模の導入に役立ちます。ゾーンを使って、アプリケーションやデスクトップをエンド
ユーザの近くに配置することで、パフォーマンスが向上します。
詳細については、ゾーンに関する解説 [英語] を参照してください。
改善されたデータベース フローと設定
サイトの作成中にデータベースを設定する場合、サイト、ロギング、データベースのモニタリングで、別の場所を指定できるようになりました。設定後に、3 つのすべてのデータベースで、複数の場所が指定できます。以前の
リリースでは、3 つのデータベースがすべて同じアドレスで作成され、設定後に、サイト データベースに異なる
アドレスを指定することができませんでした。
サイトの作成時には、複数のデリバリ コントローラを設定後に同様に追加できるようになっています。以前の
リリースでは、サイトを作成した後にしかコントローラを追加できませんでした。
詳細については、データベースおよびコントローラの解説 [英語] を参照してください。
アプリケーションの制限
アプリケーションの制限を設定して、アプリケーションの使用を管理することができます。たとえば、
アプリケーションの制限を使用することで、アプリケーションを同時に利用できるユーザの数を管理できます。
同様に、リソース集約型アプリケーションの同時インスタンスの数を管理することもできます、これにより、
サーバ パフォーマンスを維持し、サービスの低下を防ぐことができます。
詳細については、アプリケーションの管理に関する解説 [英語] を参照してください。
マシンの更新または再起動のスケジュールの前に、複数の通知を送信
次のようなアクションが開始される前に、該当のマシンに通知メッセージを繰り返し送信するか、選択できるようになりました。
· 新しいマスター イメージを使用して、マシン カタログ内のマシンを更新
· 設定されたスケジュールに沿って、デリバリ グループ内のマシンを再起動
該当するマシンに、最初のメッセージを更新や再起動の始まる 15 分前に送信するよう指定した場合、それらが
開始されるまでに 5 分間隔で繰り返し送信されるメッセージも指定できます。
詳細については、マシン カタログの管理とデリバリ グループ内にあるマシンの管理の解説 [英語] を参照してください。
セッションのローミング管理用の API のサポート
デフォルトでは、セッションがユーザとクライアント デバイス間でローミングされます。ユーザがセッションを開始し、別のデバイスに移動すると、同じセッションが使用され、両方のデバイスでアプリケーションが利用可能となります。アプリケーションは、デバイスの種類や現在のセッションの場所にかかわらず、動作します。
アプリケーションに割り当てられたプリンタやその他のリソースについても同様です。
![]() セッションのローミングの調整を行う際に、PowerShell SDK を使用できるようになりました。これは、以前のリリースでは試験的な機能でした。
セッションのローミングの調整を行う際に、PowerShell SDK を使用できるようになりました。これは、以前のリリースでは試験的な機能でした。
詳細については、セッションに関する解説 [英語] を参照してください。
ハイパーバイザのテンプレートからの VM のプロビジョニング用 API のサポート
マシン カタログの作成または更新に PowerShell SDK を使用する場合、他のハイパーバイザ接続から
テンプレートを選択できるようになりました。これにより、現在利用できる VM イメージとスナップショットに
加えて、選択できるようになります。
新規およびその他のプラットフォームのサポート
すべてのサポート情報については、システム要件の解説 [英語] を参照してください。サード パーティ製品
バージョンのサポートについては、定期的に更新されます。
デフォルトでは、デリバリ コントローラをインストールする際に、SQL Server 2012 Express SP2 がインストールされます。SP1 はインストールされません。
コンポーネント インストーラにより、Microsoft Visual C++ ランタイムのより新しいバージョン(32 ビット/ 64 ビット Microsoft Visual C++ 2013、2010 SP1、2008 SP1)が自動的に導入されます。Visual C++ 2005 は導入されません。
Windows 10 で実行されているマシンには、Windows デスクトップ OS 用の Studio もしくは VDA をインストールできます。
Microsoft Azure の仮想化リソースへの接続も作成できます。
図 29 Citrix XenDesktop の論理アーキテクチャ
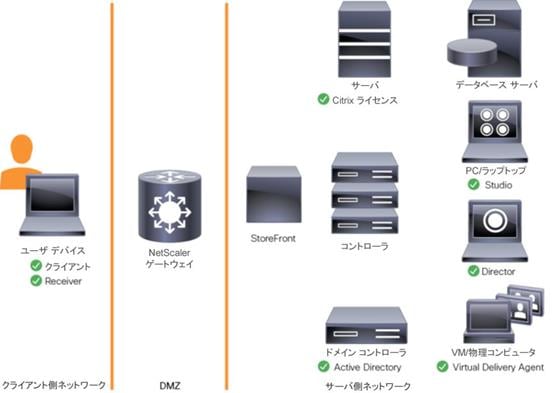
Cisco Unified Computing System の Citrix XenDesktop のアーキテクチャと設計、および Cisco HyperFlex のストレージ設計の基本
ユーザ デバイスのますます増加する多様な基盤、従来のデスクトップの管理における複雑さ、セキュリティ、
さらにはプログラムを機能させるための私物コンピュータの持ち込み (BYOC) など、仮想デスクトップ
ソリューションを検討するには多くの理由があります。仮想デスクトップ ソリューションを設計する際の最初の手順は、ユーザ コミュニティと、役割を正常に実行するために必要なタスクの種類を理解することです。次の
ユーザの分類があります。
· ナレッジ ワーカーは現在、ただオフィスで一日中作業するだけではありません。会議に出席し、支店を
訪れ、自宅やコーヒー ショップでさえも作業を行います。あらゆる場所で仕事するこのようなワーカーは、同じすべてのアプリケーションとデータに任意の場所からアクセスできることを求めています。
· 外部の請負業者は、ますます日常業務の一部となってきています。アプリケーションとデータの特定部分にアクセスする必要がありますが、管理者は、業者が使用するデバイスと作業する場所を依然としてほとんど制御できていません。このため、これらのユーザにデバイスを提供するコストと、これらのユーザに各自のデバイスからのアクセスを許可するセキュリティ リスクとが妥協点を見つける上での妨げになっています。
· タスク ワーカーは、明確に定義された一連のタスクを実行します。これらのワーカーは、少数の
アプリケーション セットにアクセスし、PC からの要件は限定されています。ただし、これらのワーカーは、顧客、パートナー、および従業員と対話するため、最も機密性の高いデータにアクセスします。
· モバイル ワーカーは、ネットワークに接続できるかどうかに関係なく、任意の場所から仮想デスクトップ
にアクセスできる必要があります。さらに、これらのワーカーは、自分の PC に独自のアプリケーションをインストールし、写真や音楽などの自身のデータを格納することによって、このようなデバイスを
パーソナライズできることを求めています。
· 共用ワークステーション ユーザは、多くの場合最先端の大学やビジネス コンピュータ ラボ、会議室や
トレーニング センターにいます。共用ワークステーション環境には、組織のニーズが変わった場合に、
上位に合わせて最新のオペレーティング システムとアプリケーションでデスクトップを再プロビジョニングするための一定の要件があります。
ユーザの分類を識別して、ユーザの分類ごとにビジネス要件を定義した後は、ユーザの要件に基づいて必要な仮想デスクトップのタイプを評価することが不可欠になります。ユーザごとに本質的には次の 5 つのデスクトップ
環境が考えられます。
· 従来の PC:従来の PC は、一般的にデスクトップ環境を構成していたもの(ローカルにオペレーティング
システムがインストールされた物理デバイス)です。
· ホステッド共有デスクトップ:ホステッド サーバベース デスクトップは、ユーザがデリバリ プロトコル
を介して対話するデスクトップです。ホステッド サーバベース デスクトップの場合、インストールされた単一のサーバ オペレーティング システム インスタンス(Microsoft Windows Server 2012 など)が複数
のユーザによって同時に共有されます。各ユーザは、デスクトップ「セッション」を受信し、隔離された
メモリ スペースで作業します。1 人のユーザによって行われた変更は他のユーザに影響を与える可能性があります。
· ホステッド仮想デスクトップ:ホステッド仮想デスクトップは、仮想化レイヤ (ESX) またはベアメタル ハードウェアのいずれかで実行される仮想デスクトップです。ユーザはデスクトップを使用して作業したり、デスクトップの前に座ったりするのではなく、デリバリ プロトコルを介して対話します。
· 発行済みアプリケーション:発行済みアプリケーションは Microsoft Session Host のみで実行され、
ユーザはデリバリ プロトコルを介して対話します。発行済みアプリケーションの場合、インストールされた単一のアプリケーション インスタンス(Microsoft など)が複数のユーザによって同時に共有されます。
各ユーザは、アプリケーション「セッション」を受信し、隔離されたメモリ スペースで作業します。
· ストリーミングされるアプリケーション:ストリーミングされるデスクトップやアプリケーションはユーザのローカル クライアント デバイスのみで実行され、要求に応じてサーバから送信されます。ユーザは
アプリケーションやデスクトップと直接対話しますが、リソースはネットワークに接続している場合にのみ使用できます。
· ローカル仮想デスクトップ:ローカル仮想デスクトップは、ユーザのローカル デバイスのみで実行される
デスクトップで、ネットワークから切断されているときも作動し続けます。この場合、ユーザのローカル
デバイスはタイプ 1 のハイパーバイザとして使用され、デバイスをネットワークに接続したときにデータ
センターと同期されます。
このドキュメントにおける検証の目的は、XenDesktop 仮想デスクトップと XenApp ホステッド共有
デスクトップ サーバの両方のセッションが検証することです。各項では、この環境の基本的な設計決定について説明します。
アプリケーションおよびデータの把握
デスクトップ ユーザ グループおよびサブグループの識別が終了したら、次のタスクとして、グループ
アプリケーションおよびデータ要件をカタログに登録する必要があります。この作業は、VDI 計画の中で最も時間のかかるプロセスの 1 つですが、VDI プロジェクトを成功させるには不可欠です。アプリケーションおよび
データを識別して同一の場所に配置しないと、パフォーマンスが低下します。
組織のさまざまなアプリケーションおよびデータのペアを分析するプロセスは、SalesForce.com などの包括的なクラウド アプリケーションが関連することによって複雑になる場合があります。このようなアプリケーション
およびデータの分析はこの Cisco Validated Design の処理対象ではありませんが、計画プロセスには含める必要があります。この重要な作業について組織を支援するサードパーティ ツールが各種提供されています。
プロジェクト計画とソリューション サイジングに関する確認事項の例
ユーザ グループ、アプリケーションおよびデータ要件を把握したら、プロジェクトとソリューション サイジングに関するいくつかの主要な確認事項を検討します。
プロジェクトに関する一般的な確認事項には、初期段階で対処しなければならないものもあります。次に例を挙げます。
· VDI のパイロット計画は、デスクトップ グループ、アプリケーション、データのビジネス分析に基づいて作成されているか。
· パイロット プログラムを実行するインフラストラクチャと予算は用意されているか。
· VDI プロジェクトの実行に必要なスキルを持つ人材はいるか。そのような人材を雇用したり、契約を結んだりすることができるか。
· デスクトップ サブグループごとにエンド ユーザ エクスペリエンスのパフォーマンス測定指標はあるか。
· 成功と失敗の評価基準をどうするか。
· 成功した場合、または失敗した場合、今後どのような影響が出るか。
次のリストは、ユーザ サブグループごとに対処する必要があるサイジングに関する確認事項の一部です。
· 導入予定のデスクトップ OS は何かWindows 7、Windows 8、Windows 10 のどれか。
· 32 ビット デスクトップ OS か、64 ビット デスクトップ OS か。
· パイロットでは何台の仮想デスクトップを導入するか。実稼働環境ではどうか。すべて Windows 10/7/8 か。
· 該当のデスクトップ グループのデスクトップには、メモリ容量はどれぐらい必要か。
· リッチ メディア、Flash、またはグラフィックを多用するワークロードはあるか。
· エンド ポイントのグラフィック処理能力はどのくらいか。
· リモート デスクトップ サーバ用の Citrix XenApp がホストするセッションは使用されるか。
· ソリューションのハイパーバイザは何か。
· 既存環境のストレージ構成はどのようなものか。
· 書き込み集中型 VDI ワークロードに十分な IOPS を確保できるか。
· VDI サービス専用に調整されたストレージはあるか。
· デスクトップに対する音声コンポーネントはあるか。
· ウイルス対策はイメージに含まれているか。
· ユーザ プロファイル管理(非ローミング プロファイルベースなど)はソリューションに含まれているか。
· 耐障害性、フェールオーバー、ディザスタ リカバリ計画はどのようなものか。
· 他にデスクトップ サブグループ固有の確認事項はないか。
Citrix XenDesktop の設計の基本
ますます増加し多様化するユーザ デバイス基盤、従来のデスクトップの管理における複雑さ、セキュリティ、
さらにはプログラムを機能させるための Bring Your Own (BYO) デバイスなどが、仮想デスクトップ
ソリューションに移行する主な理由となります。
Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 では、ホステッド共有および VDI デスクトップ仮想化テクノロジーがユニファイド
アーキテクチャに統合され、拡張性および効率性に優れたシンプルで扱いやすいソリューションによって Windows アプリケーションおよびデスクトップをサービスとして配信することができます。
ユーザは、タブレット、スマートフォン、PC、Mac、およびシン クライアントからアクセス可能な使いやすい
「ストア」からアプリケーションを選択できます。XenDesktop は、HDX 高解像度パフォーマンスを備え、
タッチ操作用に最適化されたネイティブ エクスペリエンスを提供します。このことはモバイル ネットワーク上でも同様です。
マシン カタログ
同一の仮想マシン (VM) の集まりは、マシン カタログと呼ばれる単一エンティティとして管理されます。この
CVD では、カタログ内のマシンが一貫していることを確認するために、VM プロビジョニングで Citrix Provisioning Services を利用しています。この CVD では、マシン カタログ内のマシンは、Windows Server OS(RDS ホステッド共有デスクトップの場合)または Windows デスクトップ OS(ホステッド プール VDI
デスクトップの場合)のいずれかを実行するように設定されています。
デリバリ グループ
デスクトップやアプリケーションをユーザに配信するには、マシン カタログを作成してから、デリバリ グループを作成してカタログ内のマシンをユーザに割り当てます。デリバリ グループを通して、デスクトップ、
アプリケーション、またはその組み合わせをユーザに提供します。デリバリ グループを作成することで、マシンやアプリケーションをユーザに柔軟に割り当てることができます。デリバリ グループでは、次のことが可能です。
· 複数のカタログ内のマシンを使用する
· 複数のマシンにユーザを割り当てる
· 1 つのマシンに複数のユーザを割り当てる
作成プロセスの一環として、次のデリバリ グループ プロパティを指定します。
· デリバリ グループに割り当てるユーザ、グループ、およびアプリケーション
· ユーザのニーズに合ったデスクトップ設定
· デスクトップ電源管理オプション
図 30 に、ユーザがマシン カタログおよびデリバリ グループを通じてデスクトップやアプリケーションに
アクセスする仕組みを示します
図 30 マシン カタログおよびデリバリ グループを通じたデスクトップやアプリケーションへのアクセス

XenDesktop 導入例
一般的な XenDesktop の導入例は、次の 2 つです。
· 分散コンポーネント構成
· マルチサイト構成
XenApp および XenDesktop 7.16 は統合アーキテクチャに基づいているため、ホステッド共有デスクトップ(HSD、サーバ OS マシンを使用)とホステッド仮想デスクトップ(HVD、デスクトップ OS を使用)を
組み合わせて導入することができます。
分散コンポーネント構成
導入対象コンポーネントを多数のサーバに分散させたり、サイト内のコントローラの数を増やして拡張性強化やフェールオーバーを実現したりすることができます。別のコンピュータに管理コンソールをインストールして、
導入をリモートから管理できます。NetScaler ゲートウェイ(旧称アクセス ゲートウェイ)を経由したリモート
アクセスに基づくインフラストラクチャには、分散導入が必要となります。
図 31 に、分散コンポーネント構成の例を示します。初期の概念検証 (POC) 導入では、この構成の簡易
バージョンがよく導入されます。このドキュメントで説明されている CVD では、示された分散コンポーネント
構成に似た構成で Citrix XenDesktop が導入されています。2 つの Cisco C220 ラック サーバでは、
インフラストラクチャ サービス(AD、DNS、DHCP、プロファイル、SQL、Citrix XenDesktop 管理、
および StoreFront サーバ)をホストしています。

マルチサイト構成
複数の地域にサイトがある場合、Citrix NetScaler を使用してユーザの接続を最も適切なサイトに誘導し、StoreFront を使用してデスクトップやアプリケーションをユーザに配信できます。
図 32 では複数のサイトが表現されており、2 つのデータセンターでサイトが作成されています。サイトを 1 つだけでなく 2 つグローバルに持つことで、不要な WAN トラフィックの量を最小限に抑えています。

StoreFront を使用することで、複数のサイトのリソースを集約し、ユーザに NetScaler による単一ポイントでのアクセスを提供します。各サイトを管理するのに個別の Studio コンソールが必要になります。サイトを単一
エンティティとして管理することはできません。ディレクタを使用すると、複数のサイトをまたいでユーザを
サポートできます。
Citrix NetScaler によって、アプリケーション パフォーマンスの向上、サーバのロード バランシング、
セキュリティ強化、ユーザ エクスペリエンスの最適化が促進されます。この例では、2 つの NetScaler を使用してハイ アベイラビリティ構成を実現しています。NetScaler をグローバル サーバ ロード バランシング用に構成し、DMZ に配置してマルチサイト フォールトトレラント ソリューションを提供しています。
Citrix のクラウド サービス
Citrix 製品のポートフォリオを、サービスとして簡単に提供します。Citrix Cloud サービスでは、Citrix の
テクノロジーの配信と管理がシンプルになり、既存のオンプレミス ソフトウェア導入への拡張を通じて、
ハイブリッド ワークスペース サービスを構築します。
· 高速:アプリケーションやデスクトップの導入、または安全なデジタル ワークスペースの構築を、週単位ではなく時間単位で行います。
· 適応性:クラウド、仮想インフラストラクチャ、もしくはそれらのハイブリッドでの導入を選択できます。
· セキュア:制御対象のアプリケーション、デスクトップ、データにおけるすべての機密情報の安全を維持します。
· シンプル:単一の管理プレーンを通じて完全に統合された Citrix ポートフォリオを用意することで、管理をシンプルにします。
混合ワークロードに対する XenDesktop 環境の設計
Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 では、アプリケーションまたはデスクトップをユーザに提供するために使用する方法は、ホストするアプリケーションやデスクトップのタイプ、使用可能なシステム リソース、ユーザのタイプ、および提供するユーザ エクスペリエンスによって異なります。
| サーバ OS マシン | 要件:安価なサーバベース配信によって、最小限のコストで数多くのユーザに ユーザ:明確に定義されたタスクを実行し、パーソナライゼーションや アプリケーション タイプ:アプリケーションのタイプは問いません。 |
| デスクトップ OS マシン | 要件:クライアントベースのセキュアなアプリケーション提供ソリューションによって集中管理を実現し、ホスト サーバ(またはハイパーバイザ)1 台あたりで ユーザ:社員、外部請負業者、サードパーティの協力者、および臨時のチーム アプリケーション タイプ:他のアプリケーションと一緒では適切に動作しない 旧オペレーティング システム(Windows XP や Windows Vista など)および旧アーキテクチャ(32 ビットや 16 ビットなど)で実行されるアプリケーションも同様です。各アプリケーションをそれぞれ個別の仮想マシンに分離することで、1 台のマシンで障害が発生しても、他のユーザに影響しなくなります。 |
| リモート PC アクセス | 要件:従業員が VPN を使用しなくても物理コンピュータにセキュアにリモート ユーザ:自宅から作業するという選択肢はあっても、企業のデスクトップにある ホスト:デスクトップ OS マシンと同じです。 アプリケーション タイプ:オフライン コンピュータから配信し、リモート |
Products Deployed
The architecture deployed is highly modular. While each customer’s environment might vary in its exact configuration, the reference architecture contained in this document once built, can easily be scaled as requirements and demands change. This includes scaling both up (adding additional resources within existing Cisco HyperFlex system) and out (adding additional Cisco UCS HX-series nodes, or Cisco UCS B/C-series as compute nodes).
The solution includes Cisco networking, Cisco UCS, and Cisco HyperFlex hyper-converged storage, which efficiently fits into a single data center rack, including the access layer network switches.
This validated design document details the deployment of the multiple configurations extending to 450 users for virtual desktop and hosted shared desktop workload featuring the following deployment methods:
· Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 persistent HVDs provisioned with Citrix Machine Creation Services (MCS) and using full copy on Cisco HyperFlex
· Microsoft Windows Server 2016 for User Profile Manager
· Microsoft Windows 2016 Server for Login VSI Management and data servers to simulate real world VDI workload
· Microsoft Hyper-V 2016
· Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2016
· Windows 10 64-bit Operating Systems for VDI virtual machines
· Microsoft SQL Server 2016
· Cisco HyperFlex data platform v3.0.1a
図 33 Detailed Reference Architecture with Physical Hardware Cabling Configured to Enable the Solution


Hardware Deployed
The solution contains the following hardware as shown in 図 34:
· Two Cisco Nexus 93108YC Layer 2 Access Switches
· Two Cisco UCS C220 M4 Rack Servers with dual socket Intel Xeon E5-2620v4 2.1-GHz 8-core processors, 128GB RAM 2133-MHz and VIC1227 mLOM card for the hosted infrastructure with N+1 server fault tolerance. (Not show in the diagram).
· Four Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5S Rack Servers with Intel Xeon Gold 6140 scalable family 2.3-GHz 18-core processors, 768GB RAM 2666-MHz and VIC1387 mLOM cards running Cisco HyperFlex data platform v3.0.1a for the virtual desktop workloads with N+1 server fault tolerance.
Software Deployed
Table 1 lists the software and firmware version used in the study.
Table 1 Software and Firmware Versions
| Vendor | Product | Version |
| Cisco | UCS Component Firmware | 3.2(3d) bundle release |
| Cisco | UCS Manager | 3.2(3d) bundle release |
| Cisco | UCS HXAF220c-M5S rack server | 3.2(3d) bundle release |
| Cisco | VIC 1387 | 4.2(2d) |
| Cisco | HyperFlex Data Platform | 3.0.1a-26588 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Network | Cisco Nexus 9000 NX-OS | 7.0(3)I2(2d) |
| Citrix | XenDesktop | 7.16 |
| Citrix | Provisioning Services | 7.16 |
| Citrix | User Profile Manager |
|
| Citrix | Receiver | 4.11 |
| Microsoft | SCVMM | 2016 |
| Microsoft | Hyper-V Server | 2016 |
|
|
|
|
Logical Architecture
The logical architecture of this solution is designed to support up to 450 Hosted Virtual Microsoft Windows 10 Desktops users within a four node Cisco UCS HXAF220c- HyperFlex cluster, which provides physical redundancy for each workload type.
図 35 Logical Architecture Design

Table 1 lists the software revisions for this solution.
![]() This document is intended to allow you to fully configure your environment. In this process, various steps require you to insert customer-specific naming conventions, IP addresses, and VLAN schemes, as well as to record appropriate MAC addresses. Table 2 through Table 6 lists the information you need to configure your environment.
This document is intended to allow you to fully configure your environment. In this process, various steps require you to insert customer-specific naming conventions, IP addresses, and VLAN schemes, as well as to record appropriate MAC addresses. Table 2 through Table 6 lists the information you need to configure your environment.
VLANs
The VLAN configuration recommended for the environment includes a total of seven VLANs as outlined in Table 2.
Table 2 Table 2 VLANs Configured in this Study
| VLAN Name | VLAN ID | VLAN Purpose |
| Default | 1 | Native VLAN |
| Hx-in-Band-Mgmt | 30 | VLAN for in-band management interfaces |
| Infra-Mgmt | 32 | VLAN for Virtual Infrastructure |
| Hx-storage-data | 101 | VLAN for HyperFlex Storage |
| Hx-livemigration | 33 | VLAN for Hyper-V Live Migration |
| Vm-network | 34 | VLAN for VDI Traffic |
| OOB-Mgmt | 132 | VLAN for out-of-band management interfaces |
![]() A dedicated network or subnet for physical device management is often used in datacenters. In this scenario, the mgmt0 interfaces of the two Fabric Interconnects would be connected to that dedicated network or subnet. This is a valid configuration for HyperFlex installations with the following caveat; wherever the HyperFlex installer is deployed it must have IP connectivity to the subnet of the mgmt0 interfaces of the Fabric Interconnects, and also have IP connectivity to the subnets used by the hx-inband-mgmt VLANs listed above.
A dedicated network or subnet for physical device management is often used in datacenters. In this scenario, the mgmt0 interfaces of the two Fabric Interconnects would be connected to that dedicated network or subnet. This is a valid configuration for HyperFlex installations with the following caveat; wherever the HyperFlex installer is deployed it must have IP connectivity to the subnet of the mgmt0 interfaces of the Fabric Interconnects, and also have IP connectivity to the subnets used by the hx-inband-mgmt VLANs listed above.
Jumbo Frames
All HyperFlex storage traffic traversing the hx-storage-data VLAN and subnet is configured to use jumbo frames, or to be precise all communication is configured to send IP packets with a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size of 9000 bytes. Using a larger MTU value means that each IP packet sent carries a larger payload, therefore transmitting more data per packet, and consequently sending and receiving data faster. This requirement also means that the Cisco UCS uplinks must be configured to pass jumbo frames. Failure to configure the Cisco UCS uplink switches to allow jumbo frames can lead to service interruptions during some failure scenarios, particularly when cable or port failures would cause storage traffic to traverse the northbound Cisco UCS uplink switches.
Virtual Networking Design
The Cisco HyperFlex system has a pre-defined virtual network design at the Hyper-V hypervisor level. Four different virtual switches are created by the HyperFlex installer, each using two uplinks, which are each serviced by a vNIC defined in the UCS service profile. The vSwitches created are:
· vswitch-hx-inband-mgmt: This is the default vSwitch0 which is renamed by the Hyper-V kickstart file as part of the automated installation. The default vmkernel port, vmk0, is configured in the standard Management Network port group. The switch has two uplinks, active on fabric A and standby on fabric B, without jumbo frames. A second port group is created for the Storage Platform Controller VMs to connect to with their individual management interfaces. The VLAN is not a Native VLAN as assigned to the vNIC template, and therefore assigned in Hyper-V/Hyper-V
· vswitch-hx-storage-data: This vSwitch is created as part of the automated installation. A vmkernel port, vmk1, is configured in the Storage Hypervisor Data Network port group, which is the interface used for connectivity to the HX Datastores via NFS. The switch has two uplinks, active on fabric B and standby on fabric A, with jumbo frames required. A second port group is created for the Storage Platform Controller VMs to connect to with their individual storage interfaces. The VLAN is not a Native VLAN as assigned to the vNIC template, and therefore assigned in Hyper-V/Hyper-V
· vswitch-hx-vm-network: This vSwitch is created as part of the automated installation. The switch has two uplinks, active on both fabrics A and B, and without jumbo frames. The VLAN is not a Native VLAN as assigned to the vNIC template, and therefore assigned in Hyper-V/Hyper-V
· live-migration: This vSwitch is created as part of the automated installation. The switch has two uplinks, active on fabric A and standby on fabric B, with jumbo frames required. The VLAN is not a Native VLAN as assigned to the vNIC template, and therefore assigned in Hyper-V/Hyper-V
The following table and figures help give more details into the Hyper-V virtual networking design as built by the HyperFlex installer:
Table 3 Table Hyper-V Host Virtual Switch Configuration
| Virtual Switch | Port Groups | Active vmnic(s) | Passive vmnic(s) | VLAN IDs | Jumbo |
| vswitch-hx-inband-mgmt | Management Network Storage Controller Management Network | vmnic0 | vmnic1 | hx-inband-mgmt | no |
| vswitch-hx-storage-data | Storage Controller Data Network Storage Hypervisor Data Network | vmnic3 | vmnic2 | hx-storage-data | yes |
| vswitch-hx-vm-network | none | vmnic4,vmnic5 | none | vm-network | no |
| Live-migration | none | vmnic6 | vmnic7 | 33 | yes |

Storage Platform Controller Virtual Machines
A key component of the Cisco HyperFlex system is the Storage Platform Controller Virtual Machine running on each of the nodes in the HyperFlex cluster. The controller VMs cooperate to form and coordinate the Cisco HX Distributed Filesystem, and service all the guest VM IO requests. The controller VMs are deployed as a Hyper-V agent, which is similar in concept to that of a Linux or Windows service. Hyper-V agents are tied to a specific host, they start and stop along with the Hyper-V hypervisor, and the system is not considered to be online and ready until both the hypervisor and the agents have started. Each Hyper-V hypervisor host has a single Hyper-V agent deployed, which is the controller VM for that node, and it cannot be moved or migrated to another host. The collective Hyper-V agents are managed via a Hyper-V agency in the Hyper-V cluster.
The storage controller VM runs custom software and services that manage and maintain the Cisco HX Distributed Filesystem. The services and processes that run within the controller VMs are not exposed as part of the Hyper-V agents to the agency, therefore the Hyper-V hypervisors nor SCVMM server have any direct knowledge of the storage services provided by the controller VMs. Management and visibility into the function of the controller VMs, and the Cisco HX Distributed Filesystem is done via a plugin installed to the SCVMM server or appliance managing the Hyper-V cluster. The plugin communicates directly with the controller VMs to display the information requested.
Controller VM Locations
The physical storage location of the controller VM is similar between the Cisco HXAF220c-M5S and HXAF240c-M5SX model servers. The storage controller VM is operationally no different from any other typical virtual machines in a Hyper-V environment. The VM must have a virtual disk with the bootable root filesystem available in a location separate from the SAS HBA that the VM is controlling via SR-IOV. The configuration details of the models are as follows:
Cisco HyperFlex Datastores
The new HyperFlex cluster has no default datastores configured for virtual machine storage, therefore the datastores must be created using the HyperFlex Connect GUI. Overall space consumption in the HyperFlex clustered filesystem is optimized by the default deduplication and compression features.

CPU Resource Reservations
Since the storage controller VMs provide critical functionality of the Cisco HX Distributed Data Platform, the HyperFlex installer will configure CPU resource reservations for the controller VMs. This reservation guarantees that the controller VMs will have CPU resources at a minimum level, in situations where the physical CPU resources of the Hyper-V hypervisor host are being heavily consumed by the guest VMs. Table 4 details the CPU resource reservation of the storage controller VMs.
Table 4 Controller VM CPU Reservations
| Number of vCPU | Shares | Reservation | Limit |
| 8 | Low | 10800 MHz | unlimited |
Memory Resource Reservations
Since the storage controller VMs provide critical functionality of the Cisco HX Distributed Data Platform, the HyperFlex installer will configure memory resource reservations for the controller VMs. This reservation guarantees that the controller VMs will have memory resources at a minimum level, in situations where the physical memory resources of the Hyper-V hypervisor host are being heavily consumed by the guest VMs.
Table 5 lists the memory resource reservation of the storage controller VMs.
Table 5 Controller VM Memory Reservations
| Server Model | Amount of Guest Memory | Reserve All Guest Memory |
| HX220c-M5 HXAF220c-M5 | 48 GB | Yes |
| HX240c-M5SX HXAF240c-M5SX | 72 GB | Yes |
![]() The Cisco UCS compute-only nodes have a lightweight storage controller VM; it is configured with only 1 vCPU and 512 MB of memory reservation.
The Cisco UCS compute-only nodes have a lightweight storage controller VM; it is configured with only 1 vCPU and 512 MB of memory reservation.
This section details the configuration and tuning that was performed on the individual components to produce a complete, validated solution. 図 38 illustrates the configuration topology for this solution.
図 38 Configuration Topology for Scalable Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Workload with HyperFlex

Cisco UCS Compute Platform
The following subsections detail the physical connectivity configuration of the Citrix XenDesktop environment.
Physical Infrastructure
Solution Cabling
The information in this section is provided as a reference for cabling the physical equipment in this Cisco Validated Design environment. To simplify cabling requirements, the tables include both local and remote device and port locations.
The tables in this section contain the details for the prescribed and supported configuration.
This document assumes that out-of-band management ports are plugged into an existing management infrastructure at the deployment site. These interfaces will be used in various configuration steps.
![]() Be sure to follow the cabling directions in this section. Failure to do so will result in necessary changes to the deployment procedures that follow because specific port locations are mentioned.
Be sure to follow the cabling directions in this section. Failure to do so will result in necessary changes to the deployment procedures that follow because specific port locations are mentioned.
図 39 shows a cabling diagram for a Citrix XenDesktop configuration using the Cisco Nexus 9000 and Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect.
Table 6 Cisco Nexus 93108YC-Cabling Information
| Local Device | Local Port | Connection | Remote Device | Remote Port |
| Cisco Nexus 93108YC A
| Eth1/1 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC B | Eth1/1 |
| Eth1/2 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC B | Eth1/2 | |
| Eth1/3 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | Eth1/13 | |
| Eth1/4 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | Eth1/14 | |
| Eth1/5 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B | Eth1/13 | |
| Eth1/6 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B | Eth1/14 | |
| Eth1/25 | 10GbE | Infra-host-01 | Port01 | |
| Eth1/26 | 10GbE | Infra-host-02 | Port01 | |
| Eth1/27 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-01 | Port01 | |
| Eth1/28 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-02 | Port01 | |
| Eth1/29 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-03 | Port01 | |
| Eth1/30 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-04 | Port01 | |
|
| MGMT0 | GbE | GbE management switch | Any |
![]() For devices requiring GbE connectivity, use the GbE Copper SFP+s (GLC-T=).
For devices requiring GbE connectivity, use the GbE Copper SFP+s (GLC-T=).
Table 7 Cisco Nexus 93108YC-B Cabling Information
| Local Device | Local Port | Connection | Remote Device | Remote Port |
| Cisco Nexus 93108YC B
| Eth1/1 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC A | Eth1/1 |
| Eth1/2 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC A | Eth1/2 | |
| Eth1/3 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | Eth1/15 | |
| Eth1/4 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | Eth1/16 | |
| Eth1/5 | 10GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B | Eth1/15 | |
| Eth1/6 | 40GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B | Eth1/16 | |
| Eth1/25 | 10GbE | Infra-host-01 | Port02 | |
| Eth1/26 | 10GbE | Infra-host-02 | Port02 | |
| Eth1/27 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-01 | Port02 | |
| Eth1/28 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-02 | Port02 | |
| Eth1/29 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-03 | Port02 | |
| Eth1/30 | 10GbE | Launcher-host-04 | Port02 | |
|
| MGMT0 | GbE | GbE management switch | Any |
Table 8 Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect A Cabling Information
| Local Device | Local Port | Connection | Remote Device | Remote Port |
| Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | Eth1/13 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC A | Eth1/3 |
| Eth1/14 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC A | Eth1/4 | |
| Eth1/15 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC B | Eth1/5 | |
| Eth1/16 | 10 GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC B | Eth 1/6 | |
| MGMT0 | GbE | GbE management switch | Any | |
| L1 | GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B | L1 | |
|
| L2 | GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B | L2 |
Table 9 Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect B Cabling Information
| Local Device | Local Port | Connection | Remote Device | Remote Port |
| Cisco UCS fabric interconnect B
| Eth1/13 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC B | Eth1/3 |
| Eth1/14 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC B | Eth1/4 | |
| Eth1/15 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC A | Eth1/5 | |
| Eth1/16 | 10GbE | Cisco Nexus 93108YC A | Eth 1/6 | |
| MGMT0 | GbE | GbE management switch | Any | |
| L1 | GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | L1 | |
|
| L2 | GbE | Cisco UCS fabric interconnect A | L2 |
図 39 Cable Connectivity Between Cisco Nexus 93108YC A and B to Cisco UCS 6248 Fabric A and B

Cisco Unified Computing System Configuration
This section details the Cisco UCS configuration performed as part of the infrastructure build out by the Cisco HyperFlex installer. Many of the configuration elements are fixed in nature, meanwhile the HyperFlex installer does allow for some items to be specified at the time of creation, for example VLAN names and IDs, IP pools and more. Where the elements can be manually set during the installation, those items will be noted in << >> brackets.
For complete detail on racking, power, and installation of the chassis is described in the install guide (see www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/servers-unified-computing/ucs-manager/products-installation-guides-list.html) and it is beyond the scope of this document. For more information about each step, refer to the following documents: Cisco UCS Manager Configuration Guides – GUI and Command Line Interface (CLI) Cisco UCS Manager - Configuration Guides - Cisco
During the HyperFlex Installation a Cisco UCS Sub-Organization is created named “hx-cluster”. The sub-organization is created below the root level of the Cisco UCS hierarchy, and is used to contain all policies, pools, templates and service profiles used by HyperFlex. This arrangement allows for organizational control using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and administrative locales at a later time if desired. In this way, control can be granted to administrators of only the HyperFlex specific elements of the Cisco UCS domain, separate from control of root level elements or elements in other sub-organizations.
図 40 Cisco UCS Manager Configuration: HyperFlex Sub-organization

Deploy and Configure HyperFlex Data Platform
Prerequisites
To deploy and configure the HyperFlex Data Platform, you must complete the following prerequisites:
1. Set Time Zone and NTP: From the Cisco UCS Manager, from the Admin tab, Configure TimeZone and add NTP server. Save changes.

2. Configure Server Ports: Under the Equipment tab, Select Fabric A, select port to be configured as server port to manager HyperFlex rack server through Cisco UCS Manager.

3. Repeat this step to configure server port on Fabric B.
4. Configure Uplink Ports: On Fabric A, Select port to be configured as uplink port for network connectivity to north bound switch.

5. Repeat this same on Fabric B.
6. Create Port Channels: Under LAN tab, select expand LAN > LAN cloud > Fabric A. Right-click Port Channel.
7. Select Create port-channel to connect with upstream switch as per Cisco UCS best practice. For our reference architecture, we connected a pair of Nexus 93108YCPX switches.

8. Enter port-channel ID number and name to be created, click Next.

9. Select uplink ports to add as part of the port-channel.
10. Click Finish.

11. Follow the previous steps to create the port-channel on Fabric B, using a different port-channel ID.

12. Configure QoS System Classes: From the LAN tab, below the Lan Cloud node, select QoS system class and configure the Platinum through Bronze system classes as shown in the following figure.
- Set MTU to 9216 for Platinum (Storage data) and Bronze (LiveMigration)
- Uncheck Enable Packet drop on the Platinum class
- Set Weight for Platinum and Gold priority class to 4 and everything else as best-effort.
- Enable multicast for silver class.

![]() Changing QoS system class configuration on 6300 series Fabric Interconnect requires reboot of FIs.
Changing QoS system class configuration on 6300 series Fabric Interconnect requires reboot of FIs.
13. Verify UCS Manager Software Version: In the Equipment tab, select Firmware Management > Installed Firmware.
14. Check and verify, both Fabric Interconnects and Cisco USC Manager are configure with Cisco UCS Manager v3.2.3d.

![]() It is recommended to let the HX Installer handle upgrading the server firmware automatically as designed. This will occur once the service profiles are applied to the HX nodes during the automated deployment process.
It is recommended to let the HX Installer handle upgrading the server firmware automatically as designed. This will occur once the service profiles are applied to the HX nodes during the automated deployment process.
15. Optional: If you are familiar with Cisco UCS Manager or you wish to break the install into smaller pieces, you can use the server auto firmware download to pre-stage the correct firmware on the nodes. This will speed up the association time in the HyperFlex installer at the cost of running two separate reboot operations. This method is not required or recommended if doing the install in one sitting.
Deploying HX Data Platform Installer on Hyper-V Infrastructure
To deploy HX Data Platform Installer using Microsoft Hyper-V Manager to create a HX Data Platform Installer virtual machine, complete the following steps:
1. Locate and download the HX Data Platform Installer.vhdx zipped file (for example, Cisco-HX-Data-Platform-Installer-v3.0.1a-build-hyperv.vhdx) from the Cisco Software Downloads site.
2. Extract the zipped folder to your local computer and copy the .vhdx file to the Hyper-V host where you want to host the HX Data Platform Installer. For example,
3. In Hyper-V Manager, navigate to one of the Hyper-V servers.
4. Select the Hyper-V server, and right click and select New > Create a virtual machine. The Hyper-V Manager New Virtual Machine Wizard displays.

5. In the Before you Begin page, click Next.

6. In the Specify Name and Location page, enter a name and location for the virtual machine where the virtual machine configuration files will be stored. Click Next.

![]() As a best practice, store the VM together with the .vhdx file.
As a best practice, store the VM together with the .vhdx file.
7. In the Specify Generation page, select Generation 1. Click Next.
![]() If you select Generation 2, the VM may not boot.
If you select Generation 2, the VM may not boot.

8. In the Assign Memory page, set the startup memory value to 4096 MB. Click Next.

9. In the Configure Networking page, select a network connection for the virtual machine to use from a list of existing virtual switches. Click Next.

10. In the Connect Virtual Hard Disk page, select Use an existing virtual hard disk, and browse to the folder on your Hyper-V host that contains the .vhdx file. Click Next.

11. In the Summary page, verify that the list of options displayed are correct. Click Finish.

12. After the VM is created, power it ON, and launch the GUI.
a. Right-click the VM and choose Connect.
b. Choose Action > Start (Ctrl+S).
c. When the VM is booted, make a note of the URL (IP address of the VM). You will need this information in the following steps in the installation.

Deploy the HX Data Platform Installer OVA with a Static IP Address
If your hypervisor wizard defaults to DHCP for assigning IP addresses to new VMs, deploy the Cisco HX Data Platform Installer using the following steps:
1. Log in to your Installer machine via the Hyper-V Console or putty.
2. Use ipconfig to assign an IP address to your NIC:
a. For example, ‘ifconfig eth0 x.x.x.x netmask 255.255.255.0
3. For static IPs that will be persistent use the following configuration
[root@frida root]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=frida.localdomain
GATEWAY=172.30.10.1
[root@frida root]#
[root@frida root]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=static
BROADCAST=172.30.10.255
IPADDR=172.30.10.101
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
ONBOOT=yes
[root@frida root]#
[root@frida root]# service network restart
Shutting down interface eth0: [ OK ]
Shutting down loopback interface: [ OK ]
Setting network parameters: [ OK ]
Bringing up loopback interface: [ OK ]
Bringing up interface eth0: [ OK ]
[root@frida root]#
b. Step 2 - Configure DNS server
4. Verify settings
a. Show interfaces and routing table
Cisco UCS Manager Configuration using HX Data Platform Installer
To configure Cisco UCS Manager using HX Installer, complete the following steps:
1. Log into the HX Data Platform Installer using the following steps:
a. In a browser, enter the URL for the VM where HX Data Platform Installer was installed. If you do not have the URL, go back to Step 13 in the earlier section on Deploying HX Data Platform Installer.
b. Use the credentials: username: root, password: Cisco123
![]() Important! Systems ship with a default password of Cisco123 that must be changed during installation; you cannot continue installation unless you specify a new user supplied password.
Important! Systems ship with a default password of Cisco123 that must be changed during installation; you cannot continue installation unless you specify a new user supplied password.
2. Read the EULA. Click I accept the terms and conditions.
3. Verify the product version listed in the lower right corner is correct. This version must be 3.0(1a) or later. Click Login.

4. From the HX Data Platform Installer Workflow page, select I know what I'm doing, let me customize my workflow.

5. On the next screen, click Run UCS Manager Configuration and then click Continue.
![]() Do not choose any other workflow options.
Do not choose any other workflow options.

6. Click Confirm in the popup that displays.
7. Enter the UCS Manager credentials.
![]() The right side of the page is unused. Further in the setup process a configuration JSON is saved, so in subsequent installations the JSON file can be imported to add the data quickly.
The right side of the page is unused. Further in the setup process a configuration JSON is saved, so in subsequent installations the JSON file can be imported to add the data quickly.
8. Click Confirm and Proceed to bypass the warning. Complete the following fields for Cisco UCS Manager.
| Field | Description |
| Cisco UCS Manager Host Name | FQDN or the VIP address of Cisco UCS Manager |
| Cisco UCS Manager User Name and Password | Administrator user and password or an user with Cisco UCS Manager admin rights |

9. Click Continue.
The installer will connect to UCSM and query for available servers. The configuration pane is populated as the installer progresses. You can at any time save the JSON file so you can re-use it for subsequent installations. This feature works on all the different workflows in the installer. After the query finishes a screen displays showing the available servers.

10. Choose all the servers that you want to install in the cluster and click Continue.
![]() HyperFlex for Hyper-V only supports M5 Servers.
HyperFlex for Hyper-V only supports M5 Servers.
VLAN Configuration
HyperFlex needs to have at least 4 VLANs to function; each VLAN needs to be on different IP subnets and extended from the fabric interconnects to the connecting uplink switches, to make sure that traffic can flow from Primary Fabric Interconnect (Fabric A) to Subordinate Fabric Interconnect ( Fabric B).
| Name | Usage | ID |
| hx-inband-mgmt | Hyper-V and HyperFlex VM management. | 30 |
| hx-storage-data | HyperFlex storage traffic | 101 |
| hx-livemigrate | Hyper-V LiveMigration network | 33 |
| vm-network | VM guest network | 34,35 |
![]() Do not use vlan 1 as it is not best practice and can cause issues with disjoint layer 2.
Do not use vlan 1 as it is not best practice and can cause issues with disjoint layer 2.
![]() vm-network can be multiple VLANs added as a comma separated list.
vm-network can be multiple VLANs added as a comma separated list.
![]() Renaming the 4 core networks is not supported.
Renaming the 4 core networks is not supported.
The following illustration shows the various fields in the VLAN Configuration pane where you need to enter values.
11. Enter the remaining network configuration.

| Field | Description | Value |
| MAC pool prefix | MAC address pool for the HX cluster, to be configured in UCSM by the installer. Ensure that the mac address pool isn’t used anywhere else in your layer 2 environment. | 00:25:b5:xx |
| IP blocks | The range of IP addresses that are used for Out-Of-Band management of the hyperflex nodes. | 10.193.211.124-.127 |
| Subnet Mask | The subnet mask for the Out-Of-Band network | 255.255.0.0 |
| Gateway | The gateway address for the Out-Of-Band network | 10.193.0.1 |
The Out-Of-Band network needs to be on the same subnet as the Cisco UCS Manager.
You can add multiple blocks of addresses as a comma separated line.

iSCSI Storage and FC Storage are used for adding external storage to the HyperFlex cluster.
![]() This is currently not supported for the Hyper-V Edition.
This is currently not supported for the Hyper-V Edition.
Advanced Settings
Use the table below to complete the fields in this section.
Table 10 Field Settings
| Field | Description | Example Value |
| UCS Firmware Server Version | Choose the appropriate UCS Server Firmware version. | 3.2(3a) |
| HyperFlex Cluster Name | This user defined name will be used as part of the service profile naming In UCSM for easier identification. |
|
| Org Name | The org. name is used for isolating the HX environment from the rest of the UCS platform to ensure consistency. | HX-Cluster1 |
![]() The Cisco UCS C and B packages must exist on the Fabric interconnect otherwise the installation will fail. If the right version is not available in the drop-down list, then upload it to Cisco UCS Manager before continuing.
The Cisco UCS C and B packages must exist on the Fabric interconnect otherwise the installation will fail. If the right version is not available in the drop-down list, then upload it to Cisco UCS Manager before continuing.
![]() The supported version for HyperFlex Hyper-V is 3.2(3a).
The supported version for HyperFlex Hyper-V is 3.2(3a).

12. Click Start. The installer validates your input and then begins configuring Cisco UCS Manager.
13. When the HX Data Platform Installer is finished, then you are ready to proceed to next step, Microsoft Windows OS and Hyper-V Installation, on page 26.

Microsoft Windows OS and Hyper-V Installation
For this part of the installation, you need the Windows 2016 Datacenter Edition ISO and the Cisco provided Cisco HyperFlex Driver image.
The two files must be placed on a share that is reachable from the Cisco UCS Manager and the Out-of-band subnet that was used in the previous installation step.
The following protocols are supported:
· NFS
· CIFS
· HTTP
If you do not have a place to serve the files from, you can use the installer to host the files. Please see the section: How to Upload the ISO and IMG File to the Installer VM using WinSCP.
![]() Make sure network connectivity exists between the file share and all server management IPs.
Make sure network connectivity exists between the file share and all server management IPs.
Below is a summary of steps:
1. Attach the two images to the service profiles. Follow the steps described in Configure vMedia and Boot Policies through Cisco UCS Manager, on page 26.
2. Verify the images are mounted correctly.
3. Reboot the servers and verify the OS installation completes successfully.
4. Clean up the service profiles so the HX Installer can continue.
Configure vMedia and Boot Policies through Cisco UCS Manager
To configure the Cisco UCS vMedia and Boot Policies using Cisco UCS Manager, complete the following steps:
1. Launch Cisco UCS Manager by accessing the Cisco UCS Manager IP address in a browser of your choice.

2. Click Launch UCS Manager and log in with administrator username and the password you used at the beginning of the installation.

3. In the left navigation pane, click Servers.

4. Expand Servers > Policies > root > Sub-Organizations > hx-cluster_name > vMedia Policies to view the list of vMedia Policies.

5. Double-click vMedia Policy HyperFlex.

6. In the properties for vMedia Policy HyperFlex, click Create vMedia Mount to add the mount points.
7. In the Create vMedia Mount dialog box, complete the following fields:

| Field Name | Action | Example Value |
| Name | Name for the mount point. | OS Install |
| Description | Can be used for more information. |
|
| Device Type | Type of image that you want to mount | CDD |
| Protocol | The protocol used for accessing the share where the ISO files are located. | HTTP |
| Hostname/IP Address | IP address or FQDN of the server hosting the images. | 10.101.1.92 |
| Image Name Variable | This value is not used in HyperFlex installation. | None |
| Remote File | The filename of the ISO file that you want to mount. |
|
| Remote Path | The path on the remote server to where the file resides |
|
| Username | If you use CIFS or NFS a username might be necessary |
|
| Password | If you use CIFS or NFS a password might be necessary |
|
8. Click Save Changes and click OK.
9. Click OK. When you click OK, you are returned to the vMedia policy and will see the information that you submitted.

10. Repeat steps 5 and 6 but change the type to HDD and the filename to the Cisco HyperFlex driver image.

On completion, the following screen displays:

11. In the left navigation pane, select Servers > Service Profile Templates > root > Sub-Organizations > hx-cluster_name > Service Template hx-nodes_name (example:hx-nodes-m5)

12. Choose the HyperFlex vMedia Policy from the drop-down list and click OK twice.
The vMedia policy is assigned to the HyperFlex Template during the Cisco UCS Manager phase of the HyperFlex deployment.
13. Select Servers > Policies > root > Sub-Organizations > hx-cluster_name > Boot Policies Boot Policy HyperFlex-m5.
14. In the configuration pane, click CIMC Mounted vMedia. Click Add CIMC Mounted CD/DVD to add this to the boot order.
15. Select the CIMC Mounted CD/DVD entry in the list and move it to the top of the boot order by pressing the Move Up button.

16. Click Save Changes and click OK. The boot policy is saved.
Next Steps
To verify the images are mounted correctly, complete the following steps:
1. On the Equipment tab, select one of the servers.

2. Click Inventory > CIMC, scroll down and make sure for the mount entry #1(OS image) and mount entry #2 (Cisco HyperFlex driver image) the status is Mounted and there are no failures.
3. In the menu bar, click Servers and choose the first HyperFlex service profile.

4. Click the General tab and choose KVM Console.

![]() The KVM console will try to open in a new browser. Be aware of any pop-up blockers. Allow the Pop-Ups and re-open the KVM.
The KVM console will try to open in a new browser. Be aware of any pop-up blockers. Allow the Pop-Ups and re-open the KVM.

5. Reboot the server. In the KVM console choose Server Actions and press Reset.

6. Choose Power Cycle.

The server should reboot when the server has finished. Remember to press any key to start the Windows installer.


![]() If you miss pressing any key, the server will display in the windows installation or an error page displays stating no OS is installed.
If you miss pressing any key, the server will display in the windows installation or an error page displays stating no OS is installed.
When the server starts booting the Windows image, it starts the windows installation and continues the installation automatically.

During the installation the server will reboot automatically a few times.
![]() Do not stop the installation and allow the process to continue.
Do not stop the installation and allow the process to continue.
The installation is complete when a clean command prompt displays as shown below:

7. Repeat these steps on all the nodes in the cluster.
Clean Up
When the installation is complete on all nodes, you must clean up the vMedia policy and the boot policy so they return to their previous state before continuing.
1. In Cisco UCS Manager select Servers > Polices > Root > Sub-Organizations > HX-Cluster_name > vMedia polices
2. Click the vMedia Policy HyperFlex. Click the mount points one at a time and delete both of them. Accept the changes.

3. Go to the boot policy by selecting Servers > Polices > Root > Sub-Organizations > HX-Cluster_name > boot polices > Boot Policy HyperFlex-m5
4. Select the CIMC mounted CD/DVD, click Delete and accept the changes.
Hypervisor Configuration
After the OS is installed, you need to configure the hypervisor before installing the HX Software and configure the cluster.
To configure the Hypervisor, complete the following steps:
1. Open the HX Data Platform Installer and log in.

2. You might need to “start over” since the previous workflow was finished. Click the gear icon in the top right corner and select Start Over.
3. In the main menu, select I know what I'm doing, let me customize my workflow. In the Warning dialog box, click Confirm and Proceed.

4. Select Run Hypervisor Configuration and click Continue.
5. Complete the information for the UCS Manager, Domain Information, and Hypervisor Credentials.
| Field | Description | Default Value |
| UCS Manager Host Name | FQDN or the VIP address of the UCSM | |
| UCS Manager User Name | Admin user or an user with UCSM admin rights | Admin |
| Password | Password for the UCS Manager User Name | |
| Domain Name | Active Directory domain name that the HyperFlex cluster is going to be a member off. | |
| Local Administrator User Name | Local Administrative username on the Hyper-V Hosts | Administrator |
| Local Administrator Password | Password for the local administrative user on the Hyper-V hosts | Cisco 123 |
![]() If you have not changed the Administrator password for the Windows Hyper-V in the previous step, the default value is shown.
If you have not changed the Administrator password for the Windows Hyper-V in the previous step, the default value is shown.

The HX Data Platform Installer now connects to UCSM and lists the relevant servers for the HX Cluster. The HX Data Platform Installer will validate UCS Firmware, etc.
6. Validate the selected servers and click Continue.
7. Complete the network information as you have done in section Cisco UCS Manager Configuration using HX Data Platform Installer and make sure the data is the same. Click Continue.

8. Configure Hypervisor Settings. Input the values for the Hypervisor configuration as show below:
| Field | Description | Example Value |
| Configure common Hypervisor Settings | ||
| Subnet Mask | Subnet mask for the hypervisor hosts management network | 255.255.255.0 |
| Gateway | Default gateway for the hypervisor hosts management network | 10.101.251.1 |
| DNS Servers | Comma separated list for the DNS Servers in the AD that the hypervisor hosts are going to be member of. | 10.99.2.200,10.992.201 |
| Hypervisor Settings | ||
| Static IP address | Management IP address for each host | 10.101.251.41 |
| Hostname | Hostname for each host | HX-Hypv-01 |
![]() If you leave the checkbox Make IP Addresses and Hostnames Sequential as checked then the installer will automatically fill the rest of the servers sequentially.
If you leave the checkbox Make IP Addresses and Hostnames Sequential as checked then the installer will automatically fill the rest of the servers sequentially.

9. Click Start to begin the Hypervisor Configuration.
The installation continues and configures the Hypervisor hosts.

![]() Be aware that if the steps are completed as shown above, the Hypervisor configuration is not completed. The servers are working in the background until the installer reports an overall completion as shown below.
Be aware that if the steps are completed as shown above, the Hypervisor configuration is not completed. The servers are working in the background until the installer reports an overall completion as shown below.

Deploying HX Data Platform Installer and Cluster Configuration
1. Log into HX Data Platform Installer.
2. In the top right corner of the install, select Start Over, and confirm that you wish to start over. From the HX Data Platform Installer Workflow page, select I know what I'm doing, let me customize my workflow.
3. Check both Deploy HX Software and Create HX Cluster and Continue.
4. Click Confirm and Proceed at the Warning message.
5. Enter Domain Information, Hypervisor credentials, etc.
| Field | Description | Example Value |
| Domain name | Active Directory domain that the cluster is going to a part of. | contoso.com |
| HX Service Account | The HX Service account that was created during the Pre-installation checklist | hxadmin |
| Password | Password for the HX Service account |
|
| Configure Constrained Delegation Now | Checked | |
| Use HX Service Account | Uses the HX Service Account for the Constrained delegation. The user must be a Domain admin. | Checked |
| Advanced Attributes (optional) | ||
| Domain controller | FQDN for the Domain controller that you want to use specifically for the installation. | dc.contoso.com |
| Organization Unit | The OU that was created during the Pre-Installation can be filled out here, and then this OU will be home for the HX Nodes in the Active directory | OU=HyperFlex,DC=contoso,DC=com. |
| Hypervisor Credentials | ||
| Local Administrator User Name | Local Administrative username on the Hyper-V Hosts | Administrator |
| Local Administrator Password | Password for the local administrative user on the Hyper-V hosts | Cisco123 |
6. Enter IP Addresses.
7. Click the Add server button for you to have the amount of server entries that you need for your cluster.
8. Enter the hostnames for the Hyper-Hosts and the Storage Controllers running on the Hyper-V hosts. These hostnames must be added to forward and reverse lookup prior to this step and remember that only Windows AD Integrated DNS is supported.
![]() That the management VLAN uses DNS to resolve the addresses and the Data VLAN does not.
That the management VLAN uses DNS to resolve the addresses and the Data VLAN does not.
Table 11 Cluster Addresses
| Field | Description | Example Value |
| Management | ||
| Cluster Address | Hostname for the HX Connect UI | HX-EAP-01-MGMT |
| Subnet Mask | Subnet mask for the management VLAN | 255.255.255.0 |
| Gateway | Gateway address for the management VLAN | 10.101.251.1 |
| Data | ||
| Cluster Address | IP address for the HX cluster on the data VLAN | 10.101.252.50 |
| Subnet Mask | Subnet mask for the HX data VLAN | 255.255.255.0 |
| Gateway | Gateway for the HX data VLAN | 10.101.252.1 |
Table 12 Cisco HX Cluster
| Field | Description | Example Value |
| Cisco HX Cluster | ||
| Cluster Name (SMB Access Point | The cluster name will be used as the FQDN For the datastores. | HX-EAP-01 |
| Replication Factor | How many copies of data you want. | 3 (default) |
| Failover Cluster Name | This name is used for the windows failover cluster. | HX-EAP-CLU01 |
| Controller VM | ||
| Create Admin Password | The Installer will automatically change the default password on the controllers to a user defined password* |
|
| Confirm Admin Password | Confirm the previous password. |
|
| System Services | ||
| DNS Servers | Comma separated lists of DNS Servers. | 10.99.2.200,10.99.2.201 |
| NTP Servers | The Controller VM’s needs to be in sync with the Windows AD therefore you need to point to your AD domain controllers for time synchronization. | dc1.contoso.com,dc2.contoso.com |
| DNS Domain Name | The Domain name for the Active Directory. | contoso.com |
| Time Zone | The time zone in which you want the HX controllers to report. |
|
| Auto Support | ||
| Enable Connected Services | Auto Support will ship telemetry data of the HX cluster to Cisco Support. | Checked |
| Send Service ticket to | Add your own email address or alias so you can received a copy of the ticket sent to Cisco. | |
| Advance Network | ||
| Management VLAN Tag | VLAN used for the Management network, it must be the same as used earlier in the installation process for the management network. | Management VLAN tag |
| Data VLAN Tag | VLAN used for the data network, it must be the same as used earlier in the installation process for the data network. | Data VLAN tag |
| Advance Configuration | ||
| Enable Jumbo Frames on Data Network | Ensures that we are running Jumbo frames on the links connected to the storage VM’s. | Checked |
| Disk Partitions | If you want to clean up you environment during a re-installation check this box. | Unchecked |
| VDI | Optimize for VDI only deployment | Checked |
| Hypervisor Settings | ||
| Primary DNS suffix | Already filled out by some of the earlier steps. |
|
| Additional DNS Suffixes | If you need more suffixes appended on your Hyper-V hosts. |
|
9. Fill in the fields on the page according to the following information:
![]() The password must be complex, have a minimum of 10 characters, and include at least 1 uppercase letter, 1 digit, 1 special character.
The password must be complex, have a minimum of 10 characters, and include at least 1 uppercase letter, 1 digit, 1 special character.
10. Click Continue.

![]() After clicking Start, the installation and configuration of HX will begin and can take up to 2 hours to complete.
After clicking Start, the installation and configuration of HX will begin and can take up to 2 hours to complete.

Configuring the hosts:

The cluster is created and on completion you will see the following screen:

Cluster Validation
To verify that the cluster is healthy, complete the following steps:
1. Log in to the HyperFlex Connect UI and verify that it reports cluster as healthy.
2. Click Launch HyperFlex Connect on the screen to access the HyperFlex Connect UI.

3. HyperFlex Connect UI displays. Log in with your newly created hxadmin user and password that you provided during the installation. If the cluster is healthy, it will appear as shown in the image below:

![]() Do not to change the name or any resource configuration for the controller VM.
Do not to change the name or any resource configuration for the controller VM.
![]()
4. Use the HyperFlex connect UI to create a datastore. While using HyperFlex Connect UI to create a datastore there is an option to select the block size. 8K is the default.

The HyperFlex installer configures all components of the environment from the UCS policies to the Hyper-V networking. In order to manage the environment from SCVMM for the purpose of VDI, you must perform some post-installation steps to allow Citrix XenDesktop to use the environment. Below are the steps to prepare the environment for VDI use.
Create Run As Account in VMM
A Run As account is a container for a set of stored credentials. In VMM a Run As account can be provided for any process that requires credentials. Administrators and Delegated Administrators can create Run As accounts. For this deployment, a Run As account should be created for adding Hyper-V hosts and clusters.
To create a Run As account, complete the following steps:
1. Click Settings and in Create click Create Run As Account.
2. In Create Run As Account specify name and optional description to identify the credentials in VMM.
3. In User name and Password specify the credentials. The credentials can be a valid Active Directory user or group account, or local credentials.
4. Clear Validate domain credentials if it is not required and click OK to create the Run As account.
Servers
When running the Hyperflex installer, we specified the cluster hostname of ‘HXHV1WFC’. The installer created and configured the cluster and it needs to be added to the System Center VMM server to use with XenDesktop.
· Add Cluster created by HX Installer to SCVMM

Networking
Network switches and interfaces are created by the HyperFlex installer. A network team will be created for the Management, Storage, VM Network and Live Migration networks specified during the installer.
When the teams are created, the Network Sites must be created and added to the logical networks created by the installer.
1. Under Fabric -> Networking -> Logical Networks, find the Logical Network created by the installer.
![]() In this example, it is ‘vswitch-hx-vm-network’.
In this example, it is ‘vswitch-hx-vm-network’.

2. Right-click and select ‘Properties’ of the logical network.

3. Under Network Site, add a site so a VLAN can be specified on the Logical Network.
![]() In this example VLAN 34 was used for the VM network.
In this example VLAN 34 was used for the VM network.

4. When the network site is created, make sure each host in the cluster has the proper VLAN checked in its properties. This can be found under the properties of each host, under Hardware -> and scroll to the ‘team-hx-vm-network’
Storage
The data stores created in the HyperFlex Connect interface, creates an SMB share to use to place Virtual Machines. The naming convention is ‘\\hxClustername\DatastoreName’.
To add the HX Datastores to the HX cluster, complete the following steps:
1. Right-click the Cluster ‘HXHV1WFC’, select Properties and click ‘File Share Storage’.

2. Click Add to specify the UNC path for the datastore.

3. Click OK.
Software Infrastructure Configuration
This section details how to configure the software infrastructure components that comprise this solution.
Install and configure the infrastructure virtual machines by following the process provided in Table 13
Table 13 Test Infrastructure Virtual Machine Configuration
| Configuration | Citrix XenDesktop Controllers Virtual Machines | Citrix Profile Servers Virtual Machines |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows Server 2016 | Microsoft Windows Server 2016 |
| Virtual CPU amount | 6 | 8 |
| Memory amount | 8 GB | 8 GB |
| Network | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt |
| Disk-1 (OS) size and location | 40 GB Infra-DS volume | 40 GB Infra-DS volume |
| Disk-2 size and location | – |
|
| Configuration | Microsoft Active Directory DCs Virtual Machines |
|
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 |
|
| Virtual CPU amount | 4 |
|
| Memory amount | 4 GB |
|
| Network | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt |
|
| Disk size and location | 40 GB |
|
| Configuration | Microsoft SQL Server Virtual Machine | Citrix StoreFront Virtual Machines |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Microsoft SQL Server 2016 | Microsoft Windows Server 2016 |
| Virtual CPU amount | 4 | 4 |
| Memory amount | 16 GB | 8 GB |
| Network | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt |
| Disk-1 (OS) size and location | 40 GB Infra-DS volume | 40 GB Infra-DS volume |
| Disk-2 size and location | 200 GB Infra-DS volume SQL Logs | – |
| Configuration | Citrix License Server Virtual Machines | NetScaler VPX Appliance Virtual Machine |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows Server 2016 | NS11.1 52.13.nc |
| Virtual CPU amount | 4 | 2 |
| Memory amount | 4 GB | 2 GB |
| Network | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt | VMNIC InBand-Mgmt |
| Disk size and location | 40 GB | 20 GB |
Prepare the Master Images
This section detail how to create the golden (or master) images for the environment. VMs for the master images must first be installed with the software components needed to build the golden images. For this CVD, the images contain the basics needed to run the Login VSI workload.
To prepare the master VMs for the Hosted Virtual Desktops (HVDs) and Hosted Shared Desktops (HSDs), there are three major steps to complete when the base virtual machine has been created:
· Installing OS
· Installing application software
· Installing the Virtual Delivery Agents (VDAs)
The master image HVD and HSD VMs were configured as listed in Table 14 :
Table 14 HVD and HSD Configurations
| Configuration | HVDI Virtual Machines | HSD (Not used in this study) Virtual Machines |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows 10 64-bit | Microsoft Windows Server 2016 |
| Virtual CPU amount | 2 | 6 |
| Memory amount | 2.0 GB (reserved) | 24 GB (reserved) |
| Network | VMNIC vm-network | VMNIC vm-network |
| Citrix PVS vDisk size and location | 24 GB (thick) VDI WriteCache Volume | 100 GB (thick) Infra-DS volume |
| Citrix PVS write cache Disk size | 6 GB | 24 GB |
| Additional software used for testing | Microsoft Office 2016 Login VSI 4.1.32 (Knowledge Worker Workload) | Microsoft Office 2016 Login VSI 4.1.32 (Knowledge Worker Workload) |
Install and Configure XenDesktop Delivery Controller, Citrix Licensing, and StoreFront
This section details the installation of the core components of the XenDesktop/XenApp 7.16 system. This CVD provides the process to install two XenDesktop Delivery Controllers to support hosted shared desktops (HSD), non-persistent virtual desktops (VDI), and persistent virtual desktops (VDI).
The process of installing the XenDesktop Delivery Controller also installs other key XenDesktop software components, including Studio, which is used to create and manage infrastructure components, and Director, which is used to monitor performance and troubleshoot problems.
Install Citrix License Server
To install the Citrix License Server, complete the following steps:
1. To begin the installation, connect to the first Citrix License server and launch the installer from the Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 ISO.
2. Click Start.

3. Click “Extend Deployment – Citrix License Server.”

4. Read the Citrix License Agreement.
5. If acceptable, indicate your acceptance of the license by selecting the “I have read, understand, and accept the terms of the license agreement” radio button.
6. Click Next.

7. Click Next.

8. Select the default ports and automatically configured firewall rules.
9. Click Next

10. Click Install.

11. Click Finish to complete the installation.

Install Citrix Licenses
To install the Citrix Licenses, complete the following steps:
1. Copy the license files to the default location (C:\Program Files (x86)\Citrix\Licensing\ MyFiles) on the license server.

2. Restart the server or Citrix licensing services so that the licenses are activated.
3. Run the application Citrix License Administration Console.

4. Confirm that the license files have been read and enabled correctly.

Install the XenDesktop
1. To begin the installation, connect to the first XenDesktop server and launch the installer from the Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 ISO.
2. Click Start.

The installation wizard presents a menu with three subsections.
3. Click “Get Started - Delivery Controller.”

4. Read the Citrix License Agreement.
5. If acceptable, indicate your acceptance of the license by selecting the “I have read, understand, and accept the terms of the license agreement” radio button.
6. Click Next.

7. Select the components to be installed on the first Delivery Controller Server:
a. Delivery Controller
b. Studio
c. Director
8. Click Next.

![]() Dedicated StoreFront and License servers should be implemented for large scale deployments.
Dedicated StoreFront and License servers should be implemented for large scale deployments.
9. Since a SQL Server will be used to Store the Database, leave “Install Microsoft SQL Server 2012 SP1 Express” unchecked.
10. Click Next.

11. Select the default ports and automatically configured firewall rules.
12. Click Next.

13. Click Install to begin the installation.

14. (Optional) Click the Call Home participation.
15. Click Next.

16. Click Finish to complete the installation.
17. (Optional) Check Launch Studio to launch Citrix Studio Console.

Configure the XenDesktop Site
Citrix Studio is a management console that allows you to create and manage infrastructure and resources to deliver desktops and applications. Replacing Desktop Studio from earlier releases, it provides wizards to set up your environment, create workloads to host applications and desktops, and assign applications and desktops to users.
Citrix Studio launches automatically after the XenDesktop Delivery Controller installation, or if necessary, it can be launched manually. Citrix Studio is used to create a Site, which is the core XenDesktop 7.16 environment consisting of the Delivery Controller and the Database.
To configure XenDesktop, complete the following steps:
1. From Citrix Studio, click the Deliver applications and desktops to your users button.

2. Select the “A fully configured, production-ready Site” radio button.
3. Enter a site name.
4. Click Next.

5. Provide the Database Server Locations for each data type and click Next.

6. For an AlwaysOn Availability Group, use the group’s listener DNS name.

7. Provide the FQDN of the license server.
8. Click Connect to validate and retrieve any licenses from the server.
![]() If no licenses are available, you can use the 30-day free trial or activate a license file.
If no licenses are available, you can use the 30-day free trial or activate a license file.
9. Select the appropriate product edition using the license radio button.
10. Click Next.

11. Select the Connection type of System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
12. Enter the FQDN of the SCVMM server (in Server_FQDN/sdk format).
13. Enter the username (in domain\username format) for the Hyper-V account.
14. Provide the password for the Domain Admin account.
15. Provide a connection name.
16. Select the Other tools radio button.

17. Click Next.
18. Select HyperFlex Cluster that will be used by this connection.
19. Check Studio Tools radio button required to support desktop provisioning task by this connection.
20. Click Next.

21. Make Storage selection to be used by this connection.
22. Click Next.

23. Make Network selection to be used by this connection.
24. Click Next.

25. Select Additional features.
26. Click Next.

27. Review Site configuration Summary and click Finish.

Configure the XenDesktop Site Administrators
To configure the XenDesktop site administrators, complete the following steps:
1. Connect to the XenDesktop server and open Citrix Studio Management console.
2. From the Configuration menu, right-click Administrator and select Create Administrator from the drop-down list.

3. Select/Create appropriate scope and click Next.

4. Choose an appropriate Role.

5. Review the Summary, check Enable administrator, and click Finish.

Configure Additional XenDesktop Controller
After the first controller is completely configured and the Site is operational, you can add additional controllers. In this CVD, we created two Delivery Controllers.
To configure additional XenDesktop controllers, complete the following steps:
1. To begin the installation of the second Delivery Controller, connect to the second XenDesktop server and launch the installer from the Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 ISO.
2. Click Start.

3. Click Delivery Controller.

4. Repeat the same steps used to install the first Delivery Controller, including the step of importing an SSL certificate for HTTPS between the controller and Hyper-V.
5. Review the Summary configuration.
6. Click Install.

7. (Optional) Click the “I want to participate in Call Home.”
8. Click Next.

9. Verify the components installed successfully.
10. Click Finish.

Add the Second Delivery Controller to the XenDesktop Site
To add the second Delivery Controller to the XenDesktop Site, complete the following steps:
1. In Desktop Studio click the “Connect this Delivery Controller to an existing Site” button.

2. Enter the FQDN of the first delivery controller.
3. Click OK.

4. Click Yes to allow the database to be updated with this controller’s information automatically.
5. When complete, test the site configuration and verify the Delivery Controller has been added to the list of Controllers.

Install and Configure StoreFront
Citrix StoreFront stores aggregate desktops and applications from XenDesktop sites, making resources readily available to users. In this CVD, we created two StoreFront servers on dedicated virtual machines.
To install and configure StoreFront, complete the following steps:
1. To begin the installation of the StoreFront, connect to the first StoreFront server and launch the installer from the Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 ISO.
2. Click Start.

3. Click Extend Deployment Citrix StoreFront.

4. If acceptable, indicate your acceptance of the license by selecting the “I have read, understand, and accept the terms of the license agreement” radio button.
5. Click Next.

6. Click Next.

7. Select the default ports and automatically configured firewall rules.
8. Click Next.

9. Click Install.

10. (Optional) Click “I want to participate in Call Home.”
11. Click Next.

12. Check “Open the StoreFront Management Console.”
13. Click Finish.

14. Click Create a new deployment.

15. Specify the URL of the StoreFront server and click Next.
![]() For a multiple server deployment use the load balancing environment in the Base URL box.
For a multiple server deployment use the load balancing environment in the Base URL box.

16. Click Next.

17. Specify a name for your store and click Next.

18. Add the required Delivery Controllers to the store and click Next.

19. Specify how connecting users can access the resources, in this environment only local users on the internal network are able to access the store, and click Next.

20. On the “Authentication Methods” page, select the methods your users will use to authenticate to the store and click Next. You can select from the following methods:

21. Username and password: Users enter their credentials and are authenticated when they access their stores.
22. Domain pass-through: Users authenticate to their domain-joined Windows computers and their credentials are used to log them on automatically when they access their stores.
23. Configure the XenApp Service URL for users who use PNAgent to access the applications and desktops and click Create.

24. After creating the store click Finish.

Additional StoreFront Configuration
After the first StoreFront server is completely configured and the Store is operational, you can add additional servers.
To configure additional StoreFront server, complete the following steps:
1. To begin the installation of the second StoreFront, connect to the second StoreFront server and launch the installer from the Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 ISO.
2. Click Start.

3. Click Extended Deployment Citrix StoreFront.

4. Repeat the same steps used to install the first StoreFront.
5. Review the Summary configuration.
6. Click Install.

7. (Optional) Click “I want to participate in Call Home.”
8. Click Next.

9. Check “Open the StoreFront Management Console."
10. Click Finish.

To configure the second StoreFront if used, complete the following steps:
1. From the StoreFront Console on the second server select “Join existing server group.”

2. In the Join Server Group dialog, enter the name of the first Storefront server.

3. Before the additional StoreFront server can join the server group, you must connect to the first Storefront server, add the second server, and obtain the required authorization information.
4. Connect to the first StoreFront server.
5. Using the StoreFront menu on the left, you can scroll through the StoreFront management options.
6. Select Server Group from the menu.

7. To add the second server and generate the authorization information that allows the additional StoreFront server to join the server group, select Add Server.

8. Copy the Authorization code from the Add Server dialog.

9. Connect to the second Storefront server and paste the Authorization code into the Join Server Group dialog.
10. Click Join.

11. A message appears when the second server has joined successfully.
12. Click OK.

The second StoreFront is now in the Server Group.
Install XenDesktop Virtual Desktop Agents
Virtual Delivery Agents (VDAs) are installed on the server and workstation operating systems, and enable connections for desktops and apps. The following procedure was used to install VDAs for both HVD and HSD environments.
By default, when you install the Virtual Delivery Agent, Citrix User Profile Management is installed silently on master images. (Using profile management as a profile solution is optional but was used for this CVD, and is described in a later section.)
To install XenDesktop Virtual Desktop Agents, complete the following steps:
1. Launch the XenDesktop installer from the XenDesktop 7.16 ISO.
2. Click Start on the Welcome Screen.

3. To install the VDA for the Hosted Virtual Desktops (VDI), select Virtual Delivery Agent for Windows Desktop OS. After the VDA is installed for Hosted Virtual Desktops, repeat the procedure to install the VDA for Hosted Shared Desktops (RDS). In this case, select Virtual Delivery Agent for Windows Server OS and follow the same basic steps.

4. Select “Create a Master Image.”
5. Click Next.

6. Optional: Select Citrix Receiver.
7. Click Next.

8. Click Next.

9. Select “Do it manually” and specify the FQDN of the Delivery Controllers.
10. Click Next.

11. Accept the default features.
12. Click Next.

13. Allow the firewall rules to be configured automatically.
14. Click Next.

15. Verify the Summary and click Install.

16. (Optional) Select Call Home participation.

17. (Optional) check “Restart Machine.”
18. Click Finish.

19. Repeat the procedure so that VDAs are installed for both HVD (using the Windows 10 OS image) and the HSD desktops (using the Windows Server 2016 image).
20. Select an appropriate workflow for the HSD desktop.

Persistent Static Provisioned with MCS
1. Connect to a XenDesktop server and launch Citrix Studio.
2. Choose Create Machine Catalog from the drop-down list.

3. Click Next.

4. Select Desktop OS.
5. Click Next.

6. Select appropriate machine management.
7. Click Next.

8. Select Static, Dedicated Virtual Machine for Desktop Experience.
9. Click Next.

10. Select a Virtual Machine to be used for Catalog Master image.
11. Click Next.

12. Specify the number of the desktops to create and machine configuration.
13. Set amount of memory (MB) to be used by virtual desktops.
14. Select Full Copy for machine copy mode.
15. Click Next.

16. Specify AD account naming scheme and OU where accounts will be created.
17. Click Next.

18. On Summary page specify Catalog name and click Finish to start deployment.

19. Verify the desktop machines were successfully created in the following locations:
- Delivery Controller > Citrix Studio > Machine Catalogs
- Domain Controller > Active Directory Users and Computers
Create Delivery Groups
Delivery Groups are collections of machines that control access to desktops and applications. With Delivery Groups, you can specify which users and groups can access which desktops and applications.
To create delivery groups, complete the following steps:
![]() The instructions below outline the procedure to create a Delivery Group for VDI desktops. When you have completed these steps, repeat the procedure to a Delivery Group for HVD desktops.
The instructions below outline the procedure to create a Delivery Group for VDI desktops. When you have completed these steps, repeat the procedure to a Delivery Group for HVD desktops.
1. Connect to a XenDesktop server and launch Citrix Studio.
2. Choose Create Delivery Group from the drop-down list.

3. Click Next.

4. Select Machine catalog.
5. Provide the number of machines to be added to the delivery Group.
6. Click Next.

7. To make the Delivery Group accessible, you must add users, select Allow any authenticated users to use this Delivery Group.
8. Click Next.

![]() User assignment can be updated any time after Delivery group creation by accessing Delivery group properties in Desktop Studio.
User assignment can be updated any time after Delivery group creation by accessing Delivery group properties in Desktop Studio.
9. (Optional) specify Applications catalog will deliver.
10. Click Next.

11. On the Summary dialog, review the configuration. Enter a Delivery Group name and a Display name (for example, HVD or HSD).
12. Click Finish.

13. Citrix Studio lists the created Delivery Groups and the type, number of machines created, sessions, and applications for each group in the Delivery Groups tab. Select Delivery Group and in Action List, select “Turn on Maintenance Mode.”

Citrix XenDesktop Policies and Profile Management
Policies and profiles allow the Citrix XenDesktop environment to be easily and efficiently customized.
Configure Citrix XenDesktop Policies
Citrix XenDesktop policies control user access and session environments, and are the most efficient method of controlling connection, security, and bandwidth settings. You can create policies for specific groups of users, devices, or connection types with each policy. Policies can contain multiple settings and are typically defined through Citrix Studio. (The Windows Group Policy Management Console can also be used if the network environment includes Microsoft Active Directory and permissions are set for managing Group Policy Objects). The screenshot below shows policies for Login VSI testing in this CVD.
図 41 XenDesktop Policy

Configuring User Profile Management
Profile management provides an easy, reliable, and high-performance way to manage user personalization settings in virtualized or physical Windows environments. It requires minimal infrastructure and administration, and provides users with fast logons and logoffs. A Windows user profile is a collection of folders, files, registry settings, and configuration settings that define the environment for a user who logs on with a particular user account. These settings may be customizable by the user, depending on the administrative configuration. Examples of settings that can be customized are:
· Desktop settings such as wallpaper and screen saver
· Shortcuts and Start menu setting
· Internet Explorer Favorites and Home Page
· Microsoft Outlook signature
· Printers
Some user settings and data can be redirected by means of folder redirection. However, if folder redirection is not used these settings are stored within the user profile.
The first stage in planning a profile management deployment is to decide on a set of policy settings that together form a suitable configuration for your environment and users. The automatic configuration feature simplifies some of this decision-making for XenDesktop deployments. Screenshots of the User Profile Management interfaces that establish policies for this CVD’s RDS and VDI users (for testing purposes) are shown below. Basic profile management policy settings are documented here:
http://docs.citrix.com/en-us/xenapp-and-xendesktop/7-11.html
図 42 VDI User Profile Manager Policy

In this project, we tested a single Cisco HyperFlex cluster running four Cisco UCS HXAF220C-M5SX Rack Servers in a single Cisco UCS domain. This solution is tested to illustrate linear scalability for each workload studied.
 Hardware Components:
Hardware Components:
· 2 x Cisco UCS 6332-16UP Fabric Interconnects
· 2 x Cisco Nexus 93108YCPX Access Switches
· 4 x Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M5SX Rack Servers (2 Intel Xeon Gold 6140 scalable family processor at 2.3 GHz, with 768 GB of memory per server [32 GB x 24 DIMMs at 2666 MHz])
· Cisco VIC 1387 mLOM
· 12G modular SAS HBA Controller
· 240GB M.2 SATA SSD drive (Boot and HyperFlex Data Platform controller VM)
· 240GB 2.5” 6G SATA SSD drive (Housekeeping)
· 400GB 2.5” 6G SAS SSD drive (Cache)
· 8 x 960GB 2.5” SATA SSD drive (Capacity)
· 1 x 32GB mSD card (Upgrades temporary cache)
Software Components:
· Cisco UCS firmware 3.2(3d)
· Cisco HyperFlex Data Platform 3.0.1a
· Microsoft Hyper-V 2016
· Citrix XenDesktop 7.16
· Citrix User Profile Management
· Citrix NetScaler VPX NS11.1 52.13.nc
· Microsoft SQL Server 2016
· Microsoft Windows 10
· Microsoft Windows 2016
· Microsoft Office 2016
· Login VSI 4.1.25.6
Testing Methodology and Success Criteria
All validation testing was conducted on-site within the Cisco labs in San Jose, California.
The testing results focused on the entire process of the virtual desktop lifecycle by capturing metrics during the desktop boot-up, user logon and virtual desktop acquisition (also referred to as ramp-up,) user workload execution (also referred to as steady state), and user logoff for the Hosted Shared Desktop Session under test.
Test metrics were gathered from the virtual desktop, storage, and load generation software to assess the overall success of an individual test cycle. Each test cycle was not considered passing unless all of the planned test users completed the ramp-up and steady state phases (described below) and unless all metrics were within the permissible thresholds as noted as success criteria.
Three successfully completed test cycles were conducted for each hardware configuration and results were found to be relatively consistent from one test to the next.
You can obtain additional information and a free test license from http://www.loginvsi.com.
Testing Procedure
The following protocol was used for each test cycle in this study to insure consistent results.
Pre-Test Setup for Testing
All machines were shut down utilizing the Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Administrator Console.
All Launchers for the test were shut down. They were then restarted in groups of 10 each minute until the required number of launchers was running with the Login VSI Agent at a “waiting for test to start” state.
Test Run Protocol
To simulate severe, real-world environments, Cisco requires the log-on and start-work sequence, known as Ramp Up, to complete in 48 minutes. Additionally, we require all sessions started, whether 60 single server users or 4000 full scale test users to become active within two minutes after the last session is launched.
In addition, Cisco requires that the Login VSI Benchmark method is used for all single server and scale testing. This assures that our tests represent real-world scenarios. For each of the three consecutive runs on single server tests, the same process was followed. Complete the following steps:
1. Time 0:00:00 Start esxtop Logging on the following systems:
— Infrastructure and VDI Host Blades used in test run
— All Infrastructure VMs used in test run (AD, SQL, View Connection brokers, image mgmt., etc.)
2. Time 0:00:10 Start Storage Partner Performance Logging on Storage System.
3. Time 0:05: Boot RDS Machines using Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Administrator Console.
4. Time 0:06 First machines boot.
5. Time 0:35 Single Server or Scale target number of RDS Servers registered on XD.
![]() No more than 60 Minutes of rest time is allowed after the last desktop is registered and available on Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Administrator Console dashboard. Typically a 20-30 minute rest period for Windows 10 desktops and 10 minutes for RDS VMs is sufficient.
No more than 60 Minutes of rest time is allowed after the last desktop is registered and available on Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Administrator Console dashboard. Typically a 20-30 minute rest period for Windows 10 desktops and 10 minutes for RDS VMs is sufficient.
6. Time 1:35 Start Login VSI 4.1.5 Knowledge Worker Benchmark Mode Test, setting auto-logoff time at 900 seconds, with Single Server or Scale target number of desktop VMs utilizing sufficient number of Launchers (at 20-25 sessions/Launcher).
7. Time 2:23 Single Server or Scale target number of desktop VMs desktops launched (48 minute benchmark launch rate).
8. Time 2:25 All launched sessions must become active.
![]() All sessions launched must become active for a valid test run within this window.
All sessions launched must become active for a valid test run within this window.
9. Time 2:40 Login VSI Test Ends (based on Auto Logoff 900 Second period designated above).
10. Time 2:55 All active sessions logged off.
11. All sessions launched and active must be logged off for a valid test run. The Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Administrator Dashboard must show that all desktops have been returned to the registered/available state as evidence of this condition being met.
12. Time 2:57 All logging terminated; Test complete.
13. Time 3:15 Copy all log files off to archive; Set virtual desktops to maintenance mode through broker; Shutdown all Windows 7 machines.
14. Time 3:30 Reboot all hypervisors.
15. Time 3:45 Ready for new test sequence.
Success Criteria
Our “pass” criteria for this testing is as follows: Cisco will run tests at a session count levels that effectively utilize the server capacity measured by CPU, memory, storage and network utilization. We use Login VSI version 4.1.25 to launch Knowledge Worker workload sessions. The number of launched sessions must equal active sessions within two minutes of the last session launched in a test as observed on the VSI Management console.
The Citrix XenDesktop Studio will be monitored throughout the steady state to make sure of the following:
· All running sessions report In Use throughout the steady state
· No sessions move to unregistered, unavailable or available state at any time during steady state
Within 20 minutes of the end of the test, all sessions on all launchers must have logged out automatically and the Login VSI Agent must have shut down. Cisco’s tolerance for Stuck Sessions is 0.5 percent (half of one percent.) If the Stuck Session count exceeds that value, we identify it as a test failure condition.
Cisco requires three consecutive runs with results within +/-1 percent variability to pass the Cisco Validated Design performance criteria. For white papers written by partners, two consecutive runs within +/-1 percent variability are accepted. (All test data from partner run testing must be supplied along with proposed white paper.)
We will publish Cisco Validated Designs with our recommended workload following the process above and will note that we did not reach a VSImax dynamic in our testing.
The purpose of this testing is to provide the data needed to validate Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Hosted Shared Desktop with Citrix XenDesktop 7.16 Composer provisioning using Microsoft Windows Server 2016 sessions on Cisco UCS HXAF220c-M4S, Cisco UCS 220 M4 and Cisco UCS B200 M4 servers.
The information contained in this section provides data points that a customer may reference in designing their own implementations. These validation results are an example of what is possible under the specific environment conditions outlined here and do not represent the full characterization of Citrix and Microsoft products.
Four test sequences, each containing three consecutive test runs generating the same result, were performed to establish system performance and linear scalability.
VSImax 4.1.x Description
The philosophy behind Login VSI is different to conventional benchmarks. In general, most system benchmarks are steady state benchmarks. These benchmarks execute one or multiple processes, and the measured execution time is the outcome of the test. Simply put: the faster the execution time or the bigger the throughput, the faster the system is according to the benchmark.
Login VSI is different in approach. Login VSI is not primarily designed to be a steady state benchmark (however, if needed, Login VSI can act like one). Login VSI was designed to perform benchmarks for SBC or VDI workloads through system saturation. Login VSI loads the system with simulated user workloads using well known desktop applications like Microsoft Office, Internet Explorer and Adobe PDF reader. By gradually increasing the amount of simulated users, the system will eventually be saturated. Once the system is saturated, the response time of the applications will increase significantly. This latency in application response times show a clear indication whether the system is (close to being) overloaded. As a result, by nearly overloading a system it is possible to find out what its true maximum user capacity is.
After a test is performed, the response times can be analyzed to calculate the maximum active session/desktop capacity. Within Login VSI this is calculated as VSImax. When the system is coming closer to its saturation point, response times will rise. When reviewing the average response time it will be clear the response times escalate at saturation point.
This VSImax is the “Virtual Session Index (VSI)”. With Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Terminal Services (RDS) workloads this is valid and useful information. This index simplifies comparisons and makes it possible to understand the true impact of configuration changes on hypervisor host or guest level.
Server-Side Response Time Measurements
It is important to understand why specific Login VSI design choices have been made. An important design choice is to execute the workload directly on the target system within the session instead of using remote sessions. The scripts simulating the workloads are performed by an engine that executes workload scripts on every target system, and are initiated at logon within the simulated user’s desktop session context.
An alternative to the Login VSI method would be to generate user actions client side through the remoting protocol. These methods are always specific to a product and vendor dependent. More importantly, some protocols simply do not have a method to script user actions client side.
For Login VSI the choice has been made to execute the scripts completely server side. This is the only practical and platform independent solutions, for a benchmark like Login VSI.
Calculating VSImax v4.1.x
The simulated desktop workload is scripted in a 48-minute loop when a simulated Login VSI user is logged on, performing generic Office worker activities. After the loop is finished it will restart automatically. Within each loop the response times of sixteen specific operations are measured in a regular interval: sixteen times in within each loop. The response times of these five operations are used to determine VSImax.
The five operations from which the response times are measured are:
· Notepad File Open (NFO)
Loading and initiating VSINotepad.exe and opening the openfile dialog. This operation is handled by the OS and by the VSINotepad.exe itself through execution. This operation seems almost instant from an end-user’s point of view.
· Notepad Start Load (NSLD)
Loading and initiating VSINotepad.exe and opening a file. This operation is also handled by the OS and by the VSINotepad.exe itself through execution. This operation seems almost instant from an end-user’s point of view.
· Zip High Compression (ZHC)
This action copy's a random file and compresses it (with 7zip) with high compression enabled. The compression will very briefly spike CPU and disk IO.
· Zip Low Compression (ZLC)
This action copy's a random file and compresses it (with 7zip) with low compression enabled. The compression will very briefly disk IO and creates some load on the CPU.
· CPU
Calculates a large array of random data and spikes the CPU for a short period of time.
These measured operations within Login VSI do hit considerably different subsystems such as CPU (user and kernel), Memory, Disk, the OS in general, the application itself, print, GDI, etc. These operations are specifically short by nature. When such operations become consistently long: the system is saturated because of excessive queuing on any kind of resource. As a result, the average response times will then escalate. This effect is clearly visible to end-users. If such operations consistently consume multiple seconds the user will regard the system as slow and unresponsive.
図 43 Sample of a VSI Max Response Time Graph, Representing a Normal Test
図 44 Sample of a VSI Test Response Time Graph with a Clear Performance Issue
When the test is finished, VSImax can be calculated. When the system is not saturated, and it could complete the full test without exceeding the average response time latency threshold, VSImax is not reached and the amount of sessions ran successfully.
The response times are very different per measurement type, for instance Zip with compression can be around 2800 ms, while the Zip action without compression can only take 75ms. This response time of these actions are weighted before they are added to the total. This ensures that each activity has an equal impact on the total response time.
In comparison to previous VSImax models, this weighting much better represent system performance. All actions have very similar weight in the VSImax total. The following weighting of the response times are applied.
The following actions are part of the VSImax v4.1 calculation and are weighted as follows (US notation):
· Notepad File Open (NFO): 0.75
· Notepad Start Load (NSLD): 0.2
· Zip High Compression (ZHC): 0.125
· Zip Low Compression (ZLC): 0.2
· CPU: 0.75
This weighting is applied on the baseline and normal Login VSI response times.
With the introduction of Login VSI 4.1 we also created a new method to calculate the base phase of an environment. With the new workloads (Taskworker, Powerworker, etc.) enabling 'base phase' for a more reliable baseline has become obsolete. The calculation is explained below. In total 15 lowest VSI response time samples are taken from the entire test, the lowest 2 samples are removed and the 13 remaining samples are averaged. The result is the Baseline. The calculation is as follows:
· Take the lowest 15 samples of the complete test
· From those 15 samples remove the lowest 2
· Average the 13 results that are left is the baseline
The VSImax average response time in Login VSI 4.1.x is calculated on the amount of active users that are logged on the system.
Always a 5 Login VSI response time samples are averaged + 40 percent of the amount of “active” sessions. For example, if the active sessions is 60, then latest 5 + 24 (=40 percent of 60) = 31 response time measurement are used for the average calculation.
To remove noise (accidental spikes) from the calculation, the top 5 percent and bottom 5 percent of the VSI response time samples are removed from the average calculation, with a minimum of 1 top and 1 bottom sample. As a result, with 60 active users, the last 31 VSI response time sample are taken. From those 31 samples the top 2 samples are removed and lowest 2 results are removed (5 percent of 31 = 1.55, rounded to 2). At 60 users the average is then calculated over the 27 remaining results.
VSImax v4.1.x is reached when the VSIbase + a 1000 ms latency threshold is not reached by the average VSI response time result. Depending on the tested system, VSImax response time can grow 2 - 3x the baseline average. In end-user computing, a 3x increase in response time in comparison to the baseline is typically regarded as the maximum performance degradation to be considered acceptable.
In VSImax v4.1.x this latency threshold is fixed to 1000ms, this allows better and fairer comparisons between two different systems, especially when they have different baseline results. Ultimately, in VSImax v4.1.x, the performance of the system is not decided by the total average response time, but by the latency is has under load. For all systems, this is now 1000ms (weighted).
The threshold for the total response time is: average weighted baseline response time + 1000ms.
When the system has a weighted baseline response time average of 1500ms, the maximum average response time may not be greater than 2500ms (1500+1000). If the average baseline is 3000 the maximum average response time may not be greater than 4000ms (3000+1000).
When the threshold is not exceeded by the average VSI response time during the test, VSImax is not hit and the amount of sessions ran successfully. This approach is fundamentally different in comparison to previous VSImax methods, as it was always required to saturate the system beyond VSImax threshold.
Lastly, VSImax v4.1.x is now always reported with the average baseline VSI response time result. For example: “The VSImax v4.1 was 125 with a baseline of 1526ms”. This helps considerably in the comparison of systems and gives a more complete understanding of the system. The baseline performance helps to understand the best performance the system can give to an individual user. VSImax indicates what the total user capacity is for the system. These two are not automatically connected and related:
When a server with a very fast dual core CPU, running at 3.6 GHZ, is compared to a 10 core CPU, running at 2,26 GHZ, the dual core machine will give and individual user better performance than the 10 core machine. This is indicated by the baseline VSI response time. The lower this score is, the better performance an individual user can expect.
However, the server with the slower 10 core CPU will easily have a larger capacity than the faster dual core system. This is indicated by VSImax v4.1.x, and the higher VSImax is, the larger overall user capacity can be expected.
With Login VSI 4.1.x a new VSImax method is introduced: VSImax v4.1. This methodology gives much better insight in system performance and scales to extremely large systems.
Boot Storms
A key performance metric for desktop virtualization environments is the ability to boot the virtual machines quickly and efficiently to minimize user wait time for their desktop.
As part of Cisco’s virtual desktop test protocol, we shut down each virtual machine at the conclusion of a benchmark test. When we run a new test, we cold boot all 450 desktops and measure the time it takes for the 450th virtual machine to register as available in the XenDesktop Administrator console.
The Cisco HyperFlex HXAF220c-M5SX based All-Flash cluster running Data Platform version 3.0.1a software can accomplish this task in 5 minutes.
Recommended Maximum Workload and Configuration Guidelines
Four Node Cisco HXAF220c-M5S Rack Server and HyperFlex All-Flash Cluster
For Citrix XenApp RDS Hosted Shared Desktop and Hosted Virtual Desktop use case, the recommended maximum workload was determined based on both Login VSI Knowledge Worker workload end user experience measures and HXAF220c-M5SX server operating parameters.
This recommended maximum workload approach allows you to determine the server N+1 fault tolerance load the blade can successfully support in the event of a server outage for maintenance or upgrade.
Our recommendation is that the Login VSI Average Response and VSI Index Average should not exceed the Baseline plus 2000 milliseconds to insure that end-user experience is outstanding. Additionally, during steady state, the processor utilization should average no more than 90-95 percent.
![]() Memory should never be oversubscribed for Desktop Virtualization workloads.
Memory should never be oversubscribed for Desktop Virtualization workloads.
![]() Callouts have been added throughout the data charts to indicate each phase of testing.
Callouts have been added throughout the data charts to indicate each phase of testing.
| Test Phase | Description |
| Boot | Start all RDS and/or VDI virtual machines at the same time. |
| Login | The Login VSI phase of test is where sessions are launched and start executing the workload over a 48 minutes duration. |
| Steady state | The steady state phase is where all users are logged in and performing various workload tasks such as using Microsoft Office, Web browsing, PDF printing, playing videos, and compressing files. |
| Logoff | Sessions finish executing the Login VSI workload and logoff. |
![]() The recommended maximum workload for a Cisco HyperFlex cluster configured on Cisco HXAF2240c-M5SX with Intel Xeon Gold 6140 scalable family processors and 768GB of RAM for Windows Server 2016 Hosted Sessions is 600 sessions with Office 2016 virtual desktops respectively.
The recommended maximum workload for a Cisco HyperFlex cluster configured on Cisco HXAF2240c-M5SX with Intel Xeon Gold 6140 scalable family processors and 768GB of RAM for Windows Server 2016 Hosted Sessions is 600 sessions with Office 2016 virtual desktops respectively.
450 Windows 10 Citrix MCS Persistent Testing on Four Node Cisco HyperFlex Cluster
Floating assigned automated Linked-Clone desktop pool with 450 Windows 10 VMs hosting 450 User Sessions on four HXAF220c-M5SX HyperFlex cluster.
Test result highlights include:
· 0.676 second baseline response time
· 0.839 second average response time with 450 desktops running
· Average CPU utilization of 45 percent during steady state
· Average of 320 GB of RAM used out of 768 GB available
· 1000Mbps peak network utilization per host.
· Average Read Latency 0.7ms/Max Read Latency 1.4ms
· Average Write Latency 1.9ms/Max Write Latency 4.4ms
· 3500 peak I/O operations per second (IOPS) per cluster at steady state
· 80MBps peak throughput per cluster at steady state
図 45 Login VSI Analyzer Chart for 450 Windows 10 Citrix MCS Persistent Virtual Desktops


図 46 Three Consecutive Login VSI Analyzer Chart for 450 Windows 10 Citrix MCS Persistent Virtual Desktops

図 47 Sample 4x Hyper-V Hosts CPU Core Utilization Running 450 Windows 10 Citrix MCS Persistent Virtual Desktops

図 48 HyperFlex Cluster UI Performance Chart for Knowledge Worker Workload Running 450 User Test on Citrix MCS Persistent Windows 10

This Cisco HyperFlex solution addresses urgent needs of IT by delivering a platform that is cost effective and simple to deploy and manage. The architecture and approach used provides for a flexible and high-performance system with a familiar and consistent management model from Cisco. In addition, the solution offers numerous enterprise-class data management features to deliver the next-generation hyper-converged system.
Only Cisco offers the flexibility to add compute only nodes to a true hyper-converged cluster for compute intensive workloads like desktop virtualization. This translates to lower cost for the customer, since no hyper-convergence licensing is required for those nodes.
Delivering responsive, resilient, high-performance Citrix XenDesktop provisioned Microsoft Windows 10 Virtual Machines and Microsoft Windows Server for hosted Apps or desktops has many advantages for desktop virtualization administrators.
The solution if fully capable of supporting graphics accelerated workloads. Each Cisco HyperFlex HXAF240c M5 node and each Cisco UCS C240 M5 server can support up to two NVIDIA M10 or P40 cards. The Cisco UCS B200 M5 server supports up to two NVIDIA P6 cards for high density, high performance graphics workload support. See our Cisco Graphics White Paper for our fifth generation servers with NVIDIA GPUs and software for details on how to integrate this capability with Citrix XenDesktop.
Virtual desktop end-user experience, as measured by the Login VSI tool in benchmark mode, is outstanding with Intel Xeon scalable family processors and Cisco 2666Mhz memory. In fact, we have set a new industry standard in performance for Desktop Virtualization on a hyper-converged platform.
Jeff Nichols is a Cisco Unified Computing System architect, focusing on Virtual Desktop and Application solutions with extensive experience with Microsoft ESX/Hyper-V, XenDesktop, XenApp and Microsoft Remote Desktop Services. He has expert product knowledge in application, desktop and server virtualization across all three major hypervisor platforms and supporting infrastructures including but not limited to Windows Active Directory and Group Policies, User Profiles, DNS, DHCP and major storage platforms.
Acknowledgements
For their support and contribution to the design, validation, and creation of this Cisco Validated Design, we would like to acknowledge their contribution and expertise that resulted in developing this document:
· Mike Brennan, Product Manager, Desktop Virtualization and Graphics Solutions, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Appendix A – Cisco Nexus 93108YC Switch Configuration
Switch A Configuration
!Command: show running-config
version 7.0(3)I2(2d)
switchname XXXXXXXXXXX
class-map type network-qos class-fcoe
match qos-group 1
class-map type network-qos class-all-flood
match qos-group 2
class-map type network-qos class-ip-multicast
match qos-group 2
vdc XXXXXXXXXX id 1
limit-resource vlan minimum 16 maximum 4094
limit-resource vrf minimum 2 maximum 4096
limit-resource port-channel minimum 0 maximum 511
limit-resource u4route-mem minimum 248 maximum 248
limit-resource u6route-mem minimum 96 maximum 96
limit-resource m4route-mem minimum 58 maximum 58
limit-resource m6route-mem minimum 8 maximum 8
feature telnet
cfs eth distribute
feature interface-vlan
feature hsrp
feature lacp
feature dhcp
feature vpc
feature lldp
clock protocol ntp vdc 1
no password strength-check
username admin password 5 $1$MSJwTJtn$Bo0IrVnESUVxLcbRHg86j1 role network-admin
ip domain-lookup
no service unsupported-transceiver
class-map type qos match-all class-fcoe
policy-map type qos jumbo
class class-default
set qos-group 0
copp profile strict
snmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0x71d6a9cf1ea007cd3166e91a6f3807e5
priv 0x71d6a9cf1ea007cd3166e91a6f3807e5 localizedkey
rmon event 1 log trap public description FATAL(1) owner PMON@FATAL
rmon event 2 log trap public description CRITICAL(2) owner PMON@CRITICAL
rmon event 3 log trap public description ERROR(3) owner PMON@ERROR
rmon event 4 log trap public description WARNING(4) owner PMON@WARNING
rmon event 5 log trap public description INFORMATION(5) owner PMON@INFO
ntp server 10.10.50.2
ntp peer 10.10.50.3
ntp server 171.68.38.66 use-vrf management
ntp logging
ntp master 8
vlan 1,50-54
vlan 50
name InBand-Mgmt-C1
vlan 51
name Infra-Mgmt-C1
vlan 52
name StorageIP-C1
vlan 53
name LiveMigration-C1
vlan 54
name VM-Data-C1
service dhcp
ip dhcp relay
ip dhcp relay information option
ipv6 dhcp relay
vrf context management
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 10.29.132.1
vpc domain 50
role priority 1000
peer-keepalive destination 10.29.132.20 source 10.29.132.19
interface Vlan1
no shutdown
ip address 10.29.132.2/24
interface Vlan50
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.50.2/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 50
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.50.1
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.21
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.22
interface Vlan51
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.51.2/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 51
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.51.1
interface Vlan52
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.52.2/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 52
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.52.1
interface Vlan53
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.53.2/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 53
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.53.1
interface Vlan54
no shutdown
ip address 10.54.0.2/20
hsrp version 2
hsrp 54
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.54.0.1
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.21
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.22
interface port-channel10
description vPC-PeerLink
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type network
service-policy type qos input jumbo
vpc peer-link
interface port-channel11
description FI-Uplink-K22
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
service-policy type qos input jumbo
vpc 11
interface port-channel12
description FI-Uplink-K22
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
service-policy type qos input jumbo
vpc 12
interface Ethernet1/1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/3
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/4
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/5
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 11 mode active
interface Ethernet1/6
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 11 mode active
interface Ethernet1/7
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 12 mode active
interface Ethernet1/8
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 12 mode active
interface Ethernet1/9
interface Ethernet1/10
interface Ethernet1/11
interface Ethernet1/12
interface Ethernet1/13
interface Ethernet1/14
interface Ethernet1/15
interface Ethernet1/16
interface Ethernet1/17
interface Ethernet1/18
interface Ethernet1/19
interface Ethernet1/20
interface Ethernet1/21
interface Ethernet1/22
interface Ethernet1/23
interface Ethernet1/24
interface Ethernet1/25
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/26
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/27
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/28
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/29
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/30
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/31
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/32
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/33
interface Ethernet1/34
interface Ethernet1/35
interface Ethernet1/36
interface Ethernet1/37
interface Ethernet1/38
interface Ethernet1/39
interface Ethernet1/40
interface Ethernet1/41
interface Ethernet1/42
interface Ethernet1/43
interface Ethernet1/44
interface Ethernet1/45
interface Ethernet1/46
interface Ethernet1/47
interface Ethernet1/48
interface Ethernet1/49
interface Ethernet1/50
interface Ethernet1/51
interface Ethernet1/52
interface Ethernet1/53
interface Ethernet1/54
interface mgmt0
vrf member management
ip address 10.29.132.19/24
clock timezone PST -8 0
clock summer-time PDT 2 Sunday March 02:00 1 Sunday November 02:00 60
line console
line vty
boot nxos bootflash:/nxos.7.0.3.I2.2d.bin
Switch B Configuration
!Command: show running-config
!Time: Fri Dec 15 17:18:36 2017
version 7.0(3)I2(2d)
switchname XXXXXXXXXX
class-map type network-qos class-fcoe
match qos-group 1
class-map type network-qos class-all-flood
match qos-group 2
class-map type network-qos class-ip-multicast
match qos-group 2
vdc XXXXXXXXXX id 1
limit-resource vlan minimum 16 maximum 4094
limit-resource vrf minimum 2 maximum 4096
limit-resource port-channel minimum 0 maximum 511
limit-resource u4route-mem minimum 248 maximum 248
limit-resource u6route-mem minimum 96 maximum 96
limit-resource m4route-mem minimum 58 maximum 58
limit-resource m6route-mem minimum 8 maximum 8
feature telnet
cfs eth distribute
feature interface-vlan
feature hsrp
feature lacp
feature dhcp
feature vpc
feature lldp
clock protocol ntp vdc 1
no password strength-check
username admin password 5 $1$jEwHqUvM$gpOec2hramkyX09KD3/Dn. role network-admin
ip domain-lookup
no service unsupported-transceiver
class-map type qos match-all class-fcoe
policy-map type qos jumbo
class class-default
set qos-group 0
copp profile strict
snmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0x9046c100ce1f4ecdd74ef2f92c4e83f9
priv 0x9046c100ce1f4ecdd74ef2f92c4e83f9 localizedkey
rmon event 1 log trap public description FATAL(1) owner PMON@FATAL
rmon event 2 log trap public description CRITICAL(2) owner PMON@CRITICAL
rmon event 3 log trap public description ERROR(3) owner PMON@ERROR
rmon event 4 log trap public description WARNING(4) owner PMON@WARNING
rmon event 5 log trap public description INFORMATION(5) owner PMON@INFO
ntp peer 10.10.50.2
ntp server 10.10.50.3
ntp server 171.68.38.66 use-vrf management
ntp logging
ntp master 8
vlan 1,50-54
vlan 50
name InBand-Mgmt-C1
vlan 51
name Infra-Mgmt-C1
vlan 52
name StorageIP-C1
vlan 53
name LiveMigration-C1
vlan 54
name VM-Data-C1
service dhcp
ip dhcp relay
ip dhcp relay information option
ipv6 dhcp relay
vrf context management
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 10.29.132.1
vpc domain 50
role priority 2000
peer-keepalive destination 10.29.132.19 source 10.29.132.20
interface Vlan1
no shutdown
ip address 10.29.132.3/24
interface Vlan50
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.50.3/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 50
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.50.1
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.21
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.22
interface Vlan51
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.51.3/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 51
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.51.1
interface Vlan52
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.52.3/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 52
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.52.1
interface Vlan53
no shutdown
ip address 10.10.53.3/24
hsrp version 2
hsrp 53
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.10.53.1
interface Vlan54
no shutdown
ip address 10.54.0.3/20
hsrp version 2
hsrp 54
preempt
priority 110
ip 10.54.0.1
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.21
ip dhcp relay address 10.10.51.22
interface port-channel10
description vPC-PeerLink
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type network
service-policy type qos input jumbo
vpc peer-link
interface port-channel11
description FI-Uplink-K22
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
service-policy type qos input jumbo
vpc 11
interface port-channel12
description FI-Uplink-K22
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
service-policy type qos input jumbo
vpc 12
interface Ethernet1/1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/2
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/3
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/4
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
channel-group 10 mode active
interface Ethernet1/5
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 11 mode active
interface Ethernet1/6
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 11 mode active
interface Ethernet1/7
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 12 mode active
interface Ethernet1/8
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
mtu 9216
channel-group 12 mode active
interface Ethernet1/9
interface Ethernet1/10
interface Ethernet1/11
interface Ethernet1/12
interface Ethernet1/13
interface Ethernet1/14
interface Ethernet1/15
interface Ethernet1/16
interface Ethernet1/17
interface Ethernet1/18
interface Ethernet1/19
interface Ethernet1/20
interface Ethernet1/21
interface Ethernet1/22
interface Ethernet1/23
interface Ethernet1/24
interface Ethernet1/25
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/26
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/27
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/28
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/29
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/30
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/31
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/32
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,50-54
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
interface Ethernet1/33
interface Ethernet1/34
interface Ethernet1/35
interface Ethernet1/36
interface Ethernet1/37
interface Ethernet1/38
interface Ethernet1/39
interface Ethernet1/40
interface Ethernet1/41
interface Ethernet1/42
interface Ethernet1/43
interface Ethernet1/44
interface Ethernet1/45
interface Ethernet1/46
interface Ethernet1/47
interface Ethernet1/48
switchport access vlan 50
interface Ethernet1/49
interface Ethernet1/50
interface Ethernet1/51
interface Ethernet1/52
interface Ethernet1/53
interface Ethernet1/54
interface mgmt0
vrf member management
ip address 10.29.132.20/24
clock timezone PST -8 0
clock summer-time PDT 2 Sunday March 02:00 1 Sunday November 02:00 60
line console
line vty
boot nxos bootflash:/nxos.7.0.3.I2.2d.bin






 フィードバック
フィードバック