Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Compliance with U.S. Export Laws and Regulations Regarding Encryption
Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem Cable Connections
Product Overview
This chapter provides physical and functional overviews of the Cisco uBR904 cable modem. It contains physical descriptions of the cable modem hardware and functional descriptions of hardware-related features.
The Cisco uBR904 cable modem is a part of a new class of Cisco data-over-cable products. The Cisco uBR904 cable modem is a compact, easy-to-install device that can receive and transmit digital data over hybrid fiber coaxial (HFC) cable; the same cable that brings television broadcast transmissions into a cable television (CATV) subscriber's home.
With a Cisco uBR904 cable modem, a personal computer can be connected to the HFC cable network for high-speed access to the Internet. The link that enables the transmission of two-way digital data from the HFC network to the Internet is provided by the Cisco uBR7246 universal broadband router installed at the cable headend.
The Cisco data-over-cable products, the Cisco uBR904 cable modem and the Cisco uBR7246 universal broadband router, are based on the Multimedia Cable Network Partners, Ltd. (MCNS) Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCIS) standards-based specifications. MCNS is a consortium of cable television companies whose goal is to create standards for interoperable data-over-cable systems.
The Cisco uBR904 cable modem operates with one external AC-input power supply.
The Cisco uBR904 cable modem provides the following features:
•
High-speed access to the Internet—Downstream (receive) connection speeds of up to 36 Mbps, and upstream (send) connection speeds of up to 2 Mbps
•
Multicast messages—Multiple users can receive important information at the same time
•
User data privacy—Upstream and downstream data is encrypted to provide data privacy protection
•
Downloadable software—Software and configuration information is downloaded from the cable headend to the cable modem
Note
Data-over-cable systems are capable of providing access speeds up to 36 Mbps. That bandwidth, however, is shared by several subscribers because there are very few computers today that can connect to a network at such high speeds. Typical connection speeds to be expected are 5 Mbps downstream and 1 Mbps upstream.
To compare data-over-cable speeds with other Internet access technologies available today, a file that would take eight minutes to download over standard telephone lines with a 28.8 kbps modem would take two minutes to download over ISDN. The same file would take approximately eight seconds to download over a data-over-cable system.
Cable Modem Terminology
CATV Originally stood for Community Antenna Television. Now refers to any cable (coaxial/fiber) based system that provides television services.Cable modem Any device that modulates and demodulates digital data onto a CATV plant.Cable router A modular chassis-based router optimized for the data over CATV HFC application.Channel A specific frequency allocation and bandwidth. Downstream channels used for television in the U.S. are 6 MHz wide.CM Cable modem.Downstream The set of frequencies used to send data from a headend to a subscriber.Headend Central distribution point for a CATV system. Video signals are received here from satellite (either co-located or remote), frequency converted to the appropriate channels, combined with locally originated signals, and rebroadcast onto the HFC plant. For a CATV data system, the headend is the typical place to link between the HFC system and any external data networks.HFC Hybrid fiber-coaxial (cable). Older CATV systems were provisioned using only coaxial cable. Modern systems use fiber transport from the headend to an optical node located in neighborhood to reduce system noise. Coax runs from the node to the subscriber. The fiber plant is generally a star configuration with all optical node fibers terminating at a headend. The coaxial cable part of the system is generally a trunk-and-branch configuration.Host Any end-user computer system that connects to a network. In this guide, the term host refers to computer systems connected to the LAN interface of the cable modem.Host Device See Host for details.MCNS Multimedia Cable Network System Partners Ltd., a consortium of cable companies representing the majority of homes in the U.S. and Canada who have decided to drive a standard with the goal of having interoperable cable modems.QAM Modulation scheme mostly used in the downstream direction (QAM-64,
QAM-256). QAM-16 is expected to be usable in the upstream direction. Numbers indicate number of code points per symbol. Number of bits per symbol can be computed by 2^(number of bits/symbol) = number of code points.QPSK Modulation scheme used in the upstream direction. Supports two data bits per symbol.Subscriber Unit (SU) A term used for cable modems. See Cable Modem for a description.Upstream The set of frequencies used to send data from a subscriber to the headend.Physical Description
The front of the Cisco uBR904 cable modem (see ) provides a basic operating status display using 16 LEDs. For a description of the LEDs, see the section, "Troubleshooting the Power Subsystem Using LEDs" in the chapter, "."
Figure 1-1 Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem—Front View
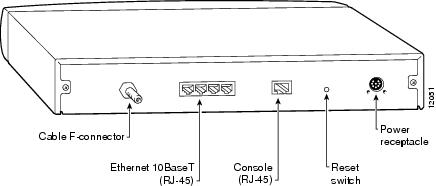
The rear of the Cisco uBR904 cable modem (see ) provides the receptacles to connect the unit to the CATV network, a console device, and a personal computer.
Figure 1-2 Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem—Rear View
The Cisco uBR904 cable modem operates as a desktop device. Place it on a sturdy desktop or platform near the personal computer to which it will be connected.
System Specifications
lists the Cisco uBR904 cable modem physical specifications and power requirements.
Table 1-1 Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem Physical Specifications
Dimensions (H x W x D)
2.30 x 13.50 x 9.30 in. (5.08cm x 34.29cm x 24.77cm)
Weight
~ 4.5 lb (~ 2.04 kg) for the Cisco uBR904
~ 0.5 lb (~ 0.23 kg) for the AC-input external power supplyAC-input voltage
120 to 240 VAC1 wide input with power factor correction
AC-input current rating
1.2A2 maximum at 120 VAC and 0.6A maximum at 240 VAC
AC-input cable
18 AWG3 three-wire cable, with a three-lead receptacle on the power supply end, and a North American (NEMA 5-15P) plug on the power source end
Power dissipation
12 to 15W
Frequency
50/60 Hz4
Temperature
23 to 113°F (0 to 40°C) operating; -13 to 95°F (-25 to 70°C) nonoperating
Humidity
5 to 95% noncondensing
Noise level
38 dBa5 maximum at desktop, 43 dBa maximum in an office
Software requirement
Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem software and Cisco IOS Release 11.3(7) NA or later.
Agency approvals
Safety: UL 1950, CSA 22.2 No. 950, EN60950
EMI: FCC Class A, FCC Class B, CSA Class A, EN60555-2, EN55022 Class B, VCC1 Class 2, AS/NZS 3548 Class A
Immunity: IEC-1000-4-2, IEC-1000-4-3, IEC-1000-4-4, IEC-1000-4-5, IEC-1000-4-6, IEC-1000-4-11, IEC-1000-3-2, IEC 60950, AS3260, TS001
See also the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco uBR904 document.
1 VAC = volts alternating current.
2 A = ampere.
3 AWG = American Wire Gauge.
4 Hz = hertz.
5 dBa = adjusted decibels.
Note
For footprint information and additional dimensions, refer to the section "Site Requirements" in the chapter "."
Power Supply
The Cisco uBR904 cable modem uses one external AC-input power supply. The OK (power) LED on the front of the cable modem indicates that the power supply is supplying power to the unit. lists the AC-input power supply power specifications, including input voltage and operating frequency ranges.
The bottom, sides, and rear of the cable modem must remain unobstructed to ensure adequate airflow and prevent overheating inside the unit. The rubber feet on the bottom of the cable modem provide enough clearance when the unit is placed on a flat, hard surface. Do not place the cable modem on an uneven or soft surface. We recommend at least 3 inches of clearance at the rear of the cable modem. (See the section "Site Requirements" in the chapter ".")
Compliance with U.S. Export Laws and Regulations Regarding Encryption
Cisco cable modem cards perform encryption and are regulated for export by the U.S. Government. Following is specific information regarding compliance with U.S. export laws and regulations for encryption products:
•
Cisco cable modem cards are not authorized for use by persons located outside the United States and Canada that do not have export license authority from the U.S. Government.
•
Cisco cable modem cards may not be exported outside the U.S. and Canada either by physical or electronic means without the prior written approval of the U.S. Government.
•
Persons outside the U.S. and Canada may not reexport, resell, or transfer Cisco cable modem cards by either physical or electronic means without prior written approval of the U.S. Government.
Functional Overview
This section provides a functional overview of the Cisco uBR904 cable modem. It describes the cable modem Media Access Control (MAC) address, connection, and configuration. These descriptions will help you become familiar with the functions of the Cisco uBR904 cable modem.
MAC-Layer Address
All local-area network (LAN) devices, such as cable modems, require unique MAC-layer addresses, also known as hardware addresses. The MAC address of a Cisco uBR904 cable modem is stored in the unit. You should record the MAC address on the site installation sheet provided in the chapter, "."
Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem Cable Connections
The Cisco uBR904 cable modem is connected to CATV coaxial cable and to an Ethernet port on a personal computer. The personal computer must have an Ethernet network card installed; either an internal card installed in the computer chassis, or a PCMCIA adapter card and cable installed on a laptop computer.
The coaxial cable connection uses standard connectors at both ends of the coaxial cable, and an F-connector on the back of the cable modem. The F-connector is labeled "Cable TV In." The Ethernet connections use straight-through Ethernet cables with RJ-45 connectors at both ends, and RJ-45 receptacles on the back of the cable modem. The
RJ-45 connectors are labeled 1X, 2X, 3X, and 4X.
Note
One straight-through Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors has been included with your Cisco uBR904 cable modem. Additional RJ-45 cables are also available from outside commercial cable vendors.
If you are connecting the Cisco uBR904 cable modem to a hub at the installation site (to provide access to the cable modem from multiple computers), you need to use a crossover Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors.
Note
Crossover Ethernet cables are not available from Cisco Systems; they are available from Cisco and outside commercial cable vendors. Optionally, you can use a straight-through Ethernet cable and connect to the uplink port on your hub (often labeled Uplink or MDI).
Airflow and Cooling
To keep the Cisco uBR904 cable modem operating at optimal internal temperature, keep the bottom, sides, and rear of the cable modem clear of obstructions and away from the exhaust of other equipment.