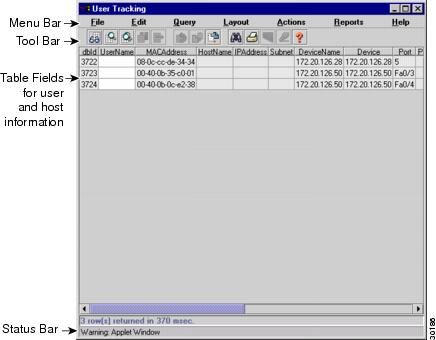
Table 3-2 User Tracking Tasks
Task
|
Purpose
|
Action
|
Enable or disable the ping sweeps option. By default, the ping sweeps option is enabled.
|
To obtain the latest Address resolution Protocol (ARP) information in routers and bridge table information in switches.
|
Select Action > Ping Sweep.
|
Discover all users and hosts.
|
To discover all users and hosts on the network and to update the ANI database.
|
Select Action > Discover All.
|
Discover hosts in a subnet.
|
To initiate the User Tracking discovery process for a specific subnet. This is less time-consuming than rediscovering all users and hosts.
|
1.  Select Action > Discover Subnet. Select Action > Discover Subnet.
2.  Enter the IP address or host name in the subnet field. Enter the IP address or host name in the subnet field.
3.  Enter the subnet mask in the Mask field. Enter the subnet mask in the Mask field.
4.  Click OK. Click OK.
|
Discover hosts on a specific switch device.
|
To initiate the User Tracking discovery process for a specific device. This is less time-consuming than rediscovering all users and hosts.
|
1.  Select Action > Discover Device. Select Action > Discover Device.
2.  Enter the IP address or device name in the Device field. Enter the IP address or device name in the Device field.
3.  Click OK. Click OK.
|
Display all users and hosts.
|
To display all discovered users and hosts in the User Tracking database.
|
Select Query > Show All.
|
Display selected users and hosts.
|
To limit the display to only those entries that match your specified information.
|
1.  Select Query > Simple Query. Select Query > Simple Query.
2.  Select the appropriate operation (contains, does not contain, begins with, does not begin with, and so on) from the drop down menu. Select the appropriate operation (contains, does not contain, begins with, does not begin with, and so on) from the drop down menu.
3.  In the left column, specify a column name. In the left column, specify a column name.
4.  In the right column, enter a search string appropriate to that column. In the right column, enter a search string appropriate to that column.
Specify up to three types of search criteria (repeat steps 2-4).
5.  Click Apply. Click Apply.
|
Create and save an advanced query.
|
To create, save, and reuse queries with complex search criteria.
|
1.  Select Query > Advanced Query. Select Query > Advanced Query.
2.  Click the Sort tab. Click the Sort tab.
3.  To activate a search setup, click a checkbox on the left. To activate a search setup, click a checkbox on the left.
4.  In the left column, specify the name of a User Tracking table column through which to search. In the left column, specify the name of a User Tracking table column through which to search.
5.  In the right column, select either Ascending or Descending. In the right column, select either Ascending or Descending.
The SQL Query Clauses window displays the condition as you construct it.
6.  To create subqueries, click the Conditions tab and click Add. To create subqueries, click the Conditions tab and click Add.
7.  Enter conditions as you would for a simple query. Enter conditions as you would for a simple query.
8.  Click OK. Click OK.
9.  To save the query, enter a name in the Save Query as field and click OK. To save the query, enter a name in the Save Query as field and click OK.
|
Customize the table format.
|
To edit the User Tracking table to include only specific columns in a preferred order.
|
1.  Select Layout > Add Layout. Select Layout > Add Layout.
2.  To specify a column that you want to include, check the selection box next to that column's name. To specify a column that you want to include, check the selection box next to that column's name.
3.  To alter the positions of that column relative to others, highlight a column name and use the blue arrows. To alter the positions of that column relative to others, highlight a column name and use the blue arrows.
4.  To save the layout, enter a name in the Save Layout as field. To save the layout, enter a name in the Save Layout as field.
|
Find entries.
|
To perform a string search to find a specific entry or range of entries in the screen display table.
|
1.  Select Edit > Find in Table. Select Edit > Find in Table.
2.  In the Find field, enter the string for the entry you want to locate. In the Find field, enter the string for the entry you want to locate.
3.  In the Find window, enter the appropriate settings in the Find, From, Ignore Case, Exact Match, and By Row fields. In the Find window, enter the appropriate settings in the Find, From, Ignore Case, Exact Match, and By Row fields.
|
Save changes to the User Tracking table.
|
To save changes, when you make changes to the User Tracking table, the changes remain local to the session in which you are running User Tracking until you send the information to the ANI database.
|
Select File > Save Changes to Server.
|
Export User Tracking data to a file.
|
To enable you to save information added to the User Name and Notes fields.
|
1.  Select File > Export. Select File > Export.
2.  Select the directory that you want to export and enter a file name. Select the directory that you want to export and enter a file name.
3.  Click Save to close the Export dialog and save the file. Click Save to close the Export dialog and save the file.
|
Import DeviceName and Notes data from a previously saved file.
|
To import lost or deleted UserName and Notes fields from the last exported file.
|
1.  Select File > Import.... Select File > Import....
2.  Select the text file you want to import and click OK. Select the text file you want to import and click OK.
|
Delete old entries from the User Tracking table.
|
To delete entries for hosts that are no longer in the network manually or automatically at specified times.
|
1.  Select Action > Delete Outdated Entries. Select Action > Delete Outdated Entries.
2.  In the Delete Outdated Entries dialog, enter the appropriate settings. In the Delete Outdated Entries dialog, enter the appropriate settings.
|
Highlight a device on the network view.
|
To highlight a selected device in User Tracking on the Layer 2 view in Topology Services.
|
1.  Select an entry from the Device column in the User Tracking table. Select an entry from the Device column in the User Tracking table.
2.  Select Action > Highlight Device in a Map. Select Action > Highlight Device in a Map.
|
Display detail on a device with CiscoView.
|
To launch CiscoView and see details about a particular device. If you attempt to launch CiscoView for multiple devices by selecting more than one device, User Tracking uses the last selected device.
|
1.  Select the device in the User Tracking table. Select the device in the User Tracking table.
2.  Select Action > Launch CiscoView. Select Action > Launch CiscoView.
|
Find duplicate IP addresses.
|
To find duplicate IP addresses. Typically, each host should have its own, unique IP address. If two hosts have the same IP address, your network will not function correctly.
|
Select Reports > Duplicate IP.
|
Find duplicate MAC addresses.
|
To find duplicate MAC addresses. Typically, each host has its own, unique MAC address. If two hosts have the same MAC address in the same VTP domain and VLAN, you have a misconfiguration.
|
Select Reports > Duplicate MAC.
|
Find duplicate MAC addresses and VLAN names.
|
To find duplicate MAC addresses and VLAN names. Typically, each host has a unique MAC/VTP/VLAN combination. Multiple hosts with the same MAC address and VLAN name indicate a network problem.
|
Select Reports > Duplicate MAC and VLAN.
|
Find ports with multiple MAC addresses.
|
To find ports with multiple MAC addresses (hubs). Ports being shared by multiple hosts may not yield the best performance.
|
Select Reports > Ports with Multiple MAC.
|
 Feedback
Feedback
Discover users and hosts in your network.
Query for users and hosts.
Display the results of queries in a table that you can customize.
Modify, add, and delete user name and notes.
Highlight devices on the Layer 2 view in Topology Services.
Starting and Navigating in User Tracking