Table Of Contents
Cabling for Nonwireless Routers
Connecting the Radio Antennas to the Wireless Router
Connecting the Power-over-Ethernet Module (Optional)
Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
Connecting an External Ethernet Switch (Optional)
Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
Connecting an Async Modem to the Console Port
Connecting an ADSL Line—ADSLoPOTS Port
Connecting an ADSL Line—ADSLoISDN Port
Router Cabling Procedures
This chapter describes the cabling procedures for Cisco 851, Cisco 857, Cisco 871, Cisco 876, Cisco 877, and Cisco 878 routers. It contains the following sections:
•
Cabling for Nonwireless Routers
•
Connecting the Radio Antennas to the Wireless Router
•
Connecting the Power-over-Ethernet Module (Optional)
•
Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
•
Connecting an External Ethernet Switch (Optional)
•
Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
•
Connecting an Async Modem to the Console Port
•
Connecting an ADSL Line—ADSLoPOTS Port
•
Connecting an ADSL Line—ADSLoISDN Port
Note
Read Chapter 2 "Preinstallation Information," before you start the cabling procedures, making sure to follow the safety warnings and guidelines in the "Safety Warnings and Guidelines" section.
Note
The router and the optional power-over-Ethernet (PoE) module should be mounted before being connected to the devices. See Chapter 3 "Router and PoE Module Mounting Procedures."
Cabling for Nonwireless Routers
Some portions of this document do not apply to nonwireless router models. Although illustrations show the router with antennas attached, the nonwireless routers do not have antennas or connectors on the back panel. However, except for the "Connecting the Radio Antennas to the Wireless Router" section, the procedures for connecting devices to the router are the same for wireless and nonwireless routers.
Typical Installations
Typical installations of the Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers are depicted in Figure 4-1 through Figure 4-4, as follows:
•
Cisco 851 and Cisco 871 router—See Figure 4-1.
•
Cisco 857 and Cisco 87 router—See Figure 4-2.
•
Cisco 876 router—See Figure 4-3.
•
Cisco 878 router—See Figure 4-4.
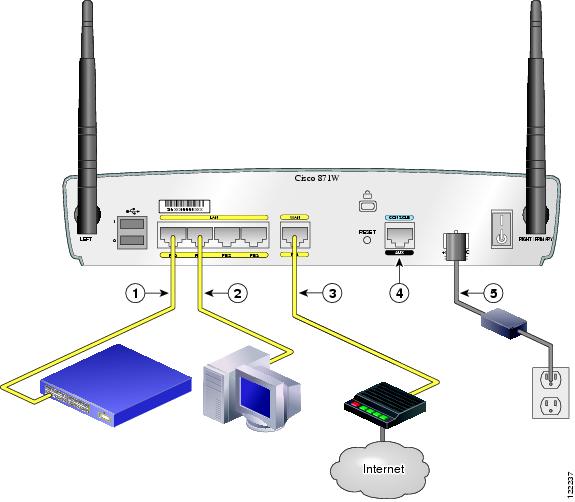
Figure 4-1 shows a typical installation of a Cisco 851 or Cisco 871 router. This figure shows the back panel of a Cisco 871 router, which has two USB ports. The Cisco 851 router does not have any USB ports; however, the connections on the other ports are the same for both the Cisco 851 and Cisco 871 routers.
Figure 4-1 Typical Installation of a Cisco 851 or Cisco 871 Router
Ethernet connection to an external switch
Console port
Ethernet connection to a PC
Power adapter
WAN connection using a broadband modem to the Internet
Figure 4-2 Typical Installation of a Cisco 857 or Cisco 877 Router
Ethernet connection to an external switch
Console port
Ethernet connection to a PC
Power adapter
ADSL-over-POTS connection
Figure 4-3 Typical Installation of a Cisco 876 Router
Ethernet connection to an external switch
ADSL-over-ISDN connection
Ethernet connection to a PC
Console port
ISDN S/T connection
Power adapter
Figure 4-4 Typical Installation of a Cisco 878 Router
Ethernet connection to an external switch
G.SHDSL connection
Ethernet connection to a PC
Console port
ISDN S/T connection
Power adapter
Connecting the Radio Antennas to the Wireless Router
If you selected the wireless option for the router, follow these steps to attach the radio antennas:
Step 1
Attach an antenna to a reverse-polarity threaded Neill-Concelman (RP-TNC) connector on the back of the router and tighten the antenna hand-tight.
Step 2
Orient the antenna vertically:
a.
If the router is being mounted on a desk, orient the antenna straight up.
b.
If the router is being mounted on a wall, orient the antenna straight down.
Connecting the Power-over-Ethernet Module (Optional)
If you purchased a power-over-Ethernet (PoE) module to provide inline power to devices, connect the four Ethernet cables on the PoE module to the four LAN Ethernet ports on the router. Make sure you connect all four Ethernet cables. If the cables are too close together for easy insertion, move the plastic cable guard away from the connector end of the cable. See Figure 4-5.
CautionDo not connect the PoE module power supply to the PoE module before you connect the PoE module to the router. For information about connecting the power supply to the PoE module, see the "Connecting the AC Adapter" section.
Figure 4-5 Connecting the Power-over-Ethernet Module to the Router
Router
PoE module
Router Ethernet ports
Plastic cable guard
Ethernet cables connecting the PoE module to the router
After you connect the PoE module to the router, connect the Ethernet devices to the ports on the PoE module, rather than to the Ethernet ports on the router.
Note
When you connect a device (such as a PC or IP phone) to the PoE module, you may notice a 1- to 2-second delay before the LED indicator for the port comes on.
Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
To connect a server, PC, or workstation to a built-in Ethernet switch port, follow the steps given after Figure 4-6, which shows a Cisco 871 router connected to a PC. The procedure applies to Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers.
Figure 4-6 Connecting a Server, PC, or Workstation
Router
PC
Yellow Ethernet cable
RJ-45 port on the network interface card (NIC)
Built-in Ethernet switch port on the router
Perform the following steps to connect the PC (or other Ethernet devices) to a port on the built-in Ethernet switch.
CautionLeave the PCs turned off until after you have completed all connections to the router.
Step 1
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to a built-in Ethernet switch port on the router.
Step 2
Connect the other end of the cable to the RJ-45 port on the NIC installed in the PC, server, or workstation.
Step 3
(Optional) Connect additional servers, PCs, or workstations to the other built-in Ethernet switch ports.
Connecting an External Ethernet Switch (Optional)
If more than four PCs need to be connected to each other in an office, you may connect an external Ethernet switch to the router's built-in switch to add additional Ethernet connections to the router.
Although Figure 4-7 shows a Cisco 871 router, the procedure in this section applies to all Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers.
To connect an external Ethernet switch to a built-in Ethernet switch port on the router, follow the steps given after Figure 4-7, which shows this connection.
Figure 4-7 Connecting to an Ethernet Switch
Yellow Ethernet cable connecting an external Ethernet switch to a built-in Ethernet switch port on the router
Available port on the external Ethernet switch
Perform the following steps to connect the router to an external Ethernet switch:
Step 1
Connect one end of the yellow Ethernet cable to a built-in Ethernet switch port on the router.
Step 2
Connect the other end of the cable to the available port on the Ethernet switch to add additional Ethernet connections.
Step 3
Turn on the Ethernet switch.
Connecting a Broadband Modem
This section applies only to Cisco 851 and Cisco 871 routers. You can connect to the Internet by connecting a broadband modem. To connect to an installed DSL, cable, or long-reach Ethernet modem, follow the steps given after Figure 4-8, which shows this connection.
Figure 4-8 Connecting to a Broadband Modem
Perform the following steps to connect the router to an installed DSL, cable, or long-reach Ethernet modem:
Step 1
Connect one end of the yellow cable to the Ethernet WAN FE4 port.
Step 2
Connect the other end of cable to an available port on the modem.
Step 3
Follow the instructions provided with your broadband modem to determine which port on the modem to connect to.
Step 4
Turn on the broadband modem if it is not already turned on.
Note
It is recommended that you use the Cisco Router and Security Device Manager (SDM) application to configure the Internet connection settings. See the Cisco Router and Security Device Manager (SDM) Quick Start Guide for more information.
Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
The console port is a service port to which you can connect a terminal or PC either to configure the software by using the command-line interface (CLI) or to troubleshoot problems with the router.
Although Figure 4-9 shows a Cisco 871 router, the procedure in this section applies to all Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers.
To connect a terminal or PC to the console port, follow the steps given after Figure 4-9.
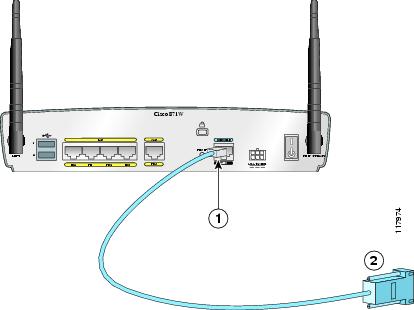
Figure 4-9 Connecting a Terminal or PC to the Console Port
Perform the following steps to connect the router's console port to a terminal or PC:
Step 1
Connect the RJ-45 connector on the light blue cable to the router console port.
Step 2
Connect the DB-9 connector to a terminal or PC.
Connecting an Async Modem to the Console Port
The Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers support the dial backup function, which allows a user to connect an analog modem to the console port as a backup link to the WAN port in case the ADSL service goes down.
Note
To connect an analog modem to the console port, you will need an optional router modem cable. Contact your router vendor to order this cable.
Although Figure 4-10 shows the async modem connection to the console port on the Cisco 857 router, this connection applies to all Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers.
Figure 4-10 Connecting an Async Modem to the Console Port
Perform the following steps to connect the console port on the router to an async modem:
Step 1
Connect the RJ-45 end of the router modem cable to the console port.
Step 2
Connect the DB-25 connector end of the router modem cable to an available port on the async modem.
Step 3
Connect one end of the RJ-11 telephone cable to a wall jack, and then connect the other end of the RJ-11 cable to the modem.
Step 4
(Optional) Connect one end of an RJ-11 telephone cable to a telephone, fax, or other device, and then connect the other end of the RJ-11 cable to the modem.
Connecting an ISDN S/T Port
This section applies to Cisco 876 and Cisco 878 routers. You can connect the ISDN S/T port to the ISDN service provider as a backup link to the WAN port in case the ADSL service goes down.
The cabling requirements and information for the ISDN S/T connection follow:
•
You must provide two unshielded Category 5 cables. The first cable connects the NT1 box to the splitter, and the second cable connects the splitter to the wall jack.
•
There are RJ-45 connectors at both ends of the default orange ISDN S/T cable. However, an RJ-45-to-RJ-11 ISDN S/T cable is available upon request if the wall jack at the site requires an RJ-11 connector. Contact your router reseller for the appropriate cable.
CautionBoth LAN and WAN ports can use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables to these connectors. To avoid damage to the router, do not connect telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits (such as ISDN or DSL circuits) to safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits (such as LAN circuits).
Although Figure 4-11 shows an ISDN S/T connection for a Cisco 876 router, this connection also applies to a Cisco 878 router.
Figure 4-11 Connecting the ISDN S/T Port to the ISDN Service Provider
Perform the following steps to connect the ISDN S/T port to the ISDN service provider:
Step 1
Connect one end of the orange ISDN S/T cable to the ISDN S/T port on the router.
Step 2
Connect the other end of the orange ISDN S/T cable to the S/T port on the NT1 box.
Step 3
Connect the first unshielded Category 5 cable from the U port on the NT1 box to the telephone line port on the splitter.
Step 4
Connect the second unshielded Category 5 cable from the telecommunication service port on the splitter to the wall jack to allow a link to the network service provider.
Connecting an ADSL Line—ADSLoPOTS Port
This section applies only to Cisco 857 and Cisco 877 routers. Follow the steps shown after Figure 4-12 to connect an asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) over plain old telephone service (ADSLoPOTS) port on the router.
Note
The DSL line must have been provisioned by your service provider and correctly configured for the LED to show the carrier detect (CD) status. If the CD LED is not on, check with the DSL service provider.
Figure 4-12 Connecting the ADSLoPOTS Port to an ADSL Line
CautionCisco Systems DSL WAN Interfaces are tested for compliance with regulatory standards such as FCC Part 68, ITU-T K.21, IEC 61000-4-5, and CSA/EN/IEC/UL 60950-1. These standards assume Primary Protection devices protect the Customer Premise Equipment (CPE). These devices are normally installed by the service provider, local exchange carrier or qualified service person and are located at the telecom service provider entrance, network interface box, or demarcation point. See Figure 4-13 for the likely location of the primary protection device. The primary protection device must be suitable for the xDSL interface employed.
Please contact your sales team or qualified service person for further information and installation.
Figure 4-13
Primary Protection Device Location
Perform the following steps to connect the ADSL cable to a cable wall jack:
Step 1
Connect one end of the ADSL cable to the ADSLoPOTS port on the router.
Step 2
Connect the other end of the cable to the wall jack.
Connecting an ADSL Line—ADSLoISDN Port
This section applies only to the Cisco 876 router. The procedure for connecting an asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) depends on the router and, in some cases, on the location. Follow the steps shown after Figure 4-15 to connect the ADSL cable to a cable wall jack.
Note
The DSL line must have been provisioned by your service provider and correctly configured for the ADSL CD LED to show the status. If the ADSL CD LED is not on, check with the DSL service provider.
Note
You must provide the unshielded Category 5 cable for connecting to the ADSL ISDN splitter that is provided by the service provider.
CautionCisco Systems DSL WAN Interfaces are tested for compliance with regulatory standards such as FCC Part 68, ITU-T K.21, IEC 61000-4-5, and CSA/EN/IEC/UL 60950-1. These standards assume Primary Protection devices protect the Customer Premise Equipment (CPE). These devices are normally installed by the service provider, local exchange carrier or qualified service person and are located at the telecom service provider entrance, network interface box, or demarcation point. See Figure 4-14 for the likely location of the primary protection device. The primary protection device must be suitable for the xDSL interface employed.
Please contact your sales team or qualified service person for further information and installation.
Figure 4-14
Primary Protection Device Location
Figure 4-15 Connecting the ADSLoISDN Port to an ADSL Line
Perform the following steps to connect the ADSL line to a cable wall jack:
Step 1
Connect the RJ-11 end of the ADSL cable to the ADSLoISDN port on the router.
Step 2
Connect the other RJ-11 end of the ADSL cable to the local ADSL connector port on the ADSL splitter (provided by the ADSL service provider).
Step 3
Connect the unshielded Category 5 cable from the outside ADSL port on the splitter to a wall jack.
Connecting a G.SHDSL Line
This section applies to the Cisco 878 router only. To connect the router to a G.SHDSL line, perform the steps given after Figure 4-16.
Figure 4-16 Connecting the G.SHDSL Line
CautionCisco Systems DSL WAN Interfaces are tested for compliance with regulatory standards such as FCC Part 68, ITU-T K.21, IEC 61000-4-5, and CSA/EN/IEC/UL 60950-1. These standards assume Primary Protection devices protect the Customer Premise Equipment (CPE). These devices are normally installed by the service provider, local exchange carrier or qualified service person and are located at the telecom service provider entrance, network interface box, or demarcation point. See Figure 4-17 for the likely location of the primary protection device. The primary protection device must be suitable for the xDSL interface employed.
Please contact your sales team or qualified service person for further information and installation.
Figure 4-17
Primary Protection Device Location
Perform the following steps to connect the router to an installed DSL:
Step 1
Connect one end of the lavender DSL cable to the G.SHDSL port on the router.
Step 2
Connect the other end of the cable to the DSL wall jack.
Connecting the AC Adapter
To connect the AC adapter, follow the steps given after Figure 4-18. Although the illustration shows the Cisco 871 router, the procedure applies to all Cisco 850 series and Cisco 870 series routers.
WarningThe device is designed to work with TN power systems. Statement 19
Figure 4-18 Connecting the AC Adapter (No PoE Module)
Figure 4-19 Connecting AC Adapters to the Router and to the PoE Module
Router
Router power adapter
Ethernet cables on the PoE module
PoE module power adapter plug
PoE module
Router power adapter plug
PoE module power adapter
Perform the following steps to connect power to the router and to the PoE module:
Step 1
Connect one end of the power supply cable to the input jack of the router.
Step 2
Connect the other end of the power supply cable to the router power adapter.
Step 3
If a PoE module is connected to the router, connect the PoE module power adapter to the PoE module.
Step 4
Plug the power cord of the router power adapter into an electrical outlet. If a PoE module is connected to the router, plug the power cord for the PoE module into an electrical outlet.
Verifying Router Operations
To verify that all devices are properly connected to the router, turn on all the connected devices; then use Table 4-1 to help you verify correct router operation by checking the LEDs.
What to Do Next
After verifying that the router cabling is correct and the power up is successful, perform the initial configuration of the router as described in Chapter 5 "Initial Configuration."

 Feedback
Feedback