- Title Page
- Introduction & Preface
- Logging into the FireSIGHT System
- Using Objects and Security Zones
- Managing Devices
- Setting Up an IPS Device
- Setting Up Virtual Switches
- Setting Up Virtual Routers
- Setting Up Aggregate Interfaces
- Setting Up Hybrid Interfaces
- Using Gateway VPNs
- Using NAT Policies
- Getting Started with Access Control Policies
- Blacklisting Using Security Intelligence IP Address Reputation
- Tuning Traffic Flow Using Access Control Rules
- Controlling Traffic with Network-Based Rules
- Controlling Traffic with Reputation-Based Rules
- Controlling Traffic Based on Users
- Controlling Traffic Using Intrusion and File Policies
- Understanding Traffic Decryption
- Getting Started with SSL Policies
- Getting Started with SSL Rules
- Tuning Traffic Decryption Using SSL Rules
- Understanding Intrusion and Network Analysis Policies
- Using Layers in Intrusion and Network Analysis Policies
- Customizing Traffic Preprocessing
- Getting Started with Network Analysis Policies
- Using Application Layer Preprocessors
- Configuring SCADA Preprocessing
- Configuring Transport & Network Layer Preprocessing
- Tuning Preprocessing in Passive Deployments
- Getting Started with Intrusion Policies
- Tuning Intrusion Rules
- Tailoring Intrusion Protection to Your Network Assets
- Detecting Specific Threats
- Limiting Intrusion Event Logging
- Understanding and Writing Intrusion Rules
- Blocking Malware and Prohibited Files
- Logging Connections in Network Traffic
- Working with Connection & Security Intelligence Data
- Analyzing Malware and File Activity
- Working with Intrusion Events
- Handling Incidents
- Configuring External Alerting
- Configuring External Alerting for Intrusion Rules
- Introduction to Network Discovery
- Enhancing Network Discovery
- Configuring Active Scanning
- Using the Network Map
- Using Host Profiles
- Working with Discovery Events
- Configuring Correlation Policies and Rules
- Using the FireSIGHT System as a Compliance Tool
- Creating Traffic Profiles
- Configuring Remediations
- Using Dashboards
- Using the Context Explorer
- Working with Reports
- Understanding and Using Workflows
- Using Custom Tables
- Searching for Events
- Managing Users
- Scheduling Tasks
- Managing System Policies
- Configuring Appliance Settings
- Licensing the FireSIGHT System
- Updating System Software
- Monitoring the System
- Using Health Monitoring
- Auditing the System
- Using Backup and Restore
- Specifying User Preferences
- Importing and Exporting Configurations
- Purging Discovery Data from the Database
- Viewing the Status of Long-Running Tasks
- Command Line Reference
- Security, Internet Access, and Communication Ports
- Third-Party Products
- glossary
- Viewing and Modifying the Appliance Information
- Using Custom HTTPS Certificates
- Enabling Access to the Database
- Configuring Management Interfaces
- Shutting Down and Restarting the System
- Setting the Time Manually
- Managing Remote Storage
- Understanding Change Reconciliation
- Managing Remote Console Access
- Enabling Cloud Communications
- Enabling VMware Tools
Configuring Appliance Settings
A FireSIGHT System appliance’s local configuration ( System > Local > Configuration ) is a group of settings that is likely to be specific to a single appliance. Contrast the local configuration with the system policy (Managing System Policies), which controls appliance settings that are likely to be similar across a deployment.
The following table summarizes an appliance’s local configuration.
Viewing and Modifying the Appliance Information
The Information page provides you with information about your appliances. The information includes read-only information, such as the product name and model number, the operating system and version, and the current appliance-level policies. The page also provides you with an option to change the name of the appliance.
The following table describes each field.
To modify the appliance information:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 To change the appliance name, type a new name in the Name field.
The name must be alphanumeric characters and cannot be composed of numeric characters only.
Step 3 To save your changes, click Save .
The page refreshes and your changes are saved.
Using Custom HTTPS Certificates
Cisco Defense Centers and managed devices that support web-based user interfaces include default SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates that you can use to initiate an encrypted communication channel between your web browser and the appliance. However, because the default certificate for an appliance is not generated by a certificate authority (CA) trusted by any globally known CA, you can replace it with a custom certificate signed by a globally known or internally trusted CA.
You can manage certificates through the local configuration for your appliance. For more information, see the following:
- Viewing the Current HTTPS Server Certificate
- Generating a Server Certificate Request
- Uploading Server Certificates
- Requiring User Certificates
Viewing the Current HTTPS Server Certificate
You can view details from the server certificate currently in place for your appliance. The certificate provides the following information:
To view the certificate details:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click HTTPS Certificate .
The HTTPS Certificate page appears, with the details of the current certificate for the appliance.
Generating a Server Certificate Request
You can generate a certificate request based on your appliance information and the identification information you supply. You can send the resulting request to a certificate authority to request a server certificate. You can also use it to self-sign a certificate if you have an internal certificate authority (CA) installed that is trusted by your browser. The generated key is in Base-64 encoded PEM format.
Note that when you generate a certificate request through the local configuration HTTPS Certificate page, you can only generate a certificate for a single server. You must type the fully qualified domain name of the server exactly as it should appear in the certificate in the Common Name field. If the common name and the DNS host name do not match, you receive a warning when connecting to the appliance. Similarly, if you install a certificate that is not signed by a globally known or internally trusted CA, you receive a security warning when you connect to the appliance.
To generate a certificate request:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click HTTPS Certificate .
The HTTPS Certificate page appears.
Step 3 Click Generate New CSR .
The Generate Certificate Signing Request pop-up window appears.
Step 4 Type the two-letter country code for your country in the Country Name (two-letter code) field.
Step 5 Type the postal abbreviation for your state or province in the State or Province field.
Step 6 Type the name of your Locality or City .
Step 7 Type your Organization name.
Step 8 Type an Organizational Unit (Department) name.
Step 9 Type the fully qualified domain name of the server for which you want to request a certificate in the Common Name field, exactly as you want it to appear in the certificate.
The Certificate Signing Request pop-up window appears.
Step 12 Copy the entire block of text in the certificate request, including the
BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST
and
END CERTIFICATE REQUEST
lines, and paste it into a blank text file.
Step 13 Save the file as servername .csr , where servername is the name of the server where you plan to use the certificate.
Step 14 Upload the CSR file to the certificate authority where you want to request a certificate or use the CSR to create a self-signed certificate.
Uploading Server Certificates
After you have a signed certificate from a certificate authority (CA), you can upload it. If the signing authority that generated the certificate requires you to trust an intermediate CA, you must also supply a certificate chain, sometimes referred to as a certificate path. If you require user certificates, they must be generated by a certificate authority whose intermediate authority is included in the certificate chain.
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click HTTPS Certificate .
The HTTPS Certificate page appears.
Step 3 Click Import HTTPS Certificate .
The Import HTTPS Certificate pop-up window appears.
Step 4 Open the server certificate in a text editor, copy the entire block of text, including the
BEGIN CERTIFICATE
and
END CERTIFICATE
lines, and paste it into the
Server Certificate
field.
Step 5 Optionally, open the private key file, copy the entire block of text, including the
BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY
and
END RSA PRIVATE KEY
lines, and paste it into the
Private Key
field.
Step 6 Open any intermediate certificates you need to provide, copy the entire block of text, for each, and paste it into the Certificate Chain field.
Step 7 Click Save to upload the certificate.
The certificate uploads and the HTTPS Certificate page updates to reflect the new certificate.
Requiring User Certificates
You can restrict access to the FireSIGHT System web server using client browser certificate checking. When you enable user certificates, the web server checks that a user’s browser client has a valid user certificate selected. That user certificate must be generated by the same trusted certificate authority used for the server certificate. If the user selects a certificate in the browser that is not valid or not generated by a certificate authority in the certificate chain on the device, the browser cannot load the web interface.
You can also load a certificate revocation list (CRL) for the server. The CRL lists any certificates that have been revoked by the certificate authority, so the web server can verify that the client browser certificate has not been revoked. If the user selects a certificate that is listed in the CRL as a revoked certificate, the browser cannot load the web interface. The appliance supports upload of CRLs in Distinguished Encoding Rules (DER) format. You can only load one CRL for a server.
To ensure that the list of revoked certificates stays current, you can create a scheduled task to update the CRL. The most recent refresh of the CRL is listed in the interface.
Make sure you use the same certificate authority used for the server certificate and that you have uploaded the intermediate certificate for the certificates. For more information, see Uploading Server Certificates.

Note You must have a valid user certificate present in your browser (or a CAC inserted in your reader) to enable user certificates and to access the web interface after doing so.
To require valid user certificates:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click HTTPS Certificate .
The HTTPS Certificate page appears.
Step 3 Select Enable User Certificates . If prompted, select the appropriate certificate from the drop-down list.
The Enable Fetching of CRL option appears.
Step 4 Optionally, select Enable Fetching of CRL .
The remaining CRL configuration options appear.
Step 5 Type a valid URL to an existing CRL file and click Refresh CRL .
The current CRL at the supplied URL loads to the server.

Note Enabling fetching of the CRL creates a scheduled task to update the CRL on a regular basis. Edit the task to set the frequency of the update. For more information, see Automating Certificate Revocation List Downloads.
Step 6 Verify that you have a valid user certificate generated by the same certificate authority that created the server certificate.

Step 7 To apply the user certificate configuration to the web server, click Save .
Note that you can disable user certificate enforcement via the command line if you enable certificates and find that your user certificate does not enable access. For more information, see disable-http-user-cert.
Enabling Access to the Database
You can configure the Defense Center to allow read-only access to its database by a third-party client. This allows you to query the database using SQL using any of the following:
- industry-standard reporting tools such as Actuate BIRT, JasperSoft iReport, or Crystal Reports
- any other reporting application (including a custom application) that supports JDBC SSL connections
- the Cisco-provided command-line Java application called RunQuery, which you can either run interactively or use to obtain comma-separated results for a single query
From the Database Settings local configuration page, you can enable database access and create an access list that allows selected hosts to query the database. Note that this access list does not also control appliance access. For more information on appliance access lists, see Configuring the Access List for Your Appliance.
You can also download a package that contains the following:
- RunQuery, the Cisco-provided database query tool
- InstallCert, a tool you can use to retrieve and accept the SSL certificate from the Defense Center you want to access
- the JDBC driver you must use to connect to the database
Note that when you connect to the database from an external client you must provide a username and password that match those for an Administrator or External Database user on the Defense Center. For more information, see Adding New User Accounts.
For detailed information on configuring external access to the FireSIGHT System database, including information on the database schema and supported queries, see the FireSIGHT System Database Access Guide .
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
The Database Settings page appears.
Step 3 Select the Allow External Database Access check box.
The Access List field appears. See step 6 for more information.
Step 4 Type the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), IPv4 address, or IPv6 address of the Defense Center in the Server Hostname field, depending on your third-party application requirements.
If you type a FQDN, you must make sure that the client can resolve the FQDN of the Defense Center. If you type an IP address, you must make sure that the client can connect to the Defense Center using the IP address.
Step 5 Next to
Client JDBC Driver
, click
Download
and follow your browser’s prompts to download the
client.zip
package.
See the FireSIGHT System Database Access Guide for information on using the tools in the package you downloaded to configure database access.
Step 6 To add database access for one or more IP addresses, click Add Hosts .
An IP Address field appears in the Access List field.
Step 7 In the IP Address field, you have the following options, depending on the IP addresses you want to add:
For information on using CIDR in the FireSIGHT System, see IP Address Conventions.
The IP address is added to the database access list.
Step 9 Optionally, to remove an entry in the database access list, click the delete icon ( ).
).
Your database access settings are saved.

Tip Click Refresh to revert to the last saved database settings.
Configuring Management Interfaces
When you first set up an appliance, you configure its network settings so that it can communicate on your internal, protected management network. You can change any network settings you created when you first set up your appliance and configure additional network settings, such as proxies. On Series 3 appliances and virtual Defense Centers, you can enable traffic channels and configure additional management interfaces to improve performance, and create routes to manage and isolate traffic between the Defense Center and devices on different networks. On Series 3 devices, you can also enable or disable LCD panel access on the device. To change these settings and to configure additional network settings such as proxies, use the Management Interfaces page ( System > Local > Configuration , then click Management Interfaces ).

Note You must use command-line tools to modify network and proxy settings for virtual devices, and to modify network settings for Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series. Note that Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series does not support a proxy. For more information, see the FireSIGHT System Virtual Installation Guide and the Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series Installation and Configuration Guide.
See the following sections for configuration options and procedures:
Understanding Management Interface Options
You may want to change your settings to improve performance, enable different functionality, or otherwise alter the network configuration in your deployment. On Series 3 appliances, you can also configure traffic channels, enable an additional management interface, and create a route to isolate traffic from devices on different networks. For more information, see Understanding Management Interfaces.
Interfaces
The FireSIGHT System provides a dual stack implementation for both IPv4 and IPv6 management environments. You can choose one or both protocols; disable the protocol (if any) you do not want to use.
For each management protocol, you must specify the IP address of the default (
eth0
) management interface, a netmask or prefix length, and the default gateway. You can either set these manually or configure the appliance to retrieve them from a local DHCP server or IPv6 router. Note that you must manually configure each additional (
eth1
and so on) management interface that you enable.
You can configure the following options on your management interface:
- Enabled - enables the management interface. Do not disable the default management interface until after you have already enabled and saved another management interface.
- Channels - enables the Management Traffic and Event Traffic channels on the interface.
You can enable the traffic channels (management traffic, event traffic, or both) to create different connections in the communication channel on the management interface. In addition, you can separate traffic channels over multiple management interfaces, combining the throughput of both interfaces to further improve performance. For more information, see Understanding Management Interfaces.
- Mode - allows you to change the default Autonegotiation or specify a link mode. Note that any changes you make to the Auto Negotiate value are ignored for Gigabit interfaces.
Note that when you register an 8000 Series managed device to your Defense Center, you must either auto-negotiate on both sides of the connection, or set both sides to the same static speed to ensure a stable network link. 8000 Series managed devices do not support half duplex network links; they also do not support differences in speed or duplex configurations at opposite ends of a connection.

Note Unlike other interfaces, changing the maximum transmission unit (MTU) on a management interface does not interrupt traffic.
The following table lists MTU configuration ranges for management interfaces:
Because the system automatically trims 18 bytes from the configured MTU value, any value below 1298 does not comply with the minimum IPv6 MTU setting of 1280, and any value below 594 does not comply with the minimum IPv4 MTU setting of 576. For example, the system automatically trims a configured value of 576 to 558.
– Select Static to enter the IPv4 management IP address and netmask.
– Select
DHCP
to retrieve network settings from a DHCP server. (
eth0
only)
– Select Disabled to disable the protocol. Do not disable both IPv4 and IPv6.
– Select Static to enter the IPv4 management IP address and netmask.
– Select
DHCP
to retrieve network settings from a DHCP server. (
eth0
only)
– Select Router Assigned to retrieve network settings from a local IPv6 router.
– Select Disabled to disable the protocol. Do not disable both IPv4 and IPv6.
Routes
You can view or edit the route to your default management interface when you click the Edit icon, or view the route statistics when you click the View icon.
You can create a new route to an additional network. Click the Add icon to display a pop-up window where you can enter the destination network IP address, netmask or prefix length, interface dropdown (
eth0
and so on) and the gateway. The following examples show some ways you can use a route to a different network:
- On a Defense Center, you can create a route to a device on a different network to allow one Defense Center to manage and isolate traffic from devices on different networks.
- On a device, you can create a route and register your device to Defense Centers on two different networks to configure high availability for Defense Centers over a wider deployment.
You can configure the following settings on a specific management interface to create a route to a network:
Shared Settings
Regardless of your management environment, you can specify up to three DNS servers, as well as the host name and domain for the device.
You can change the management port. FireSIGHT System appliances communicate using a two-way, SSL-encrypted communication channel, which by default is on port 8305. Although Cisco strongly recommends that you keep the default setting, if the management port conflicts with other communications on your network, you can choose a different port.

LCD Panel
Series 3 devices allow you view device information using an LCD panel on the front of the device. On the Series 3 Management Interfaces page, you can allow people to change network settings using the LCD panel.
If you edit the IP address of a managed device using the LCD panel, confirm that the changes are reflected on the managing Defense Center. In some cases, you may need to edit the device management settings manually. For more information, see Editing Device Management Settings.

Proxy
All FireSIGHT System appliances are configured to directly connect to the Internet on ports 443/tcp (HTTPS) and 80/tcp (HTTP); see Security, Internet Access, and Communication Ports. With the exception of Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series, FireSIGHT System appliances support the use of a proxy server, to which you can authenticate via HTTP Digest.

Editing Management Interfaces
You can use the Management Interfaces page to modify the default settings for the default management interface on your Defense Center. On Series 3 appliances and virtual Defense Centers, you can also enable and configure traffic channels and additional management interfaces. Any changes you make to the Auto Negotiate value are ignored for Gigabit interfaces.

To edit a management interface:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click Management Interfaces .
The Management Interfaces page appears, listing the current settings for each interface on your Defense Center.
Step 3 Optionally, under Interfaces , click Edit next to the interface that you want to configure.
You can modify the default management interface (
eth0
) or enable and configure an additional management interface (
eth1
and so on). For each additional management interface, you must assign a unique, static IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) or hostname. You can select which traffic channels to carry, in addition to setting the mode, link, MTU, and IP configuration.
Step 4 Optionally, under Routes , enter the destination network IP address, netmask or prefix length, and gateway, and specify the management interface you want to use for this network route.
You can also view the route statistics when you click the magnifying glass icon.
Step 5 Optionally, under Shared Settings , specify network settings that do not depend on the management network protocol.
You can specify up to three DNS servers, as well as the host name and domain for the appliance. Note that if you selected DHCP in the previous step, you cannot manually specify these shared settings.

Step 6 Optionally, on Series 3 devices, under LCD Panel, select the Allow reconfiguration of network settings check box to enable changing network settings using the device’s LCD panel.

Step 7 Optionally, under Proxy , select the check box to enable proxy, and then:
Step 8 When you are finished configuring the appliance’s network settings, click Save .
The network settings are changed. If you changed the appliance’s hostname, the new name is not reflected in the syslog until after you reboot the appliance.
Shutting Down and Restarting the System
You have several options for controlling the processes on your appliance. You can:

- reboot the appliance
- restart communications, database, and HTTP server processes on the appliance (this is typically used during troubleshooting)
- restart the Snort process

To shut down or restart your appliance:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
The Appliance Process page appears.
Step 3 Specify the command you want to perform:
- To shut down the appliance, click Run Command next to Shutdown Defense Center .
- To reboot the appliance, click Run Command next to Reboot Defense Center . Note that this logs you out of the Defense Center.
- To restart the appliance, click Run Command next to Restart Defense Center Console . Note that restarting the Defense Center may cause deleted hosts to reappear in the network map.

Note When you reboot your Defense Center, the system runs a database check that can take up to an hour to complete.
- To shut down the appliance, click Run Command next to Shutdown Appliance .
- To reboot the appliance, click Run Command next to Reboot Appliance . Note that this logs you out of the device.
- To restart the appliance, click Run Command next to Restart Appliance Console .
- To restart the Snort process, click Run Command next to Restart Snort .

Note When you reboot your managed device, the system runs a database check that can take up to an hour to complete.
Setting the Time Manually
If the Time Synchronization setting in the currently applied system policy is set to Manually in Local Configuration , then you can manually set the time for the appliance using the Time page in the local configuration.
You must use native applications, such as command line interfaces or the operating system interface, to manage time settings for Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series. For more information, see the Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series Installation Guide .
If the appliance is synchronizing its time based on NTP, you cannot change the time manually. Instead, the NTP Status section on the Time page provides the following information:
See Synchronizing Time for more information about the time settings in the system policy.
To manually configure the time:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 3 Select the following from the Set Time drop-down lists:
The time is updated. For information about changing your time zone, see Setting Your Default Time Zone.
Managing Remote Storage
On Defense Centers, you can use local or remote storage for backups and reports. You can use Network File System (NFS), Secure Shell (SSH), or Server Message Block (SMB)/Common Internet File System (CIFS) for backup and report remote storage. You cannot send backups to one remote system and reports to another, but you can choose to send either to a remote system and store the other on the local Defense Center. For information on backup and restore, see Using Backup and Restore.

Tip After configuring and selecting remote storage, you can switch back to local storage only if you have not increased the connection database limit.
You must ensure that your external remote storage system is functional and accessible from the Defense Center.
Select one of the backup and report storage options:
- To disable external remote storage and use the local Defense Center for backup and report storage, see Using Local Storage.
- To use NFS for backup and report storage, see Using NFS for Remote Storage.
- To use secure shell (SCP) via SSH for backup and report storage, see Using SSH for Remote Storage.
- To use SMB for backup and report storage, see Using SMB for Remote Storage.

Note You cannot use remote backup and restore to manage data on Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series.
Using Local Storage
You can store backups and reports on the local Defense Center.
To store backups and reports locally:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click Remote Storage Device .
The Remote Storage Device page appears.
Step 3 Select Local (No Remote Storage) from the Storage Type drop-down list.
Your storage location choice is saved.

Tip You do not use the Test button with local storage.
Using NFS for Remote Storage
You can select Network File System (NFS) protocol to store your reports and backups. Optionally, select the Use Advanced Options check box to use one of the mount binary options as documented in an NFS mount man page.
To store backups and reports using NFS:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click Remote Storage Device .
The Remote Storage Device page appears.
Step 3 Select NFS from the Storage Type drop-down list.
The page refreshes to display the NFS storage configuration options.
Step 4 Add the connection information:
Step 5 If there are any required command line options, select Use Advanced Options .
A Command Line Options field appears where you can enter mount binary options.
Step 6 Under System Usage , select either or both of the following:
Step 7 Optionally, click Test .
The test ensures that the Defense Center can access the designated host and directory.
Your remote storage configuration is saved.
Using SSH for Remote Storage
You can select
SSH
to use secure copy (SCP) to store your reports and backups. Optionally, select the
Use Advanced Options
check box to use one of the mount binary options as documented in a SSH mount man page.

To store backups and reports using SSH:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click Remote Storage Device .
The Remote Storage Device page appears.
Step 3 At Storage Type , select SSH .
The page refreshes to display the SCP via SSH storage configuration options.
Step 4 Add the connection information:
- Enter the IP address or hostname of the storage system in the Host field.
- Enter the path to your storage area in the Directory field.
- Enter the storage system’s user name in the Username field and the password for that user in the Password field. To specify a domain, precede the user name with the domain followed by a forward slash (/).
- To use SSH keys, copy the content of the SSH Public Key field and place it in your authorized_keys file.
Step 5 If there are any required command line options, select Use Advanced Options .
A Command Line Options field appears where you can enter mount binary options.
Step 6 Under System Usage, select either or both of the following:
Step 7 Optionally, click Test .
The test ensures that the Defense Center can access the designated host and directory.
Your remote storage configuration is saved.
Using SMB for Remote Storage
You can select Server Message Block (SMB) protocol to store your reports and backups. Optionally, select the Use Advanced Options check box to use one of the mount binary options, as documented in an SMB mount man page. For example, using SMB, you can enter the security mode in the Command Line Options field using the following format:
where mode is the security mode you want to use for remote storage. See the Security Mode Settings table for setting options.
Use NTLM password hashing with signing (may be Default if |
|
To store backups and reports using SMB:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click Remote Storage Device .
The Remote Storage Device page appears.
Step 3 Under Storage Type , select SMB .
The page refreshes to display the SMB storage configuration options.
Step 4 Add the connection information:
- Enter the IPv4 address or hostname of the storage system in the Host field.
- Enter the share of your storage area in the Share field. Note that the system only recognizes top-level shares and not full file paths. To use the specified Share directory as a remote backup destination, it must be shared on the Windows system.
- Optionally, enter the domain name for the remote storage system in the Domain field.
- Enter the user name for the storage system in the Username field and the password for that user in the Password field.
Step 5 If there are any required command line options, select Use Advanced Options .
A Command Line Options field appears where you can enter the mount binary commands, such as security modes. See Security Mode Settings for more information.
Step 6 Under System Usage, select either or both of the following:
Step 7 Optionally, click Test .
The test ensures that the Defense Center can access the designated host and directory.
Your remote storage configuration is saved.
Understanding Change Reconciliation
To monitor the changes that users make and ensure that they follow your organization’s preferred standard, you can configure your system to send, via email, a detailed report of changes made to your system over the past 24 hours. Whenever a user saves changes to the system configuration, a snapshot is taken of the changes. The change reconciliation report combines information from these snapshots to present a clear summary of recent system changes.
The following sample graphic displays a User section of an example change reconciliation report and lists both the previous value for each configuration and the value after changes. When users make multiple changes to the same configuration, the report lists summaries of each distinct change in chronological order, beginning with the most recent.
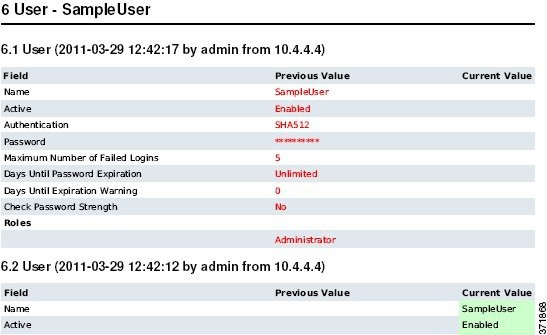
You can view changes made during the previous 24 hours. However, to view prior changes, you must view the audit log. See Using the Audit Log to Examine Changes for more information.
To use the change reconciliation feature:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Click Change Reconciliation .
The Change Reconciliation page appears.
Step 3 Select the Enable check box.
Step 4 Select the time of day you want the system to send out the change reconciliation report from the Time to Run drop-down lists.
Step 5 In the Email to field, enter the email addresses of report recipients. At any time, you can click Resend Last Report to send recipients another copy of the most recent change reconciliation report.

Note To receive change reconciliation reports, you must first configure a mail relay host and notification address. For more information, see Configuring a Mail Relay Host and Notification Address.
Step 6 Optionally, select Include Policy Configuration to include records of policy changes in the change reconciliation report. This includes changes to access control, intrusion, system, health, and network discovery policies. If you do not select this option, the report will not show changes to any policies.

Note This option is not available on managed devices.
Step 7 Optionally, select Show Full Change History to include records of all changes over the past 24 hours in the change reconciliation report. If you do not select this option, the report includes only a consolidated view of changes for each category.
Your changes are saved. The report runs daily at the time you selected.
Managing Remote Console Access
Supported Devices: feature dependent
Supported Defense Centers: feature dependent
You can use a Linux system console for remote access on any appliance via either the VGA port (which is the default) or the serial port on the physical appliance. Choose the option most suitable to the physical layout of your organization’s Cisco deployment.
You can use Lights-Out Management (LOM) on the default (
eth0
) management interface on a Serial Over LAN (SOL) connection to remotely monitor or manage Series 3 appliances without logging into the management interface of the appliance. You can perform limited tasks, such as viewing the chassis serial number or monitoring such conditions as fan speed and temperature, using a command line interface on an out-of-band management connection. Series 2, virtual appliances, ASA FirePOWER module, and Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series do not support LOM.
You must enable LOM for both the appliance and the user you want to manage the appliance. After you enable the appliance and the user, you use a third-party Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) utility to access and manage your appliance.

Note The baseboard management controller (BMC) for a 3D71xx, 3D82xx, or a 3D83xx device is only accessible via 1Gbps link speeds when the host is powered on. When the device is powered down the BMC can only establish Ethernet link at 10 and 100Mbps. Therefore if LOM is being used to remotely power the device, connect the device to the network using 10 and 100Mbps link speeds only.
For more information, see the following topics:
- Configuring Remote Console Settings on the Appliance
- Enabling Lights-Out Management User Access
- Using a Serial Over LAN Connection
- Using Lights-Out Management
Configuring Remote Console Settings on the Appliance
Supported Devices: feature dependent
Supported Defense Centers: feature dependent
Use the web interface of the appliance you want to remotely manage to select and configure the remote console access option you want to use.
Note that Series 2, virtual appliances, ASA FirePOWER module, and Cisco NGIPS for Blue Coat X-Series do not support LOM.

Note Before you can connect to a Series 3 device using LOM/SOL, you must disable Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on any third-party switching equipment connected to the device’s management interface.
To configure remote console settings:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
Step 2 Select Console Configuration .
The Console Configuration page appears.
Step 3 Select a remote console access option:
Note that 3D2100, 3D2500, 3D3500, and 3D4500 managed devices do not have serial ports.
If you selected Physical Serial Port or Lights-Out Management , the LOM settings appear.

Note When you change your remote console from Physical Serial Port to Lights-Out Management or from Lights-Out Management to Physical Serial Port on the 70xx Family of devices (except the 3D7050), you may have to reboot the appliance twice to see the expected boot prompt.
Step 4 To configure LOM via SOL, enter the appropriate settings:

Note The LOM IP address must be different from the management interface IP address of the appliance.
Remote console configuration for the appliance is saved. If you configured Lights-Out Management, you must enable it for at least one user; see Enabling Lights-Out Management User Access.
Enabling Lights-Out Management User Access
Supported Defense Centers: Series 3
You must explicitly grant Lights-Out Management permissions to users who will use the feature. You configure LOM and LOM users on a per-appliance basis using each appliance’s local web interface. That is, you cannot use the Defense Center to configure LOM on a managed device. Similarly, because users are managed independently per appliance, enabling or creating a LOM-enabled user on the Defense Center does not transfer that capability to users on managed devices.
LOM users also have the following restrictions:
- You must assign the Administrator role to the user.
- The username may have up to 16 alphanumeric characters. Hyphens and longer user names are not supported for LOM users.
- The password may have up to 20 alphanumeric characters, except for 3D7100 Family devices. If LOM is enabled on a 3D7110, 3D7115, 3D7120, or 3D7125 device, the password may have up to 16 alphanumeric characters. Passwords longer than 20 or 16 characters, respectively, are not supported for LOM users. A user’s LOM password is the same as that user’s system password. Cisco recommends that you use a complex, non-dictionary-based password of the maximum supported length for your appliance and change it every three months.
- Series 3 Defense Centers and 8000 Series devices can have up to 13 LOM users. 7000 Series devices can have up to eight LOM users.
Note that if you deactivate, then reactivate, a role with LOM while a user with that role is logged in, or restore a user or user role from a backup during that user’s login session, that user must log back into the web interface to regain access to IPMItool commands. For more information, see Managing Predefined User Roles.
To enable or view Lights-Out Management user access:
Step 1 Select System > Local > User Management.
The User Management page appears.
Step 2 You have the following options:
 ) next to a user name in the list.
) next to a user name in the list.Step 3 Under User Configuration, enable the Administrator role.
Step 4 Select the Allow Lights-Out Management Access check box.
The user has LOM access for this appliance.
Using a Serial Over LAN Connection
Supported Defense Centers: Series 3
You use a third-party IPMI utility on your computer to create a Serial Over LAN connection to the appliance. If your computer uses a Linux-like or Mac environment, use IPMItool; for Windows environments, use IPMIutil.

Note Cisco recommends using IPMItool version 1.8.12 or greater.
IPMItool is standard with many distributions and is ready to use.
You must install IPMItool on a Mac. First, confirm that your Mac has Apple's XCode Developer tools installed, making sure that the optional components for command line development are installed (UNIX Development and System Tools in newer versions, or Command Line Support in older versions). Then you can install macports and the IPMItool. Use your favorite search engine for more information or try these sites:
You must compile IPMIutil on Windows. If you do not have access to a compiler, you can use IPMIutil itself to compile. Use your favorite search engine for more information or try this site:
Understanding IPMI Utility Commands
Commands used for IPMI utilities are composed of segments as in the following IPMItool example:
–
ipmitool
invokes the utility
–
-I lanplus
enables encryption for the session
–
-H
IP_address
indicates the IP address of the appliance you want to access
–
-U
user_name
is the name of an authorized user
–
-
command
is the name of the command you want to give

Note Cisco recommends using IPMItool version 1.8.12 or greater.
The same command for Windows looks like this:
This command connects you to the command line on the appliance where you can log in as if you were physically present at the appliance. You may be prompted to enter a password.
To create a Serial Over LAN connection:
Step 1 Enter the following command:

Note Cisco recommends using IPMItool version 1.8.12 or greater.
The command line login for the appliance appears. You may be prompted to enter a password.
Using Lights-Out Management
Supported Defense Centers: Series 3
Lights-Out Management provides the ability to perform a limited set of actions over an SOL connection on the default (
eth0
) management interface without the need to log into the appliance. You use the command to create a SOL connection followed by one of the commands listed in the following table. After the command is completed, the connection ends. Note that not all power control commands are valid on 70xx Family devices.

Note The baseboard management controller (BMC) for a 3D71xx, 3D82xx, or a 3D83xx device is only accessible via 1Gbps link speeds when the host is powered on. When the device is powered down the BMC can only establish Ethernet link at 10 and 100Mbps. Therefore if LOM is being used to remotely power the device, connect the device to the network using 10 and 100Mbps link speeds only.


If all attempts to access your appliance have failed, you can use LOM to restart your appliance remotely. Note that if a system is restarted while the SOL connection is active, the LOM session may disconnect or time out.

Powers down the appliance (not valid on |
||
Displays appliance information, such as fan speeds and temperatures |
For example, to display a list of appliance information, the IPMItool command is:

Note Cisco recommends using IPMItool version 1.8.12 or greater.
The same command with the IPMIutil utility is:
Step 1 Enter the following command:

Note Cisco recommends using IPMItool version 1.8.12 or greater.
where command is one of the commands from the Lights-Out Management Commands table.
The corresponding action as noted in the table is performed. You may be prompted to enter a password.
Enabling Cloud Communications
License: URL Filtering or Malware
Supported Defense Centers: Any except DC500
The FireSIGHT System contacts Cisco’s Collective Security Intelligence Cloud to obtain various types of information:
- If your organization has a FireAMP subscription, you can receive endpoint-based malware events; see Working with Cloud Connections for FireAMP.
- File policies associated with access control rules allow managed devices to detect files transmitted in network traffic. The Defense Center uses data from the Cisco cloud to determine if the files represent malware; see Understanding and Creating File Policies.
- When you enable URL filtering, the Defense Center can retrieve category and reputation data for many commonly visited URLs, as well as perform lookups for uncategorized URLs. You can then quickly create URL conditions for access control rules; see Performing Reputation-Based URL Blocking.
For file and malware cloud-based features, you can use a FireAMP Private Cloud instead of the standard cloud connection if your organization requires additional security or wishes to limit outside connections. All file and malware cloud lookups, as well as collection and relaying of event data from FireAMP endpoints, are handled through the private cloud; when the private cloud contacts the public Cisco cloud, it does so through an anonymized proxy connection. Although it does not support dynamic analysis or non-FireAMP cloud features such as Security Intelligence or URL filtering, the private cloud, from a user’s perspective, functions much the same as a standard public cloud connection. For more information on configuring a private cloud, see Working with the FireAMP Private Cloud.
Use the Defense Center’s local configuration to specify the following options:
You must enable this option to perform category and reputation-based URL filtering.
Due to memory limitations, some device models perform URL filtering with a smaller, less granular, set of categories and reputations. For example, if a parent domain's subsites have different URL categories and reputations, some devices may use the parent site's data for all subsites. These devices include the 7100 Family and the following ASA FirePOWER models: ASA 5506-X, ASA 5506H-X, ASA 5506W-X, ASA 5508-X, ASA 5512-X, ASA 5515-X, ASA 5516-X, and the ASA 5525-X.
For virtual devices, see the installation guide for information on allocating the correct amount of memory to perform category and reputation-based URL filtering.
Allows the system to query the cloud when someone on your monitored network attempts to browse to a URL that is not in the local data set.
If the cloud does not know the category or reputation of a URL, or if the Defense Center cannot contact the cloud, the URL does not match access control rules with category or reputation-based URL conditions. You cannot assign categories or reputations to URLs manually.
Disable this option if you do not want your uncategorized URLs to be cataloged by the Cisco cloud, for example, for privacy reasons.
Allows the system to contact the cloud on a regular basis to obtain updates to the URL data in your appliances’ local data sets. Although the cloud typically updates its data once per day, enabling automatic updates forces the Defense Center to check every 30 minutes to make sure that you always have up-to-date information.
Although daily updates tend to be small, if it has been more than five days since your last update, new URL filtering data may take up to 20 minutes to download, depending on your bandwidth. Then, it may take up to 30 minutes to perform the update itself.
If you want to have strict control of when the system contacts the cloud, you can disable automatic updates and use the scheduler instead, as described in Automating URL Filtering Updates.

Note Cisco recommends that you either enable automatic updates or use the scheduler to schedule updates. Although you can manually perform on-demand updates, allowing the system to automatically contact the cloud on a regular basis provides you with the most up-to-date, relevant URL data.
Share URI Information of malware events with Cisco
Optionally, Defense Centers can send information about the files detected in network traffic to the cloud. This information includes URI information associated with detected files and their SHA-256 hash values. Although sharing is opt-in, transmitting this information to Cisco will help with future efforts to identify and track malware.
Use legacy port 32137 for network AMP lookups
Selecting this check box allows your system to use port 32137/tcp (the previous default port) for network cloud lookups instead of port 443/tcp. If you updated your appliances from a previous version of the FireSIGHT System, this check box is selected by default.
Performing category and reputation-based URL filtering and device-based malware detection require that you enable the appropriate licenses on your managed devices; see Licensing the FireSIGHT System.
You cannot configure cloud connection options if you have no URL Filtering or Malware licenses on the Defense Center. If you have one license but not the other, the Cloud Services local configuration page displays only the options for which you are licensed. Defense Centers with expired licenses cannot contact the cloud.
Note that, in addition to causing the URL Filtering configuration options to appear, adding a URL Filtering license to your Defense Center automatically enables Enable URL Filtering and Enable Automatic Updates . You can manually disable the options if needed.
Note that receiving endpoint-based malware events using a FireAMP subscription does not require a license, nor does specifying individual URLs or groups of URLs to allow or block. For more information, see Understanding Malware Protection and File Control and Performing Manual URL Blocking.
Internet Access and High Availability
The system uses ports 80/HTTP and 443/HTTPS to contact the Cisco cloud and also supports use of a proxy; see Configuring Management Interfaces.
Although all URL filtering configurations and information are synchronized between Defense Centers in a high availability deployment, only the primary Defense Center downloads URL filtering data. If the primary Defense Center fails, you must make sure that the secondary Defense Center has direct access to the Internet and use the web interface on the secondary Defense Center to promote it to Active. For more information, see Monitoring and Changing High Availability Status.
On the other hand, although they share file policies and related configurations, Defense Centers in a high availability pair share neither cloud connections nor malware dispositions. To ensure continuity of operations, and to ensure that detected files’ malware dispositions are the same on both Defense Centers, both primary and secondary Defense Centers must have access to the cloud.
The default health policy includes the following modules that track the state and stability of the Defense Center’s cloud connections:
– URL Filtering Monitor, which also warns you if the Defense Center fails to push category and reputation updates to its managed devices

Tip Another module, the FireAMP Status Monitor, tracks the Defense Center’s connection to the Cisco cloud for FireAMP subscription holders. For more information on health monitoring, see Using the Health Monitor.
The following procedures explain how to enable communications the Cisco cloud, and how to perform an on-demand update of URL data. Note that you cannot start an on-demand update if an update is already in progress.
To enable communications with the cloud:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
The Cloud Services page appears. If you have a URL Filtering license, the page displays the last time URL data was updated.
Step 3 Configure cloud connection options as described above.
You must Enable URL Filtering before you can Enable Automatic Updates or Query Cloud for Unknown URLs .
Your settings are saved. If you enabled URL filtering, depending on how long it has been since URL filtering was last enabled, or if this is the first time you enabled URL filtering, the Defense Center retrieves URL filtering data from the cloud.
To perform an on-demand update of the system’s URL data:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
The URL Filtering page appears.
The Defense Center contacts the cloud and updates its URL filtering data if an update is available.
Enabling VMware Tools
Supported Defense Centers: virtual
VMware Tools is a suite of utilities intended to enhance the performance of the virtual machine. These utilities allow you to make full use of the convenient features of VMware products. The system supports the following plugins on all virtual appliances:
You can also enable VMware Tools on all supported ESXi versions. For a list of supported versions, see the FireSIGHT System Virtual Installation Guide . For information on the full functionality of VMware Tools, see the VMware website ( http://www.vmware.com/ ).
The following procedure describes how to enable VMware Tools on the virtual Defense Center using the Configuration menu on the web interface. Because the virtual device does not have a web interface, you must use the command line interface to enable VMware Tools on a virtual device; see the FireSIGHT System Virtual Installation Guide.
To enable VMware Tools on a virtual Defense Center:
Step 1 Select System > Local > Configuration .
The VMware Tools page appears.
Step 3 Click Enable VMware Tools and click Save .
 Feedback
Feedback