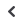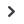43
Cybersecurity in ASEAN: An Urgent Call to Action
remained very fragmented geographically. This makes it difficult for companies to compete on
the national, regional, and global level and reduces the choice of viable and usable cybersecurity
technologies that citizens and businesses have access to. Certification can play a significant role
in increasing trust and security in products and services. In addition to certification, the European
Commission is exploring the creation of a European, commercially oriented, voluntary labeling
scheme for the security of ICT products.
3.4.3 Foster R&Daround emerging threat vectors
Most R&D cybersecurity solutions focus on solving yesterday’s problemwithout looking ahead
to the next great challenge. R&D activities need to focus on products that are easy to use,
intuitive, and secure. R&D should also take into consideration the lack of skilled talent. Our
interviews highlight the need for efforts to be focused on three areas:
•
Automation and artificial intelligence
•
Tackling disinformation
•
Security in the OT environment
“Singapore has established a fund of SGD 190million for
spending on cybersecurity research over the period from
2015 to 2020. The focus is on developing products which
are easy to use, intuitive as well as secure by design. Security
in an IoT environment is another major area of focus.”
—deputy chief executive, CSAof Singapore
Note: MDEC is Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation.
Sources: interview with Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation; A.T. Kearney analysis
Figure
MDEC’s three-tier capacity-building program
Five skills that require focus
Recent highlights of MDEC’s eorts include multiple
partnership agreements with cybersecurity academies
from the United Kingdom and the United States,
such as Protection Group International, and signing
a memorandum of understanding with ISACA in an eort
to certify and professionalize the cybersecurity industry
1
Penetration testing and assurance services
2
Provisioning
3
Governance and compliance
4
Incident handling and response
5
Digital forensics
Youth-level
To create awareness,
via outreach programs
to educate the general
public, including children
University-level
To promote cybersecurity
as a career, by industry-
linked programs, targeted
university courses, and
innovation opportunities
Industry-level
To scale up cybersecurity professional
development, via specialized skill-building and
conversion programs for existing professionals