- DHCP Overview
- Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
- DHCP Server MIB
- Configuring the DHCP Server On-Demand Address Pool Manager
- DHCP Server RADIUS Proxy
- Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Relay Agent
- Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Client
- DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Configuring DHCP Services for Accounting and Security
- Configuring DHCP Enhancements for Edge Session Management
- ISSU and SSO--DHCP High Availability Features
- DHCP Option 82 Support for Routed Bridge Encapsulation
- DHCPv6 Bulk-Lease Query
- DHCPv6 Relay and Server - MPLS VPN Support
- DHCPv6 Relay Source Configuration
- IPv6 Access Services: DHCPv6 Relay Agent
- DHCPv6 Server Stateless Autoconfiguration
- IPv6 Access Services: Stateless DHCPv6
- DHCPv6 Repackaging
- IPv6 Access Services: DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
- DHCPv6 Guard
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Information About DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- How to Configure DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Configuration Example for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Additional References
- Feature Information for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
The Cisco DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID provides more naming choices in the Option 82 Remote ID and Option 82 Circuit ID suboptions. For example, you can use a switch-configured hostname or specify an ASCII text string for the remote ID, and you can configure an ASCII text string to override the circuit ID.
 Note |
Refer to the configuration guide for your platform for information about configuring Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). See the "Configuring DHCP Snooping" section of the Cisco 7600 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, Release 12.2SR, for information about configuring DHCP on Cisco 7600 series routers. See the "Additional References" section for sources of information about configuring DHCP on other Cisco platforms. |
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Information About DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- How to Configure DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Configuration Example for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
- Additional References
- Feature Information for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
When DHCP snooping is configured on a primary VLAN, you cannot configure snooping with different settings on any of its secondary VLANs. You must configure DHCP snooping for all associated VLANs on the primary VLAN. If DHCP snooping is not configured on the primary VLAN and you try to configure it on the secondary VLAN, for example, VLAN 200, this message appears:
2w5d:%DHCP_SNOOPING-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_PVLAN_WARNING:DHCP Snooping configuration may not take effect on secondary vlan 200. DHCP Snooping configuration on secondary vlan is derived from its primary vlan.
You can use the show ip dhcp snooping command to display all VLANs, both primary and secondary, that have DHCP snooping enabled.
Information About DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
The DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID feature enhances validation security by allowing you to determine what information is provided in the Option 82 Remote ID and Option 82 Circuit ID suboptions.
You can enable DHCP snooping on private VLANs. When DHCP snooping is enabled, the configuration is propagated to both a primary VLAN and its associated secondary VLANs. When DHCP snooping is enabled on a primary VLAN, it is also enabled on its secondary VLANs.
See the "DHCP Snooping Option-82 Data Insertion" section of the Cisco 7600 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for information about using DHCP to centrally manage the IP address assignments for a large number of subscribers in residential, metropolitan Ethernet-access environments.
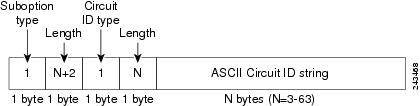
The figure below shows the packet format used when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and the ip dhcp snooping information option global configuration command is entered with the Circuit ID suboption.
| Figure 1 | Suboption Packet Formats, Circuit ID Specified |
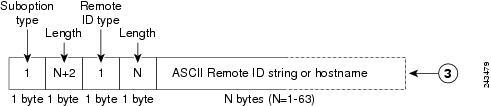
The figure below shows the packet format used when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and the ip dhcp snooping information option global configuration command is entered with the Remote ID suboption.
| Figure 2 | Suboption Packet Formats, Remote ID Specified |
How to Configure DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
Configuring DHCP Snooping on Private VLANs
Perform these tasks to configure DHCP snooping on private primary and secondary VLANs:
- Configure a private, primary VLAN.
- Associate with it an isolated VLAN.
- Create an SVI interface for the primary VLAN, and associate it with the appropriate loopback IP and helper address.
- Enable DHCP snooping on the primary VLAN, which also enables it on the associated VLAN.
 Note |
You must also configure a server to assign the IP address, a DHCP pool, and a relay route so that snooping can be effective. |
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Example for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
Mapping Private-VLAN Associations Example
The following interface configuration example shows how to map the private-VLAN associations. The user-configurable circuit ID "aabb11" is inserted on the secondary VLAN, vlan 7.
interface GigabitEthernet9/0/1 switchport switchport private-vlan host-association 70 7 switchport mode private-vlan host no mls qos trust spanning-tree portfast ip dhcp snooping vlan 7 information option format-type circuit-id string aabb11
The following example shows how to define a DHCP class "C1" and specify the hex string of the corresponding class at the server by using the hex string that matches the circuit-ID value entered in the interface configuration example. That is, the hex string 00000000000000000000000000000006616162623131 mask fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff0000000000000 matches the circuit ID aabb11.
ip dhcp class C1 relay agent information relay-information hex 00000000000000000000000000000006616162623131 mask fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff0000000000000
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| Configuring DHCP on the Cisco 7600 series router |
"Configuring DHCP Snooping" section of the Cisco 7600 Series Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide |
| Configuring DHCP on the Cisco Catalyst 3550 multilayer switch |
"Configuring DHCP Features" section of the Catalyst 3550 Multilayer Switch Software Configuration Guide |
| Configuring DHCP on the Cisco Catalyst 2970 switch |
"Configuring DHCP Features" section of the Catalyst 2970 Switch Software Configuration Guide |
| Configuring DHCP on the Cisco Catalyst 3560 switch |
"Configuring DHCP Features and IP Source Guard" section of the Catalyst 3560 Switch Software Configuration Guide |
| Configuring DHCP on the Cisco Catalyst 3750 switch |
"Configuring DHCP Features and IP Source Guard" section of the Catalyst 3750 Switch Software Configuration Guide |
| DHCP commands: complete command syntax, command mode command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples |
Cisco IOS IP Addressing Services Command Reference |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID |
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| DHCP Option 82 Configurable Circuit ID and Remote ID |
12.2(33)SRD1 |
Provides naming choices in the Option 82 Remote ID and Option 82 Circuit ID suboptions. The following commands were introduced or modified: ip dhcp snooping vlan. |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback