- MPLS High Availability Overview
- MPLS High Availability Command Changes
- MPLS LDP Graceful Restart
- NSF SSO - MPLS LDP and LDP Graceful Restart
- AToM Graceful Restart
- NSF SSO�Any Transport over MPLS and AToM Graceful Restart
- NSF SSO - MPLS VPN
- NSF SSO--MPLS TE and RSVP Graceful Restart
- ISSU MPLS Clients
- NSF SSO ISSU Support for VPLS
- NSF SSO and ISSU�MPLS VPN 6VPE and 6PE
- Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- SSO Support for MPLS TE Autotunnel and Automesh
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Information About Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- How to Configure Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Configuration Examples for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
The Circuit Emulation Service over UDP feature extends the implementation of Cisco IOS Circuit Emulation Service (CES) by supporting pseudowire emulation (PWE) function to be performed over an Internet Protocol (IP) network directly.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Information About Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- How to Configure Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Configuration Examples for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Because CLI on Route Processor (RP) is used to install the Access Control List (ACL) entry, the ACL programming is decoupled from the Layer 2 virtual private network (L2VPN) control plane update. As a result, when a pseudowire circuit goes down, the ACL is still present. Any traffic coming in from the core which matches the ACL is redirected to the egress line card, where it is dropped due to the absence of appropriate entries in the disposition table.
- Pseudowires redundancy is not supported.
- Fragmentation of IP packets is not supported. The Don’t Fragment (DF) bit is set when the IP header is inserted.
- Path MTU is not supported.
- Differential synchronization mode is not supported.
- Only the basic Circuit Emulation Service over Packet Switching Networks (CESoPSN) over UDP/IP encapsulation without the optional Real-Time Protocol (RTP) header is supported.
Information About Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- CES Overview
- Pseudowire Emulation over Packet
- Circuit Emulation Services over Packet Switched Network over UDP
CES Overview
Circuit Emulation Service—Internetworking Function (CES-IWF) is a service based on ATM forum standards that allows communications to occur between Constant Bit Rate (CBR) or AAL1 CES and ATM User Network Interfaces (UNI); that is, between non-ATM telephony devices (such as classic private branch exchange (PBX) or Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and ATM devices (such as Cisco 3600 or 7200 series routers). Thus, a Cisco 3600 series router equipped with an OC-3/STM-1 ATM CES network module or a Cisco 7200 series router equipped with an ATM-CES port adapter offers a migration path from classic T1/E1 CBR data communications services to emulated CES T1/E1 unstructured (clear channel) services or structured (N x 64) services in an ATM network.
CES allows you to interconnect existing T1 or E1 interfaces and other kinds of CBR equipment. CES includes features such as PBX interconnect, consolidated voice and data traffic, and video conferencing.
With circuit emulation, data received from an external device at the edge of an ATM network is converted to ATM cells, sent through the network, reassembled into a bit stream, and passed out of the ATM network to its destination. T1/E1 circuit emulation does not interpret the contents of the data stream. All the bits flowing into the input edge port of the ATM network are reproduced at one corresponding output edge port.
An emulated circuit is carried across the ATM network on a PVC, which is configured through the network management system or the router command line interface (CLI).
For more information on configuring CES, see the Configuring ATM module.
Pseudowire Emulation over Packet
Pseudowire Emulation over Packet (PWEoP) is one of the key components that you can use to migrate to a packet-based multi-service network. Circuit Emulation over Packet (CEoP) is a subset of PWEoP. It is used to migrate to all-packet networks from legacy TDM networks, yet providing transport for legacy applications transparently over a packet network. CEoP is the imitation of a physical connection. Many service providers and enterprises operate both packet switched networks and TDM networks. These service providers and enterprises have moved many of their data services from the TDM network to their packet network for scalability and efficiency. Cisco provides routing and switching solutions capable of transporting Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols such as Ethernet, IP, and Frame Relay. Most applications and services have been migrated to the packet-based network, including voice and legacy applications.
Circuit Emulation Services over Packet Switched Network over UDP
CESoPSN mode is used to encapsulate T1/E1 structured (channelized) services over PSN. Also refered to as structured mode, CESoPSN identifies framing and sends only payload, which can be channelized T1s within DS3 and DS0s within T1. DS0s can be bundled to the same packet. This mode is based on IETF RFC 5086.
SPAs can aggregate individual interfaces and flexibly bundle them together. They can be configured to support either structured or unstructured CES modes of operation per each T1/E1/J1 as well as clear channel DS3 interfaces. Note that DS3 does not support CESoPSN/SAToP currently. It is only supported on 1-Port Channelized OC-3 STM1 ATM CEoP SPA channelized to T1/E1, or on 24-Port Channelized T1/E1 ATM CEoP SPA.
Each supported interface can be configured individually to any supported mode. The supported services comply with IETF and ITU drafts and standards.
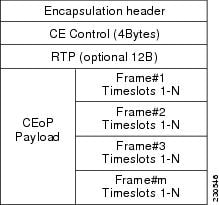
The figure below shows the frame format in CESoPSN mode.
How to Configure Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
Perform the following task to configure Circuit Emulation Service over UDP:
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface loopback interface-number
4. ip address ip-address mask [secondary]
5. mls cemoudp reserve slot slot-number
6. pseudowire-class pseudowire-class-name
7. encapsulation udp
8. ip local interface loopback interface-number
9. ip tos value number
10. ip ttl number
11. exit
12. controller {e1 | t1} slot / subslot / port
13. clock source {internal | line | loop}
14. cem-group number timeslots number
15. exit
16. interface cem slot / subslot / port
17. cem group-number
18. xconnect peer-router-id vcid pseudowire-class name
19. udp port local local-udp-port remote remote-udp-port
20. exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Example Configuring Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
- Example Verifying the Configuration of Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
Example Configuring Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface loopback 0 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.2.2.8 255.255.255.255 Router(config-if)# mls cemoudp reserve slot 2 Router(config)# pseudowire-class udpClass Router(config-pw-class)# encapsulation udp Router(config-pw-class)# ip local interface loopback 0 Router(config-pw-class)# ip tos value 100 Router(config-pw-class)# ip ttl 100 Router(config-pw-class)# exit Router(config)# controller ethernet 2/0/0 Router(config-controller)# clock source internal Router(config-controller)# cem-group 5 timeslots 1-24 Router(config-controller)# exit Router(config)# interface cem 2/0/0 Router(config-if)# cem 5 Router(config-if-cem)# xconnect 10.30.30.2 305 pw-class udpClass Router(config-if-cem)# udp port local 50000 remote 55000 Router(config-if-cem)# exit
Example Verifying the Configuration of Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
Router# show xconnect all Legend: XC ST=Xconnect State S1=Segment1 State S2=Segment2 State UP=Up DN=Down AD=Admin Down IA=Inactive SB=Standby HS=Hot Standby RV=Recovering NH=No Hardware XC ST Segment 1 S1 Segment 2 S2 ------+---------------------------------+--+---------------------------------+-- UP ac CE3/0/0:1(CESoPSN Basic) UP udp 66.66.66.66:180 UP UP ac CE3/0/0:6(CESoPSN Basic) UP udp 66.66.66.66:181 UP Router# show pw vc Local intf Local circuit VC ID Status -------------- -------------------------- ---------- -------- CE3/0/0 CESoPSN Basic 180 established LAddr: 55.55.55.55 LPort: 50002 RAddr: 66.66.66.66 RPort: 50002 CE3/0/0 CESoPSN Basic 181 established LAddr: 55.55.55.55 LPort: 50004 RAddr: 66.66.66.66 RPort: 50004
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the MPLS High Availability feature.
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| MPLS VPNs Non Stop Forwarding |
NSF/SSO—MPLS VPN |
| MPLS LDP Non Stop Forwarding |
NSF/SSO—MPLS LDP and LDP Graceful Restart |
| AToM Non Stop Forwarding |
NSF/SSO: Any Transport over MPLS and Graceful Restart |
| Cisco Express Forwarding |
Cisco Express Forwarding: Command Changes |
| MIBs |
|
| NSF/SSO |
Cisco Nonstop Forwarding MPLS High Availability: Command Changes |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| draft-ietf-mpls-bgp-mpls-restart.txt |
Graceful Restart Mechanism for BGP with MPLS |
| draft-ietf-mpls-idr-restart.txt |
Graceful Restart Mechanism for BGP |
MIBs
| MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
|
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| RFC 3478 |
Graceful Restart Mechanism for Label Distribution |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register on Cisco.com. |
Feature Information for Circuit Emulation Service over UDP
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Emulation Service over UDP |
15.1(2)S |
The Circuit Emulation Service over UDP feature extends the implementation of Cisco IOS CES by supporting PWE function to be performed over an IP network directly. |
 Feedback
Feedback