- Read Me First
- L2VPN Protocol-Based CLIs
- Any Transport over MPLS
- L2VPN Interworking
- L2VPN Pseudowire Preferential Forwarding
- L2VPN Multisegment Pseudowires
- MPLS Quality of Service
- QoS Policy Support on L2VPN ATM PVPs
- MPLS Pseudowire Status Signaling
- L2VPN VPLS Inter-AS Option B
- IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ) for AToM
- Configuring the Managed IPv6 Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Network Server
- L2VPN Pseudowire Redundancy
- Pseudowire Group Switchover
- L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- Xconnect as a Client of BFD
- H-VPLS N-PE Redundancy for QinQ Access
- H-VPLS N-PE Redundancy for MPLS Access
- VPLS MAC Address Withdrawal
- Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
- Routed Pseudo-Wire and Routed VPLS
- VPLS Autodiscovery BGP Based
- N:1 PVC Mapping to PWE with Nonunique VPIs
- QoS Policies for VFI Pseudowires
- VPLS BGP Signaling L2VPN Inter-AS Option A
- VPLS BGP Signaling L2VPN Inter-AS Option B
- Frame Relay over L2TPv3
- Loop-Free Alternate Fast Reroute with L2VPN
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- Information About L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- How to Configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- How to Configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching using the commands associated with the L2VPN Protocol-Based CLIs feature
- Configuration Examples for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- Additional References
- Feature Information for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
This feature module explains how to configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching, which extends layer 2 virtual private network (L2VPN) pseudowires across an interautonomous system (inter-AS) boundary or across two separate multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) networks.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- Information About L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- How to Configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- How to Configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching using the commands associated with the L2VPN Protocol-Based CLIs feature
- Configuration Examples for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
- Additional References
- Feature Information for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
In Cisco IOS XE Release 2.4, Pseudowire Switching is supported on Ethernet over MPLS attachment circuits.
L2VPN Pseudowire Switching is supported with AToM.
Only static, on-box provisioning is supported.
Sequencing numbers in AToM packets are not processed by L2VPN Pseudowire Switching. The feature blindly passes the sequencing data through the xconnect packet paths, a process that is called transparent sequencing. The endpoint PE-CE connections enforce the sequencing.
You can ping the adjacent next-hop PE router. End-to-end LSP pings are not supported.
Do not configure IP or Ethernet interworking on a router where L2VPN Pseudowire Switching is enabled. Instead, configure interworking on the routers at the edge PEs of the network.
The control word negotiation results must match. If either segment does not negotiate the control word, the control word is disabled for both segments.
AToM Graceful Restart is negotiated independently on each pseudowire segment. If there is a transient loss of the LDP session between two AToM PE routers, packets continue to flow.
Per-pseudowire quality of service (QoS) is not supported. Traffic Engineering (TE) tunnel selection is supported.
Attachment circuit interworking is not supported.
Information About L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
How L2VPN Pseudowire Switching Works
L2VPN Pseudowire Switching allows the user to extend L2VPN pseudowires across an inter-AS boundary or across two separate MPLS networks, as shown in the figures below. L2VPN Pseudowire Switching connects two or more contiguous pseudowire segments to form an end-to-end multihop pseudowire. This end-to-end pseudowire functions as a single point-to-point pseudowire.
As shown in the second figure below, L2VPN Pseudowire Switching enables you to keep the IP addresses of the edge PE routers private across inter-AS boundaries. You can use the IP address of the autonomous system boundary routers (ASBRs) and treat them as pseudowire aggregation (PE-agg) routers. The ASBRs join the pseudowires of the two domains.
L2VPN Pseudowire Switching also enables you to keep different administrative or provisioning domains to manage the end-to-end service. At the boundaries of these networks, PE-agg routers delineate the management responsibilities.


How Packets Are Manipulated at the Aggregation Point
Switching AToM packets between two AToM pseudowires is the same as switching any MPLS packet. The MPLS switching data path switches AToM packets between two AToM pseudowires. The following list explains exceptions:
The outgoing virtual circuit (VC) label replaces the incoming VC label in the packet. New Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) labels and Layer 2 encapsulation are added.
The incoming VC label time-to-live (TTL) field is decremented by one and copied to the outgoing VC label TTL field.
The incoming VC label EXP value is copied to the outgoing VC label EXP field.
The outgoing VC label ‘Bottom of Stack’ S bit in the outgoing VC label is set to1.
AToM control word processing is not performed at the L2VPN Pseudowire Switching aggregation point. Sequence numbers are not validated. Use the Router Alert label for LSP Ping; do not require control word inspection to determine an LSP Ping packet.
How to Configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
Configuring
Use the following procedure to configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching on each of the PE-agg routers.
This procedure assumes that you have configured basic AToM L2VPNs. This procedure does not explain how to configure basic AToM L2VPNs that transport Layer 2 packets over an MPLS backbone. For information on the basic configuration, see Any Transport over MPLS.
For inter-Autonomous configurations, ASBRs require a labeled interface.
In this configuration, you are limited to two
neighborcommands after entering the
l2
vficommand.

Note
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
l2
vfi
name
point-to-point
4.
neighbor
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
|
pw-class
pw-class-name
5.
exit
6.
exit
7.
show
mpls
l2transport
vc
[vcid [vc-id | [vc-id-min
vc-id-max]] [interface
name[local-circuit-id]] [destination
ip-address |
name] [detail]
8.
show
vfi
[vfi-name]
9.
ping
[protocol] [tag] {host-name|
system-address}
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following example displays the output of the show mpls l2transport vc command:
Router# show mpls l2transport vc Local intf Local circuit Dest address VC ID Status ------------- -------------------------- --------------- ----- ---- MPLS PW 10.0.1.1:100 10.0.1.1 100 UP MPLS PW 10.0.1.1:100 10.0.1.1 100 UP
The following example displays the output of the show vficommand:
Router# show vfi VFI name: test, type: point-to-point Neighbors connected via pseudowires: Router ID Pseudowire ID 10.0.1.1 100 10.0.1.1 100
How to Configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching using the commands associated with the L2VPN Protocol-Based CLIs feature
Perform this task to configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching on each of the PE-agg routers. In this configuration, you are limited to two neighbor commands after entering the l2vpn xconnect command.
This task assumes that you have configured basic AToM L2VPNs. This task does not explain how to configure basic AToM L2VPNs that transport Layer 2 packets over an MPLS backbone. For information on the basic configuration, see the “Any Transport over MPLS” section.
For interautonomous configurations, autonomous system boundary routers (ASBRs) require a labeled interface.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
pseudowire
number
4.
encapsulation
mpls
5.
neighbor
peer-address
vcid-value
6.
exit
7.
interface
pseudowire
number
8.
encapsulation
mpls
9.
neighbor
peer-address
vcid-value
10.
exit
11.
l2vpn
xconnect
context
context-name
12.
member pseudowire
interface-number
13.
member
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
14.
member pseudowire
interface-number
15.
member
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
16.
exit
17.
exit
18.
show
l2vpn
atom
vc
[vcid [vc-id |
vc-id-min
vc-id-max]] [interface
type number [local-circuit-id]] [destination
ip-address |
name] [detail]
19.
ping
[protocol] [tag] {hostname|
system-address}
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
pseudowire
number
Example: Router(config)# interface pseudowire 100 |
Specifies the pseudowire interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 |
encapsulation
mpls
Example: Router(config-if)# encapsulation mpls |
Specifies that Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is used as the data encapsulation method. | ||
| Step 5 |
neighbor
peer-address
vcid-value Example: Router(config-if)# neighbor 10.0.0.1 123 |
Specifies the peer IP address and virtual circuit (VC) ID value of the Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) pseudowire. | ||
| Step 6 |
exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit |
Exits interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 7 |
interface
pseudowire
number
Example: Router(config)# interface pseudowire 200 |
Specifies the pseudowire interface and enters interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 8 |
encapsulation
mpls
Example: Router(config-if)# encapsulation mpls |
Specifies that Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is used as the data encapsulation method. | ||
| Step 9 |
neighbor
peer-address
vcid-value Example: Router(config-if)# neighbor 10.0.0.2 124 |
Specifies the peer IP address and virtual circuit (VC) ID value of the Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) pseudowire. | ||
| Step 10 |
exit
Example: Router(config-if)# exit |
Exits interface configuration mode. | ||
| Step 11 |
l2vpn
xconnect
context
context-name
Example: Device(config)# l2vpn xconnect context con1 |
Creates a Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) cross connect context and enters xconnect configuration mode. | ||
| Step 12 |
member pseudowire
interface-number
Example: Router(config-xconnect)# member pseudowire 100 |
Specifies a member pseudowire to form a Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) cross connect. | ||
| Step 13 |
member
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
Example: Device(config-xconnect)# member 10.0.0.1 123 encapsulation mpls |
Specifies the devices that form a point-to-point Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) virtual forwarding interface (VFI) connection.
| ||
| Step 14 |
member pseudowire
interface-number
Example: Router(config-xconnect)# member pseudowire 200 |
Specifies a member pseudowire to form a Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) cross connect. | ||
| Step 15 |
member
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
Example: Device(config-xconnect)# member 10.0.0.2 124 encapsulation mpls |
Specifies the devices that form a point-to-point Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) virtual forwarding interface (VFI) connection.
| ||
| Step 16 |
exit
Example: Device(config-xconnect)# exit |
Exits Xconnect configuration mode. | ||
| Step 17 |
exit
Example: Device(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 18 |
show
l2vpn
atom
vc
[vcid [vc-id |
vc-id-min
vc-id-max]] [interface
type number [local-circuit-id]] [destination
ip-address |
name] [detail]
Example: Device# show l2vpn atom vc |
Displays information about Any Transport over MPLS (AToM) virtual circuits (VCs) and static pseudowires that have been enabled to route Layer 2 packets on a device. | ||
| Step 19 |
ping
[protocol] [tag] {hostname|
system-address}
Example: Device# ping 10.1.1.1 |
When issued from the CE routers, verifies end-to-end connectivity. |
Configuring
Use the following procedure to configure L2VPN Pseudowire Switching on each of the PE-agg routers.
This procedure assumes that you have configured basic AToM L2VPNs. This procedure does not explain how to configure basic AToM L2VPNs that transport Layer 2 packets over an MPLS backbone. For information on the basic configuration, see Any Transport over MPLS.
For inter-Autonomous configurations, ASBRs require a labeled interface.
In this configuration, you are limited to two
neighborcommands after entering the
l2
vficommand.

Note
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
l2
vfi
name
point-to-point
4.
neighbor
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
|
pw-class
pw-class-name
5.
exit
6.
exit
7.
show
mpls
l2transport
vc
[vcid [vc-id | [vc-id-min
vc-id-max]] [interface
name[local-circuit-id]] [destination
ip-address |
name] [detail]
8.
show
vfi
[vfi-name]
9.
ping
[protocol] [tag] {host-name|
system-address}
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
l2
vfi
name
point-to-point
Example: Router(config)# l2 vfi atomtunnel point-to-point |
Creates a point-to-point Layer 2 virtual forwarding interface (VFI) and enters VFI configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 |
neighbor
ip-address
vcid
encapsulation
mpls
|
pw-class
pw-class-name
Example: Router(config-vfi)# neighbor 10.0.0.1 100 pw-class mpls |
Sets up an emulated VC. Specify the IP address and the VC ID of the remote router. Also specify the pseudowire class to use for the emulated VC.
| ||
| Step 5 |
exit
Example: Router(config-vfi)# exit |
Exits VFI configuration mode. | ||
| Step 6 |
exit
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 7 |
show
mpls
l2transport
vc
[vcid [vc-id | [vc-id-min
vc-id-max]] [interface
name[local-circuit-id]] [destination
ip-address |
name] [detail]
Example: Router# show mpls l2transport vc |
Verifies that the L2VPN Pseudowire Switching session has been established. | ||
| Step 8 |
show
vfi
[vfi-name]
Example:
Router# show vfi atomtunnel
|
Verifies that a point-to-point VFI has been established. | ||
| Step 9 |
ping
[protocol] [tag] {host-name|
system-address}
Example: Router# ping 10.1.1.1 |
When issued from the CE routers, this command verifies end-to-end connectivity. |
Examples
The following example displays the output of the show mpls l2transport vc command:
Router# show mpls l2transport vc Local intf Local circuit Dest address VC ID Status ------------- -------------------------- --------------- ----- ---- MPLS PW 10.0.1.1:100 10.0.1.1 100 UP MPLS PW 10.0.1.1:100 10.0.1.1 100 UP
The following example displays the output of the show vficommand:
Router# show vfi VFI name: test, type: point-to-point Neighbors connected via pseudowires: Router ID Pseudowire ID 10.0.1.1 100 10.0.1.1 100
Configuration Examples for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
L2VPN Pseudowire Switching in an Inter-AS Configuration Example
Two separate autonomous systems are able to pass L2VPN packets, because the two PE-agg routers have been configured with L2VPN Pseudowire Switching. This example configuration is shown in the figure below.
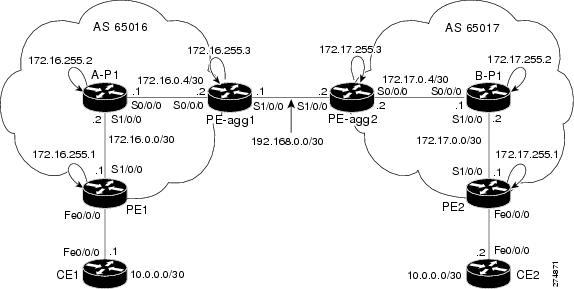
|
CE1 |
CE2 |
|---|---|
version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime service password-encryption ! hostname [ce1] ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$o9N6$LSrxHufTn0vjCY0nW8hQX. ! ip subnet-zero ip cef no ip domain-lookup ! interface FastEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast ! ip classless ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! no cns aaa enable end |
version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime service password-encryption ! hostname [ce2] ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$YHo6$LQ4z5PdrF5B9dnL75Xvvm1 ! ip subnet-zero ip cef no ip domain-lookup ! interface FastEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast ! ip classless ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login ! no cns aaa enable end |
Additional References
Related Documents
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
MPLS commands |
|
|
L2VPN pseudowire redundancy |
“L2VPN Pseudowire Redundancy” feature module in the MPLS Layer 2 VPNs Configuration Guide. |
|
H-VPLS |
“Configuring VPLS” in the “Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching on the Optical Services Modules” chapter in the Optical Services Modules Installation and Configuration Notes, 12.2SR document. |
|
MPLS traffic engineering |
“MPLS Traffic Engineering Fast Reroute Link and Node Protection” feature module in the MPLS Traffic Engineering: Path, Link, and Node Protection Configuration Guide (part of the Multiprotocol Label Switching Configuration Guide Library) |
Standards
Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
|
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4447.txt |
Pseudowire Setup and Maintenance Using the Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) |
|
http://www3.ietf.org/proceedings/06mar/IDs/draft-ietf-l2vpn-vpls-ldp-08.txt |
Virtual Private LAN Services over MPLS |
|
http://www.ietf.org/internet-drafts/draft-ietf-pwe3-segmented-pw-02.txt |
Segmented Pseudo Wire |
|
draft-ietf-pwe3-vccv-10.txt |
Pseudo Wire Virtual Circuit Connectivity Verification (VCCV) |
|
draft-ietf-pwe3-oam-msg-map-03.txt |
Pseudo Wire (PW) OAM Message Mapping |
MIBs
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
Pseudowire Emulation Edge-to-Edge MIBs for Ethernet, Frame Relay, and ATM Services |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for L2VPN Pseudowire Switching
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
L2VPN Pseudowire Switching |
Cisco IOS XE Release 2.4 |
The L2VPN Pseudowire Switching feature extends layer 2 virtual private network (L2VPN) pseudowires across an interautonomous system (inter-AS) boundary or across two separate multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) networks. In Cisco IOS XE Release 2.4, The L2VPN Pseudowire Switching feature is supported with Ethernet over MPLS. The following commands were introduced or modified: l2 vfi point-to-point, neighbor(L2VPN Pseudowire Switching), show vfi. |
 Feedback
Feedback